Bones and bone tissues
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

22 Terms
Functions of bone tissue
Provide attachment for skeletal muscles
Assist in movements along with skeletal muscles
Contain red bone marrow (produce RBC)
Contain yellow bone marrow (store triglycerides)
Types of bones
long, short, flat, irregular, sesamoid
long bones
longer than they are wide, bones of the arms and legs
short bones
bones of the wrist and ankles
flat bones
thin, flat, and curved; form the ribs, breastbone, and skull.
sesamoid bones
patella and pisiform
Parts of a long bone
diaphysis, epiphyses, metaphyses, articular cartilage, periosteum (line outside of bone), medullary cavity (yellow bone marrow), endosteum (line medullary cavity)
Bone surface markings
tuberosity, tubercle, trochanter, process, spine, line, crest, head, condyle, epicondyle, fossa, fovea, impression, sulcus, incisura, fissure, foramen, canal, meatus
composition of intercellular matrix of bone tissue
type 1 collagen (organic matrix); inorganic matrix (calcium hydroxyapatite crystal); ground substance (proteoglycans + osteocalcin, osteopontin...)
osteoprogenitor cells
only bone cells that can divide; mesenchyme derived
Osteoblasts
produce bone ECM; become osteocytes after being trapped in their secretions; located on forming bone surface
Osteocytes
maintain bone tissue; located in lacunas; connect with each other through processes (gap junctions)
osteoclasts
breakdown of bone ECM (lysosomal enzymes); large cells with many nuclei; located on interior bone surface (Howship lacunas)
woven bone
high cellular density; low organized ; uneven mineralization; produced when growing fast, fracture healing, forming embryonic bone
lamellar bone
compact and spongy bone; structural units - osteon
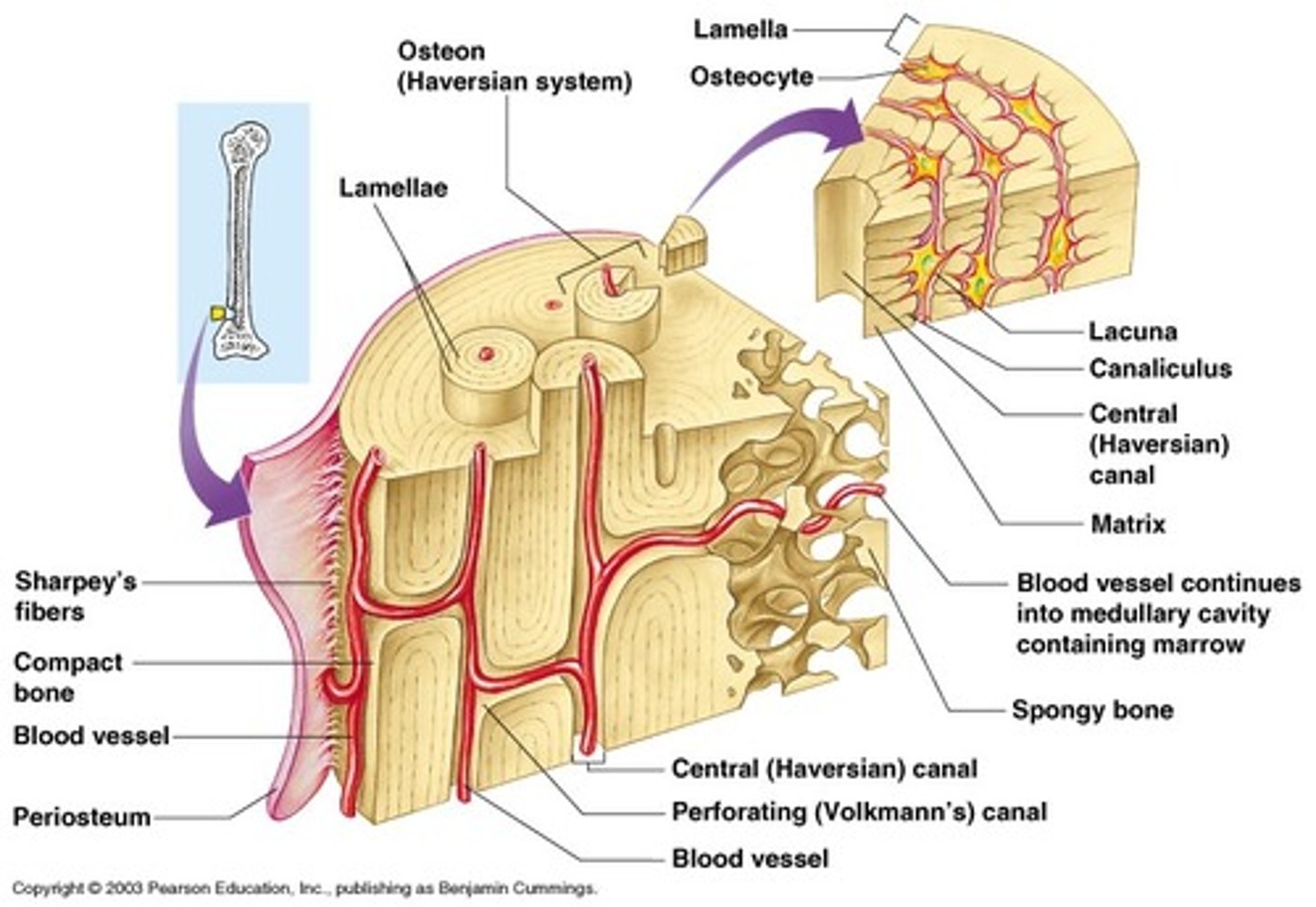
primary ossification
undifferentiated mesenchymal cells form osteoblasts directly
secondary ossification
pre-existing supporting tissue is converted into bone; intramembranous and endochondral ossification
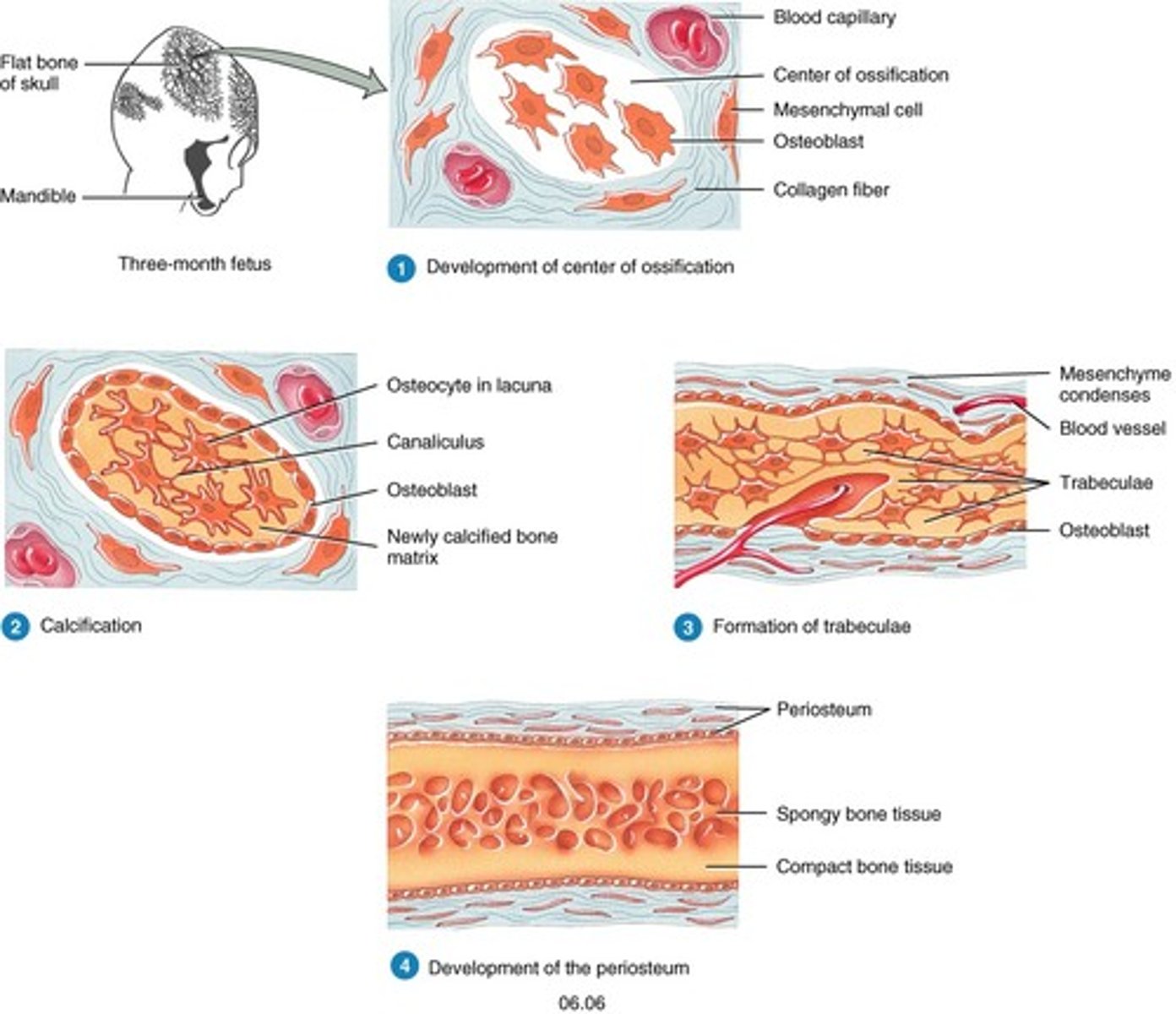
intramembranous ossification
initial tissue - connective tissue; flat bones of skull, mandible, clavicles
endochondral ossification
initial tissue - cartilage
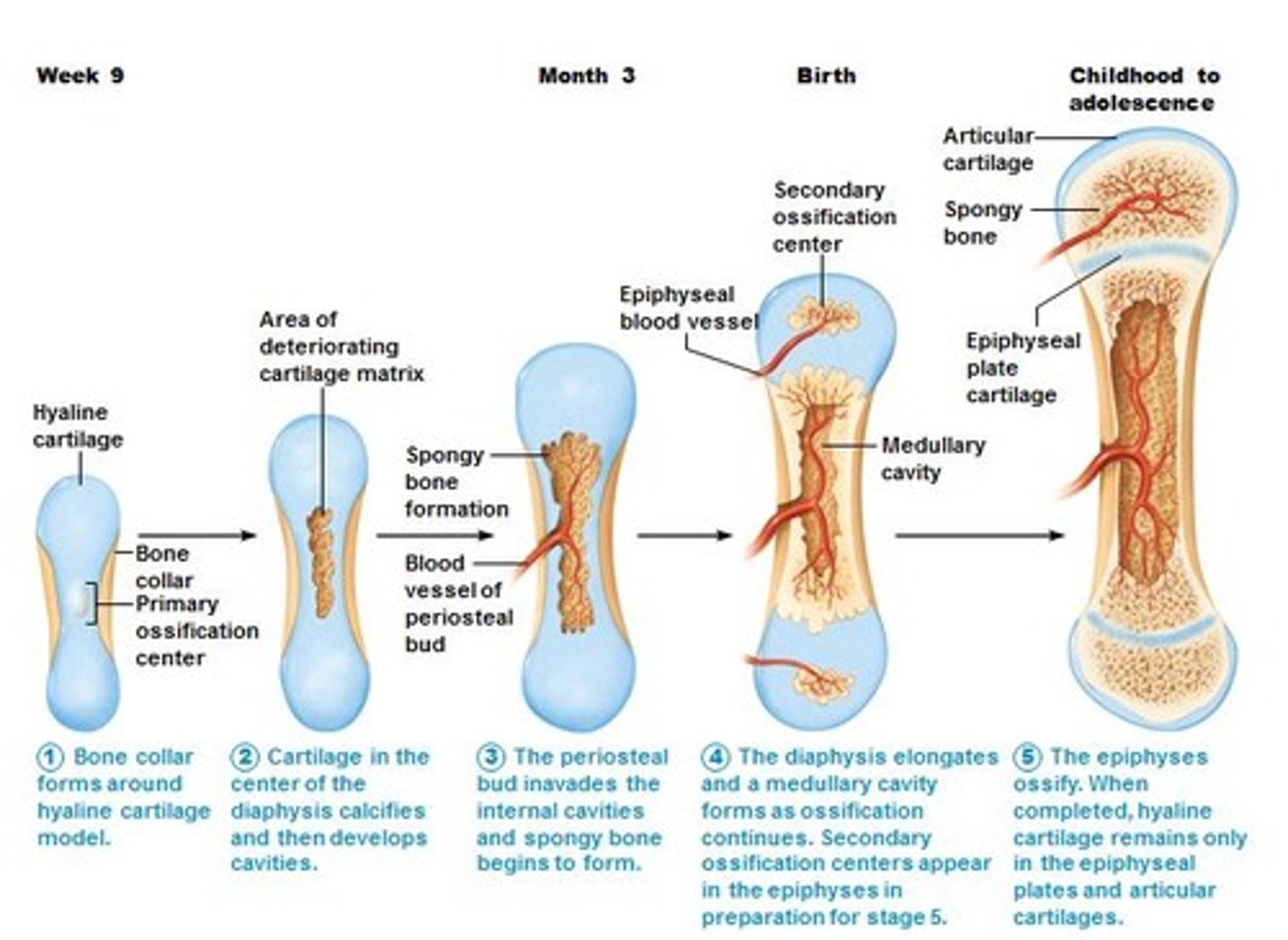
epiphyseal plate
hyaline cartilage; allow diaphysis of bone to increase in length; found between epiphysis and metaphysis
appositional growth
thickening of long bone; increase in the diameter of bones by the addition of bony tissue at the surface of bones (under periosteum)
remodeling of bone
Resorption by osteoclasts and replacement by osteoblasts
Bone remodeling units: osteoclast and osteoblast
Triggered by parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Active when young, slow down in old age