Nitrogen groups
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is an amide
A nitrogen directly bonded to a carboxyl bond
What is an amine
A nitrogen group in the carbon chain
What is the difference between a primary, secondary and tertiary amine/amide
Primary/secondary/tertiary refer to the number of carbons attached to the nitrogen
How to form an amide
Use an acyl chloride and react with ammonia for a primary amide (use methylamine for a secondary amide)
What can amine groups act as
Bases
Definition of a salt
The molecule formed when a hydrogen ion is replaced by a metal or ammonium ion
How can we form aliphatic amines
Using haloalkanes, as the lone pair on the nitrogen acts as a nucleophile, and the molecule undergoes nucleophilic substitution
What are the conditions used in the synthesis of amines and why
excess ethanolic ammonia
Excess to avoid further substitution
Ethanol to avoid the reaction of haloalkane and water to form alcohols
How can we form aromatic amines
We form nitrobenzene using electrophilic substitution (benzene topic) then we can react this with concentrated HCl and tin to reduce the NO2 to NH2
What is an amino acid
A molecule with an amine group and a carboxylic acid group (bonded to the same carbon)
Are amino acids basic or acidic
They can react like both, as amines are basic and carboxylic acids are acidic
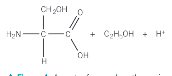
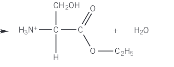
What is chirality
A non superimposable mirror image of a molecule onto itself
How to find a chiral centre
The chiral centre has 4 different atom/groups of atoms attached to one carbon
Formula for the number of stereoisomers in a molecule
2^(no. of bonds that can have E/Z + no. of chiral centres)
What are the 2 ways of forming polyesters/polyamides
Using one monomer with 2 functional groups, or using 2 monomers each containing 2 of a functional group
What is another name for polyamides
nylon
Use of polyamides
Ropes, strings
Condensation polymerisation definition
The joining of monomers with the loss of a small molecule
What is different about acid vs alkali hydrolysis
How to determine the products of hydrolysis
Break all amide and ester links
if acid hydrolysis: protonate all amines/basic groups
If alkali hydroysis: de protonate all acid groups