Exam 3
1/115
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
Ionization energy
amount of energy required to expel and electron from its outermost shell
Quadrupoles
2 sets
2 vertical are positive
2 horizontal are negative
Use electrostatic attractions and momentum to get ions through the quarupoles
Time of Flight MS
all ions leave ion source at the same time WITH same kinetic energy
larger the ion, the slower the velocity, the longer it takes to traverse through the field-free region
Key components of tuning and calibration GC/MS
mass accuracy
properly assigns masses for calibrant
important for database searching
Mass resolution
can distinguish between adjacent masses
important for isotope id
Appropriate sensitivity
dynamic system must be adjusted as the source gets dirty
need for consistency
No air leaks
need to minimize secondary interactions
secondary fragements
loss of focus to the detector
Two types of high vacuum pumps
Turbomolecular pump
has fixed blades that spin like jet engine
most common
Diffusion pump
high molecular fluid is heated
Repeller, IonFocus, EntLens, EntOffs
optimized voltages determined from autotune
Emission and EIEnergy
energies associated with the filament necessary to ionize and create fragments
Filament
indicates which of the two is in use
Stepsize
value between scans
Samples
number of readings taken for the profile data
Averages
number of averages done to the sampled scans
HEDEnab
high energy dynode
reduces background signal
EMVolts
voltage of the tube electron multiplier tube
over time higher voltages are required to maintain consistent abundances
Centroid data
typical mass spectra
has bars for the ions
smaller file size
some information loss
profile data
looks like a typical chromatogram
has peaks that resolve to baseline
large file size
no information loss
Manual tune
can be used to diagnose issues
leaks
pump oil
column bleed
can manually input settings if there are issues in tune or with data
Ion source differences
High pressure
ion source is located IN high vacuum
Atmospheric pressure
ion source is located OUT of high vacuum
Where is the mass analyzer located?
in the high vacuum
Electrospray ionization
sample is dissolved in polar solvent
pumped through stainless steel capillary with voltage between 2000-4000 volts
liquid is aerosolized as it exits the capillary
solvent is evaporated by drying gas and removed by vacuum pumps
additional fragmentation can be done in this area
fragmentor
cone voltage
2 modes
positive
negative
positive mode
best suited to basic drugs that form a stable HCl salt
[M+H]+ is the primary ion formed
[M+nH]n+ and [M+Na+]+ can also be formed
lose electrons
negative mode
best suited to acidic drugs that form stable Na salts
[M-H]-, [M-nH]n-, and [M+I-]-
lose hydrogen
Cone voltage
extracts ions from atmospheric pressure region of the ion source into the high vacuum region of the mass analyzer
to induce in-source fragmentation (CID) for structural determination
for declustering heavily hydrated ion sin order to reduce their mass
Typical cone voltage is 10-60 V
Homolytic cleavage
breaking of a covalent bond in such a way that each fragment gets one of the shared electrons
produces free radicals
Heterolytic cleavage
breaking of a covalent bond in such a way that one atom gets both of the shared electrons
occurs in polar bonds
electrons will move to the most electronegative atom
Alpha cleavage
happens at the alpha position on the molecule
lose the electron from oxygen radical + bond adjacent
loss from other side of the molecule
Beta cleavage
occurs for both homolytic and heterolytic cleavages
breaks bond in the beta position
Alcohol preferred fragmentation
cleavage of C-C bond next to oxygen
loss of water may occur
possible small molecular ion
Amine preferred fragmentation
small molecular ion is an odd number if odd number of N atoms
Base peak forms from cleavage adjacent to the C-N bond
Deconvolution Reporting Software
noise is defined and compensation factored in
scan skew is compensated for
true peak max is found
to the nearest 1/10th scan
Full spectrum deconvolution= all ions used
resulting spectra called components
Components matched against Target Library
full spectrum used
GC/MS interpretation procedure
Identify molecular ion if present
Evaluate any isotopic observations
use isotopes to calculate probable carbons numbers for molecule and/or fragments
Review all losses observed to determine substructures
review major fragments
hypothesize a molecular structure consistent with above observations
CONFIRM Hypothesis with additional data
chemical ionization MS
High res MS
IR
NMR
Steps to generate a “good” spectrum
scan for masses that are high enough
ensure that there are enough points across the peak
scan speed
subtract the background
column bleed
co-eluting peak
dirty chromatogram
Scan averaging
scan skew
look for signal saturation
nitrogen rule
Rings and double bonds
Nitrogen rule
If molecular mass of an unknown compound to the nearest integer value is an odd number, then the compound contains an odd number of nitrogen atoms
What does HPLC stand for?
High Performance Liquid Chromatography
Basic Components of liquid chromatography
Mobile phase
degasser
high pressure pump
mixing (proportioning) valve
Pulse-dampener
pre-column/guard column
column
injector system
oven
detector system
HPLC mobile phase
Typically a binary system
Mobile phase A and mobile phase B
quaternary system (4 solvents)
polar solvent (aqueous)
non-polar solvent (organic)
Modifieres
Filters/frits for containers
Modifiers
additives to maintain pH (buffers, ion-pairing agents, inorganic salts, organic amines) and other agents that can affect performance
Degassers
remove any dissolved gases in liquid
sonication
vacuum filtration
Why a degasser?
all liquids have dissolved gasses from the air
dissolved gases reduce pump flow stability, detector baseline, and stability, and increase detector noise
influence analytical results
Types of pumps
Reciprocating pump
majority of commercial HPLC use this design
Displacement pumps
produce flow that is independent of viscosity and back pressure
syringe pump
aka metering pump
Pneumatic pump
mobile phase in container is pressurized to force the liquid out at a pre-defined rate
Requirements of HPLC pumping system
generation of pressures up to 6000 psi
pulse free output
flow rates ranging fom 0.1-10 mL/min
flow control and flow reproducibility of 0.5% or better
Corrosion-resistant components
Mixing chamber
mobile phases brought together and mixed depending upon the requested proportions
Isocratic= static proportions
Gradient=dynamic proportions
Pulse damper
tubing stretches when pressure rises so extra flow flow from the pump at this moment is accommodated by extra volume of the damper
Acts as a shock absorber to smooth out pulsating flow
Pre-column
small disposable cartridges packed with a frit and some column material
designed to catch any particulate material so that the column does not become clogged
Column
Dimensions
4.6mm x100 mm (id x length)
Particle size
3.5 um for HPLC
2 um for UPLC
Pore size
300 angstrom
Stationary phase
C18, C8, CN, etc.)
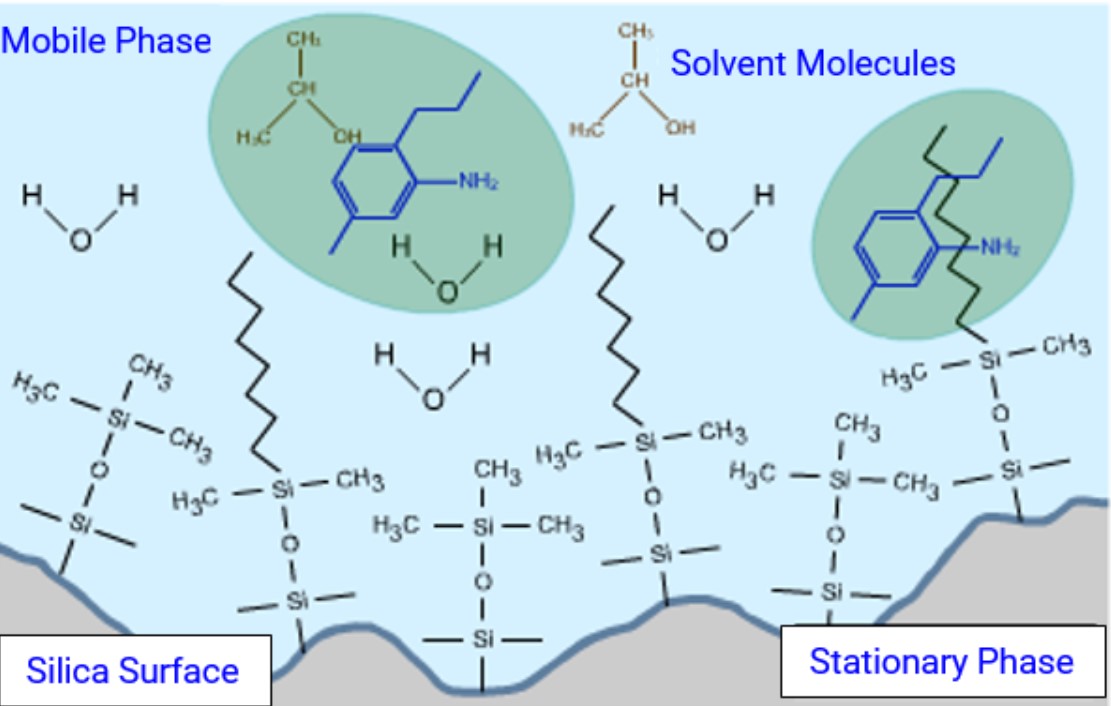
Reverse Phase HPLC
Stationary phase is NON-POLAR
Mobile phase is POLAR
most commonly used
base on partitioning of analyte between aqueous mobile phase and analytical column
Polar analytes less retained
Normal phase HPLC
Stationary phase is POLAR
Mobile phase is NON-POLAR
non-polar analytes less retained
UPLC
accommodates sub 2 um particles and very high operating pressure
significant improvements in resolution over HPLC and/or faster runtimes
Isocratic mode
constant proportion of mobile phase A and mobile phase B employed. Good for target compound analysis
Gradient mode
employs a constantly varying proportion of mobile phase A to mobile phase B starting highly aqueous (A) and changes to highly organic (B). Allows for multiple analyte detection in a single run
Ion-paring mode
An ion pair reagent is added to the mobile phase to bond to the charged species to shield and cancel apparent changes to allow for retention on the stationary phase
End-capping
A process used in chromatography to modify the surface of the stationary phase, reducing unwanted interactions and improving peak shape.
Avoids secondary interactions with the silica
Factor affecting liquid chromatography
Flow rate
temperature
mobile phase composition
solvent strength
mode
isocratic vs gradient
Amount injected
pH stationary phase
column attributes/dimesions
LC detectors
Uv-Vis
Uses absorbance of UV radiation at specific wavelengths
Diode array
entire spectrum is monitored instead of 1 wavelength. Range is 210-300 nm.
Fluorescence
energy of a specific (excitation) wavelength is absorbed. Compound gives off energy at another (emission) wavelength
Electrochemical
based on the measurement of electrical output of a chemical being oxidized or reduced
MS and tandem MS
LC problems
plugged frit
column contamination
plugged packing
leak
flow incorrect
split peaks from injection solvent effects
fronting peak
peak splitting
Column overload
Phase collapse
irresesevible
silica in column gets tangled and does not stick straight out to catch particles like it should
Why HPLC?
low temperature analysis
polar compounds do not require derivatization
numerous detectors
can be interfaced directly to MS
numerous column phases
can inject aqueous samples directly
more variables to work with
pH
mobile phase composition
many column phases
derivatization to enhance performance
enatiometic separation
Other HPLC techniques
Size Exclusion chromatography
Gel-permeation chromatography
Ion chromatography
mode of HPLC
strong ion exchange columns
strong ionic strength mobile phase
useful for determination of anions
LC applications
pharmaceuticals
vitamins
chiral separations
proteins
peptides
amino acids
drugs
HPLC vs GC
HPLC
non-volatile samples
thermally unstable compounds
resolution not as good
macromolecules
inorganic and ionic samples
more complex interface to MS
GC
volatile and thermally stable
rapid analysis
simple instrumentation
good resolution
easily interfaces to MS
limited in injection solvents
Analyte Polarity
can predict the retention time of analytes relative to each other based on functional groups and how they interact with the mobile and stationary phases.
Mobile phase polarity
Needs to mix with water
cannot be 100% aqueous or 100% organic
Water is most polar and hexane is most non-polar
Stationary phase polarity
What kind of molecules do we want to stick to the column?
Silica is most polar and ODS (octodecyl-silica) is most non-polar
Properties of good HPLC detectors
Selectivity-can look at specific types of molecules
Sensitivity- should match needs of analysis. If looking in ng/mL, then need super sensitive detector like MS
Minimal background- ignores it to focus on analytes
Linear response- needs a large dynamic range to allow for quantitation
Non-destructive
HPLC UV-vis is like GC FID
Detector sensitivity
Refractive index- LOW (1-5 ug)
Conductivity- LOW (10-50 ng)
UV-Vis- MEDIUM (0.5-1.0 ng)
Electrochemical- HIGH (50-500 pg)
Fluorescence- HIGH (10-100 pg)
Mass Spectrometer (10-100 fg)
As the components elute from the column they pass into a detector where some physicochemical property of the analyte is measured (the response).
True
Use the checkboxes to indicate which three of the following statements are TRUE
Solubility in the mobile phase may preclude the HPLC analysis of very large molecules
In HPLC mobile phase components are selected to ensure sample solubility
GC is suitable to analyze volatile components
Pick the correct answer
Mass spectrometer produce spectra that can assist with the identification of sample components for both GC and LC
Reversed phase HPLC uses a system in which the mobile phase is more polar than the stationary phase
True
Select the option that best completes the sentence. In HPLC analytes with strong affinity for the stationary phase
Elute later than those with lower affinity for the stationary phase
Use the checkboxes to indicate which two of the following statements are TRUE (analyte)
HPLC analysis has no volatility issues; however, the analyte must be soluble in the mobile phase
HPLC can analyze samples over a wide polarity range and is able to analyze ionic samples
Use the checkboxes to indicate which two of the following statements are TRUE (mobile phase)
HPLC analysis has no volatility issues; however, the analyte must be soluble in the mobile phase
HPLC uses a liquid mobile phase to transport the analytes (sample) through the column
HPLC is able to analyze samples which are both polar and non-polar.
True
The majority of HPLC detectors are destructive.
False
Use the checkboxes to indicate which three of the following statements are TRUE (detectors)
Some HPLC detectors are non-destructive
Mass Spectrometers can be used as detection systems for HPLC or GC to assist with analyte identification
HPLC should be selected instead of GC when dealing with high molecular weight analytes
Use the checkboxes to indicate which two of the following statements are TRUE (protein)
Large proteins and peptides can be analyzed by HPLC
HPLC is usually carried out at or around room temp
Use the checkboxes to indicate which two of the following statements are TRUE (chromatogram)
High efficiency (narrow) chromatographic peaks have a better chance of being resolved from one another
Good chromatographic peaks are symmetrical
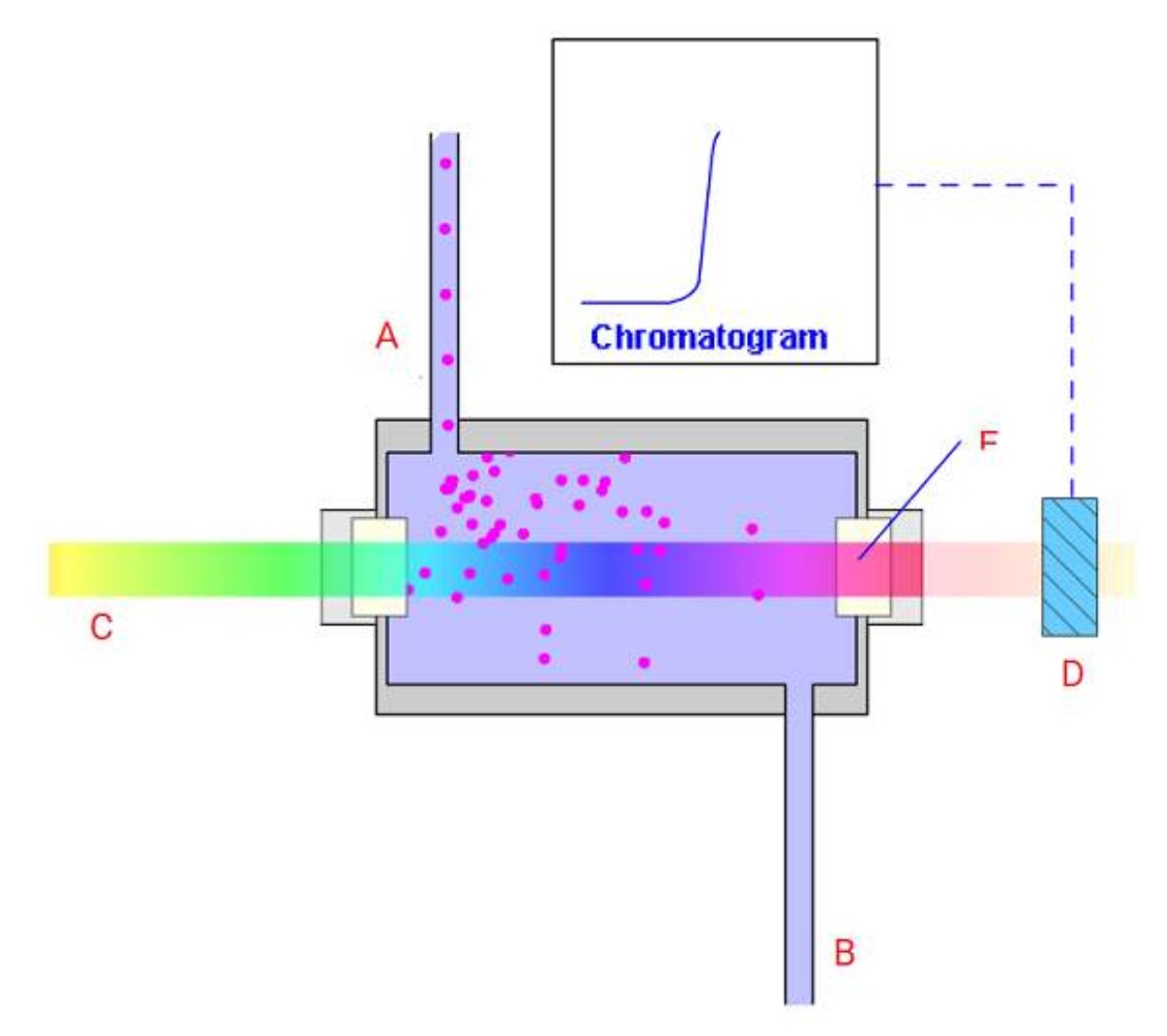
Identify the various components of the UV flow cell and detector:
A=inlet capillary
B=outlet capillary
C=collimated light
D=photodiode
E=flow cell window
Which of the following properties is essential for mobile phase components to be compatible with charged aerosol detection?
Volatile
The recommended minimum signal to noise ratio for the limit of detection (LOD) of a detector for HPLC is:
3:1
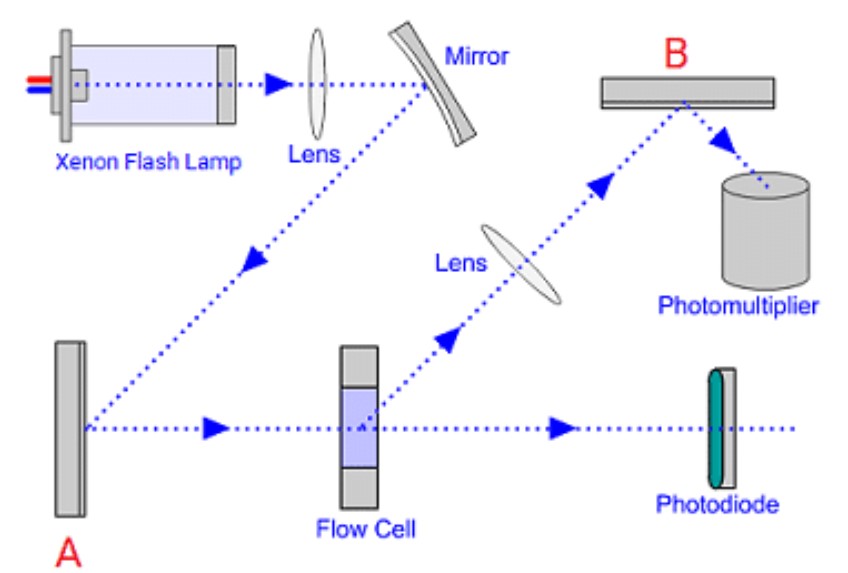
Identify the monochromator type from the schematic diagram of the fluorescence detector blow
A=excitation monochromator
B=emission monochromator
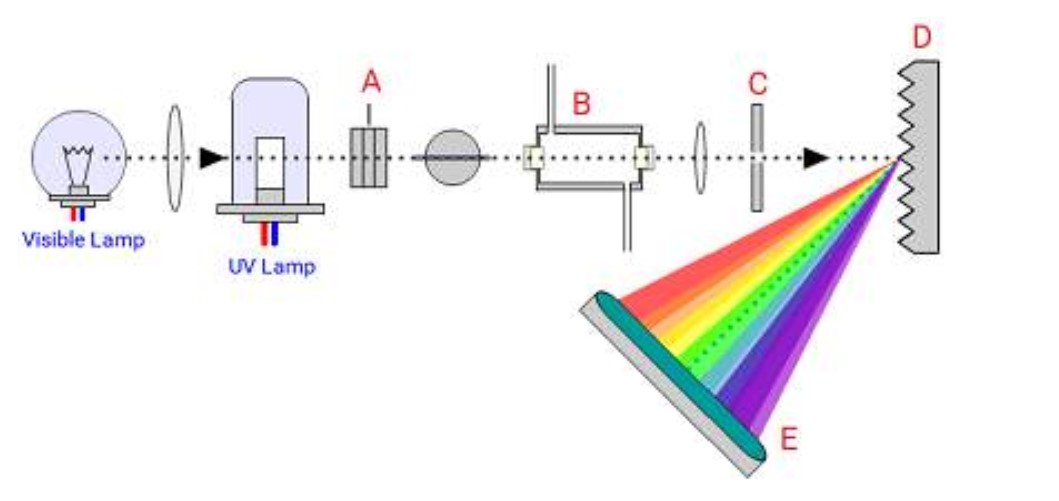
Identify the components of the diode array detector:
A=Achromatic lens system
B=flow cell
C=slit
D=grating
E=photodiode
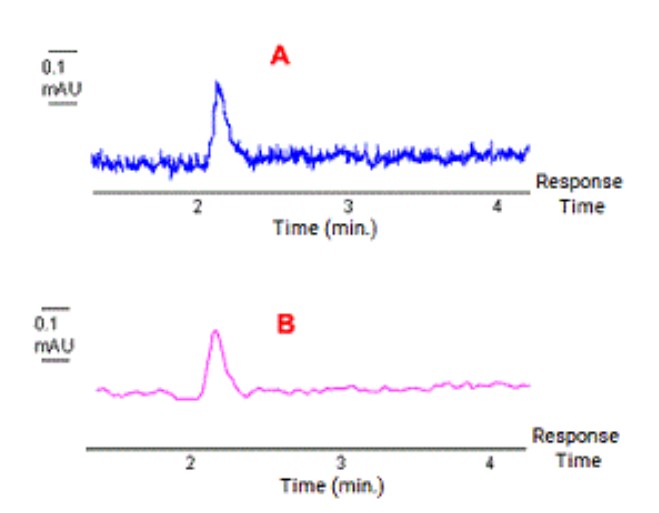
Match the chromatographic output with the detector response time used for the data acquisition:
A=0.1 second
B=2.3 seconds
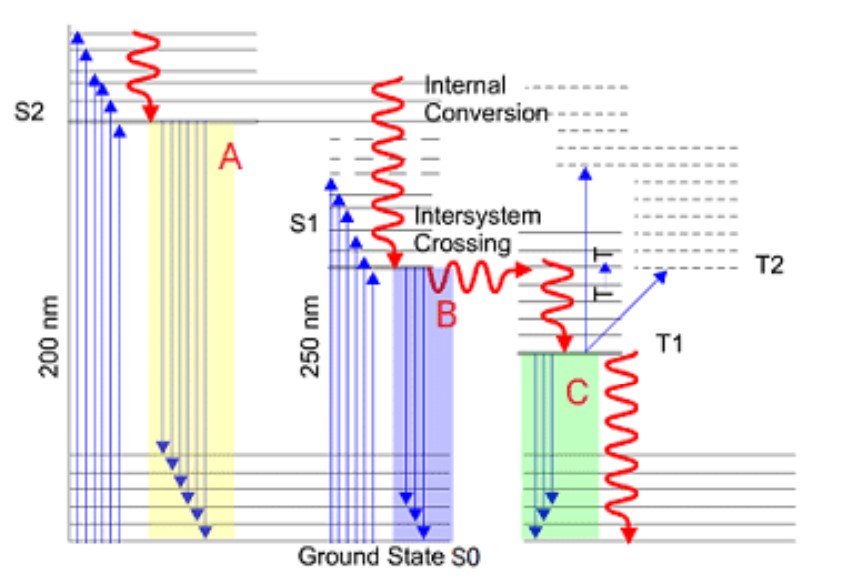
Which of the processes shown represents fluorescence
B
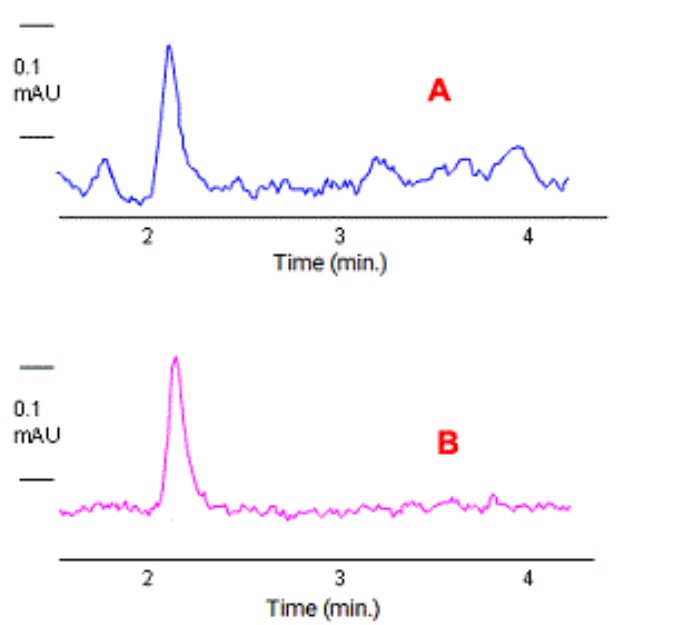
Which of the chromatograms below was acquired using a reference wavelength?
B
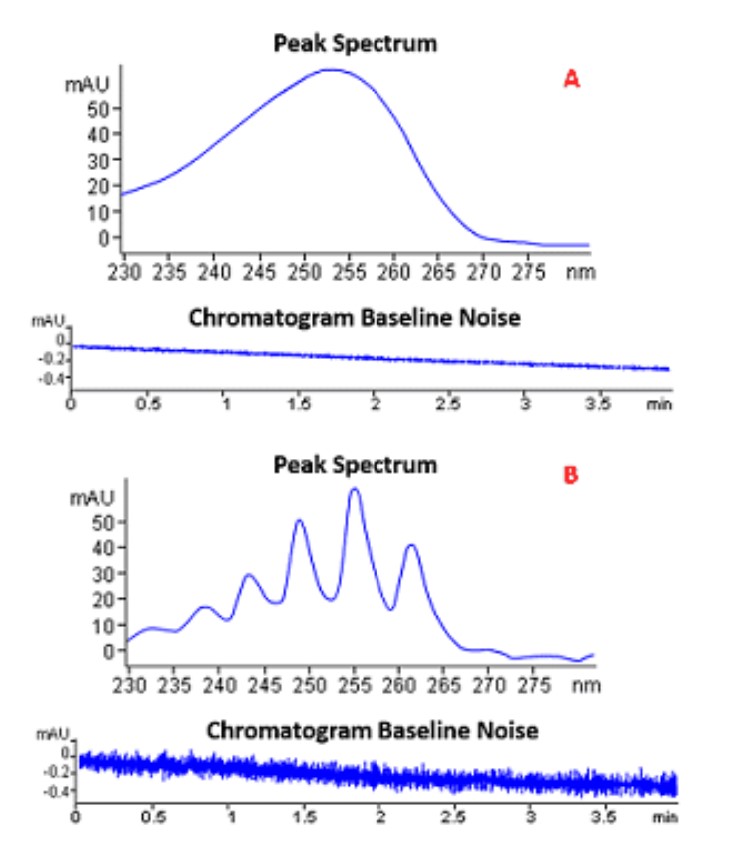
Match the output shown below with the DAD slit width setting used for the data acquisition:
A= 16 nm slit width
B= 1 nm slit width
Which of the following buffers would not be suitable for evaporative light scattering detectors?
Sodium phosphate
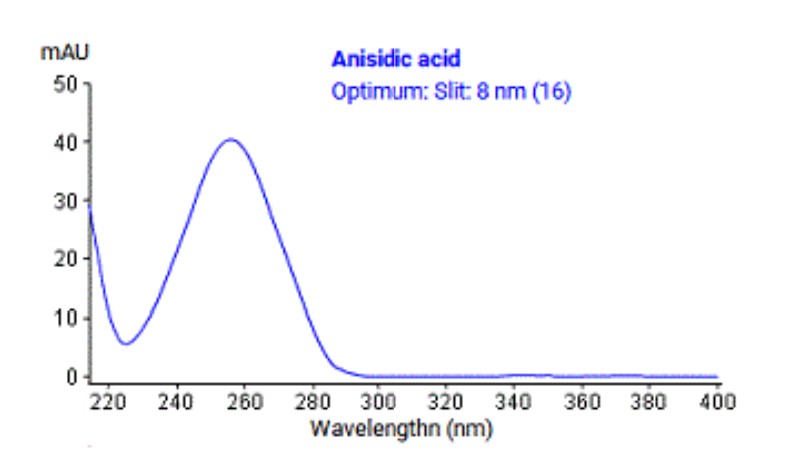
From the analyte UV spectrum below select an appropriate reference wavelength setting for diode array data acquisition:
350 nm
A variable wavelength detector can be used to achieve which of the following
Measure absorbance at a single wavelength
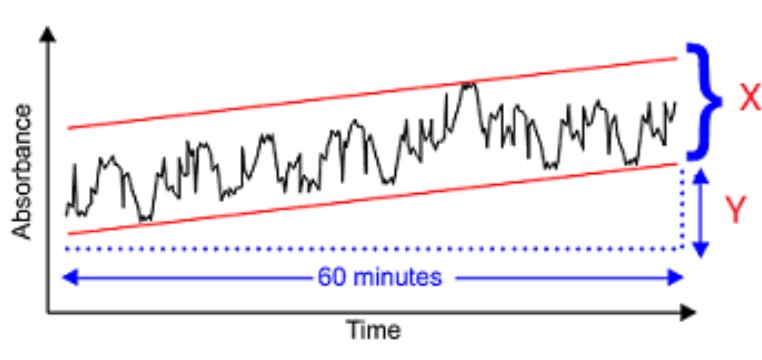
What is the parameter X marked on the detector response schematic below?
Noise
The linear range of an analytical method represents
The concentration range over which the signal obtained is directly proportional to the analyte amount
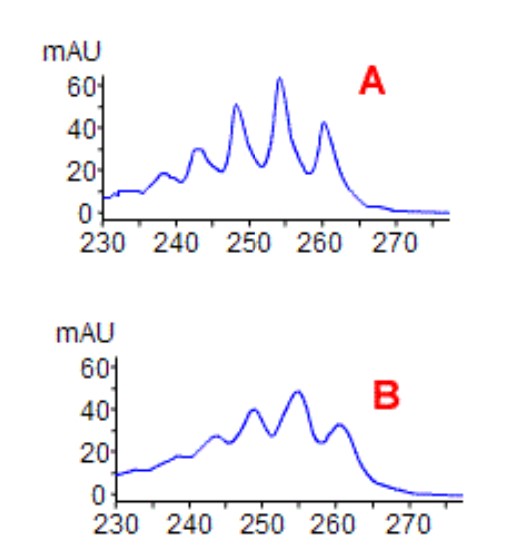
Match the spectrum obtained with the DAD bandwidth setting used to acquire the data:
A= 8nm bandwith
B=30 nm bandwith
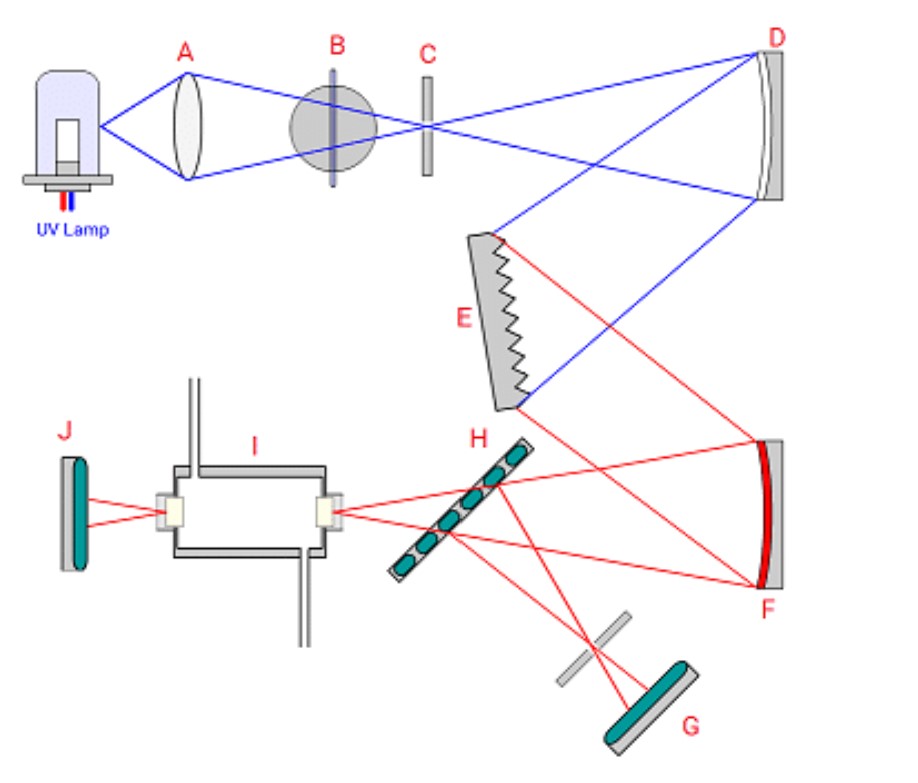
Identify the component in the variable wavelength detector shown that is used to select the desired wavelength for the absorbance measurement
E
To increase charged aerosol detector response for low volatility analytes which of the detector parameters should you adjust?
Increase evaporation temperature
Identify the excitation and emission maxima from the method development experiment below:
A= excitation wavelength
B=emission wavelength
Which 3 of the following could cause excessive baseline noise in evaporative light scattering detectors?
non-volatile mobile phase components
column bleed
nebulizer temperature set too high
In reversed phase HPLC the term sacrificial base refers to
A base that is sued to minimize unwanted secondary silanol retention
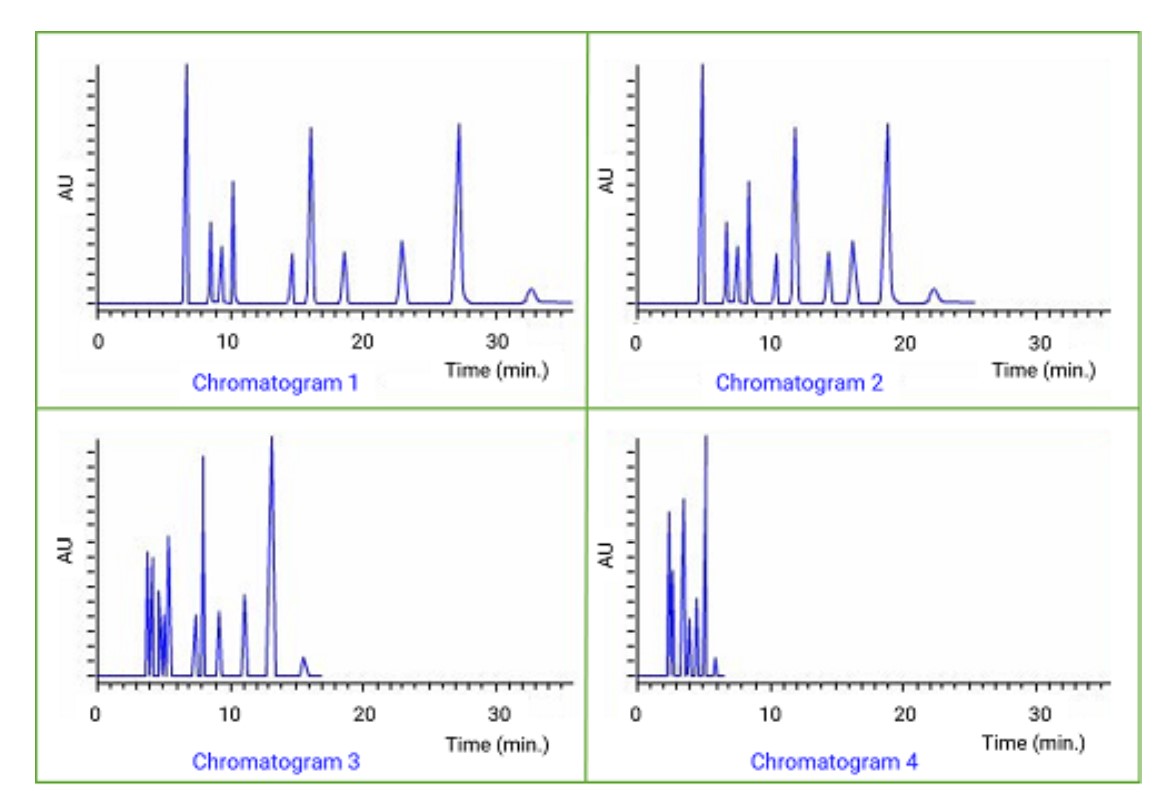
The chromatograms shown were obtained with four different mobile phase systems (same sample, reversed phase conditions): 30%THF, 30% acetonitrile, 30% methanol, and 40% methanol. Which chromatogram was obtained with 30% methanol?
Chromatogram 1
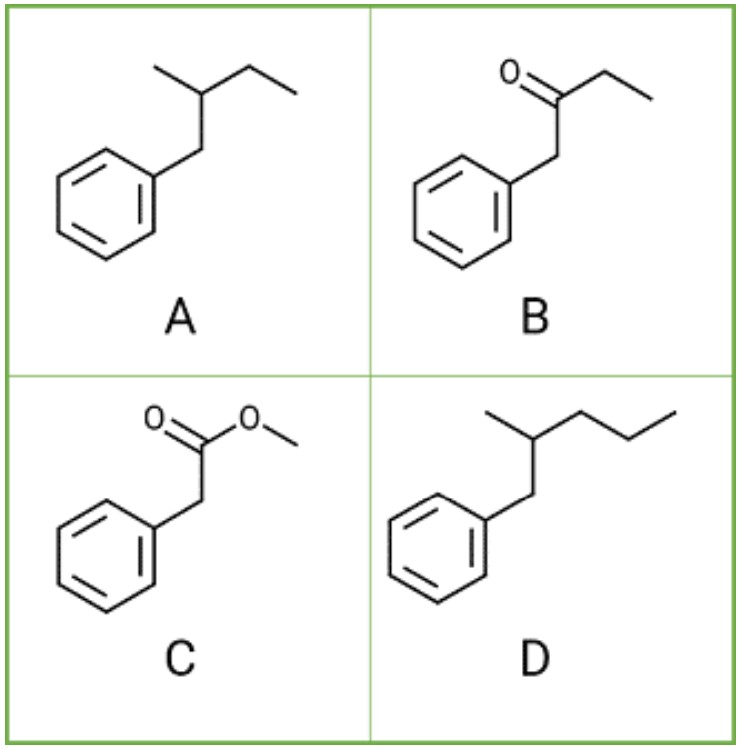
Rank the molecules shown in order of retention . Place the LEAST retained molecule in the first place and the MOST retained molecule in the fourth place
C is 1st
B is 2nd
A is third
D is fourth
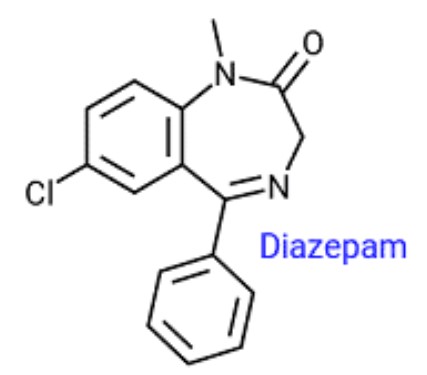
When increasing mobile phase water content in reversed phase HPLC the retention time for the presented analyte will:
Increase
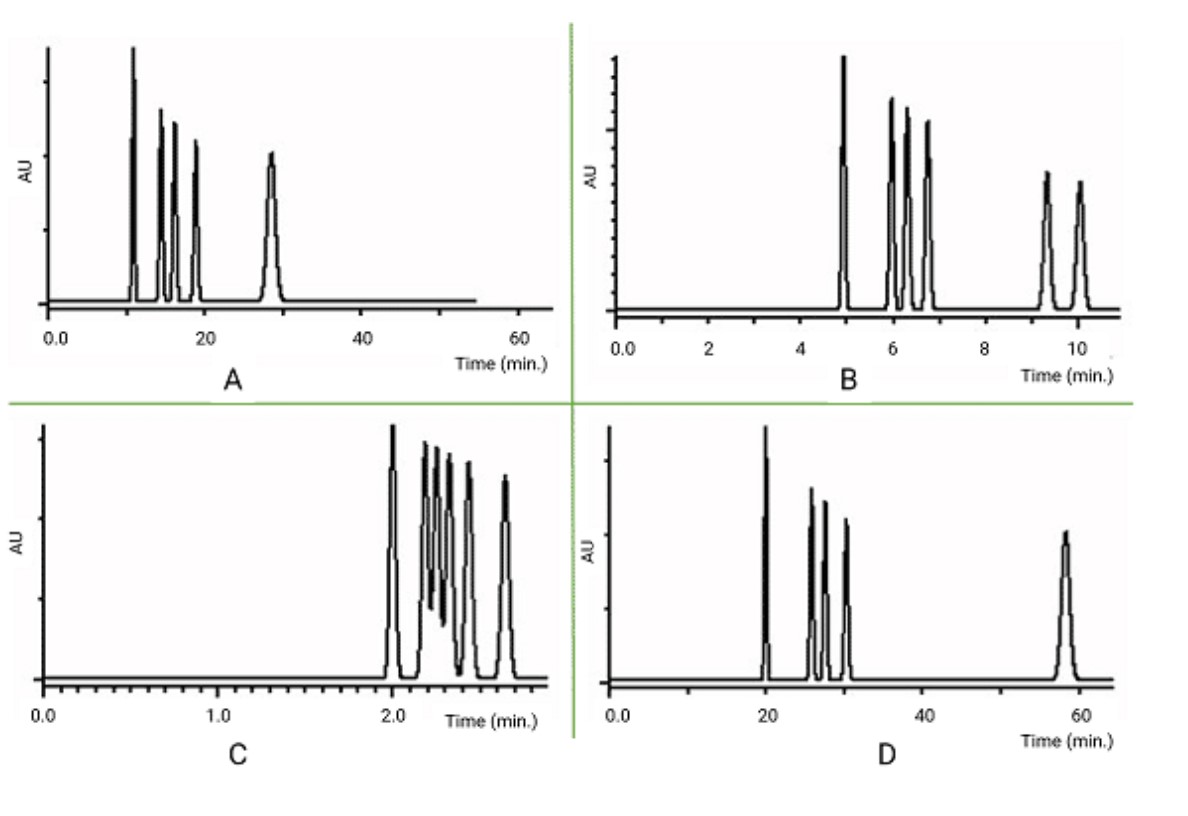
Match the chromatogram with the mobile phase composition that was used for the separation
A=30% organic
B=50% organic
C= 70% organic
D=15% organic