Smart Drugs/Antibodies
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What are the requirements for a molecule to be able to cross the BBB
Without a specific protein transport system, in order to cross the blood-brain barrier, a molecule must:
Have a molecular weight of less than 300
Have a clogP of no more than 3
Have no more than 3 hydrogen bond donors
Have no more than 6 hydrogen bond acceptors
How does L-DOPA cross the BBB
It exploits the alpha-amino acid shuttle protein, where anything with the L-amino acid group is transported.
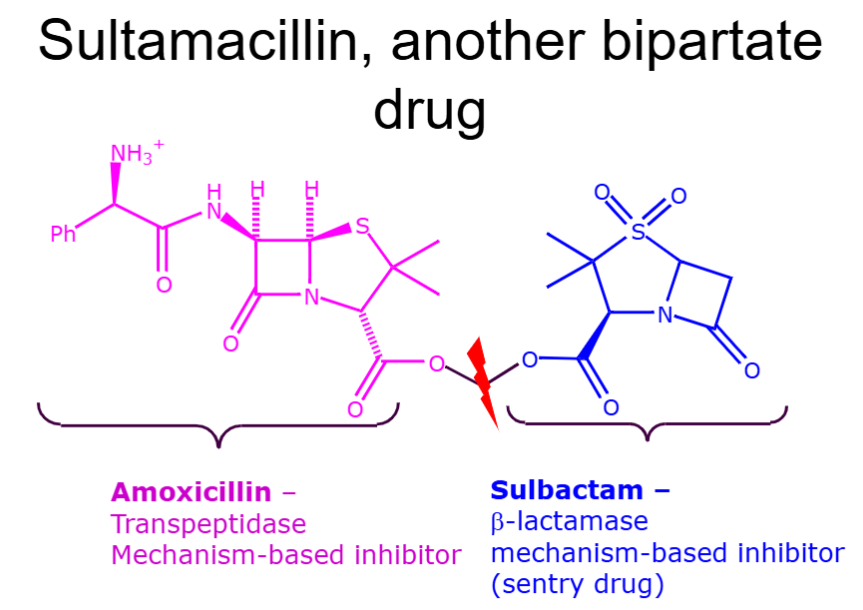
What is an example of a bipartate drug
CarbiDOPA. It competitively inhibits DOPA decarboxylase and forms a complex (acetaldehyde linkage) with it in the blood.
Sentry drug - protects the active drug we want to deliver from being degraded
What are IgM antibodies
The first response to an infection → large pentamers that are less specific
Are good at promoting agglutination
What are some features IgG antibodies
Secreted after IgMs, made up of 4 peptide chains linked together via cys-cys disulfide bonds, with two antigen-binding sites.
Bind directly to pathogens, inactivating them or marking them for destruction.
Present for a long time after infection.
Mr - 150,000
What are ADCs
Antibody drug conjugates
3-5 drug molecules are covalently attached to the antibody (lysine residue - COOH, aspartate/glutamate residues - amine groups)
Antibody can attach to the outside of the cell (CSM protein or oligosaccharide) and deliver the drug (must be very potent)
Covalent bonds are designed to break under certain conditions
How do ADCs release the active drug into cells?
If the ADC binds to the right receptor on the cell membrane, it will stimulate endocytosis.
The ADC is engulfed and contained within an endosome
As the endosome moves from the early to the late stage it can either be recycled or form a lysosome
The pH of the lysosome gradually drops, and the protein is degraded, hopefully releasing the active drug into the cytoplasm
How can ADCs target tumour cells
Tumour cells may have an overexpressed cell membrane protein or oligosaccharide so the ADC is able to selectively bind
Why would you use an antibody enzyme conjugate over an ADC
You can only attach 3-5 drug molecules to an antibody so the dosage is low. If you deliver a specific enzyme to target cells that enzyme can be used to convert prodrug molecules to active drug molecules.
What is ADEPT
Antibody Directed Enzyme Prodrug Therapy
Tumour cells overexpress target antigen
Inject Antibody-enzyme conjugate and wait for it to immobilise on target cells
Add prodrug molecule
On target cells the enzyme will catalyse the formation of the active drug
Active drug is taken up by target cells
What is HAMA
Human Anti-Mouse Antibody
Previously, antibodies for ADEPT systems were made using adapted mouse antibodies, so could only be used as a one time treatment. The human body recognised the foreign antibodies and starts producing antibodies against them.
Now less of a problem as we can engineer mouse antibodies so that the body does not recognise them as foreign.