Nervous System: Synapses
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
how are neurons functionally connected?
synapses
what type of junction is found between a neuron and muscle fiber?
neuromuscular junction
what type of junction is found between a neuron and gland?
neuroglandular junction
what type of junctions are found between two neurons?
axodendritic, axosomatic, axoaxonic
what is an axodendritic junction?
axon to dendrite (most common)
what is an axosomatic junction?
axon to cell body
what is an axoaxonic junction?
axon to axon
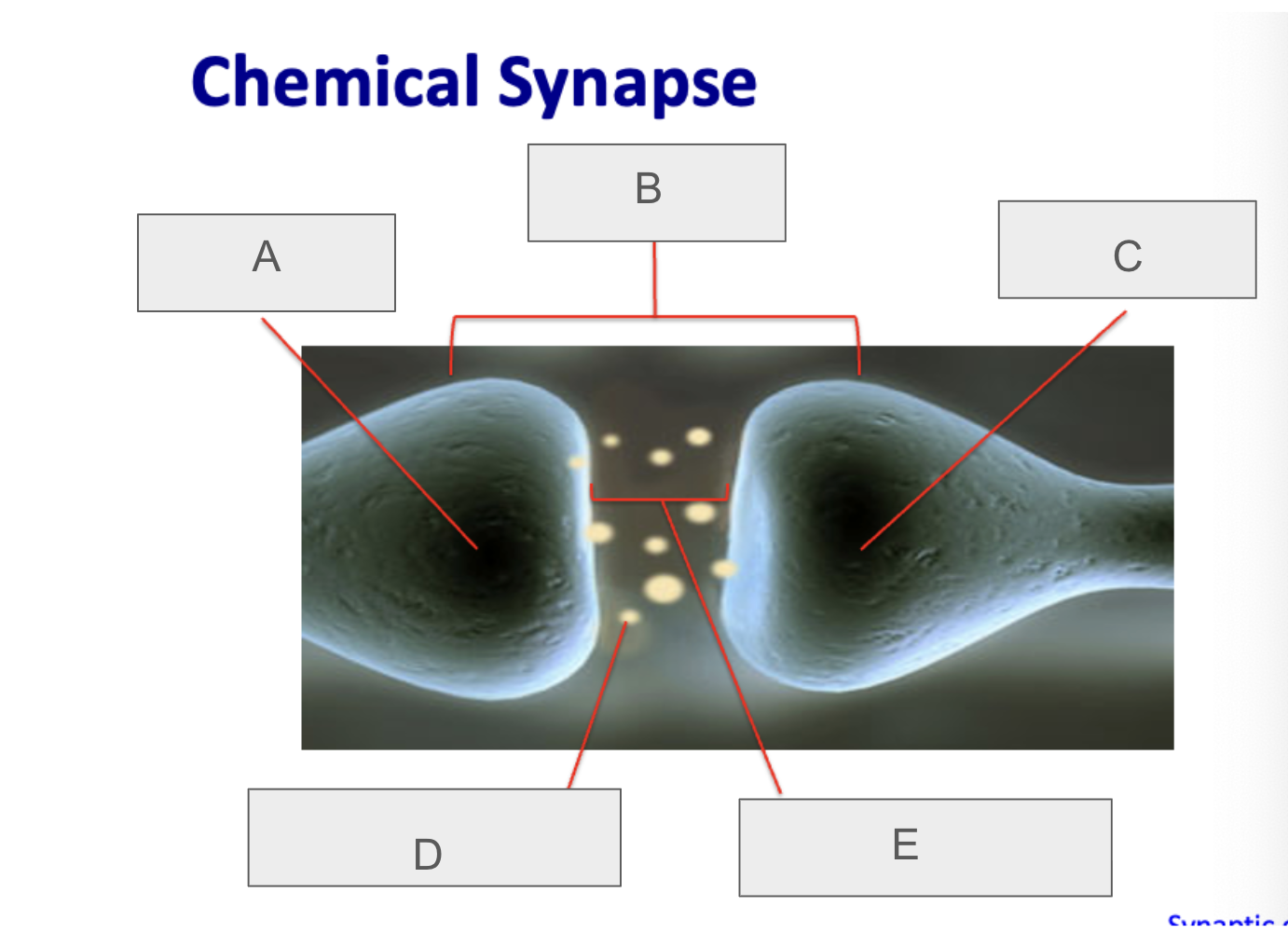
what is A?
presynaptic neuron
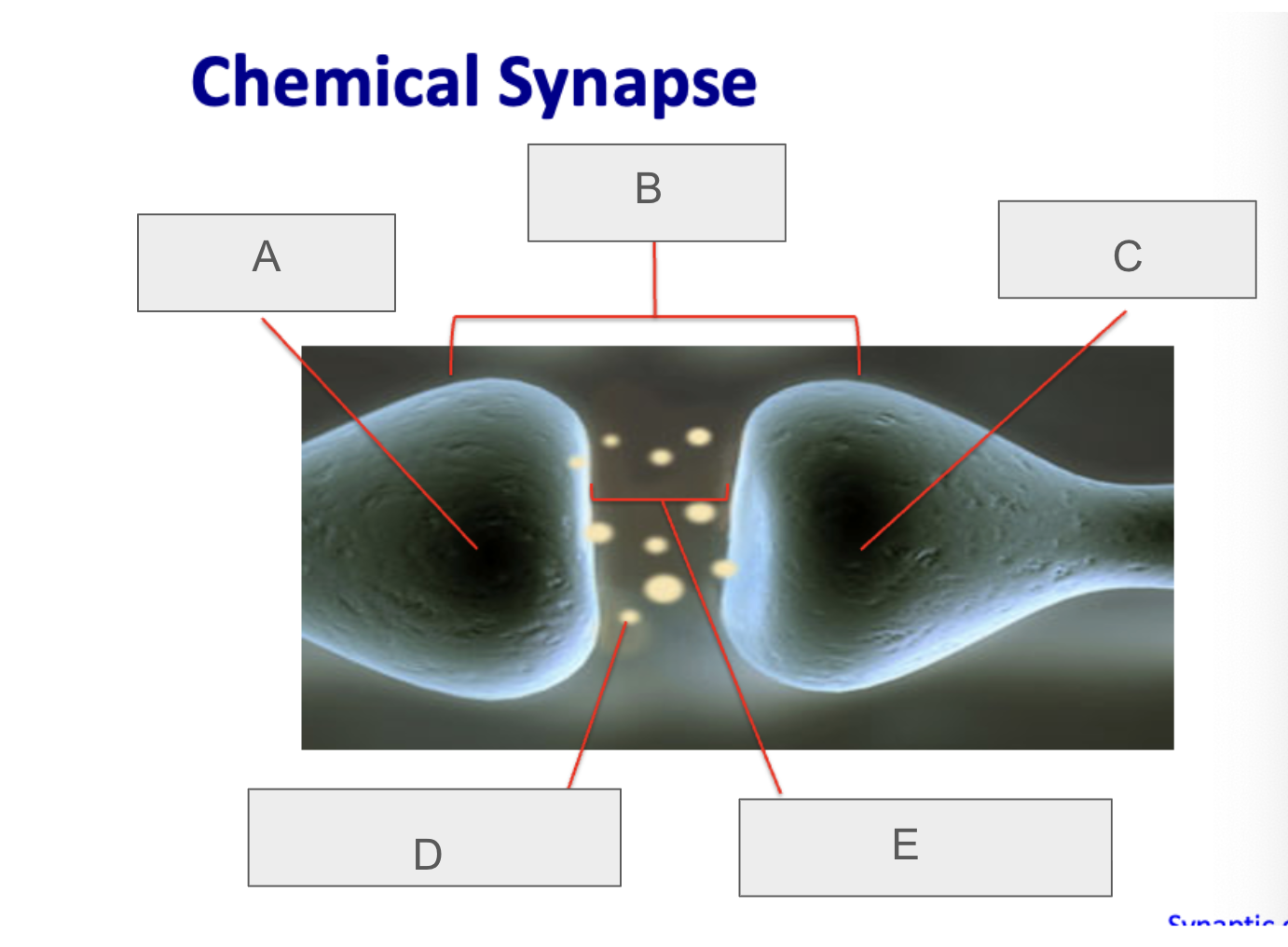
what is B?
synapse
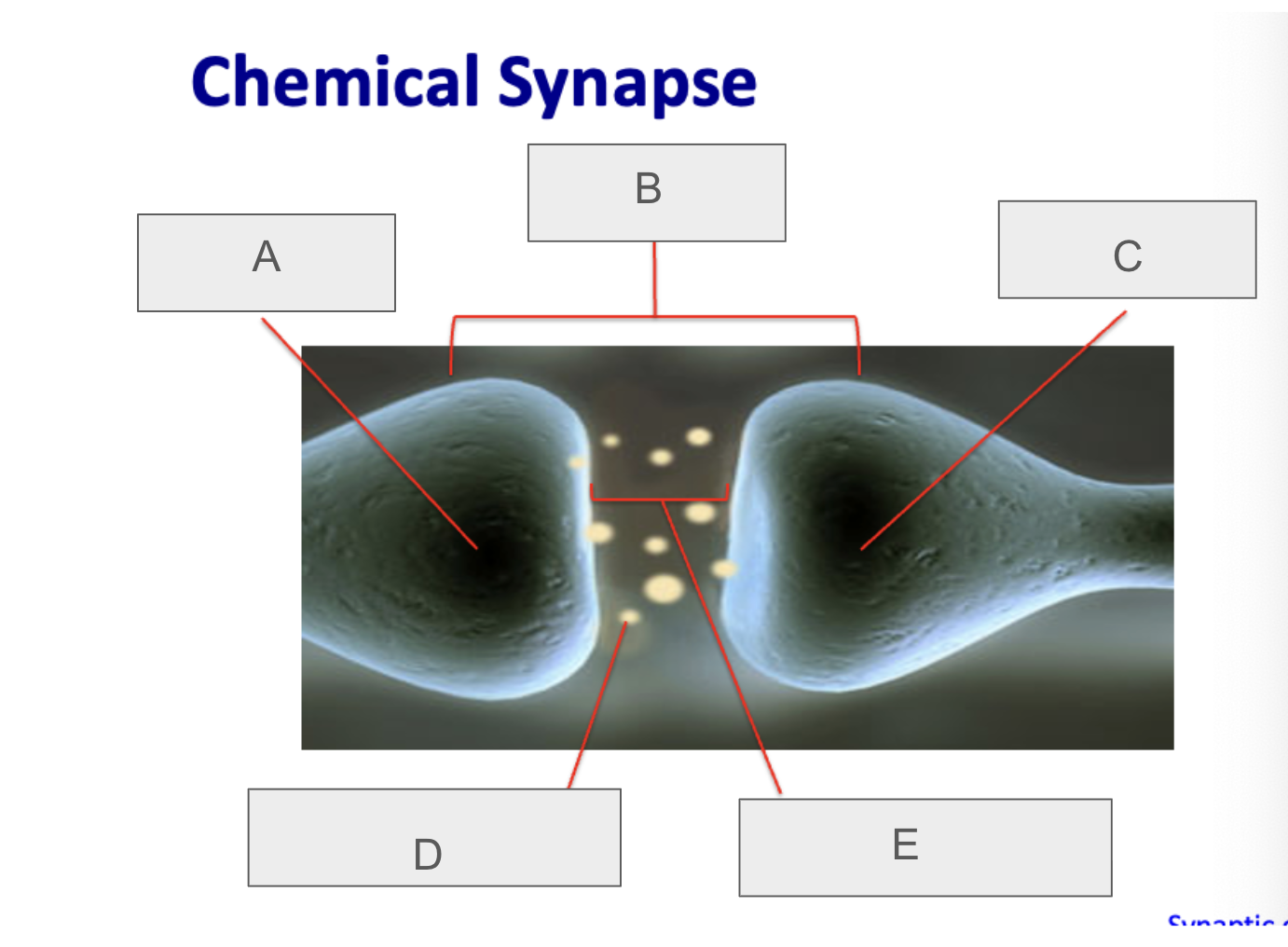
what is C?
postsynaptic neuron
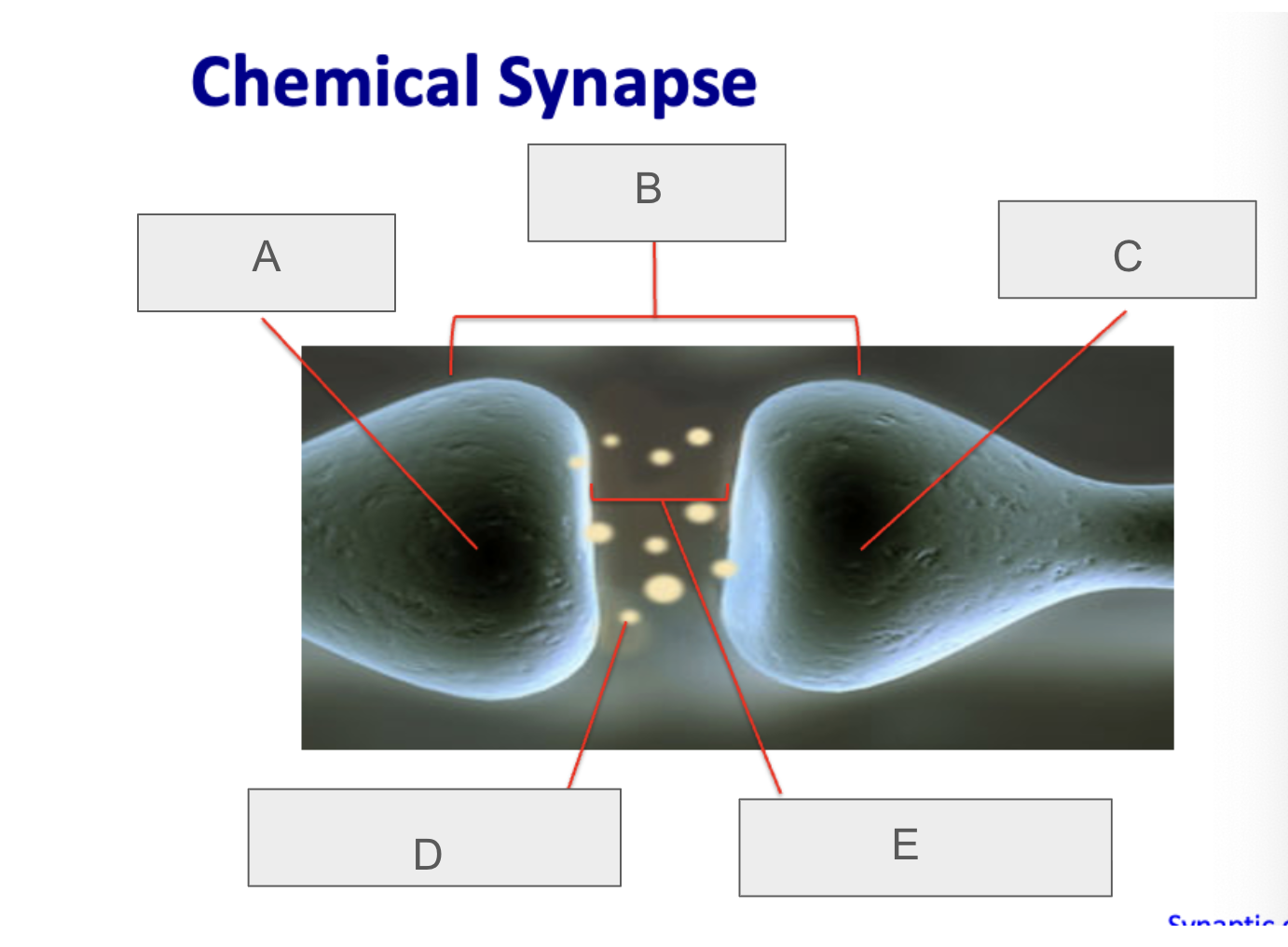
what is D?
neurotransmitter
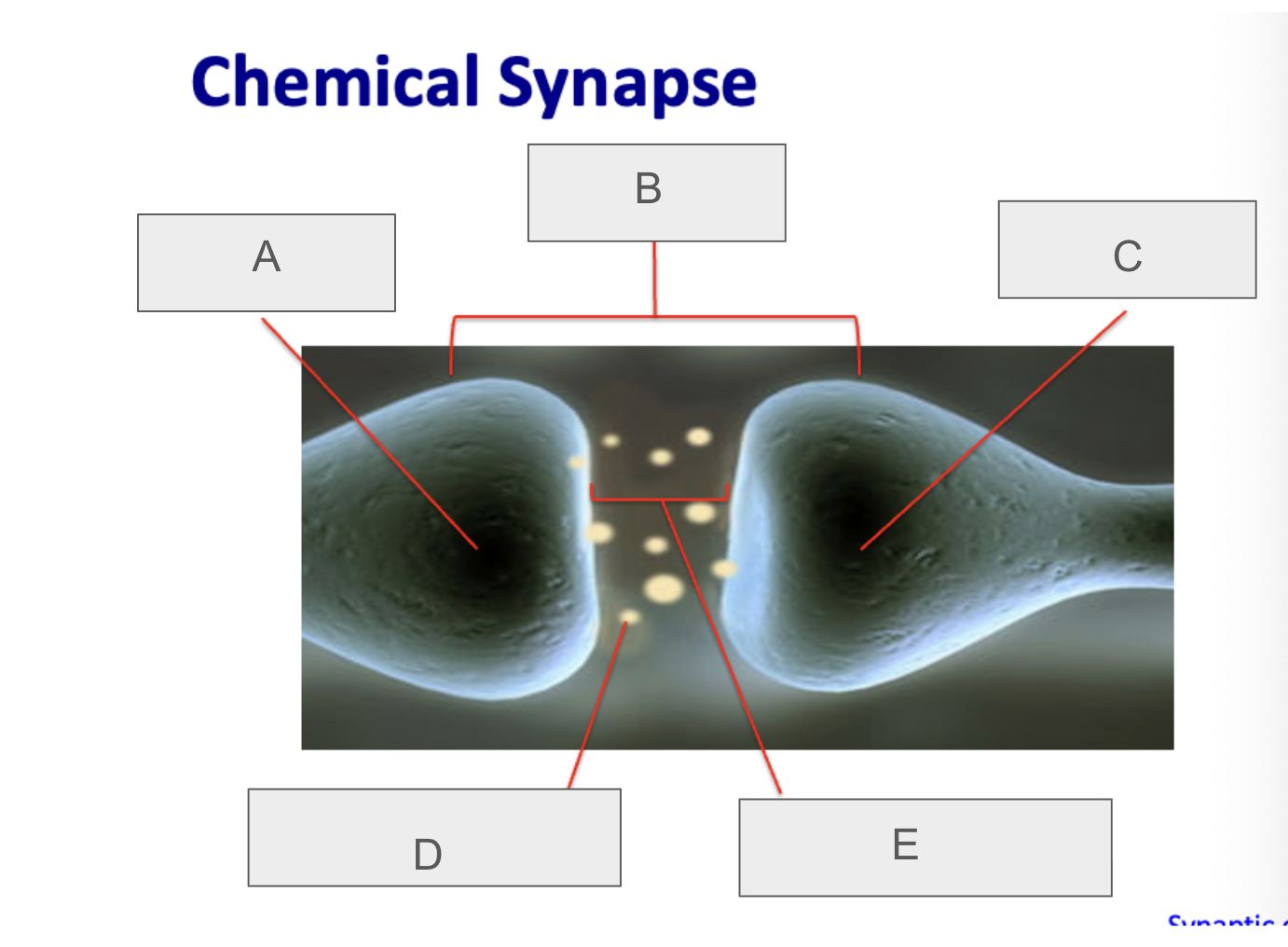
what is E?
synaptic cleft
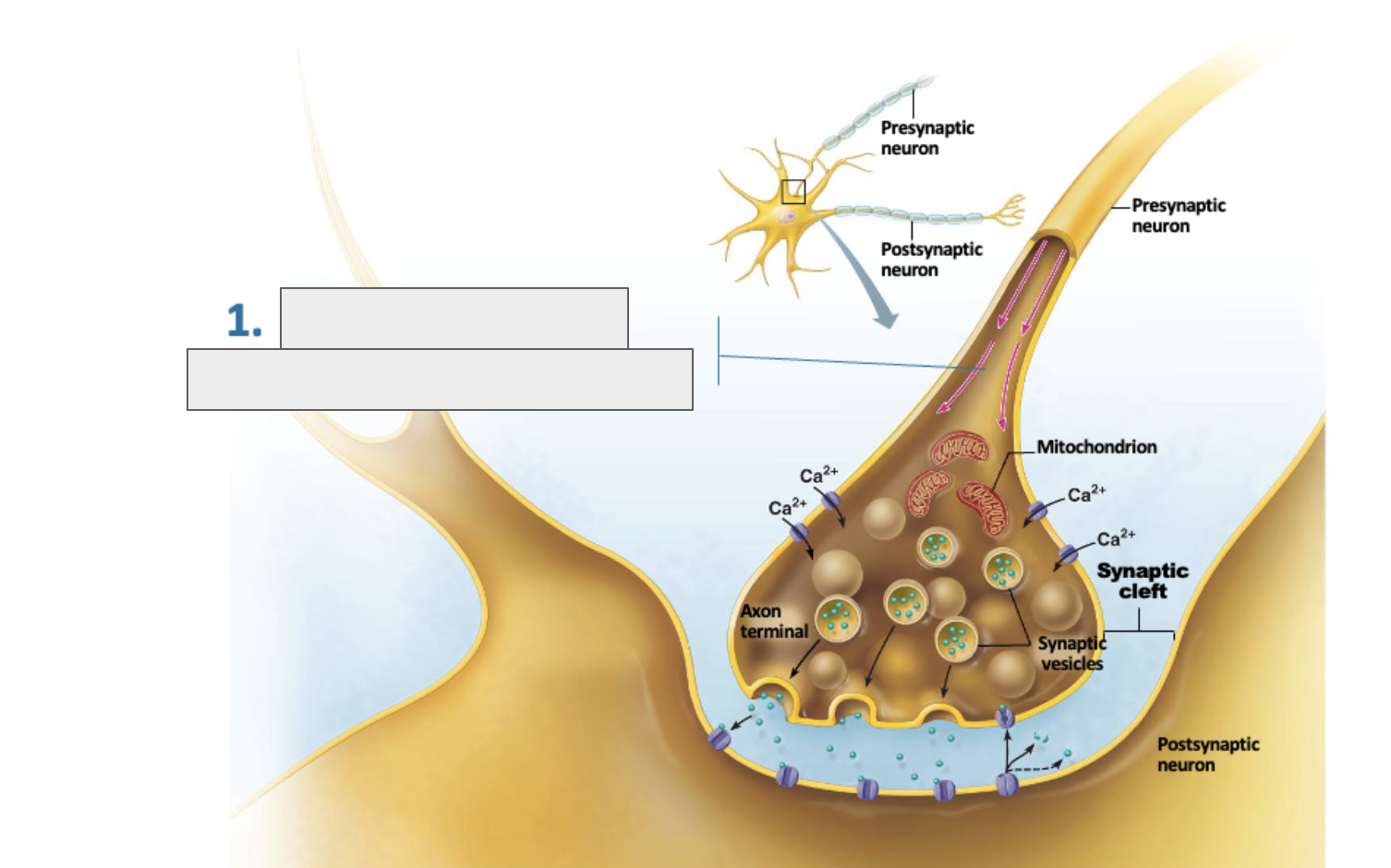
what is happening in this image?
action potential is arriving at axon terminal
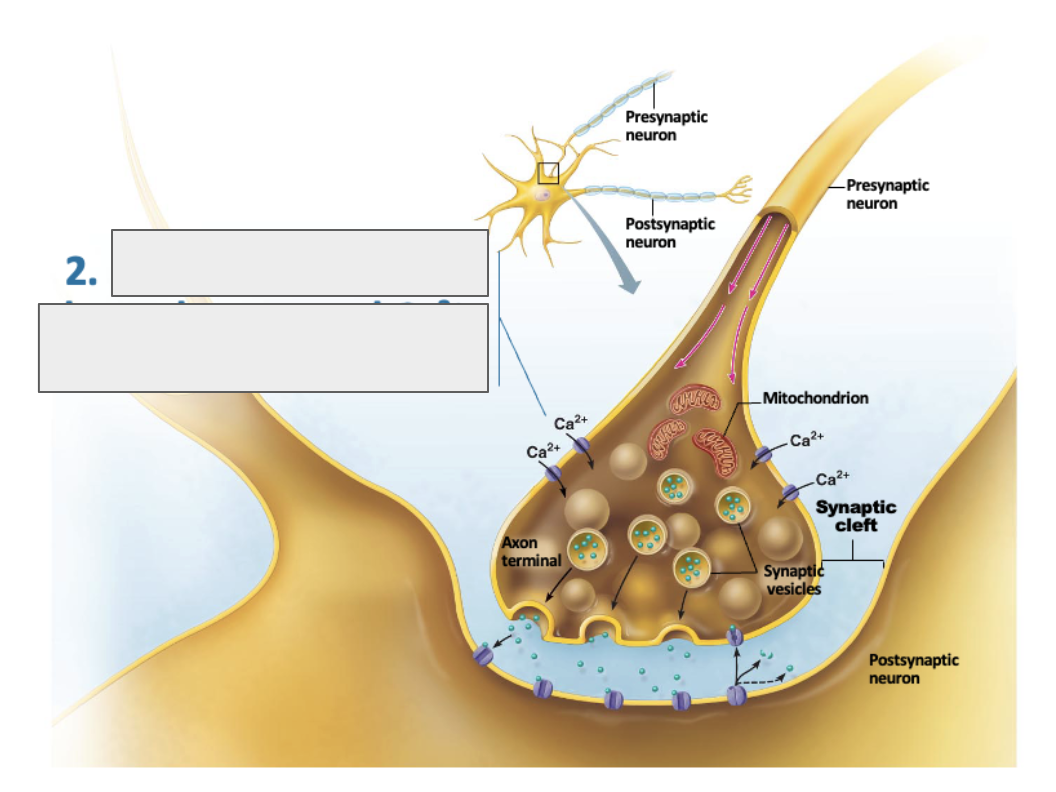
what is happening in this image?
voltage gated calcium channels open and calcium enters the axon terminal
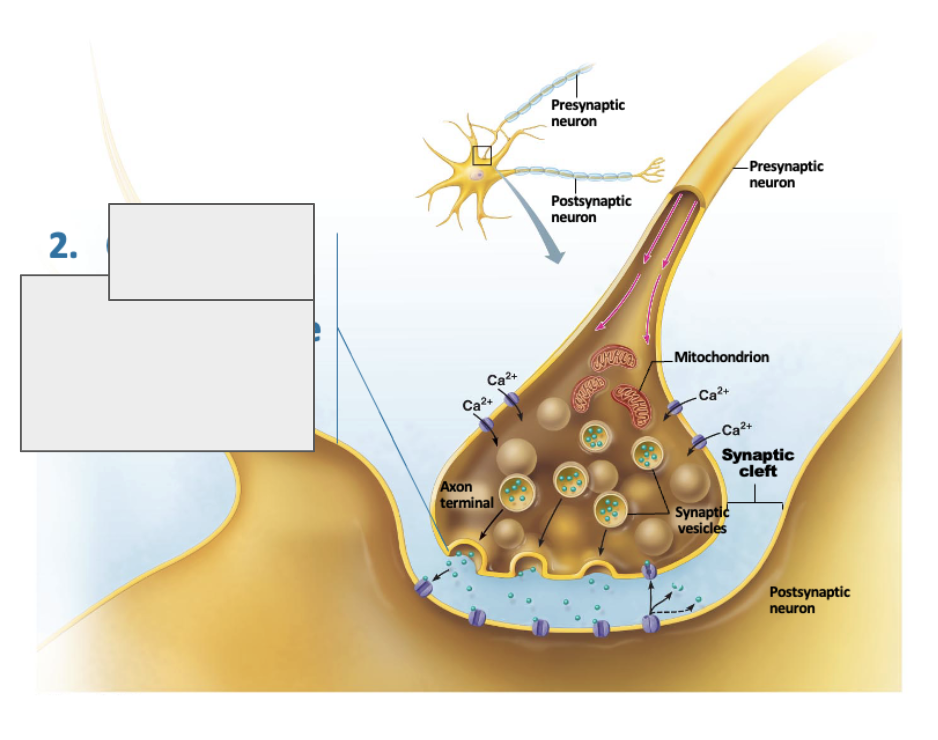
what is happening in this image?
calcium entry causes synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters by exocytosis
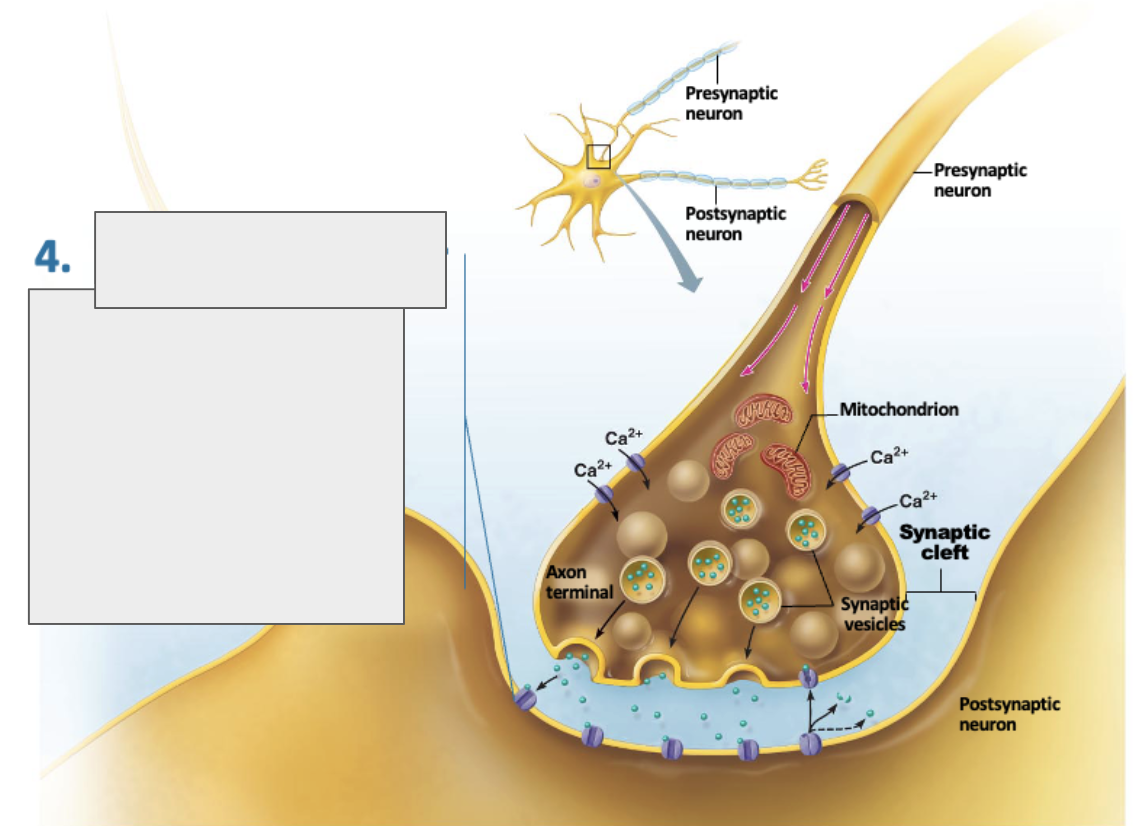
what is happening in this image?
neurotransmitter diffuses across synaptic cleft and binds to specific receptors on the postsynaptic membrane
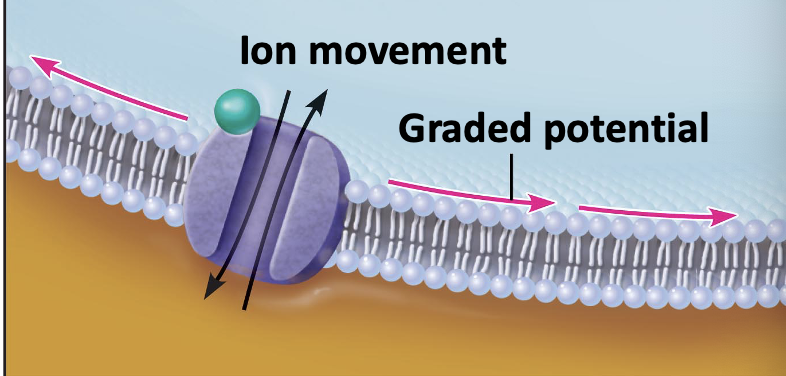
what is happening in this image?
binding of neurotransmitter opens ion channels, resulting in graded potentials on post synaptic nerve
what are the three ways to stop neurotransmitter effects?
enzyme degradation, uptake back into presynaptic neuron for storage or destruction, and diffusion of neurotransmitter away from synaptic cleft
what are the two types of postsynaptic potentials?
excitatory postsynaptic, inhibitory postsynaptic
what determines the magnitude of depolarization in excitation postsynaptic potentials
amount of neurotransmitters
what is an excitatory postsynaptic potential?
a local depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane that brings the neuron closer to action potential threshold
what does neurotransmitter binding during the excitatory postsynaptic potential allow for?
chemically gated ion channels open, allowing sodium and potassium to pass through simultaneously
what is inhibitory postsynaptic potential?
a local hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane that drives the neuron away from action potential threshold
what does neurotransmitter binding during inhibitory postsynaptic potential cause?
potassium and/or chlorine chemical-graded channels open
what is temporal summation:?
one or more presynaptic neurons transmit impulses in rapid-fire order
what is spatial summation?
postsynaptic neuron stimulated by presynaptic neurons at the same time
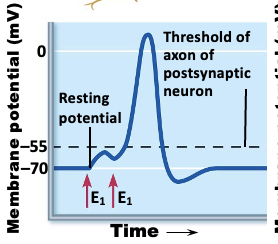
what is this an image of?
temporal summation
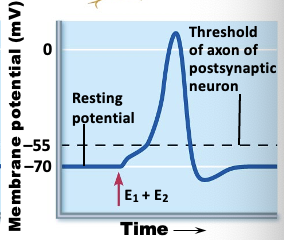
what is this an image of?
spatial summation
how are neurotransmitters classified?
chemical structure and function
where is acetylcholine released?
at neuromuscular junctions
how is acetylcholine degraded?
by enzyme acetylcholinesterase
what is epinephrine important for?
adrenalin, regulates sleep/wake cycle, attention, and feeding behaviors
what is dopamine important for?
movement coordination, emotion, and motivation
what is serotonin important for?
mood regulation, emotions, attention, feeding behaviors, and daily rhytms
what is the important inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system?
GABA
what is the important excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system?
glutamate
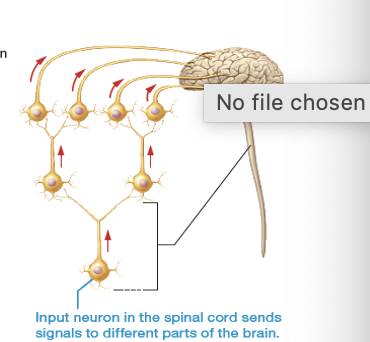
what is this an image of?
diverging circuits
what do diverging circuits allow for?
single neuron to communicate with multiple parts of brain and body
what is a diverging circuit?
single input neuron axon branches out to make contact with multiple postsynaptic neurons
what is a converging circuit?
axon terminals from multiple input neurons converge onto single postsynaptic neuron
what do converging circuits allow for?
nervous system to respond to sensory information that it collects and processes
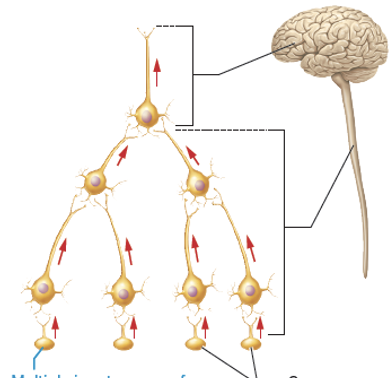
what is this an image of?
converging circuits