Electricity
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All of the topics I think
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Potential Difference
Energy transferred per unit charge
Unit: V
V = E/Q
Voltmeter
Connected in parallel
Current
Rate of flow of charge
Unit: A
I = Q/t
Ammeter
Connected in series
Resistance
A measure of how much a component resists the flow of current
Unit: Ω
Ohm’s Law
V = IR → R = V/
Ohmic Resistor
Obeys Ohm’s Law:
V-I graph is a straight line

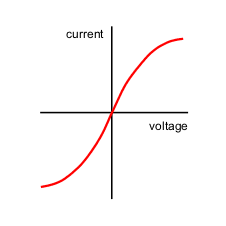
Filament Lamp
Resistance is not constant, therefore V-I graph curves
Delocalised electrons collide with ionic lattice, causing them to vibrate more and increase temperature
Larger current results in increased resistance - NON-OHMIC
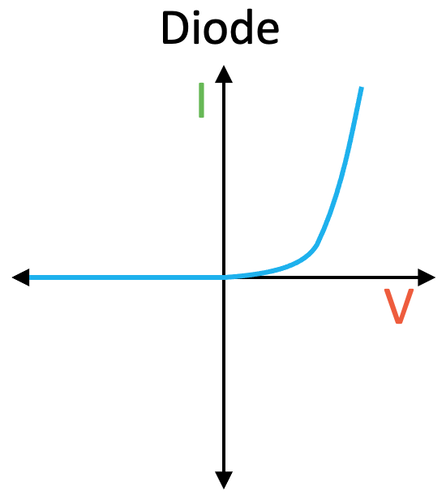
Diode
Lets current flow in one direction
Resistance in forward direction is LOW
Resistance in reverse direction is HIGH
Resistivity, ρ
How resistive a material is to the flow of charge.
Unit: Ωm
Measuring resistivity
Measure diameter of wire in multiple places using micrometer and find mean.
Use this to find the cross-sectional area
Change L of wire measuring with meter rule by moving croc clip
Plot graph of R against L
ρ = RA / L
Series Circuit
Total p.d is shared between all components
Current is the same for all components
Total Resistance is sum of all resistances
Parallel Circuit
P.d across each branch = e.m.f of battery
Current is split between branches
Adding more resistors in parallel reduces total R
Kirchoff’s 1st Law
Charge (and therefore current since Q = It) is conserved at any junction (Iin = Iout)
Kirchoff’s 2nd Law
Sum of EMF’s (pd rises) must equal the sum of pd drops in a closed loop
Thermistor
If temperature increases, resistance decreases: opposite to a metal wire essentially
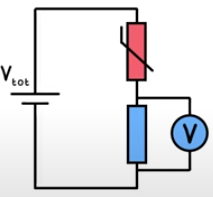
Thermistor circuit
If temperature increases, R of thermistor decreases, so thermistor gets a smaller share of Vtotal
Bottom resistor gets a bigger share of Vtotal which could be used to turn off heating
LDR
When light intensity increases, resistance decreases
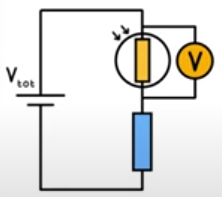
LDR circuit
If light intensity decreases, R of LDR decreases, so LDR gets a larger share of Vtotal
Bottom resistor gets a bigger share of Vtotal which could be used to turn on a street lamp
Power
P = IV
P = I2R
P = V2/R
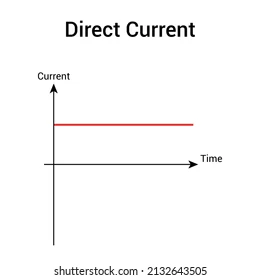
Direct Current
Result of a direct p.d (p.d that acts in one direction) from a battery
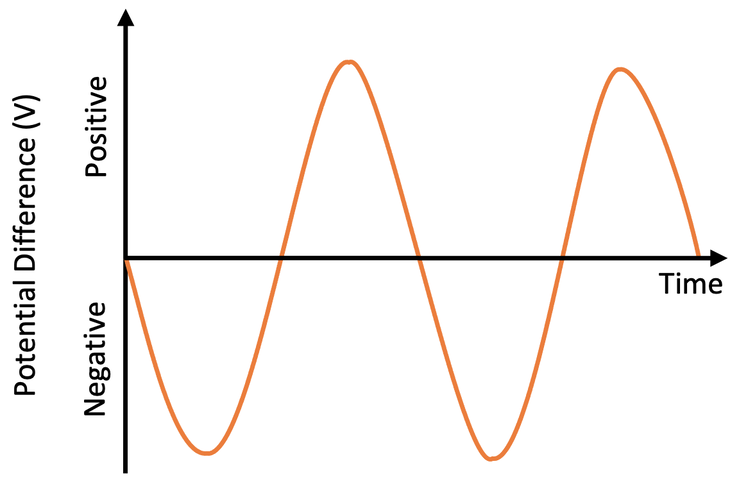
Alternating Current
Result of alternating p.d (both reverse direction at regular intervals)
Electromotive Force
Energy supplied to each unit charge
Internal resistance
Some p.d is lost in the circuit due to internal resistance, r, of the cell.
Terminal Potential difference
Potential difference across the terminals of a power source
Electromotive Force, ε
Energy supplied to each unit charge
Internal Resistance
Resistance in the source. This means that the circuit will not receive the full EMF of the cell
Electromotive force and internal resistance
ε = I(R+r)
ε = IR + Ir
ε = V + Ir
V = Terminal p.d
I = Current
r = internal resistance
R = Total Resistance of circuit
Number Density, n
Free charge carriers that can flow per m3 of a material.
Higher number density = better conductivity
Drift Velocity
Distance travelled by an electron per unit time in a wire
Mean drift velocity and current
I = Anev → v = I / Ane
I = current (A)
A = Cross-sectional Area (m2)
n = number density (m-3)
e = elementary charge (1.6×10-19)
v = mean drift velocity (ms-1)