403M: Clouds, Precipitation, and Fog
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
What are the three possible components of clouds?
Water droplets (liquid T > 0°C),
Supercooled water droplets (liquid T < 0°C),
Ice crystals (solid).
Approximately how many cloud droplets does it take to form a single drop of rain?
1,000,000 cloud droplets.
What are the three main factors that determine the characteristics of a cloud?
The temperature of the air (type of droplet),
Stability of the air (type of cloud),
Moisture available (thickness of cloud)
What is the NC-SWOP definition of a Stratiform Cloud?
Clouds composed of rolls or elements, sometimes uniform in structure and normally stretched out in layers. The associated characters of precipitation are continuous and intermittent.
Stratiform type clouds are associated with what type of air mass stability?
Stable air.
What is the NC-SWOP definition of a Cumuliform Cloud?
Clouds which are composed of individual elements or bases and tend to have large vertical extent. The associated character of precipitation is showery.
Cumuliform type clouds are associated with what type of air mass stability?
Unstable air.
The altitude where the air temperature and dew point temperature in a rising column of air become equal (T=Td) is known as the _ level.
Condensation or saturation level.
What determines the height of a cloud's base?
The altitude of the condensation level.
In stable air, when does the vertical motion that forms a cloud cease?
When the lifting agent ceases to operate at a given altitude.
In unstable air, vertical cloud growth continues until the temperature of the rising air reaches _____ with the surrounding air.
Equilibrium.
List the nine stratiform cloud types formed in stable conditions as reported in Canada.
CI, CC, CS, AC, AS, NS, ST, SF, SC.
List the five cumuliform (vertical development) cloud types formed in unstable conditions.
CF, CU, TCU, CB, ACC.
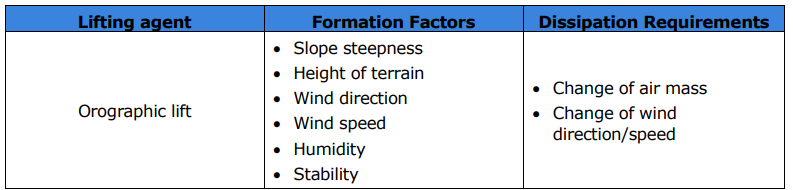
What is the lifting process called when an air mass is forced to a higher elevation as it moves over rising terrain?
Orographic lift.
What are the six formation factors for orographic lift?
Slope steepness
Height of terrain
Wind direction
Wind speed
Humidity
Stability
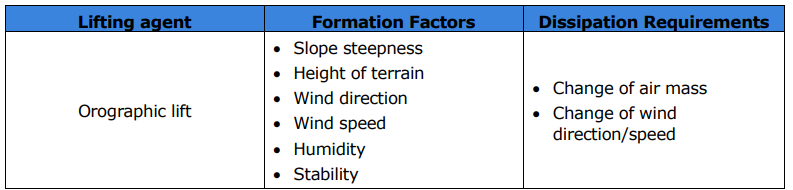
What is the two requirements for orographic lift to dissipate?
A change of air mass
Change of wind direction/speed.
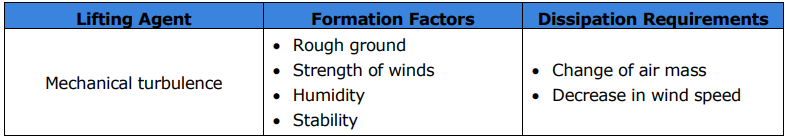
What type of turbulence results from wind flowing over or around irregular terrain or man-made obstructions?
Mechanical turbulence.
What are the four formation factors for mechanical turbulence?
Rough ground
Strength of winds
Humidity
Stability
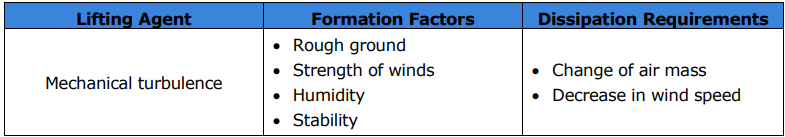
What are the two dissipation requirements for mechanical turbulence?
Change of air mass
Decrease in wind speed
The atmospheric condition that exists when there is a horizontal net inflow of air into a region, forcing the air to rise, is called _.
Convergence.
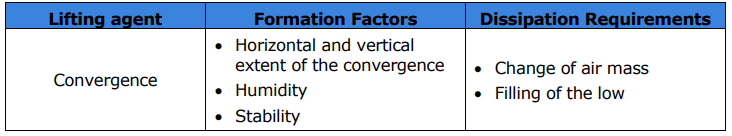
What are the three formation factors for convergence?
Horizontal and vertical extent of the convergence
Humidity
Stability
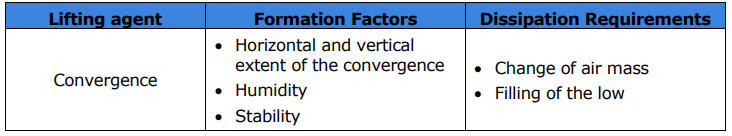
What are the two dissipation requirements for convergence?
Change of air mass
Filling of the low
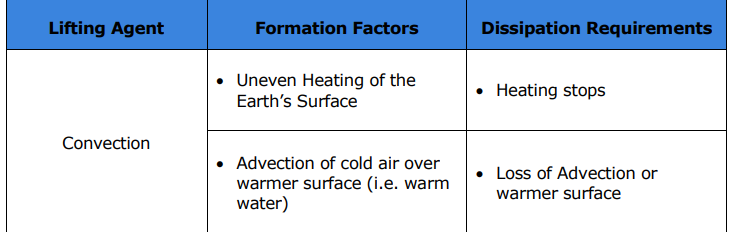
What is the lifting process called when heat is transferred by the mass motion of air, occurring because hot air expands and rises?
Convection.
What are the two formation factors for convection?
Uneven heating of the Earth’s surface
Advection of cold air over warmer surface (i.e. warm water)
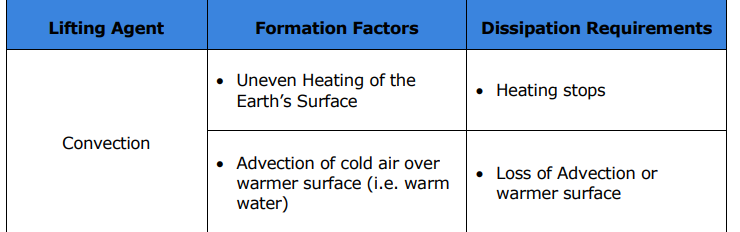
What are the two dissipation requirements for convection?
Heating stops
Loss of advection or warmer surface
What is the lifting process called when one air mass along a front is lifted over another?
Frontal lift.
According to NC-SWOP, what is the definition of fog?
A suspension of very small water droplets or ice crystals in the air, reducing visibility to 1/2 SM or less at the earth's surface.
Like clouds, fog can be composed of what three things?
Water droplets,
Supercooled water droplets,
Ice crystals.
What are the three general conditions required for the formation of fog?
High relative humidity,
The presence of condensation nuclei,
Cooling of the air (decrease in temperature) or addition of water vapour (increase in the dew point temperature).
Fog types are classified into two main categories based on their formation process:
Cooling of the air
Radiation Fog
Advection Fog
Upslope Fog
Addition of water vapour
Frontal Fog
Steam Fog
Ice Fog
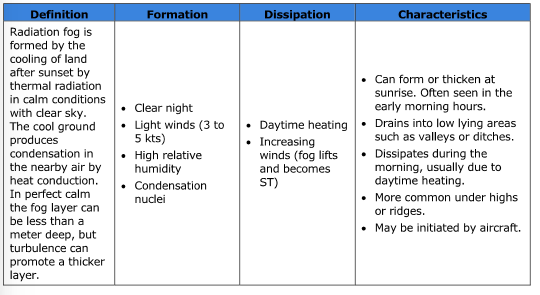
What type of fog is formed by the cooling of land after sunset by thermal radiation in calm, clear sky conditions?
Radiation fog.
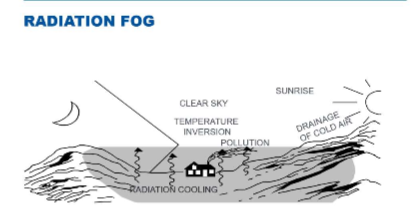
What are the four conditions for the formation of radiation fog?
Clear night
Light winds (3 - 5 kts)
High relative humidity
Condensation nuclei
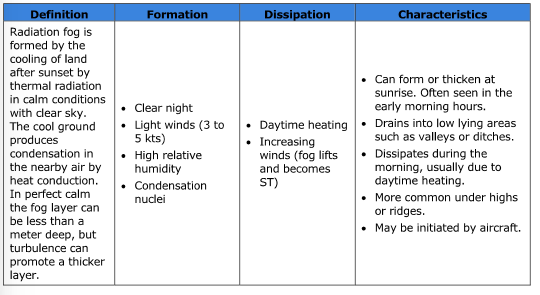
What are the two main conditions for the dissipation of radiation fog?
Daytime heating
Increasing winds.
What type of fog forms when warm, moist, and stable air is blown across a cooler surface?
Advection fog.
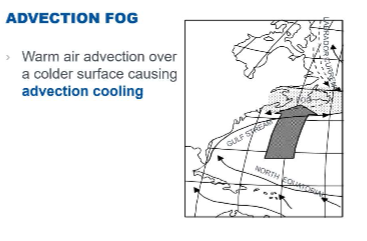
What are the four conditions for the formation of advection fog?
Advection of warm, humid air over a cold surface
Moderate winds (13 - 17 kts)
High relative humidity
Condensation nuclei
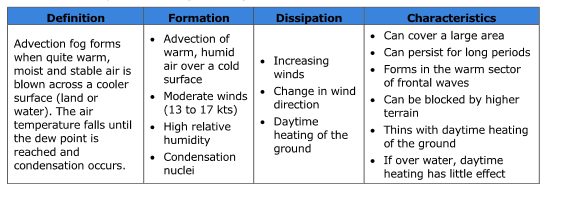
What are three conditions that can cause advection fog to dissipate?
Increasing winds
Change in wind direction
Daytime heating of the ground
What type of fog forms when moist air is forced up the slope of a mountain, causing it to cool adiabatically?
Upslope fog.
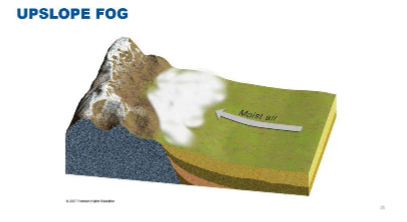
What are the four conditions for the formation of upslope fog?
Sloping ground (orographic lift)
Moderate winds (13 to 17 kts)
High relative humidity
Condensation nuclei
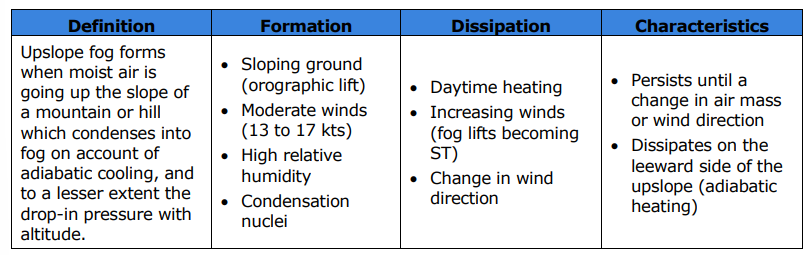
What are the three conditions for the dissipation of upslope fog?
Daytime heating
Increasing winds (fog lifts becoming ST)
Change in wind direction
What type of fog forms when precipitation falls into drier air below a cloud, evaporates, and then condenses?
Frontal fog (or precipitation fog).
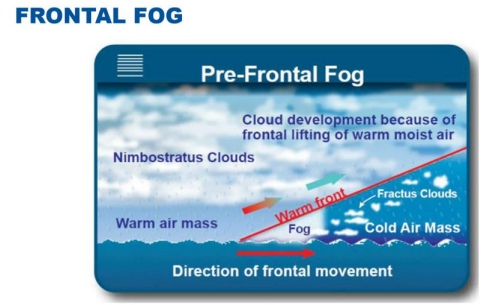
What are the four conditions for the formation of frontal fog?
Warm air over cold air
Frontal precipitation
High relative humidity
Condensation nuclei
What are the two conditions for the dissipation of frontal fog?
Movement of the front and pressure pattern
Precipitation moves away
What type of fog, also known as Arctic Sea smoke, forms over bodies of water overlain by much colder air?
Steam fog.
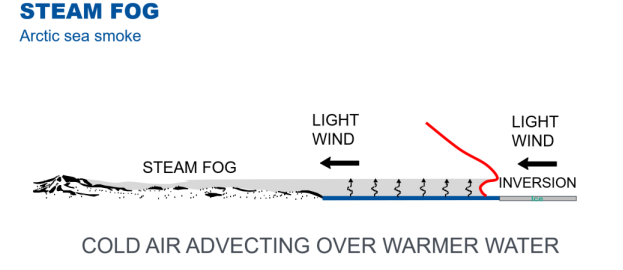
What are the three conditions for formation of steam fog?
Cold air above warmer water
High relative humidity
Condensation nuclei
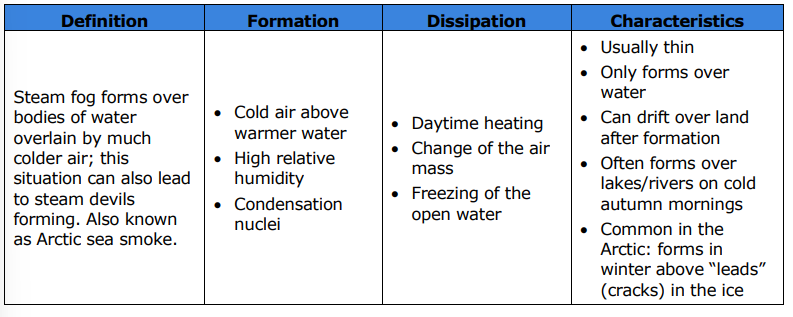
What are the three conditions for the dissipation of steam fog?
Daytime heating
Change of the air mass
Freezing of the open water
What type of fog consists of fine ice crystals suspended in the air and generally occurs at temperatures of -10°C or colder?
Ice fog.
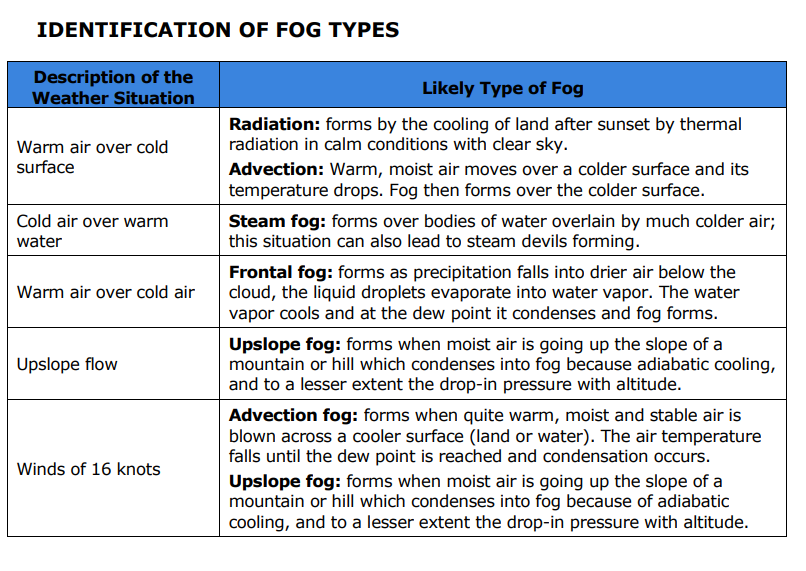
If there is warm air over a cold surface what is the likely type of fog to form?
Radiation: forms by the cooling of land after sunset by thermal radiation in calm conditions with clear sky.
Advection: Warm, moist air moves over a colder surface and its temperature drops. Fog then forms over the colder surface.
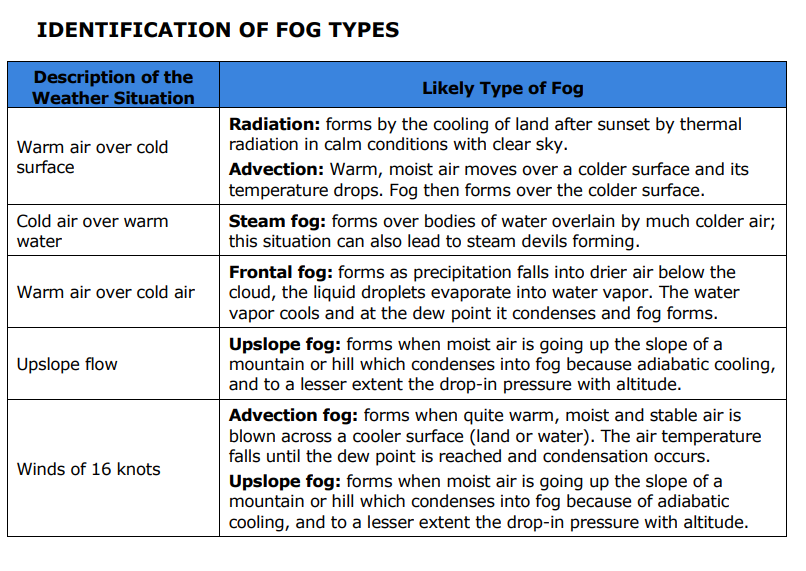
If there is cold air over warm water what is the likely type of fog to form?
Steam fog: forms over bodies of water overlain by much colder air; this situation can also lead to steam devils forming
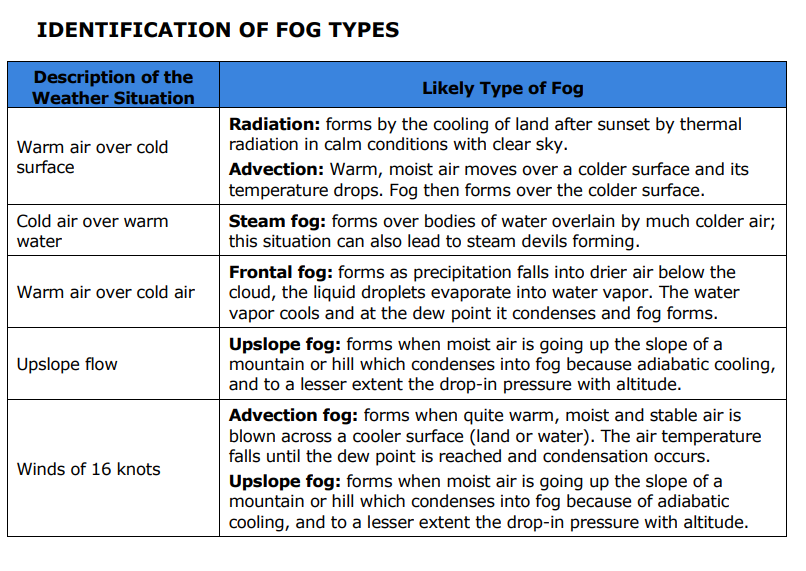
If there is warm air over cold air what type of fog is likely to form?
Frontal fog: forms as precipitation falls into drier air below the cloud, the liquid droplets evaporate into water vapor. The water vapor cools and at the dew point it condenses and fog forms.
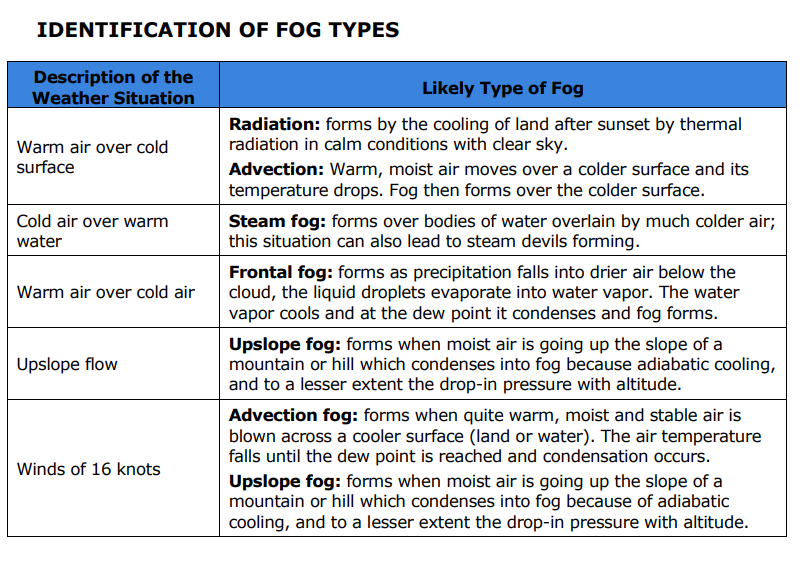
If there is upslope flow of wind what type of fog is likely to form?
Upslope fog: forms when moist air is going up the slope of a mountain or hill which condenses into fog because adiabatic cooling, and to a lesser extent the drop-in pressure with altitude.
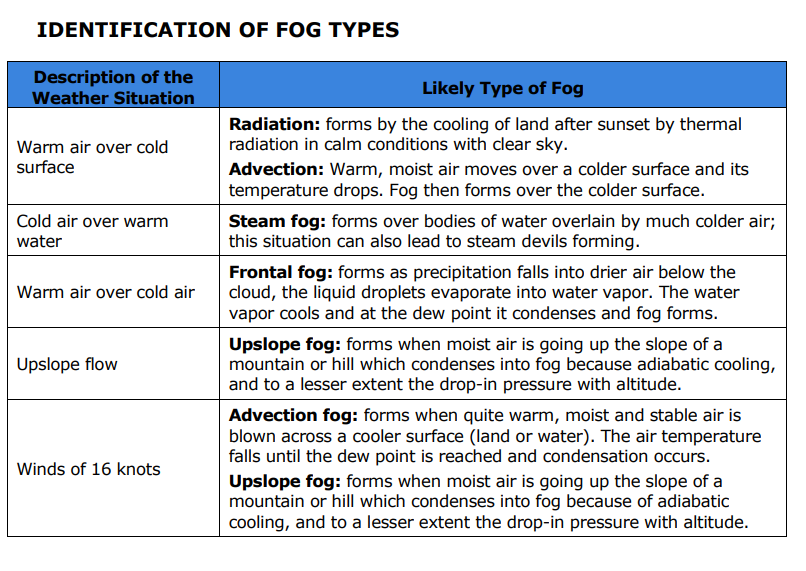
If there is a wind of 16 knots what type of fog is likely to form?
Advection fog: forms when quite warm, moist and stable air is blown across a cooler surface (land or water). The air temperature falls until the dew point is reached and condensation occurs.
Upslope fog: forms when moist air is going up the slope of a mountain or hill which condenses into fog because of adiabatic cooling, and to a lesser extent the drop-in pressure with altitude
What is defined as any product of the condensation/sublimation of atmospheric water vapour that is deposited on the Earth's surface?
Precipitation.
For precipitation to occur, cloud droplets must grow to approximately _ times their original size.
One hundred (100x).
What is the name of the process where ice crystals grow through sublimation at the expense of supercooled water droplets?
The Bergeron process (or ice crystal process).
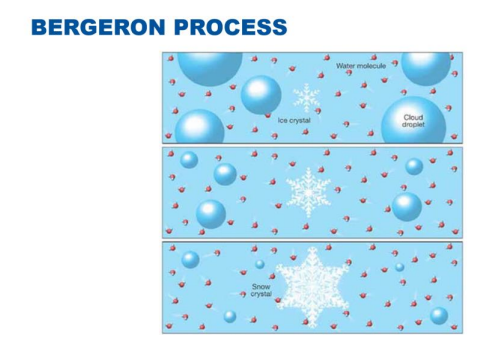
The Bergeron process requires a combination of ice crystals and _ to be present in a cloud.
Supercooled water droplets.
What is the name of the process where falling ice crystals or water droplets grow by colliding with other particles in their path?
The collision process (or coalescence).
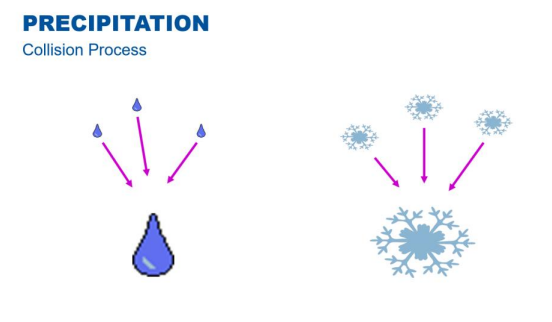
What atmospheric condition enhances the collision process by carrying water vapour and droplets to higher altitudes?
Strong vertical air currents.