Ichthyology Quiz 1
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What is Ichthyology
the study of fishes
What is known about fish biomass
Fish take up the second most abundant biomass on the planet, after insects
What are 6 common things that are seen in most fishes
aquatic
gills
scales
fins
cold blooded
swim
What is Poikilothermic
an organism whose internal body temperature has great fluctuation and range
What is Homothermic
organisms whose internal body temperature stays consistent without much fluctuation
What is the difference between endothermic and ectothermic
endo: create their own body heat
ecto: use enviornment for heat
What does Cephalized mean
an organism with nervous system concentrated towards one end making a brain
What does Chordate mean
they have dorsal support rods, gill slits, and a dorsal nerve cord
difference between the term fish and fishes
Fish: used for one fish or many of the same species
Fishes: used for many of different species
What are the 8 big pros and cons about living in water for fish
Common living area: a common medium that can be interconnected and isolated for creation of highly unique diversity
Stability and predictability: temperature stays pretty stable
Universal solvent: makes it hard for oxygen to be in it creating the use of gills
Density: Has a high density so it creates the ability for streamlined bodies and buoyancy organs
Incompressibility: allowing fish to fell movements and create lateral line systems
Productivity: light has a low penetration strength to deep water bodies so the activity tends to be at the surface and lowers eyesight usage in fish
Salt Solubility: Water has high salt solubility and can contain a lot creating salt water fish to conserve water and fresh water to stop drinking water
Sound: water can tranmit sound even better than air creating good hearing fish
How are fish distributed between fresh and salt water
fish are almost equal in their distribution of fresh and saltwater fish because freshwater systems create high speciation events to match the species in the vast ocean
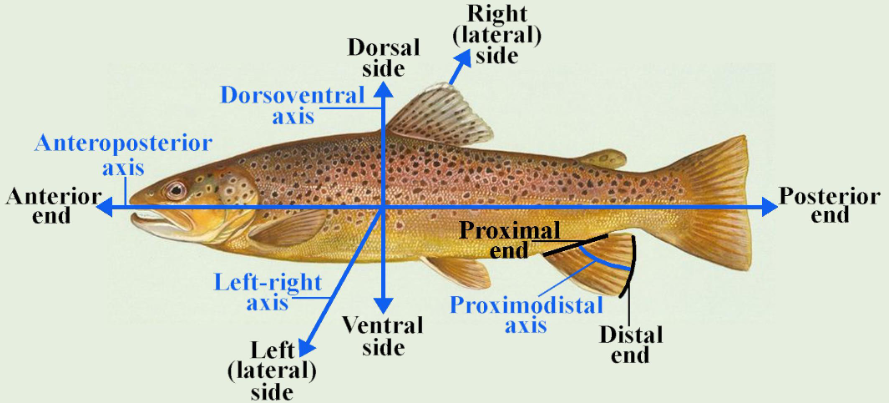
draw and label where the listed are
anterior
posterior
proximal
distal
ventral
dorsal
right lateral side
left lateral side
what is a functional trait
a measurable characteristics of induvial both anatomically and life history features
what does functional traits allow us to do
tell when new species are forming
notice invasive species
understand suitable traits for certain environments
what are the 5 main fish body types
fusiform: fast streamlike body
Compressed: slow coral rocky fish
depressed: flat-bottom dwelling fish
eel like: long ribbon-like bodies
combination: more globular for deep-sea dwellers
what are common features of Rover predators
streamlines
pointed heads
terminal mouths
narrow caudal peduncles
forked tails
prey seraches
what are common features of ambush predators
fish eaters
fast swimmers
elongated stream like bodies
flat heads
large toothy mouth
large tail fins
dorsal and anal fins are on the far back
what are common rover predator species
bass
salmon
tuna
what are common ambush predators
pikes
barracudas
needlefish
common traits of bottom fish
small
superior mouth
flattened heads
large dorsal-directed eyes
Common traits of Benthic fish
wide body verity
adapt for touching the ground/bottom of the water
mostly flat
small subterminal mouths
small eyes
common bottom fish species
mosquitofish
minnows
flying fish
common species of benthic bottom fish
catfish
flatfish
suckers
common traits of deep body fish
laterally compressed
short deep bodies
long dorsal and anal fins
small mouths
big eyes
short snouts
pelvic fin hangs under pectoral fin
common traits of eel like bodies
elongated bodies
blunt heads
parried or absent fins
dorsal and anal fins run length of the body
common deep body fish
clownfish
blue tang
other rock/coral fish
common eel like fish
eels
loaches
picklebacks
What are tetraodontiforms
a fish shape that doesn’t fit the normal structure seen in pufferfish and boxfish
what is a Syngnathiforms
a type of fish body that doesn’t fit the norm seen in seahorses
What is the difference between medial and lateral fins
medial: nonpaired fins like the dorsal, anal, and tail fin
lateral: paired fins like the pelvic and pectoral fins
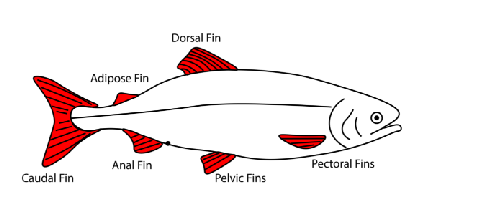
Draw a diagram of all the fish fins timed
this picture
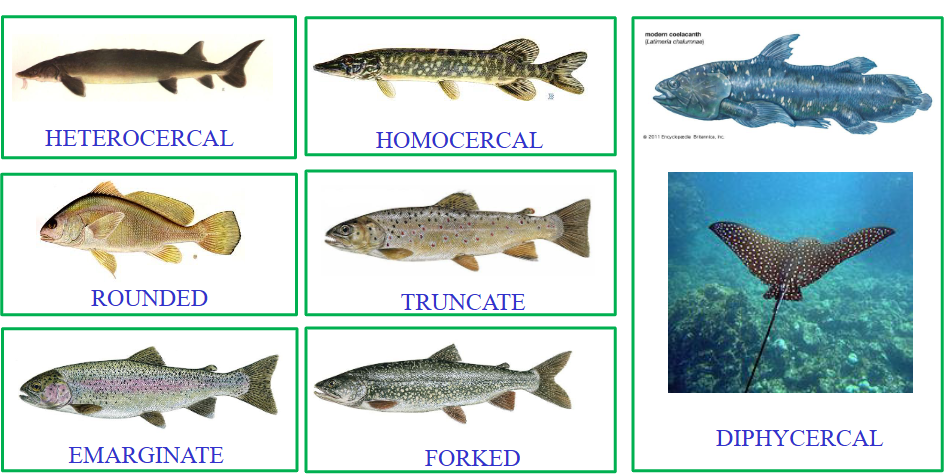
Draw a diagram of all fish tails
this picture
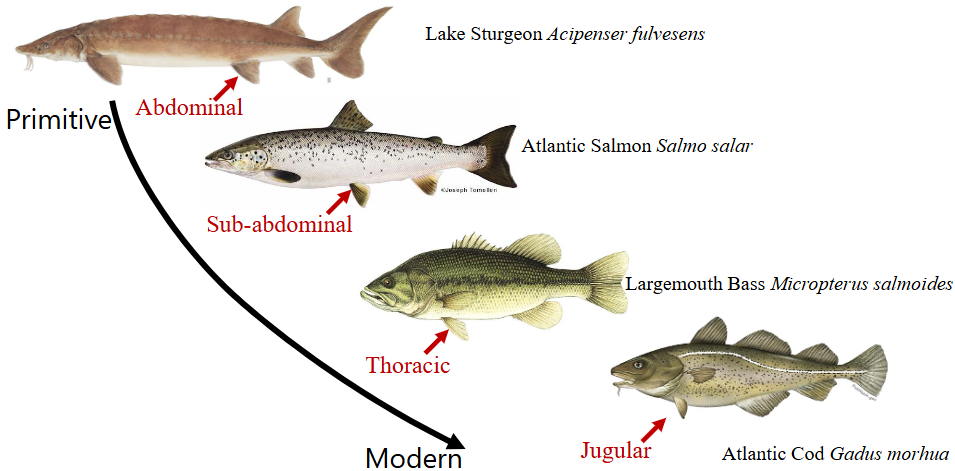
draw a diagram of all position the anal fin can be in
this photo
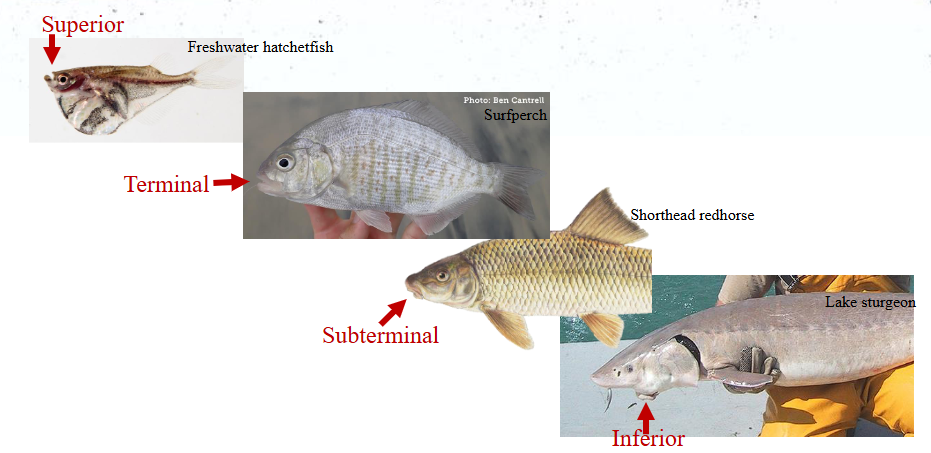
draw each mouth type
this photo
draw each type of scale
this photo
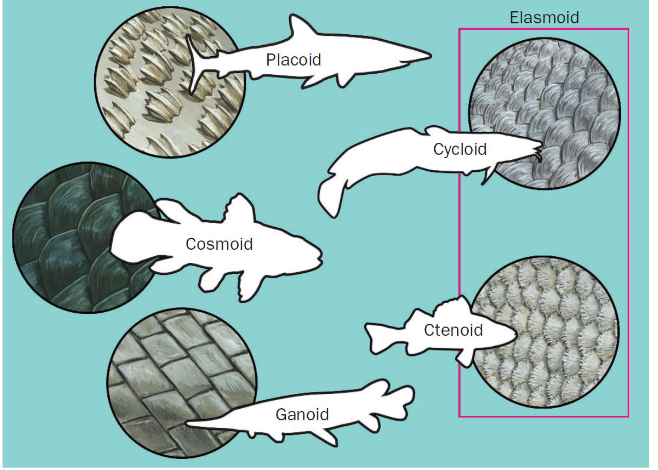
what makes up garnoid scles
they are made up of a basal bone layer, dentine, and ganoine
what makes up cosmoids sacles
They are ancient fish scales made up of two layers of bone plus cosmine and vitrodentine
difference between Ctenoid and Cycloid scales
both are newer scales but Ctenoid have comb-like ends while Cycloids are smooth
What are scutes
they are a boney point structure located on a fish
Who was the first person to really start studying fish and biology
Aristotle
Who is the father of ichthyology and classified fish
Peter Artedi
Who adapted Artedi’s system and made the well-known Systema naturae
Carolus Linneaus
Who was the first to detail north American fish and have a theory of evolution in mind
Constanine Rafinesque
Who created the well-known measurements and ways to dissect and study fish autonomy
Georges Cuvier
Who worked on classifying fossilized fish and bring popularity to science in America
Louis Agassiz
Who was the last person to describe all fish species
Albert Gunther
Who created a lot of the first ichthyology textbooks
David Starr Jordan