Approaches in Psychology AQA
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Imitation
Copying behaviour of others
Identification
When an observer associates themselves with a role model and wants to be like the role model.
live models - e.g teaches, siblings, parents
symbolic models - people in the media
Modelling
From the observer's perspective, its imitating behaviour of the role model. From the role model's perspective, its the precise demonstration of a specific behaviour that may be imitated by the observer.
Vicarious reinforcement
Not directly experienced but occurs through observing someone else being reinforced for their behaviour - key factor in imitation.
Mediational processes
Cognitive factors that influence learning a behaviour and come between stimulus and response. for modelling to occur there must be attention, retention,motor reproduction, motivation.
Attention
noticing certain behaviorus
Retention
remembering the behaviour
Motor reproduction
whether the behaviour is physically possible to carry out.
Motivation
there has to be a reason to want to copy their behaviour
Cognitive approach
-Focused on how our mental processes affect behaviour
- thinking causes behaviour
- The mind actively processes information from our senses (touch, taste etc.).
Internal mental processes
'Private' operations of the minds such as perception and attention that mediate between stimulus and response
Schema
A mental shortcut of beliefs and expectations developed from experience.
Pros and cons of schemas
+ mental shortcut -we don't have to rethink the same ideas- helps us to remember
- a schemas can lead to phobias e.g about exams can cause panic attacks
- can lead to prejudice and racism
Inference
The process whereby cognitive psychologists draw conclusions about the way mental processes operate on the basis of observed behaviour
Cognitive neuroscience
The scientific study of biological structures that underpin cognitive processes.
The biological approach
Sees all out behaviour is rooted for our biological structure and that everything psychological has a biological basis
1) genes- specific genes and combinations of genes will have an influence on both the physical and psychological aspects of people. Genes that code for characteristics or behaviours that are beneficial to survival will be passed on to the next generation
2) The biological structure-the behaviour of the individual is controlled and coordinated by the brain and the nervous system
3) The chemistry of the body-hormones in the body and neurotransmitters in the brain have a much impact on our behaviour
Genotype
Particular set of genes that a person possesses
Genes
Made of DNA which codes physical features of an organism and psychological features. Inherited.
Biological structure
Arrangement or organisation of parts to form an organ/system/living thing
Evolution
The changes in inherited characteristics in a biological population over successive generations
Phenotype
Characteristics of an individual determined by both genes and the environment
Neurochemistry
Relating to chemicals in the brain that regulate psychological functioning
Psychodynamic approach
-Behaviour is influenced by early childhood experiances
-behaviour is motivated by two instincts- sex and life
The unconcious
The part of the mind that we are unaware of but which continues to direct much of our behaviour.
The conscious
the part of our mind we are aware of on a daily basis- can be influenced by the unconscious
Id
Entirely unconscious, the id is made up of selfish aggressive instincts that demand immediate gratification.
Ego
The 'reality check' that balances the conflicting demands of the id and superego.
Superego
The moralistic part of our personality which represents the ideal self: how we ought to be.
Defence mechanisms
Unconscious strategies that the ego uses to manage the conflict between the id and the superego.
Repression
forcing a distressing memory out of the conscious mind
Denial
refusing to acknowledge some parts of reality
Displacement
transferring feelings from true source of distressing emotion onto a substitute target
Psychosexual stages
According to Freud, five developmental stages that all children pass through. At most stages there is a specific conflict, the outcome of which determines future development.
Oral 1-0 yr
focus of pleasure is the mothers's breast - object of desire
unresolved conflict leads to fixation
Anal 1-3 yr
focus of pleasure is the anus. Child holds pleasure by withholding and expelling faeces. Unresolved conflict leads to anal retentive or anal expulsive
Phallic 3-5 yrs
focus of pleasure - genital area
child experiences the Oedipus or electra complex
Unresolved complex leads to phallic personality- narcissistic, reckless, possible homosexual
Latent
earlier conflicts are repressed
genital
sexual desires become conscious along onset of puberty
Little Hans
- 5 year old with a phobia of horses
- freud thought the horse represented his father as he was scared his father would castrate him for desiring his mother - this is the Oedipus complex theory
Psychodynamic therapy
- Free association - client talking freely to the therapist - saying the first things that come to mind - allows for true thoughts and feelings to emerge
- dream analysis
Evaluation of Little Hans
+ evidence
-the father was already familiar with this research - biased
-even if true shows that it is vey uncommon nd freud thought it was universal
- lacks population validity
Evaluation of the Psychodynamic Approach
+influential - this theory started the debate in psychology and the behaviourists developed their ideas to challenge his view
+ led to effective treatment -lead to the treatment of many mental health issues
- Untestable concepts for example we can't measure people superegos so can't know for certain if it is more powerful with people who have OCD- unscientific
-based on case studies - unreliable ungeneralisable to other people in other situations
Humanistic psychology
-not about mental health
-everyone can relate to it -looks at healthy individuals
- we have free will
Free will
The notion that humans can make choices and are not determined by biological or external forces
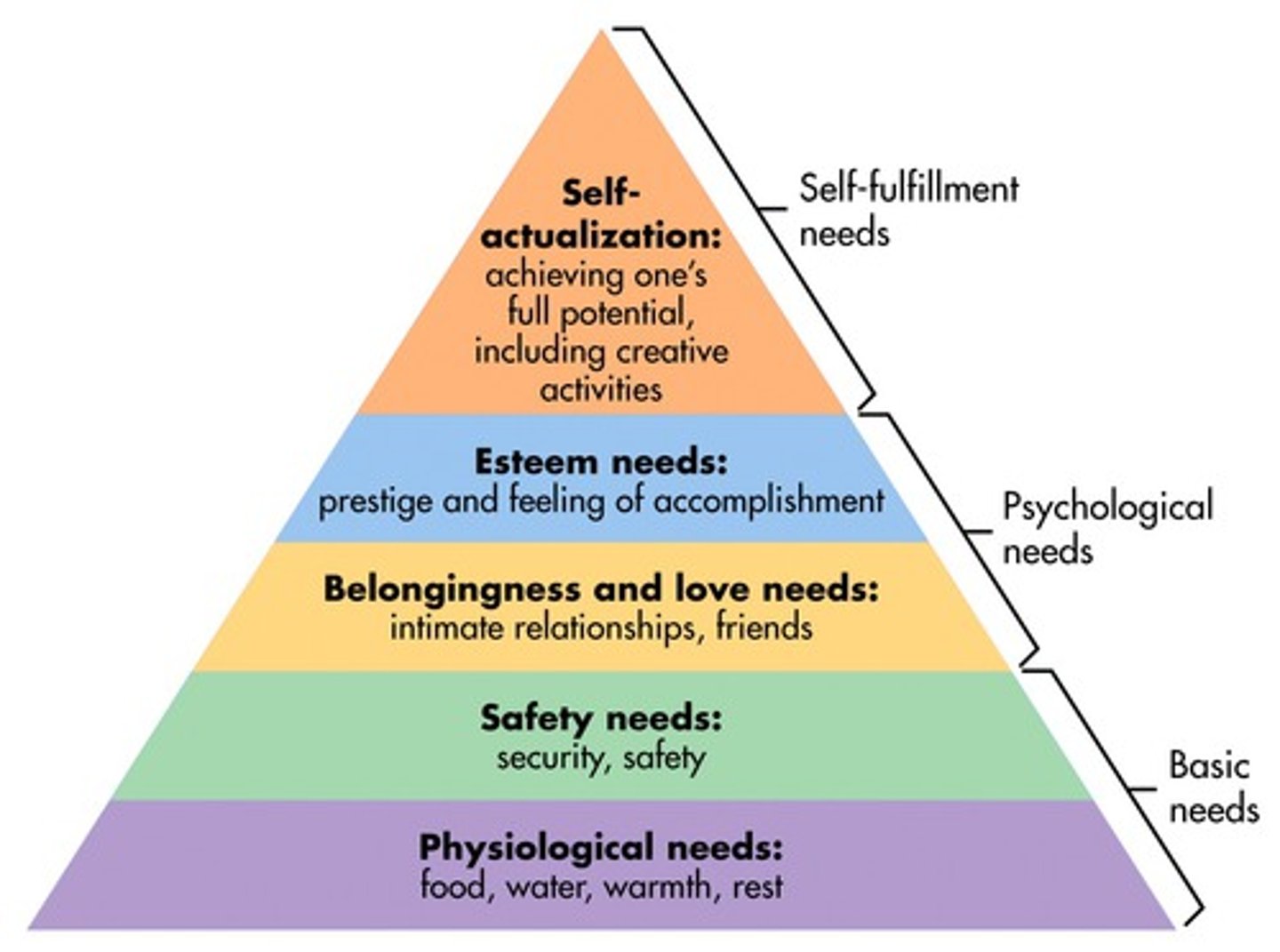
Self-actualisation
The desire to grow psychologically and fulfil one's full potential - becoming what you are capable of
Maslow's Hierarchy of needs
A five-levelled hierarchical sequence in which basic needs (such as hunger) must be satisfied before higher psychological needs such as self actualisation can be achieved.
humanistic counselling
- when the client is always right
-client concentrated
Rogers
self concept - who i think i am
real self concept - what your actually like
ideal self - what id like to be like
Congruence
when you ideal self matches up to your real self
Self
The ideas and values that characterise 'I' and 'me' and includes perception and valuing of 'what I am' and 'what I can do'
Conditions of worth
When a parent places limits or boundaries on their love of their children; for instance a parent saying to a child 'I will only love you if...'
Wundts beliefs
- father of psychology
-He defined psychology as the science of consciousness emphasised a technique called INTROSPECTION which is the break down of one's own mental and emotional processes into thoughts, images and sensations which he then analysed.
- His work helped the study of mental processes.
Evaluation of Wundt's work
Strength: precise measures were taken to make sure that his records were detailed
Weakness: asking participants to say how they feel is very subjective
The emergence of psychology as a science
Psychology is seen as a scientific discipline which in part can be credited to the work of Wundt. He emphasise key concepts which are consistently applied to modern psychology e.g. intensity, duration and sense modality. His approach in psychology stress the importance upon precise definitions of stimulus and response been studied. Psychology at the discipline is reliant upon the philosophical viewpoint called empiricism which states that knowledge comes from experiment. Psychology then focused on two view points:
1) all behaviour is caused
2) as all behaviour is caused it is possible to predict how humans will behave
Beyond Wundts work the scientific process was made which focuses on investigating phenomena
Evaluation of psychology as a science
Weakness: not all psychologist believe that the scientific method is the best way to study human behaviour
Strength: the scientific method allows psychologists to have flexibility when experiments produce inconsistent results which means the scientific knowledge is self corrective
Operant conditioning
A form of learning in which behaviour is shaped and maintained by its consequences. Possible consequences of behaviour include positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement and punishment.
Behaviourist approach
- all behaviour is learnt
- we are born with a blank slate
- genes are not related to behaviour
- we can study human behaviour by looking at animals
The behavioural approach used two types of conditioning
Operate and classical
Classical conditioning
This is a behaviourist theory which says that humans and animals learn new behaviours by the process of association.
There are 3 stages of classical conditioning:
1) before conditioning- end of the lesson before lunch makes peoples stomachs rumble - A neutral stimulus produces no response e.g a bell ringing
2) during conditioning- the neutral stimulus is paired with the unconditioned stimulus resulting in an unconditioned response, this needs to happen serval times for it to occur e.g whenever we hear the bell ring we know it is the end of the lesson and lunch is next so we become hungry
3) after conditioning- the neutral stimulus has become the conditioned stimulus, resulting in the conditioned response e.g whenever we hear the bell even if it isn't lunch time we still get hungry and our stomachs rumble
Pavlov dogs
Pavlov demonstrated classical conditioning in dogs using the sound of a bell as the neutral stimulus and a bowl of meat powder as the unconditioned stimulus
1)before the experiment the dogs would salivate ( unconditioned response ) in respond to the meat powder but not the bell
2) when a bell was rung the first time with no food there was no response - neutral stimulus
3) during conditioning the bell was rung wherever the meat powder was presented
4) after many trials the dogs would salivate at the sound of the bell alone, the bell had become a conditioned response.
Evaluation of Pavlovs study
Strength: he highly controlled the conditions to make sure that nothing else would make the dogs salivate, even the experiment stayed outside the room to make sure that the dogs would associate him with the food and was purely the bell
Weakness: he used a salinometer which have him a more statistical way of seeing how much the dogs were salivating. However he was highly criticised on within all grounds, the salinometer was surgically implanted which meant they could never actually swallow the food so many died
Watson and Rayner - Little Albert experiment
-Aim whether humans learn through classical condition and can see if a fear resource can be successfully conditioned in a human child.
- healthy baby little Albert whose mother was a nurse at the hospital they worked at. Albert was given a white rat which liked
- then whenever he reached out to stroke it a metal bar was hit to make a loud noise which scared him.
-This procedure was repeated three times a day each month, eventually whenever Albert say the rat he would cry, this fear was also generalised with white rabbits, a white fur coat, cotton wool and santas beard
Evaluation of Watson and rayner
strength - provides evidence
Weakness:
-it has been suggested that littler Albert had neurological problems so he may not of been a typical baby.
- left him with life long phobias, although they planned to de condition him his mother removed him from the experiment before they could do this
- it is deterministic- This means that it does not allow for any degree of free will will in the individual.
Operant conditioning
This states that we learn new behaviours as a result of the consequences of our actions
1) positive reinforcement- when behaviour is followed by a pleasant consequence the frequency of the behaviour is increased.
2) negative reinforcement- when a behaviour leads to something unpleasant stopping, the frequency of the behaviour increases e.g going to the dentist which you hate in order to make sure your teeth don't rot.
3) punishment- when a behaviour is filleted by a unpleasant consequence the frequency of the behaviour decreases
Behavioural shaping- when you teach something slowly to reinforce a behaviour
She duals of reinforcement- a continues reinforcement schedule is most effected reinforcing it every 3rd time the behaviour occurs means it is most likely to become a response
Skinner
-skinners box,- where an animal ( rat or pigeon ) can be placed.
-There is a lever which delivers food pelts
-The rat learnt while it was exploring that if it pressed the lever it would release food, which makes the rat repeat the response as it gets positive reinforcement.
- if the animal got tired the box would make loud noises or electrocute the bird which would stop if the rat pressed the lever this also increased the amount the lever was pressed this showed negative reinforcement.
- the other experiment was if the rat pressed the lever he got punished by an electric shock which decreased the amount of times he touched the lever
Evaluation of skinner
Strength: his conditions were highly controlled and he made sure there was no other stimuli that would affect the amount of times the lever was pressed
Weakness: we may not be able to generalise these findings to humans, although we might learn the same way our brains are more complex
Overall Evaluation of the behavioural theories
Strength: Watson and rayener and Pavlov can be credited for introducing the scientific method into psychology
Weakness: all behaviour is studied under artificial conditions which mean it doesn't reflect well to real life making it low in ecological validity
Strength: classical conditioning has led to the development of systematic desensitisation to treat phobia and operant conditioning had led to the development of token economy shown in Higgins et al where people who were addicted to cocaine had urine test, if it was clear the got vouchers to spend there money on, the programs help 85% of people compared to the 33% who had counselling
Social learning theory
-Social learning theory suggests that behaviour is learnt from society/ or individuals.
- a bridge between the behaviourist and the cognitive approach
-concerned with human behaviour
-sees humans as active manipulators their own environment
there are four factors that affect imitation:
1) we are more likely to imitate a model we identify with. This is most likely if the model is similar to us e.g same age or gender or if a very powerful and successful
2) individuals with low self-esteem and more likely to imitate the behaviour of models
3) if they see models are receiving positive reinforcement for their actions they are most likely to imitate them this is called vicarious reinforcement
4) The internal mediational processes suggests that the observer will use the behaviour he is seen in the future where is able to do so only if the positive consequence is greater than the expectation of negative consequences
Bandura et al
- 3-5 yr old
- half the kids shown an adult infant of them beat up the Bobo doll aggressively
- they were then left alone in a room with the doll ordinary toys
-found that the children acted aggressively toward the doll when they left
-most aggression can be seen when the adult was the same gender as the child
- the other half of the kids were shown an adult playing nicely with the doll
- when they were left alone they saw a lot less violence towards it.
- they also did the same experiment but showed a video of the adult beating the doll and the same results were shown
- therefore violent tv shows can influence children
Evaulation
strength:
-highly controlled the adults behaviour was pre recorded which means each child was exposed to the same amount of aggression.
-ecological validity
-easily replicated
-used matched pairs design
weakness:
-lack of ecological validity the child and the model had no interaction which they would have done in a normal family life
-overlooks role of biology
-might not work with older chi;drew
- children might have known the outcome of the experiment as all the kids were friends-
Overall evaluation of the social learning theory
Strength:
-it has explained areas which the behavioural theory can't
-practical application
-research
-explains cultural variations in behaviour
weaknesses
- doesn't explain all our behaviour
-overlooks biological factors
-overlooks personality -nature/nurture debate
- lab experiment - limited
The use of theoretical and computer models
Cognitive psychology uses conceptual models to explain how the kind works e.g the multi store model and allows psychologists to predict when they do testing and experiments
the Computer (informational) process model
- mind functions like a computer as we both input - process information, have memory and an output - retrieve info
- there stages in processing steps for information
The emergence of cognitive neuroscience
- Explains how mental functions are undertaken within the brain.
- This combined the study of brain damage, neuropsychology, cognitive psychology and computer modelling.
- Pet scans and Mri scans are used to understand how the brain supports the different parts for emotions and functions when asked to perform different tasks.
- looks at biological processes and neural connections that are involved in mental processes
Burrnett et al - cognitive approach evidence
found that when someone feels guilt it is active in serval different pats of the brain e.g prefrontal cortex which is responsible for social emotions.
Overall evaluation of the cognitive approach
Strength:
- schemas are widely held to valid in cognitive psychology
-: the cognitive approach has led to useful applications in everyday life e.g cbt treatment for depression
- evidence mri scans - scientific evidence
Weaknesses
- It could be argued that cognitive models over-simplify explanations for complex mental processes.
- The data supporting cognitive theories often come from unrealistic tasks used in laboratory experiments, which puts the ecological validity of theories into question (i.e. whether or not they are truly representative of our normal cognitive patterns).
- Comparing a human mind to a machine or computer is arguably an unsophisticated analogy.
Explain the role of family, twin studies and the potential effects on the environment
If a characteristic or illness is genetic, it is likely that it runs in families. The more closely related individuals are the more likely they are to both have certain characteristics or illness.
Family study on OCD by nestadt et al. He investigated the influence on genes on OCD by looking at first degree relatives of 80 suffers. They found that first degree relative of OCD suffered had a 11.7% chance of developing the disorder compare to a 2.7 chance in first-degree relative's of healthy parents. They suggest the OCD might be genetically transmitted through families.
There has also been twin studies done. Monozygotic Twins develop wanna fertilise eggs divides and therefore sure 100% of their DNA. Dizygotic ( non-identical ) Twins develop from separate fertilised eggs and share around 50% of the DNA no more than siblings. When studying effective change research is look at concordance which is known as similarity rights they referred to the probability of people both having certain characteristics e.g. rate of eyecolour in monozygotic twins would be 100%. Something is genetically inherited them monozygotic twin should have higher concordance rate then dizygoric. Twin studies done by grootherst et al. He did a meta analysis where he assessed 70 years of twin studies into OCD. there were over 10,000 participants. They found a 45-65% role for inheritance in children and a 27 to 47% inheritance for adults. This shows the heritability have a strong interest in children who developed OCD with perhaps a great environmental role for adults. However it could be argued that much of the research study did not have a Knouff controls as it is tight as far back as the 1929 before Controls employed. The study also didn't take into account different types of OCD and how this may change heritability
Evaluate the genetic basis of behaviour
Weakness: if characteristic is completely genetic we would expect 100% concordance rate for monozygotic twins. The concordance rate for disorders the money exotic twins is never 100%, this suggests that there must be other environmental influences such as stress upbringing and learning weakness: is very difficult to separate out the effects of jeans and the environment the higher car accordance rights in monozygotic twins might be a dude and sharing a similar environment than dizygotic twins. They may be treated more similarly as they have the same experiences due to their age and environment rather than other siblings who have different ages and experience things at different times
Outline the evolutionary basis of behaviour
Human behaviour is thought to have involved in the same way as physical characteristics. According to darwin's theory of natural selection the random mutation in jeans produce individuals that are better suited to the environment. In a world where there may be competition for resources like territory food and mates some individuals will have characteristics that make the most successful. This means they have selected advantages, they survive and reproduce and pass on those characteristics to that offspring. Characteristics that make individual lessons due to the environment would use the chances of surviving and reproduce into those jeans will be lost
Lea et al looked at their MAOA Warrior gene that is linked to aggression and found in about one third of men. This Jane will survive because of aggressive men may have more likely to survive and reproduce this is because:
1) Think Chris aggression may have made them better hunters they would be able to provide for the family and insure the survival of the children
2) they could protect themselves and their families more effectively
3) they may have had high status in society and been more attracted to females
However some animals have a vote characteristics that make them less suited to the environment and less likely to survive for example a peacocks towel is cumbersome and makes them more vulnerable to being caught by predators. Darwin suggested that this characteristic my Bavaro because female penhens found it attractive and nice peacocks with big gamble beautiful towns were successful in May in and had some sleep beautiful tattoos he called this sexual selection. Anderson carried out a study and I Longtown widow bed which is about the size of a sparrow but my have a tad up to half a metre. Anderson compare the three groups on the mating success
1) Metal bed with tails shortened by cutting off the feathers
2) Malpas with length and towels by adding feathers cut up from the first group
3) Control group of male birds with normal long tails.
The mouse with a limp and towels are actually more successful with the females that even the long tail but Anderson concluded that through revelation the professors of females for longtailed mouse has increased the average size of the males tail. Darwin's theory of natural and sexual selection can be applied to humans. Individuals may have characteristics that make the most successful or more attractive and therefore more likely to survive and three produce and pass those characteristics of onto their offspring.
Evaluate the evolutionary basis of behaviour
Weakness: the ever louche me a price see she must behaviour has been determined by the edge to survive and reproduce. It tends to ignore the huge effect of culture and society and behaviour e.g. aggression and reproductive behaviour are very affected by coach and morality and religion
The nervous system divisions
1) the central nervous sysyem- consists of the brian and spinal cord and contols and rehulated all the physiological processes of the individual. Some parts dealt with more basic functioning such as breathing anything, other posted with more complex things such as thinking and decision-making
2) The spinal-cord-relays information between the brain and the body. The brain can then regulate bodily processes such as breathing and I jesting and control voluntary movements of the body. Pairs of the spinal nerves branch off from the spinal cord and connect with specific muscles or organs.
3) The brain-the brain is made up of different parts that are responsible for different functions. The Srebro is part of the brain and is made up of different lives, the superhero is also divided into two hemispheres that a specialist for particular behaviours. The two hearts communicate with each other through the corpus callosum. The dirncephalon lies beneath the cerrbrum I don't top of the brainstem. It consists of thalamus and hypothalamus that have a mumber of important functions.
Case stufy done on the influence of rhe biological strucr: Henry Molaison was born in 1926 and develop severe epilepsy at an early age. In 1953 he had an operation to remove an area of damaged that was causing life-threatening seizures, the operation left him with severe amnesia. His memory for events before the operation was relatively intact a good never remember any new information this meant he could remember his friends and family but could never remember anybody no. No operationally part of his hippocampus and this seems to play a role in the transfer of information from short term to long-term memory
The different part of the nervous system
The prleripheral nervous system: it transmits messages from the brain and spinal cord to the whole body and back again it is made up of the semantic an automatic nervous system. The cementing nervous system is made up of nerves extending from the brain and spinal cord. These nerves have sensory and motor neurons and transmit messages between the senses and the central nervous system and are important in the movement of the muscles. The autonomic nervous system transmits messages to and from the internal organs and realise in voluntary action such as digestion or breathing. The autonomic nervous system is made up of the sympathetic nervous system that genuine creases body activities and the parasympathetic nervous system that maintains or decreases bodily activity. The sympathetic nervous system is primarily involved with dealing with emergencies such as flight or fight. Nearest from the sympathetic nervous system travel to organs and glands around the body and prepare the body for action. Fruit sample in response to stress the heart rate and blood pressure will increase and the pupils will dilate processes such as digestion a less important in emergencies so we slowed down. The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible to return in the body to normal after an emergency for sample heart rate and blood pressure will be slowed down in indigestion will begin again
Structure and function of sensory, relay and motor neurons
The neuron: the neuron is a nerve cells that carry information around the nervous system. The body is made up of billions of neurons and trillions of connections. They can vary in size for a very few millimetres to a meter, nearest typically consist of body cells that Treitz and axons. The messages are carried along in a room by the electrical impulse across a signups between neurons are chemical message I called a neurotransmitter
Centring around: these are afferent no as they carry nerve impulses from the sensory receptors two of the spinal cord and brain there found in various sensory receptors around the body such it is eyes and tongue and infant inform the brain that the external and internal environment. They are known as unipolar Neurons as they only transmit messages
Motoneurons: these are called efferent nerves as I carry signals away from the central nervous system. They are known as multipolar neurons as they send and receive messages from many sources. The function of the motor neuron is to carry an electrical signal from the brain to a muscle checking if it's a contract or relax. The basic structure includes a receptor on one end and a transmitter on the other connected by nail elongated body called the axon, some of which can be 1m long in humans. Motoneurons are connected to muscles by the signups, when stimulated the motor neurone produces Nero transmitter is that bind to receptors on the muscle and produce a muscle contraction. Muscles will relax when motoneurons are inhibited
Read I neurons: these are multipolar neuron is found only in the brain and spinal cord and Allow sensory and motor neurons to communicate with each other
The process of the synaptic transmission
Signups is a gap between a presynaptic neuron and a post synaptic Mirren. Neurotransmitters are substances in the brain that carry electrical in processes across the signups between wonder and another. And electrical impulse will cause signup tick vessels to migrate to the end of the sale and release the neurotransmitter into the signups. This then binds to specialise postsynaptic receptors sites and these will have an excotarory or an inhibitory effect on the post synaptic neurone. Activity at the synapses to have a fundamental effect on the behaviour voice sample it is thought that an excess of time main activity can produce schizophrenic symptoms, a lack of serotonin can produce symptoms of depression OCD, drugs and out of whole affect the activity of neurotransmitters and the synaps has a bad effect on our behaviour
A study by 0L tested the hippocampus that low levels of serotonin where about in obsessive compulsive disorder is, they tested the effects of MCPP known as the drug trade you serotonin activity on OCD's symptoms 12 patients with OCD and 20 controls were given a single days of MCPP administered orally and a double-blind randomised Simon conditions. Following MCPP but not following placebo patients with OCD experience a temporary promoted increase in OCD symptoms these findings support the role neurotransmitter serotonin in the OCD symptoms.
Excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters
Excitatory neurotransmitters: chicken nerve impulses that stimulate brain activity. They act as a kind of on switch was out singing at Excitatory post synaptic potential and increases the likelihood of a neuron firing for example dopamine can increase motivation and reward
Inhibitory neurotransmitters: inhibit nerve impulses and have a calming effect on the brain they act as an off switch resulting in a heap a Tory post Sidon at the potential and decreases the chances of a neuron firing for example serotonin have a calming and stabilising effect on a mood.
A nerve cells can produce both EPSPS and IPSPS and therefore whether or not I fires depends on the relative amount of H if one of the synapses produces a large number of EPSP for many synapses produce EPSP then the cell will fire
The function of the endocrine system
The Endo crying system is made up of a network of plans that manner facture chemical messages nine is hormones. He is home and I deliver to the target sites in the body for the blood vessels. The Endo crying system works with the nerve system is to regulate the psychological process of the body. Hormones identical area of the body stimulates receptors sites on the sales in that area. It's a major brands of the Endocrine system are:
1) the pituitary gland
2) the testes and ovaries
The pituitary glad
It is the kind of masterplanned David directly cause changes in some parts of the body or stimulate of a glass to produce hormones it is controlled by the hypothalamus and this receives information from many parts of the body and use it to regulate body functions e.g. releases a hormone called oxytocin which has a number of effects it induces labour contractions and is released when we hug someone and also happens during sex.
Studies have been done into the effects of oxytocin on behaviour research has shown that inhibiting oxytocin in Labre Tori rats make new mothers reject their young also oxytocin injected into females that never mate it makes the show nurturing behaviour towards their Young of other rats reduce sensitivity to oxytocin could be a factor in human child abuse.
Testes and ovaries
The test is a male reproductive glands and produce testosterone. To sister and is also produced by women but in smaller amounts. Testosterone serves a number of functions in males
1) deepening of the voice
2) growth of facial hair
3) sperm production
4) sex drive
5) maintenance of muscle strength
Testosterone is associated with increased levels of aggression for example dabbs et al measured selling very testosterone in violent and non-violent criminals. Those with the highest testosterone levels had a history of primary violent crimes where as those of the lowest levels had committed only non-violent crimes.
The ovaries form part of the reproductive system and females and produce eggs along with oestrogen and progesterone. Oestrogen place an important role in preparing to you just for pregnancy, Percys to Jane maintains the uterus during pregnancy and prevents further release of eggs from the ovary. It is also responsible for the development of milk secreting cells in the breasts.
Outline and explain how he flight and fight response
The fight or flight response is generated when part of the brain called the brain called the amygdaloid recognises a friend and sends a message to the hippocampus which activates the sympathetic branch of the automatic nervous system it prepares the body for acting quickly to fight the fridge or van away. The sympathetic nervous system commands that all the time and nervous system to activate the sympathetic branch then the adrenal medulla is triggered to produce adrenaline and noradrenaline. Then fight or flight takes response including increased heart rate blood pressure and Decreased digestion
The fight or flight respondes
Increase heart rate speed up the blood for a device organs and increases speed of a genuine from the body. Next increased breathing rate increases oxygen intake next muscle tension improve reaction time and spade lastly do you start gesture and saves energy for my appalling actions like running
Evaluation of flight or fight responce
Weakness: the fight flight response is very important when in preparing the body to do with Fred however modern human humans don't face for it that often require the physical activity and problems arise a stress response in activated repeatedly without using XS energy produced for example the increase in blood pressure over a long period of time can lead to cardiovascular problems And reduced digestion functioning can lead to digestive illness
Evaluation of the biological approach
Strengths: the biological approach is a scientific methods and Labre Tori experiments as it's my method of investigation. This means the study is a highly controlled and can be replicated to increase the reliability and validity of its findings
Weakness: establishing cause and effect can be difficult because much of the research is correlational for example aggression is correlated with increased levels of the testerone. It may well be that testosterone causes increased levels of aggression they could be that being the aggressive increased levels of testosterone
The emergence of cognitive neuroscience
Explains how mental functions are undertaken within the brain. This combined the study of brain damage, neuropsychology, cognitive psychology and computer modelling. Pet scans and Mri scans are used to understand how the brain supports the different parts for emotions and functions when asked to perform different tasks. Burrnett et al found that when someone feels guilt it is active in serval different pats of the brain e.g prefrontal cortex which is responsible for social emotions.
Overall evaluation of the cognitive approach
Strength: schemas are widely held to valid in cognitive psychology
Strength: the cognitive approach has led to useful applications in everyday life e.g cbt treatment for depression
The biological approach
Sees all out behaviour is rooted for our biological structure and that everything psychological has a biological basis
1) genes- specific genes and combinations of genes will have an influence on both the physical and psychological aspects of people. Genes that code for characteristics or behaviours that are beneficial to survival will be passed on to the next generation
2) The biological structure-the behaviour of the individual is controlled and coordinated by the brain and the nervous system
3) The chemistry of the body-hormones in the body and neurotransmitters in the brain have a much impact on our behaviour
The cognitive approach
This emphasised the important of inner mental functions, it states the human behaviour is governed nu the way we process information from the environment
Stimulus + rumination ( rationalisation) = response
In relation to this process they have mad cognitive assumptions
1) thought process can and should be studied scientifically
2) the mind works like a computer in that it had input from our senses which it them process and producers an output such as language or specific behaviours
3) stimulus and response is appropriate but only if the thought processes that accounts between s&r are recognised
The internal mental process
Cognitive psychologist have decided numerous experiment to test specific aspects of the interim mental processing, in a study of inattentive blindness conducted by Simmons and Chabris where undergraduate were presented with a science where a group of individuals were playing basketball with each other. During the scene no longer than one and a half minutes participants are required to count the amount of times the ball is passed to each player. Awarded ward the participant we asked how many passes were and then asked if the saw the gorilla.
Findings: only 54% out of 288 participants noticed the gorilla. This was thought to be be jade there were never aware of the inexperienced object to assume that the saw the l gorilla and then forgot about it, this suggests that we doing noticed everything we performed in our visual filed due to inattention
The genetic basis within the biological approach
The genotype is the individual is unique set of genes that code for their development. Humans have around 100,000 genes code 1846 chromosomes in every cell of my body, the genotype dictate physical characteristics such as eyecolour or hair colour but psychologist consider how much this genotype may be responsible for psychological characteristics such as aggression or schizophrenia or phobias. The phenotype is the observable result of the Internetaitons between genotype and the environment. E.g smoking and drinking during pregnancy can produce toxins and effect the development of an unborn child. Also may be the external environment e.g nutrition might effect the weight of a person. This approach is firmly on the nature side of the nature nurture debate of his behavioural as determined by our genes rather than being learned through interactions with the environment. However a person might have a genotype includes a gene that includes schizophrenia but whether or not they actually go on to the develop schizophrenia might depend on at exposure of stress in the environment.
Explain the role of family, twin studies and the potential effects on the environment
If a characteristic or illness is genetic, it is likely that it runs in families. The more closely related individuals are the more likely they are to both have certain characteristics or illness.
Family study on OCD by nestadt et al. He investigated the influence on genes on OCD by looking at first degree relatives of 80 suffers. They found that first degree relative of OCD suffered had a 11.7% chance of developing the disorder compare to a 2.7 chance in first-degree relative's of healthy parents. They suggest the OCD might be genetically transmitted through families.
There has also been twin studies done. Monozygotic Twins develop wanna fertilise eggs divides and therefore sure 100% of their DNA. Dizygotic ( non-identical ) Twins develop from separate fertilised eggs and share around 50% of the DNA no more than siblings. When studying effective change research is look at concordance which is known as similarity rights they referred to the probability of people both having certain characteristics e.g. rate of eyecolour in monozygotic twins would be 100%. Something is genetically inherited them monozygotic twin should have higher concordance rate then dizygoric. Twin studies done by grootherst et al. He did a meta analysis where he assessed 70 years of twin studies into OCD. there were over 10,000 participants. They found a 45-65% role for inheritance in children and a 27 to 47% inheritance for adults. This shows the heritability have a strong interest in children who developed OCD with perhaps a great environmental role for adults. However it could be argued that much of the research study did not have a Knouff controls as it is tight as far back as the 1929 before Controls employed. The study also didn't take into account different types of OCD and how this may change heritability