Biology 1.2 The Respiratory System
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Why do large multicellular organisms require a respiratory system?
Small SA/V ratio. Diffusion insufficient to provide all cells with the required oxygen and to remove all carbon dioxide. Large organisms are more active than smaller organisms.
Why do some multicellular organisms (e.g. trees) not require specialised exchange surfaces?
Trees have a large number of leaves which provide a large SA/V ratio for diffusion.
Describe the pathway of gas through the respiratory system
Nose → trachea → bronchi → bronchioles → alveoli → capillaries.
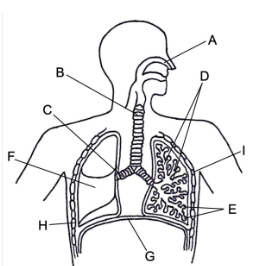
Identify the structures of the respiratory system labelled in the diagram below

What is the function of mucus in the respiratory system?
It traps harmful substances and organisms, preventing entry into the lungs.
Where are ciliated epithelial cells found?
Found lining the surface of the respiratory tract.
Describe the function of ciliated epithelial cells lining the airways
Move in synchronised waves to beat mucus (containing dirt and pathogens) up to the back of the throat where it is swallowed.
What are the lungs?
A pair of organs consisting of the bronchioles, alveoli, and surrounding tissues.
What is the thorax?
Area between the neck and abdomen. Includes organs found within the chest and lungs.
What is ventilation?
The movement of fresh air into the lungs and stale air out of the lungs via inhalation and exhalation.
What does ventilation require?
Rib cage. Intercostal muscles. Diaphragm.
What is inspiration?
Breathing in.
Describe the process of inspiration
Ribs move up and out. Diaphragm contracts and flattens. Volume of thorax increases. Pressure in thorax decreases below air pressure. Air moves into the trachea.
What is expiration?
Breathing out.
Describe the process of expiration
Ribs move down and in. Diaphragm relaxes and reverts to dome shape. Volume of thorax decreases. Pressure in thorax increases above air pressure. Air moves out of the trachea.
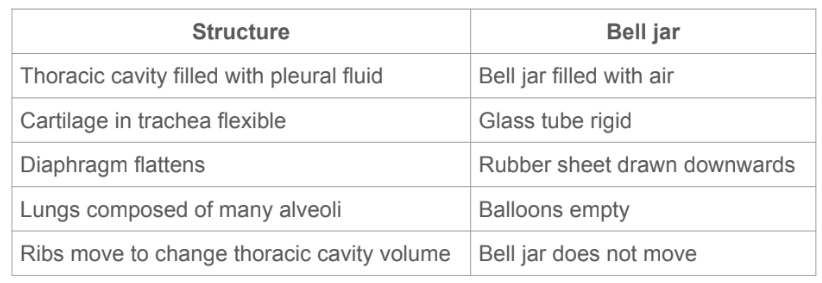
How is ventilation modelled?
Using the bell jar model.
Describe the limitations of the bell jar model
What are the alveoli?
A cluster of air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs.
Describe the process of gas exchange at the alveoli
Oxygen diffuses from air in the alveoli into blood in the capillaries. Carbon dioxide diffuses from blood in the capillaries into air in the alveoli.
How are alveoli adapted for gaseous exchange? (5)
Large surface area. Surrounded by a network of capillaries giving a good blood supply. Rapid blood flow maintains a steep concentration gradient. Thin wall (one cell thick) giving a short diffusion distance. Walls covered by a thin, moist film, enabling gases to dissolve and increasing the rate of diffusion.
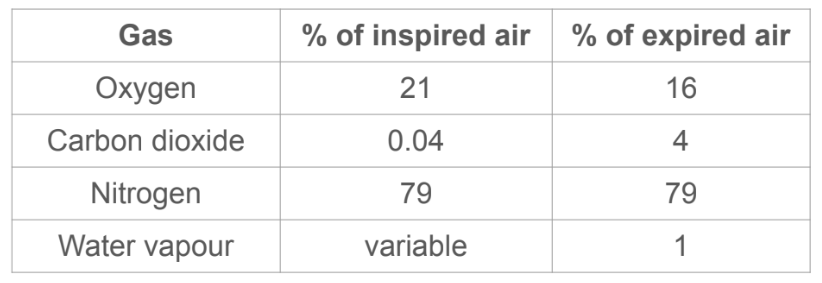
Describe the composition of inspired and expired air
What is the chemical test for carbon dioxide?
Bubble gas through lime water. CO2 turns lime water milky.
What chemicals found in tobacco smoke damage the lungs?
Carcinogens. Tar. Nicotine. Carbon monoxide.
What is a carcinogen?
A chemical that causes cancer.
How does tar affect the airways?
Sticky substance deposited in the airways. Stimulates mucus production. Paralyses the cilia, preventing mucus from being swept away. Mucus containing microorganisms and dirt builds. Leads to smoker’s cough.
Describe the effects of nicotine on the body
Increases heart rate. Addictive. Damages the lungs.
What effect does carbon monoxide have on the body?
Binds with haemoglobin in red blood cells irreversibly. Reduces oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
How does smoking cause emphysema?
Damage to the alveoli walls and loss of elasticity in the alveoli lead to emphysema.