Chemistry Unit 1 - Organic Chemistry
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Fossil fuels
Formed from remains of dead organic matter over millions of years at high Temp./Pressure
Ex. of Fossil Fuels
Coal (s) = dirtiest
Crude oil (l) = petroleum
Natural gas (g) = cleanest
Issues with Fossil fuels
Carbon Dioxide Emissions
Non-renewable
Alternatives to fossil fuels
Renewable energy: wind, solar, hydroelectric
Nuclear E (no Carbon dioxide emissions)
Complete Combustion
Fossil Fuel (Hydrocarbon) + O2 ➡ CO2 + H2O
Incomplete Combustion
Insufficient O2, produces toxic CO (Carbon Monoxide)
Crude Oil
Mixture of Hydrocarbons called alkanes
Can be separated through fractional distillation
Fractional Distillation
Separating mixtures according to boiling point
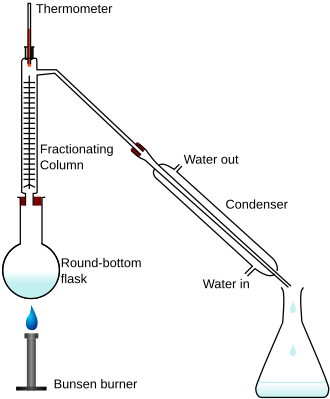
Fractional Distillation of Crude Oil
Oil is heated in a heater to 400 Celsius, becoming vapour, and then sent through a fractionating column (attached to thermometer), where substances with high boiling points settle in lower levels while substances with low boiling points settle higher before condensing into individual substances.
Small Molecules
Low boiling point
Very volatile
Flows easily
Ignites easily
Large molecules
High boiling point
Not very volatile
Does not flow easily
Does not ignite easily
volatile
Evaporates easily
viscous
Thick and sticky
Refining
Purification of substances through physical separation
Refinery gas
Non-condensable gases
Organic compound prefix for one
Mono-
Organic compound prefix for two
Eth-
Organic compound prefix for three
Prop-
Organic compound prefix for four
But-
What do organic compounds form when in groups?
Families
Functional Group
Group of atoms that gives a family its particular reactivity
Homologous series
Family of similar compounds with similar compounds with similar chemical properties
Carbon forms x bonds
4
Hydrogen forms x bonds
1
Alkanes
Hydrocarbons
Only SINGLE C-C bonds
Suffix -ane
Alkanes General Formula
Cn H(2n+2)
Alkenes
Hydrocarbons
Contain a DOUBLE C-C Bond
Suffix -ene
Alkenes General Formula
Cn H(2n)
Alcohols
Suffix -ol
Functional Group: OH
Has to be bonded to C
Alcohols General Formula
CnH(2n+1)OH
How do you differentiate between the same organic compound when the double bond/OH is placed differently?
Number the carbon an write the number of the carbon where the thing is located in between pre and suffix
Eg. Butene (double bond at start)
But-1-ene
Carboxylic Acids
Suffix -oic acid
Functional Group COOH
They are weak acids
General Formula for Carboxylic Acids
CnH(2n+1)COOH
Alkane Reactions
saturated (can’t fit any more bonds around the C)
This makes them quite unreactive
They do burn (combustion), releasing E
Alkenes Reactions
unsaturated (when double bond breaks, more atoms can be added)
Undergo addition reactions with H2, Br2, Hydrogen Halides and H20
Alkane + H2
ethene (C2H4) + H2 ➡ ethane (C2H6)
Alkane + Bromine Water (Br2)
ethene (C2H4) + Br2 ➡ 1,2 - dibromoethane (C2H4Br2)
Alkene + Hydrogen Halide (H + Hydrogen)
ethene (C2H4) + HCl ➡ chloroethane (C2H5CL)
Alkene + H20 (g)/Steam
ethene (C2H4) + H2O (g) ➡ Ethanol (C2H5OH)
Alkenes Polymerisation
Making plastics using Alkenes
Where do Alkenes come from?
Crude oil (Fractional Distillation at 400C) ➡ Alkanes (Cracking at 800C w Catalyst) ➡ Alkenes
Cracking
The process of turning larger Alkenes (not so useful) into smaller, more useful Alkenes
Thermal Decomposition at High T using a Catalyst
Alcohols Reactions
Ethanol: burns well in O2, giving out high E
2 ways Ethanol can be formed
adding steam (H20) to ethene (industrial ethanol for perfumes, deodorants, etc.)
Fermentation of glucose (simple sugar found in fruit/grains)
C6H1206 (Glucose) ➡(yeast catalyst) = 2C2H5OH (Ethanol) 2CO2
Anaerobic fermentation (no O2)
Ethanol in O2
Ethanol burns well, giving out high E
C2H5OH (Ethanol) + 3O2 (Oxygen) ➡ 3H2O + 2CO2
Ethanol in Cars
Can be used as fuel due to combustion abilities
Bio-fuels (renewable E sources)
Brazil are global leaders (use bioethanol from sugarcane fermentation to fuel cars)
Pros: renewable, clean no CO2 emissions
Cons: lots of land required, deforestation
Crude Oil to Plastic
Crude Oil (thru Fractional Distillation) ➡Alkanes (thru Cracking)➡Alkenes (Polymerisation) ➡ Plastics
Polymerisation
Many small molecules (monomers) join to form long chains (polymers)
Monomer
Small Molecule (ex. ethene)
Polymer
Long chain of small molecules (Polyethene)
Natural Polymers
Proteins, Carbohydrates, Fats, DNA
Synthetic Polymers
Plastics
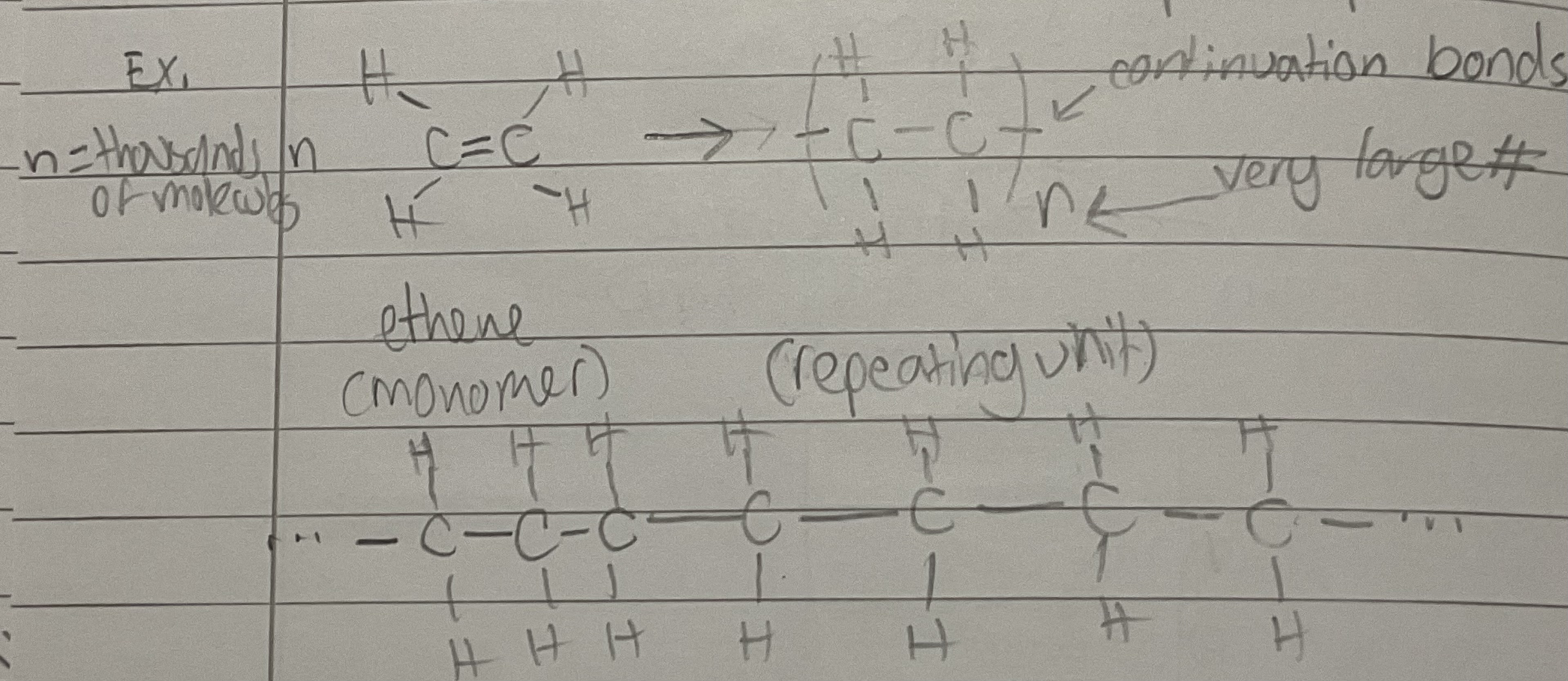
ex.
ethene (monomer) ➡ polyethylene (polymer)
Polyethene (PE)
made from ethene
used in bags, bottles, cling film
Polypropene (PP)
made from propene
used in crates, ropes
Polyamide (PA)
made from amide
used in tights, clothes, fishing nets
Polystyrene (PS)
styrofoam
made from styrene
used for insulation and packaging
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
made from vinyl chloride
used water pipes, vinyl discs
Plastic Pollution
Plastics are:
Non-biodegradable
Filling landfills
Collecting in rivers/oceans
Wildlife eating plastic
Types of Polymerisation
Addition
Condensation
Addition Polymerisation
-many monomers add up to form a polymer
-monomer is a small alkene (C=C)
-double bond breaks and opens up
Repeating Unit
A single unit that is part of the polymer chain after polymerisation
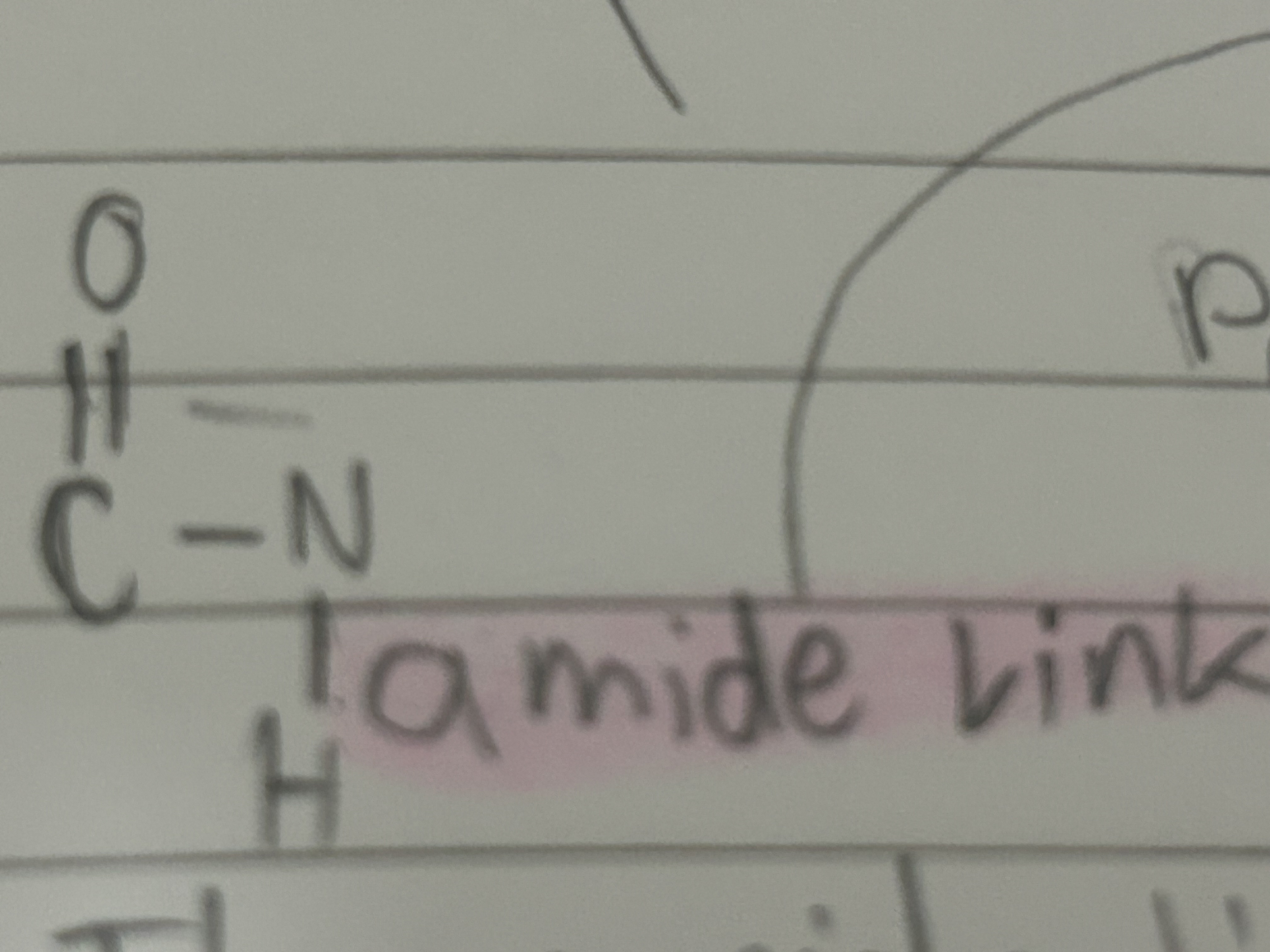
Condensation Polymerisation
two diff monomers join and form a polymer and a small molecule (ex. H2O or HCl)

Amide link
The same link that joins amino acids to make proteins