Angiosperm Sexual Reproduction: Life Cycle, Gametophytes, and Seed Dispersal
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Diploid (2n)
A cell or organism that has paired chromosomes, one from each parent.
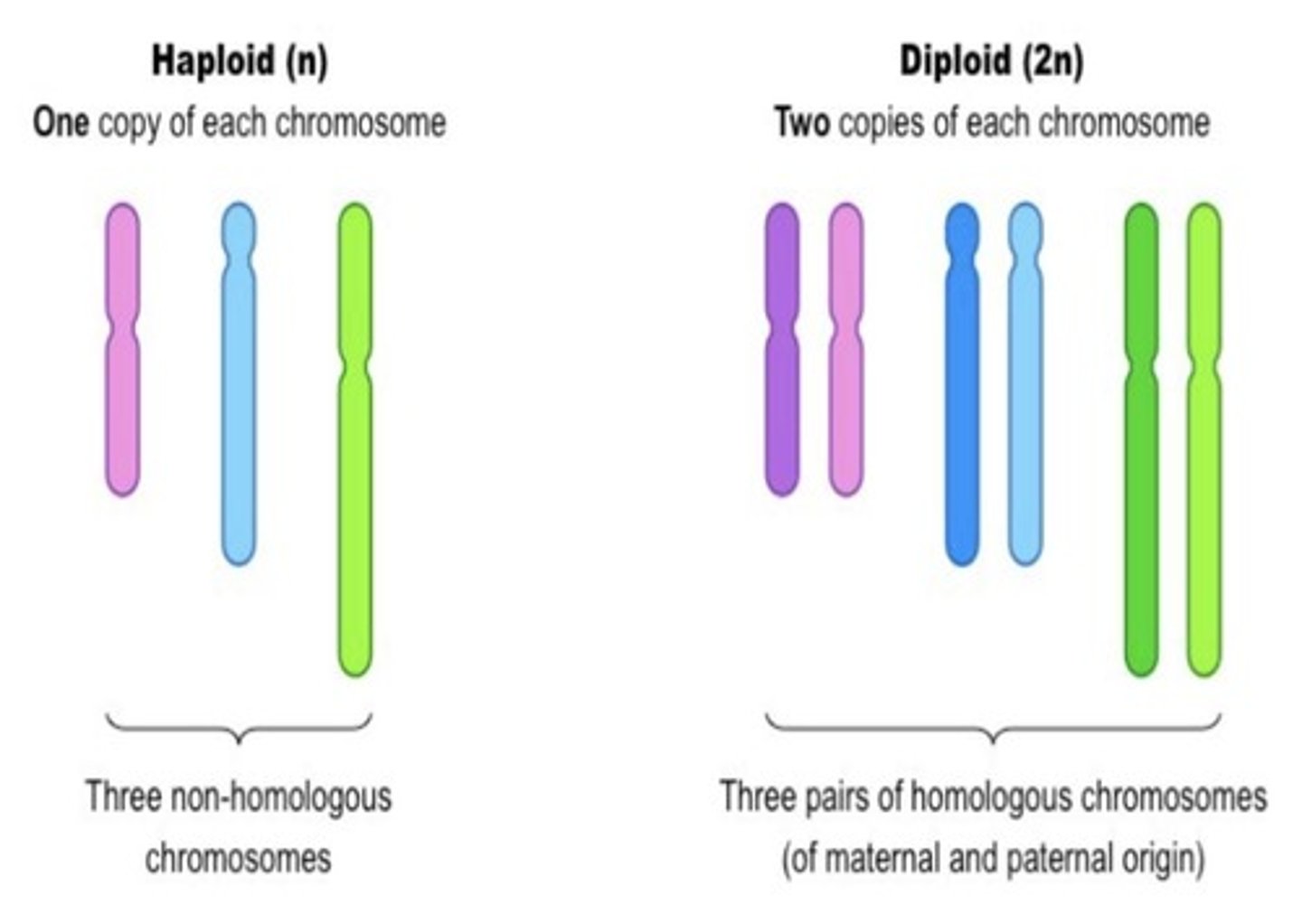
Haploid (n)
A cell or organism that contains a single set of chromosomes.
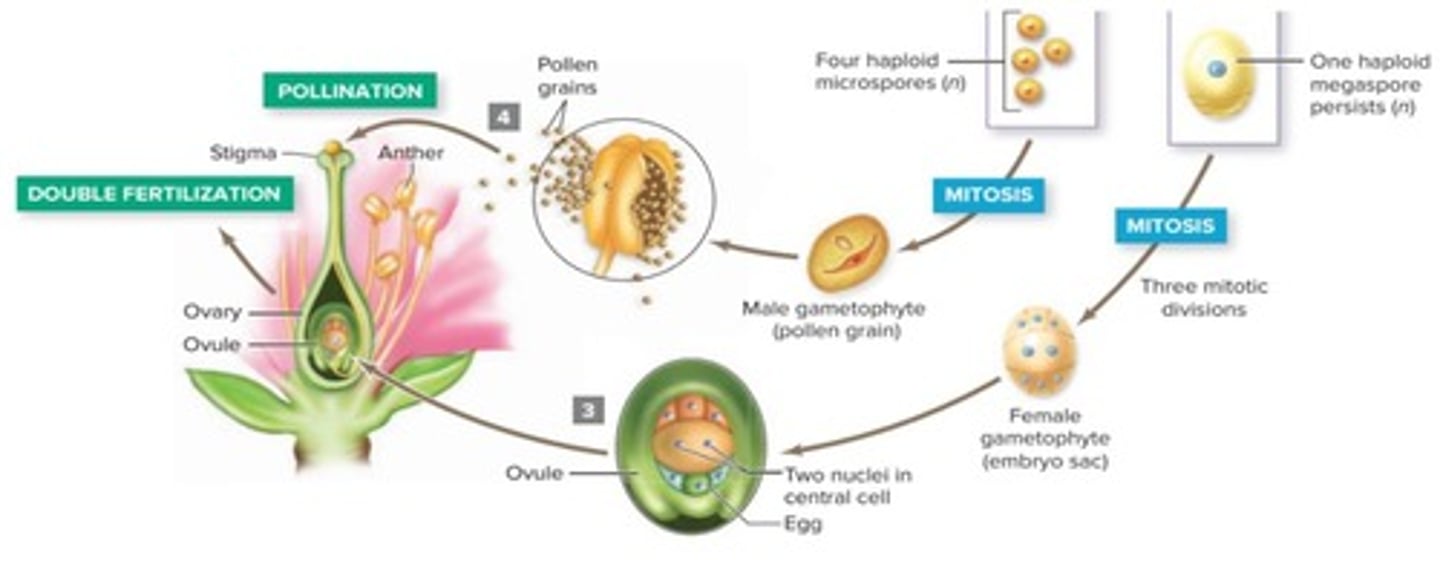
Microspore
A haploid spore that develops into a pollen grain.
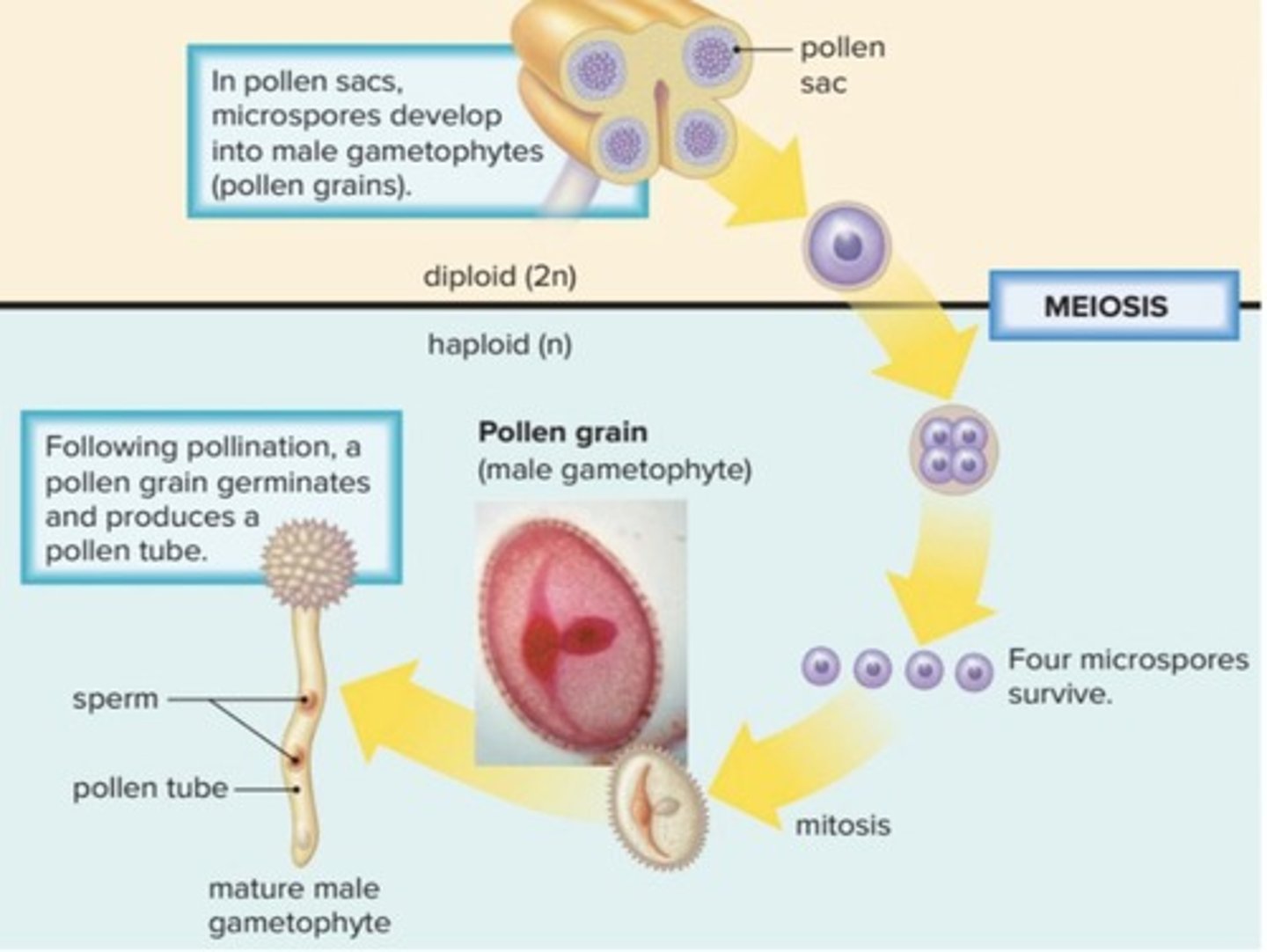
Pollen Grain
A structure that initially consists of two cells, one of which will produce a pollen tube.
Sperm
The smaller cell that divides to become two sperm nuclei.
Megaspore
A haploid spore that develops into an embryo sac, with only one surviving from four produced.
Embryo Sac
A seven-celled structure developed from a megaspore containing a single egg cell.
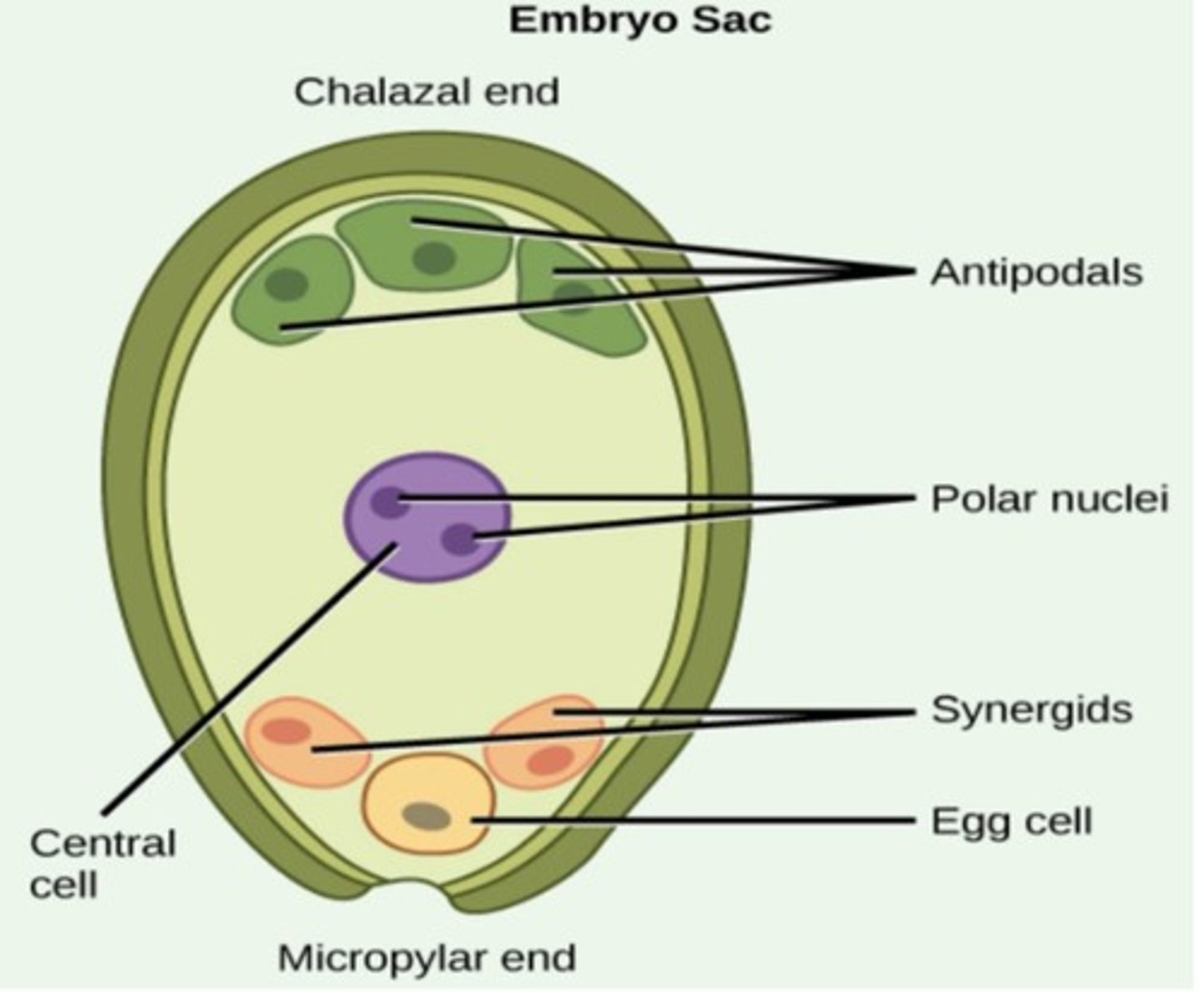
Eight-Nucleate, Seven-Cell Female Gametophyte
A structure formed from the fusion of haploid cells, resulting in a seven-celled structure.
Fertilization
The process where one sperm nucleus fertilizes the egg cell to form a diploid zygote.
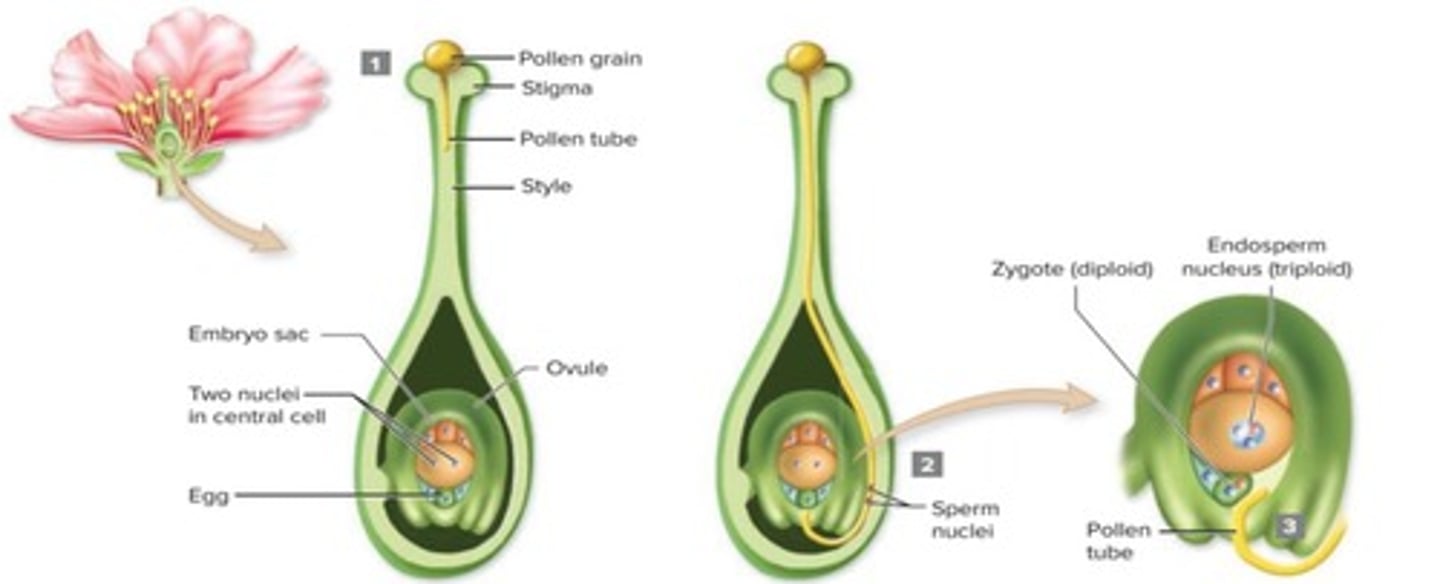
Zygote
A diploid cell formed from the fertilization of an egg cell by a sperm nucleus.
Endosperm
A triploid cell formed when the other sperm nucleus fuses with the central cell's two nuclei.
Seed
A plant embryo together with its stored food, surrounded by a seed coat.
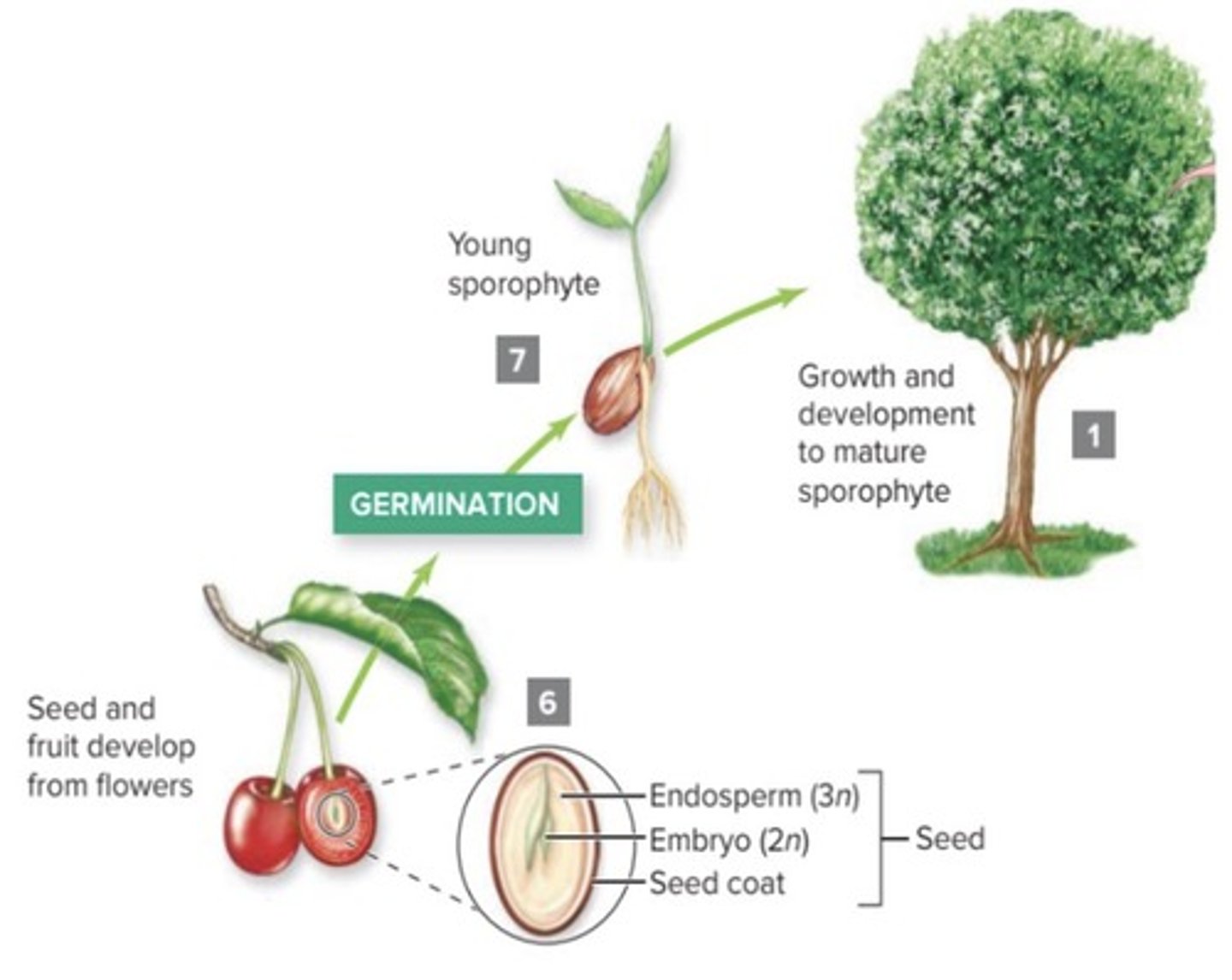
Fruit
A structure that protects seeds and promotes seed dispersal.
Seed Dispersal
The mechanism by which seeds are spread away from the parent plant.
Biotic Dispersal Agents
Living organisms that assist in the dispersal of seeds, such as animals.
Abiotic Dispersal Agents
Non-living factors that assist in the dispersal of seeds, such as water and wind.
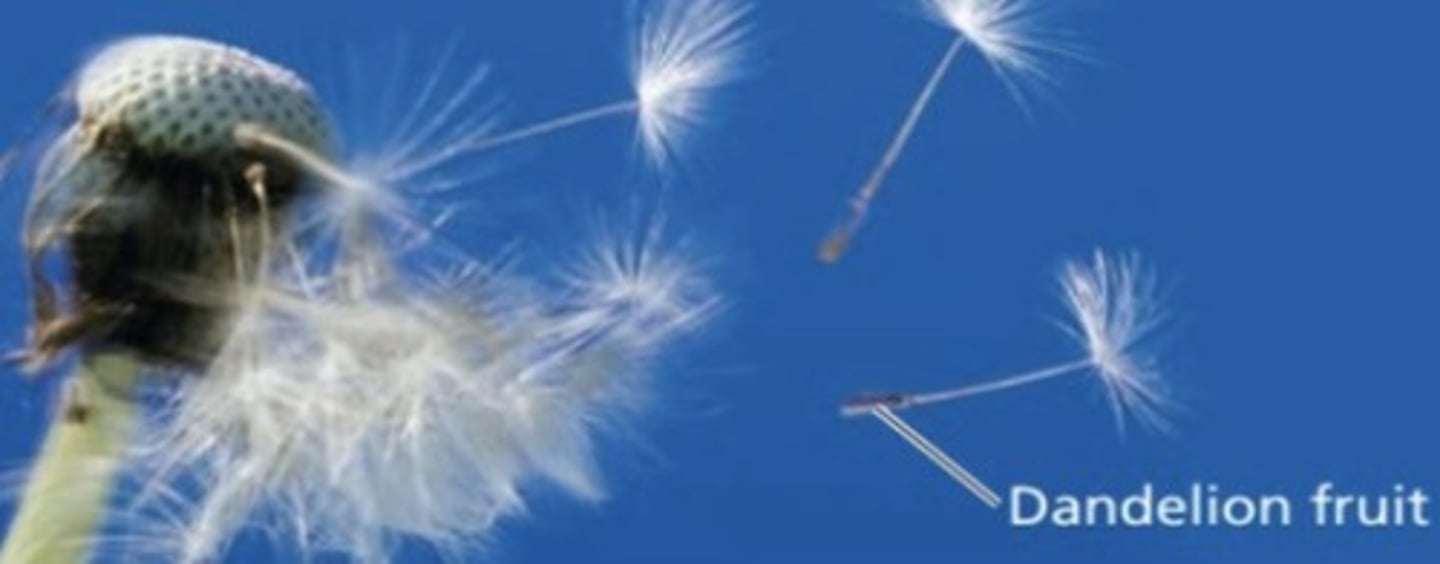
Dandelion
An example of a plant that uses wind as a mechanism for seed dispersal.

Maple Fruit
An example of a plant that uses wind as a mechanism for seed dispersal.
Tumbleweeds
An example of a plant that uses wind as a mechanism for seed dispersal.

Ants
An example of a biotic dispersal agent that helps in seed dispersal.
Sporophytes
These (2n) produce haploid spores by meiosis. The spores develop into pollen grains and embryo sacs.
Gametophytes
What produce the egg cells and the sperm cells?