ARTH 2400 Cornell
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Guild
an association of craftsman, or merchants, often holding considerable political and economic power
Campanile
a bell tower, usually attached to a church, castle, or palace
Loggia
a gallery or room with one or more open sides
Humanism
the worldview centered on the nature and important of humanity and human achievement, which emerged from the study of Classical antiquity
All’antica
in the manner of the ancients particularly referring to Renaissance architecture inspired by classical Roman and Greek styles.
Magnificence
A moral virtue that consists of spending great amounts of money on appropriately large scale and grand things, befitting to ones station in societyand demonstrating one's status and wealth through lavish expenditures.
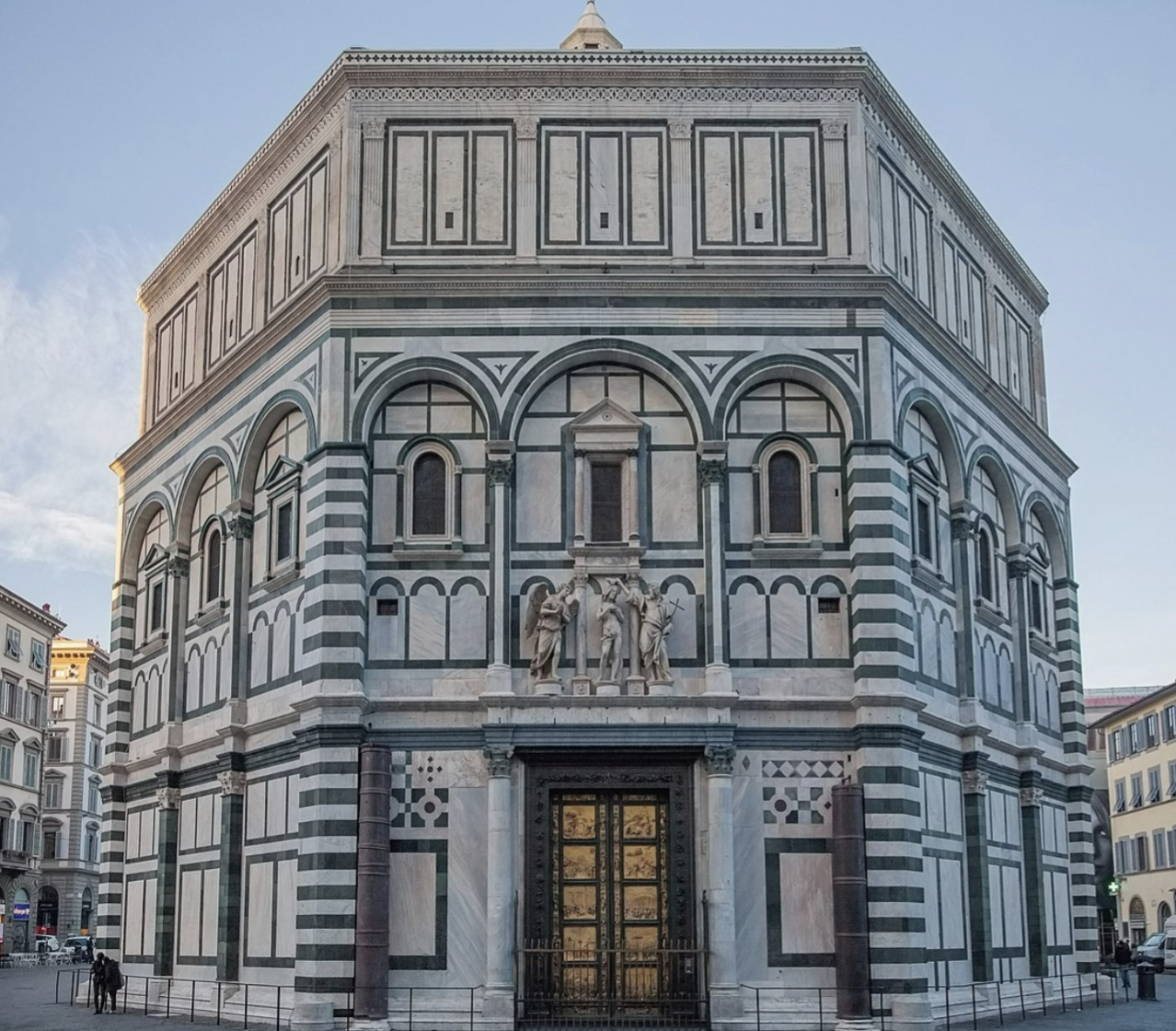
St. John’s Baptistery
constructed from 1059 to 1128, constructed from sandstone and marble, first example of Linear Perspective and an important example of Romanesque architecture in Florence, Italy.

Horizon Line
Where the sky appears to meet the ground
Orthoganals
All parallel lines that converge in a single vanishing point on the pieces horizon
Vanishing Point
The point where parallel lines appear to converge in a perspective drawing.
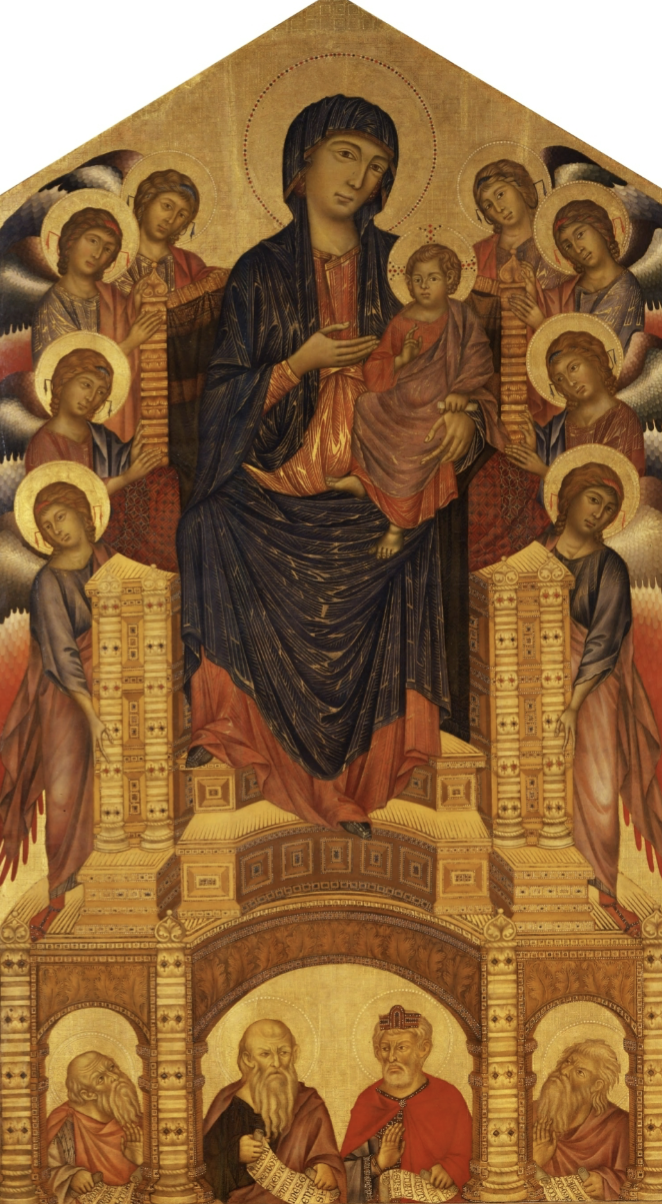
Maesta
A compositional format depicting an enthroned Madonna with the child Jesus generally, accompanied by angel and/or saints
Cimabue, Santa Trinita Maesta

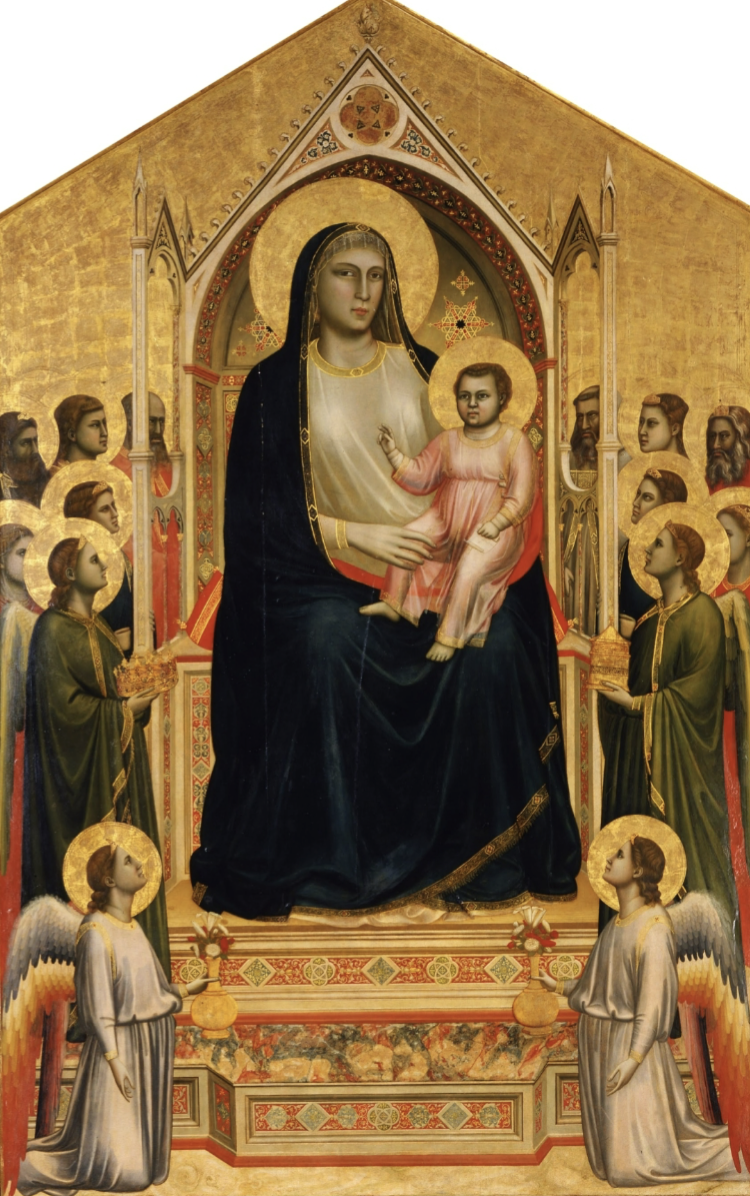
Naturalism
a lifelike accuracy, or artistic interest in representing things as they appear in real life
Giotto di Bondone, Ognissant Madonna

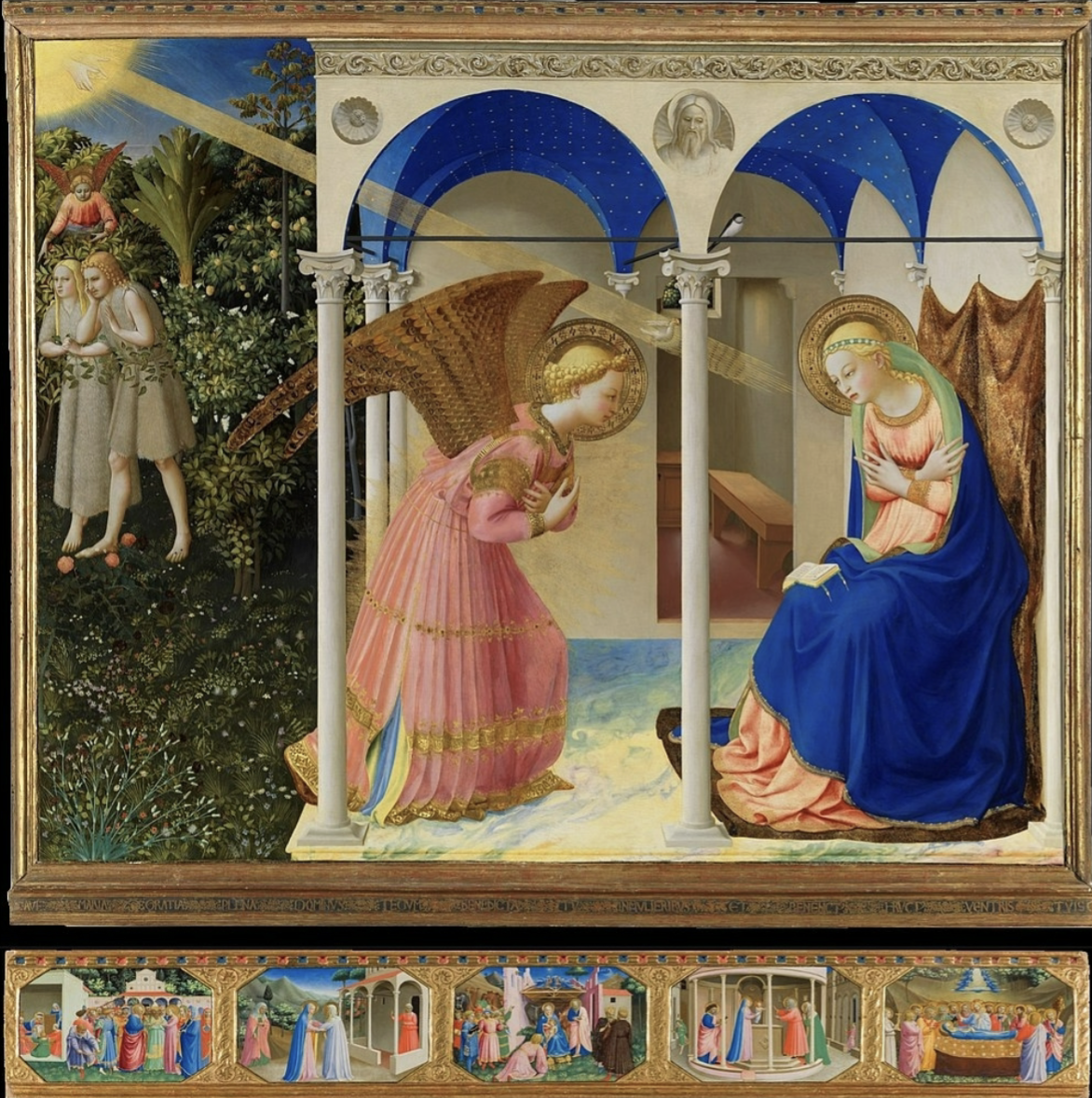
Fra Angelico, The annunciation

Masaccio, The Holy Trinity
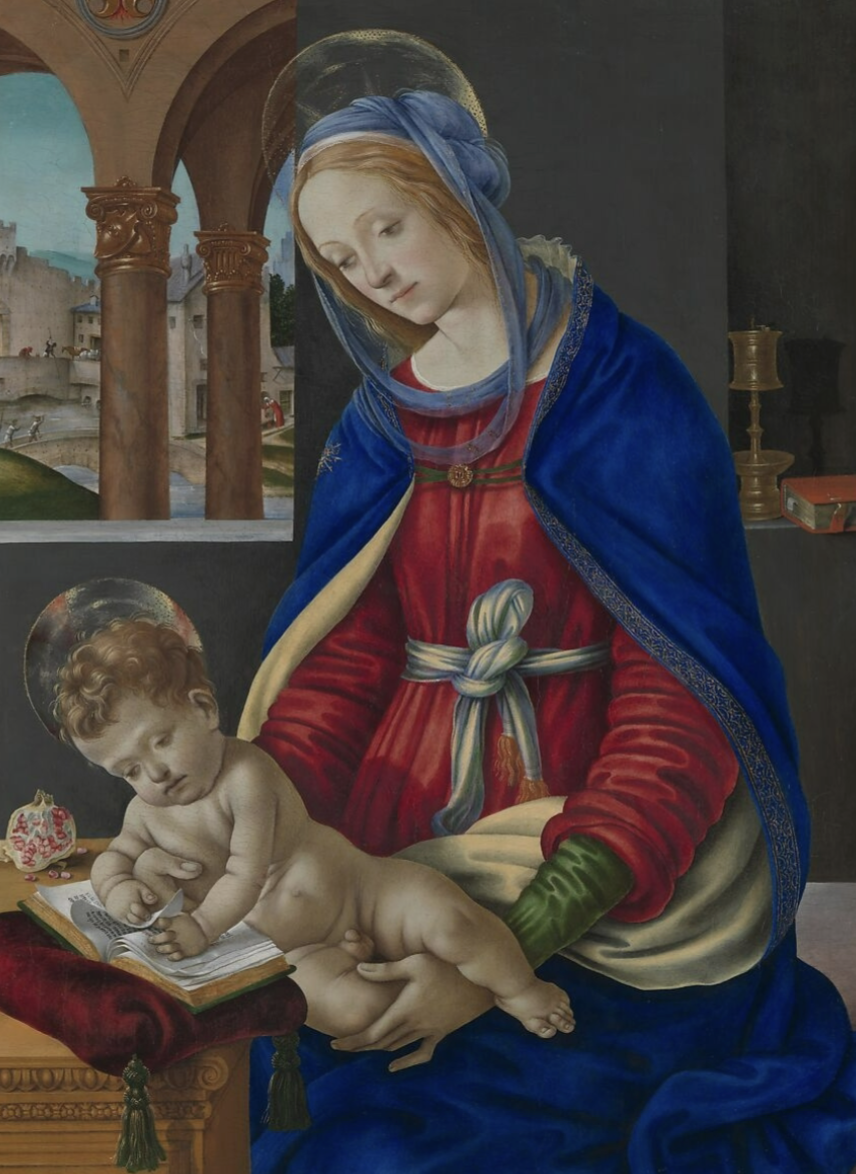
Filippino Lippi, Madonna and Child

Renaissance
a period of cultural dynamism between the 14th and 17th centuries in Europe
Baroque
A western style of artistic production from 1600-1750 characterized by material exuberance, dramatic, exaggerated motion, and a sense of grandeur, awe and surprise
Early modern period
describes the era from the 15th century and 18th century
Sacra conversazione
a composition type of renaissance painting in which ‘attendant saints are group in a unified space around the centralized virgin and child in a single panel
iconography
symbolic representation, especially the conventional meanings attached to an image
Stigmata
marks corresponding to those left on Jesus’ body by the crucifixion, said to have been impressed by divine favor on the bodies of certain saints
Pieta
the Virgin Mary holding Jesus immediately after the crucifixion, him laying atop her