optical isomerism
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
When does optical isomerism occur?
When there are 4 different substituents attached to a chiral carbon centre. Resulting in 2 isomers that are non superimposable mirror images of one another but not identical.
Describe the features of a optical isomer pair
One of them rotates clockwise and the other anti clockwise when a beam of polarised light is shone.
What is used to measure optical rotations?
A polarimeter
Describe what happens in Optical activity
When light passes through a Polaroid/polarizing filter and only vibrations that are parallel to the plane will be transmitted
Describe what occurs when a polarimeter is used to measure optical rotations of 2 optical isomers of the same substance
Polarised light is passed through the two solutions of the same conc. With different optical isomers of the same substance.
2 one solution will rotate clockwise by the same angle
2 the other will rotate anti clockwise by the same angle
What isomers is an isomer that rotates clockwise and one that rotates anti clockwise
Clockwise- + isomer
Anti clockwise- - isomer
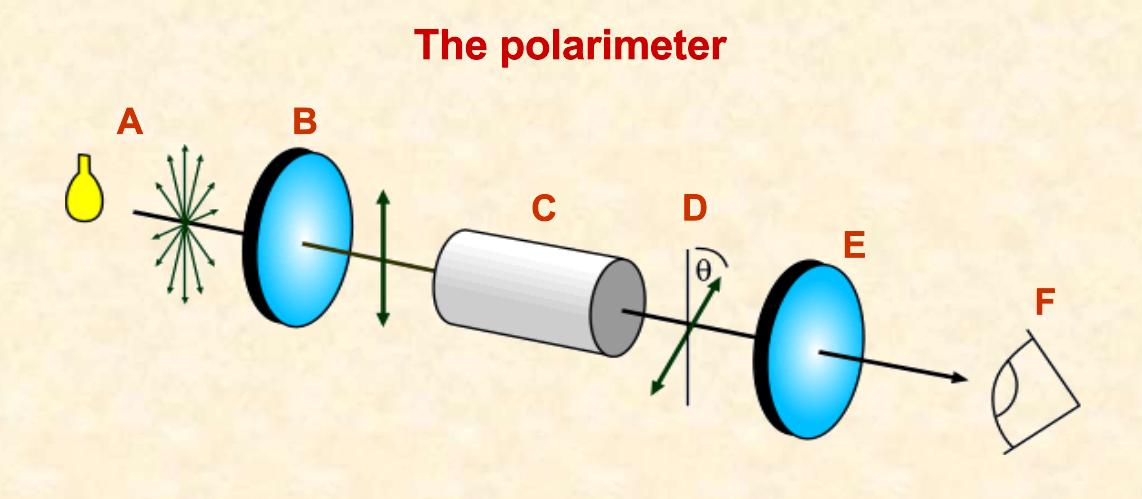
What occurs at each stage?
A-a light source produces light vibrating in all directions
B-a polarising filter only allows light to pass in one direction
C-the polarised light passes through the sample
D-if the substance is optically active it rotates the plane of polarised light
E-thecanalysing filter is turned so that light reaches a maximum
F-the direction of rotation is measured coming towards the observer
If the light appears to have turned to the right it is….
Dextrorotatory
If light appears to be turned to the left it is……
Laevorotatory