forensic microscopy exam 2
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
hair, glass, color, polarization
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
The outermost layer of a hair strand, consisting of overlapping scales that protect the inner structures. It plays a crucial role in identifying species and specific individual hair characteristics.
cuticle
middle layer of the hair cuticle, rich in keratin and keratin associated proteins
exocuticle
underside of a scale, derived from remains of nuclei and organelles
endocuticle
ridge of the scale, rich in cysteine
a-layer
main body of the hair shaft made of spindle-shaped cortical cells, contains pigment granules
cortex
composed of macrofibril bundles and intermediate filaments embedded within a matrix
cortical cells
curly architype for hair
orthocortical
straight architype for hair
mesocortical
wavy architype for hair
paracortical
curvature in wool fibers is determined by the relative length of
othocortical and paracrotical cells
yellow pigment in hair
pheomelanin
black pigment in hair
eumelanin
porous central canal in the middle of hair mainly composed of trichohyalin and presence of citrulline, predominant in thick hair but not always present
medulla
the flatter the hair & medulla means
curlier hair
layer model of the hair follicle (inner to outer)
hair shaft, inner root sheath, outer root sheath, fibrous sheath
hair shaft is made up of (inner to outer)
medulla, cortex, cuticle
defines location of the hair
induction phase of embryo hair development
creates the hair “organs”
organogenesis phase of embryo hair development
“organ” mature into organized hair cell types
cytodifferentiation phase of embryo hair development
hair growth cycle
anagen, catagen, telogen, exogen, kenogen
active growth of hair, attached to root
anagen phase of hair growth
hair detaches from dermal papilla and prepares for shed
catagen phase of hair growth
follicle no longer attached to papilla, hair is not growing, will be pushed out by new hair
telogen phase of hair growth
hair falls/exits
exogen phase of hair growth
balding
kenogen phase of hair growth
fetus hair, first hair produced by hair follicles
lanugo hair phase
thin hair developed during childhood
vellus hair phase
hair obtained at puberty, development sensitive to hormones
terminal hair phase
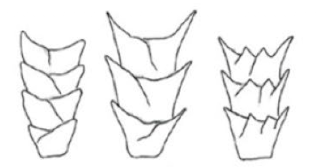
coronal scale pattern
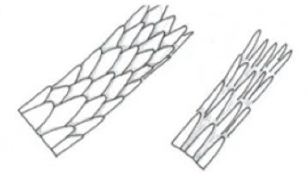
spinous scale pattern
humans have this scale pattern
imbricate scale pattern
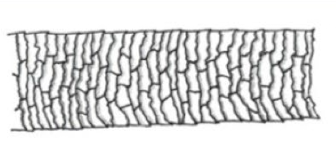
imbricate scale pattern
predominant in animal hair
medulla
human medullary index (medulla diameter/hair diameter)
MI < 1/3
animal medullary index (medulla diameter/hair diameter)
MI > 1/2

deer medulla
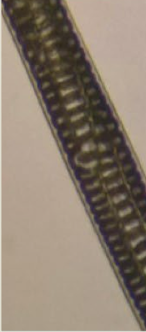
rabbit medulla

cat medulla
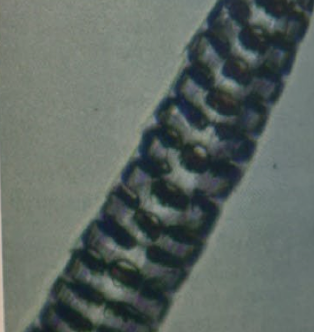
mouse medulla
long with moderate shaft diameter, absent-continuous medulla, narrow medulla, soft, cut or split ends
scalp hair
stiff & wiry texture, variation in diameter, potential buckling, broad & continuous medulla when present
pubic hair
soft, fine diameter, arc-like shape, discontinuous-trace medulla with granular appearance, tips are usually tapered and worn/rounded
limb hair
coarse, irregular or triangular cross-sectional, broad & continuous medulla
facial hair
dense with uneven pigmentation, circular cross-section
african hair
black, medulla present, round cross-sectional
asian hair
fine to coarse, even pigmentation, oval cross-sectional
caucasian hair
linked to the spectrum of light received by a detector
color
color interpreted from a very narrow part of the spectrum
spectral color
light will not go through the matter, scatters across the irregular surface in many different directions
diffused reflection
more of a molecular reaction of light being absorbed and released right after
scattered light
light is absorbed by some part of the spectrum
absorbed light
mirror-like reflection of light from a surface
specular reflection
goal is to make white light
LED RGB combination
use blue light on sample to emit green/red
LED phosphor
contain filaments that illuminate different colors based on the gas within the filament
gas discharge lamps
we see color as light going through our oxygen atmosphere at normal temperature and pressure
relativity of colors
“night vision” that uses relies on red light to see
Purkinje shift
humans are sensitive to 3 areas of the visible color spectrum
Young-Helmholtz theory
measure the amount of light that reaches our eyes
rods
determine/measure color
cones
cones responsible for blue color
S cones
cones responsible for green color
M cones
cones responsible for red color
L cones
used during the day, more sensitive to green
photopic vision
used at night, more sensitive to blue
scotopic vision
number of rods in the human eye
100 million
number of cones in the human eye
6 million
3D model that scientifically describes color
munsell color system
describes the color in the munsell color system
hue
how much white or black is added to the paint color
value
how vivid the color is
chroma
the most common trace evidence
glass
identifying characteristics of glass
chemical composition to density to refractive index
used to determine refractive index
oil immersion method with phase contrast microscope
oldest method of identifying glass chemical composition
micro x-ray fluorescence spectrometry
uses HF to liquidify glass for ionization to determine chemical composition
inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
expensive method that focuses a laser on glass and removes a piece via aerosols for analysis
laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
glass is ordered at short range, but ________ at large range
amorphous
glass is a very very rigid ______
liquid
light slows down in matter due to its interaction with _________
the electrons of the material
the way electrons interact with light depends on the material
refractive index
refractive index is linked to the
polarizability of the medium
dipole movement associated with the excitement of electrons by light
polarizability
_____ changes volume, which changes density, which changes refractive index
temperature
Becke line goes inward, medium has _______
lower RI, increase
Becke line goes outward, medium has _____
higher RI, decrease
importance of annealing glass
makes glass cohesive and reduces RI variation
refractive index and density are ______ correlated for a given class of chemical composition
positively
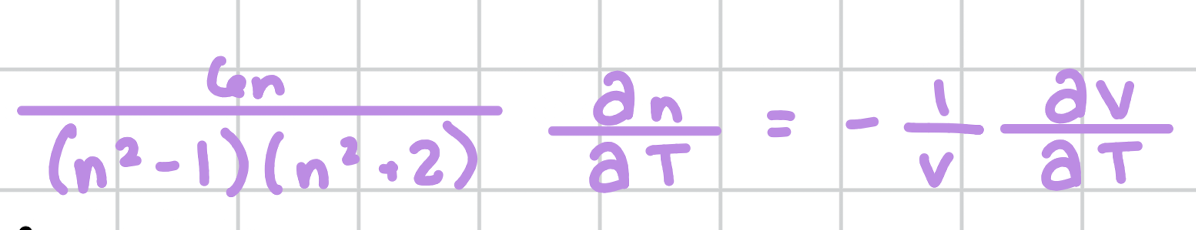
represents how ___________ decreases when ________ decreases
refractive index, temperature
the _____ will never change going from one material to another, only the ______
frequency, wavelength
oscillation of a wave is defined by its
frequency and wavelength
every electromagnetic wave is _____
polarized
three main types of polarization
linear, elliptical, and circular
term for when emissions from a large group of atoms are uncorrelated
unpolarized light
basically states that the transmitted light through a polarizer or analyzer is HALF of the original intensity
Malus’ law
______ temperature = _______ RI
higher, lower
lights splits bc electrons are moving at different wavelengths
dispersion
_____ occurs due to variation in refractive index
dispersion
longitudinal components of hair
root, shaft, tip
purpose of hair analysis
determine human vs animal