8th Grade Science MCAS
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
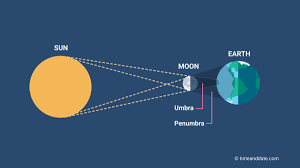
Solar Eclipse
The moon blocks the Sun from being visible from the Earth
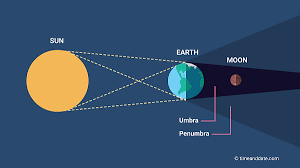
Lunar Eclipse
The moon is hidden in the Earth's shadow
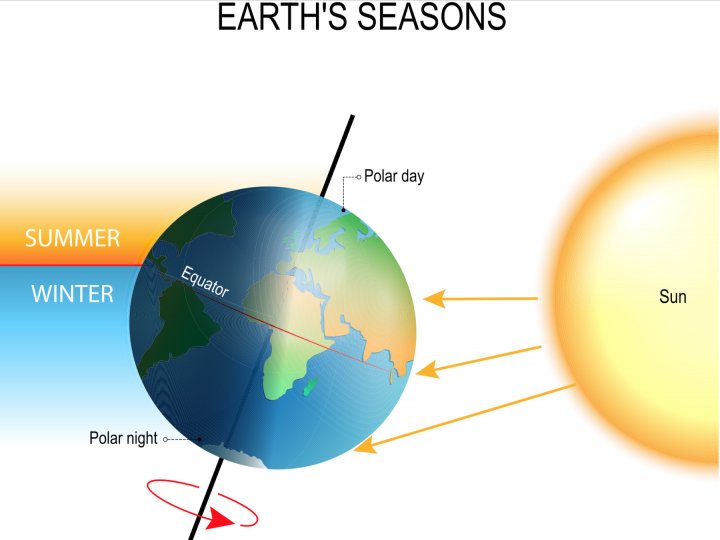
Causes of Seasons
Earth's tilt and revolution around the Sun affect the amount of direct sunlght. Summer occurs when we are tilted towards the Sun and receive more direct sunlight. Winter occurs when we're tilted away from the sun and receive less direct sunlight.
Galaxy
A collection of gas, dust, and billions of stars held together by gravity.
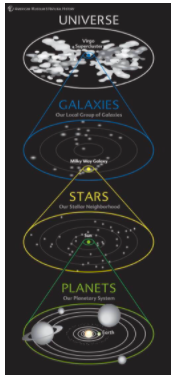
Planet
An object that orbits a star, is large enough to be made a sphere by gravity, and has cleared its own orbit.
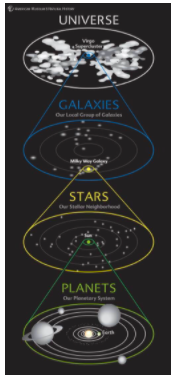
Solar System
A star and all of the planets and other objects that orbit it
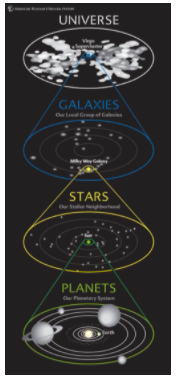
Sun
A star at the center of a solar system
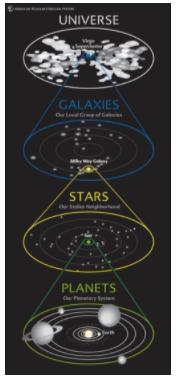
Universe
All of space and everything in it
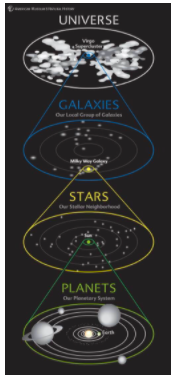
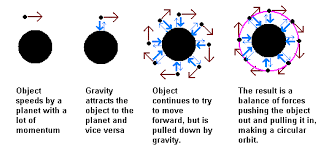
The reason planets orbit the sun
Gravity causes planets to orbit
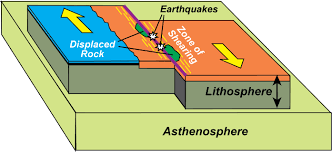
Transform Boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions
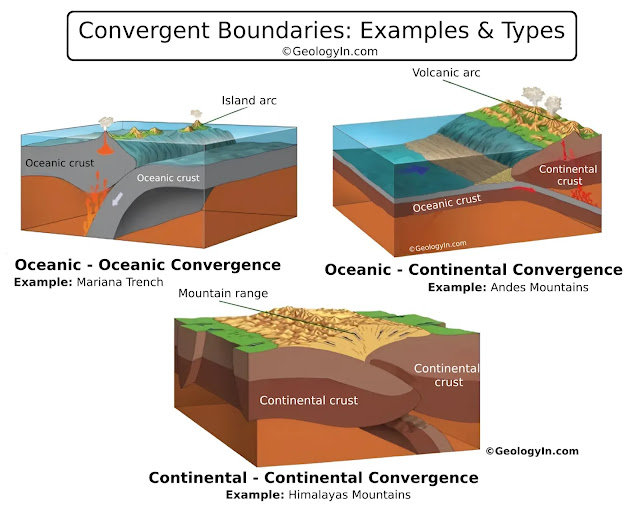
Convergent Boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move toward each other.
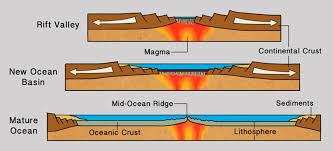
Divergent Boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move away from each other.
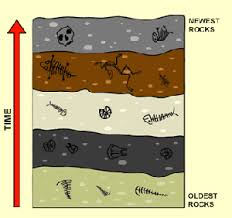
The top layer of rock is _ compared to the _ layer.
The top layer is newer than the bottom layer. (As new sediment gets laid down on the Earth's surface older rock gets buried deeper and deeper)
Evidence of Plate Movement
Continents fit together, Fossil Evidence, Earthquakes, Volcanoes, Mountain Ranges
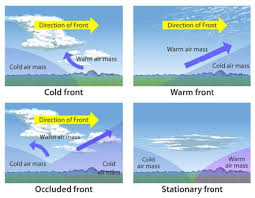
What happens when air masses collide
Warm air rises over the cold air. Water vapor in the rising air condenses into water and clouds are formed.
Characteristics of Plants
Multicellular, Eukaryotic, Cell Walls, Make their own food, , most can't move

Characteristics of Animals
Multicellular, Eukaryotic, Heterotrophic (need to eat food), Most take in oxygen, Most are motile, Most have organs

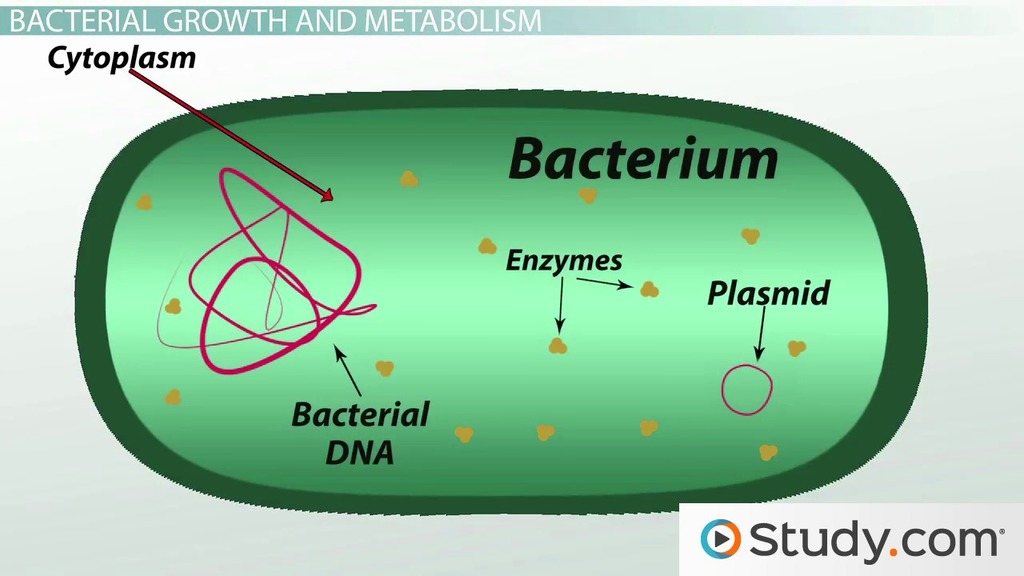
Characteristics of Bacteria
No organelles, Single-Celled, Most are microscopic
Characteristics of Fungi
Multicellular, Eukaryotic, Heterotrophic (need to eat food), Have cell walls, Reproduce sexually & asexually, Most are immobile, Most grow in soil

Reactants and Products of Photosynthesis
Reactants: Light Energy, Carbon Dioxide, Water
Products: Glucose, Oxygen
Reactants and Products of Cellular Respiration
Reactants: Glucose, Oxygen
Products: Energy, Carbon Dioxide, & Water Vapor
Plant Cell
Contains a cell wall, chloroplast and large vacuole; rectangular shape
Animal Cell
Does not have a cell wall or chloroplast and a small vacuole; rounded shape
Digestive System
Breaks down food to distribute energy and nutrients throughout the body
Respiratory System
Brings oxygen into the body. Gets rid of carbon dioxide.
Excretory System
Removes waste from the body
Circulatory System
Uses blood to transport oxygen, waste, nutrients, hormones, heat, etc… around the body
Muscular/Skeletal System
Muscles and bones working together to cause movement and support the body.
Nervous System
Sends messages to and from your brain, responding to stimuli and telling your body what to do.
Fats (Lipids)
Molecules that store energy in your body
Proteins
Molecules that your body uses to build and repair itself
Carbohydrates
Molecules that your body use for energy
Why organisms need food
For energy and growth
Environmental factors that influence the growth of organisms
Temperature and Nutrient Availability
Advantages of Sexual Reproduction
Diversity causes different weaknesses, Weaknesses are not always passed down, Evolution happens easier (in fewer generations)
Advantages of Asexual Reproduction
Saves time and energy, Don't need to find a mate, Beneficial traits are always passed down
Producer
Organism that makes its own food (typically through photosynthesis)
Consumer
An organism that obtains energy by consuming other organisms
Decomposer
Breaks down dead organisms
Change to a Gene
Mutation
Gene
A segment of DNA which tells the cell what protein to make
Allele
One version of a gene (can be dominant or recessive)
Chromosome
Bundles of DNA in the nucleus; make it easier to store DNA
Natural Selection
A process in which individuals that have certain inherited traits tend to survive and reproduce at higher rates than other individuals because of those traits.
Density
How packed together an objects' molecules are; Mass divided by volume
Solids turn into Liquids and Liquids turn into Gases when…
When heat energy is added
Gases turn into Liquids and Liquids turn into Solids when…
When heat energy is removed
Melting
When a solid turns into a liquid
Evaporation
When a liquid turns into a gas
Condensation
When a gas turns into a liquid
Freezing
When a liquid turns into a solid
When kinetic energy increases…
potential energy decreases
Gravitational Potential Energy
Increases when an object's height increases
Conduction
The direct transfer of heat from one substance to another substance that it is touching.
Convection
The transfer of heat by the movement of a fluid when the hot (less dense) fluid rises and the cooler (more dense) fluid sinks
Radiation
The transfer of heat through waves in space
Element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom
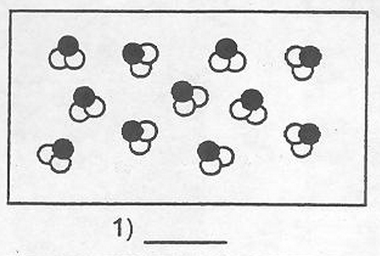
Molecule
A group of atoms bonded together

Compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
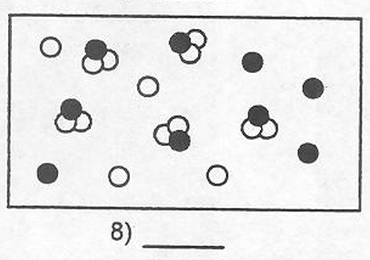
Mixture
A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined
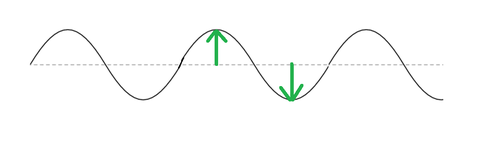
Amplitude
The distance from a wave's resting point to its peak; the "strength" of a wave
Energy
The sum of a wave's potential and kinetic energy
Frequency
The speed at which a wave repeats
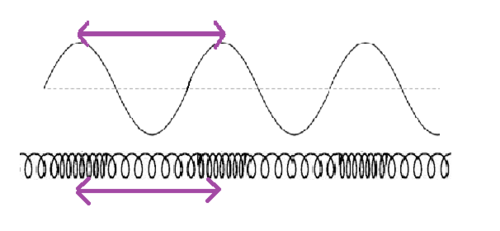
Wavelength
The distance between the peaks in a wave
Absorb
The process in which light is taken into an object and converted into energy
Reflect
The bouncing back of light off a smooth surface
Refract
The bending of light when it travels between surfaces
Transmit
Light passing through an object
Potential Energy
stored energy
Kinetic Energy
energy of motion
Nucleus
Control center of the cell. Contains DNA.
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell; makes energy by cellular respiration
Chloroplast
Organelle found in cells of plants that does photosynthesis
Vacuole
A sac inside a cell that acts as a storage area
Cell Membrane
thin, flexible barrier around a cell; regulates what enters and leaves the cell
Cell Wall
A rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support to the cell