Fun. I - Type I Hypersensitivity
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Hypersensitivity
An exaggerated response by the immune system to an antigen that poses little or no threat
A response to self-antigen is considered ____.
autoimmunity
Type I Hypersensitivity Reaction
IgE mediated reaction that causes degranulation of sensitized mast cells/basophils: Releases Histamine
Atopy
A hypersensitivity or allergic state
____ stimulate Type I Hypersensitivity Reactions.
Allergens
Allergens usually have what 3 characteristics?
(1) Internal enzymatic activity
(2) PAMPs/PAMP-Like Structures
(3) Enter host through mucosal tissue
All Hypersensitivity Reactions consist of what 2 phases?
(1) Sensitization Phase: Primary immune response to antigen "primes" mast cells
(2) Effector Stage: Secondary immune response to same antigen
Type I Sensitization Phase
- Allergen-Specific IgE is produced after the first exposure to an antigen
- IgE binds mast cells and basophils
IgE binds to ____.
Fc(epsilon) Receptors on mast cells
Type I Effector Phase
Mast Cell Degranulation induces inflammation, smooth muscle contraction, and vascular dilation
What are the 2 parts to the Type I Hypersensitivity Effector Phase?
Immediate
- Mediated by release of pre-formed molecules in Mast Cells
Late
- Released Chemokines/Cytokines recruit Eosinophils, Basophils, and Lymphocytes to the site
____ play a principal role in allergies.
Eosinophils
Eosinophils
Release Major Basic Protein (MBP) which stimulates continual degranulation of Mast Cells
Histamine drives the ____ phase of Type I Hypersensitivity Reactions.
immediate
____ drive the Late Effector Response of Type I Hypersensitivity Reactions.
Eosinophils
____ and ____, released by Eosinophils, drives the Late Effector Response.
MBP/ECP
ECP
Eosinophil Cationic Protein
What does release of Prostaglandins and Leukotrienes by Mast Cells/Eosinophils cause?
- Tissue Edema
- Smooth Muscle Contraction
- Eosinophil and Th2 Activation
Causes the continual inflammation of an Allergic Reaction
Type I Hypersensitivity GI Effects
- Increased Secretion
- Increased Peristalsis
Type I Hypersensitivity Airway Effects
- Bronchoconstriction
- Mucus Secretion
Type I Hypersensitivity Blood Vessel Effects
- Increased Blood Flow
- Increased Permeability
Systemic Anaphylaxis
Release of IgE leads to mass mast cell/basophil activation
- Bronchoconstriction
- Vasodilation: Low BP
- Tachycardia
- Swelling
Wheal-and-Flare
Rash/Hives that appear due to release of serum into tissues (swelling) and dilation of blood vessels (redness)
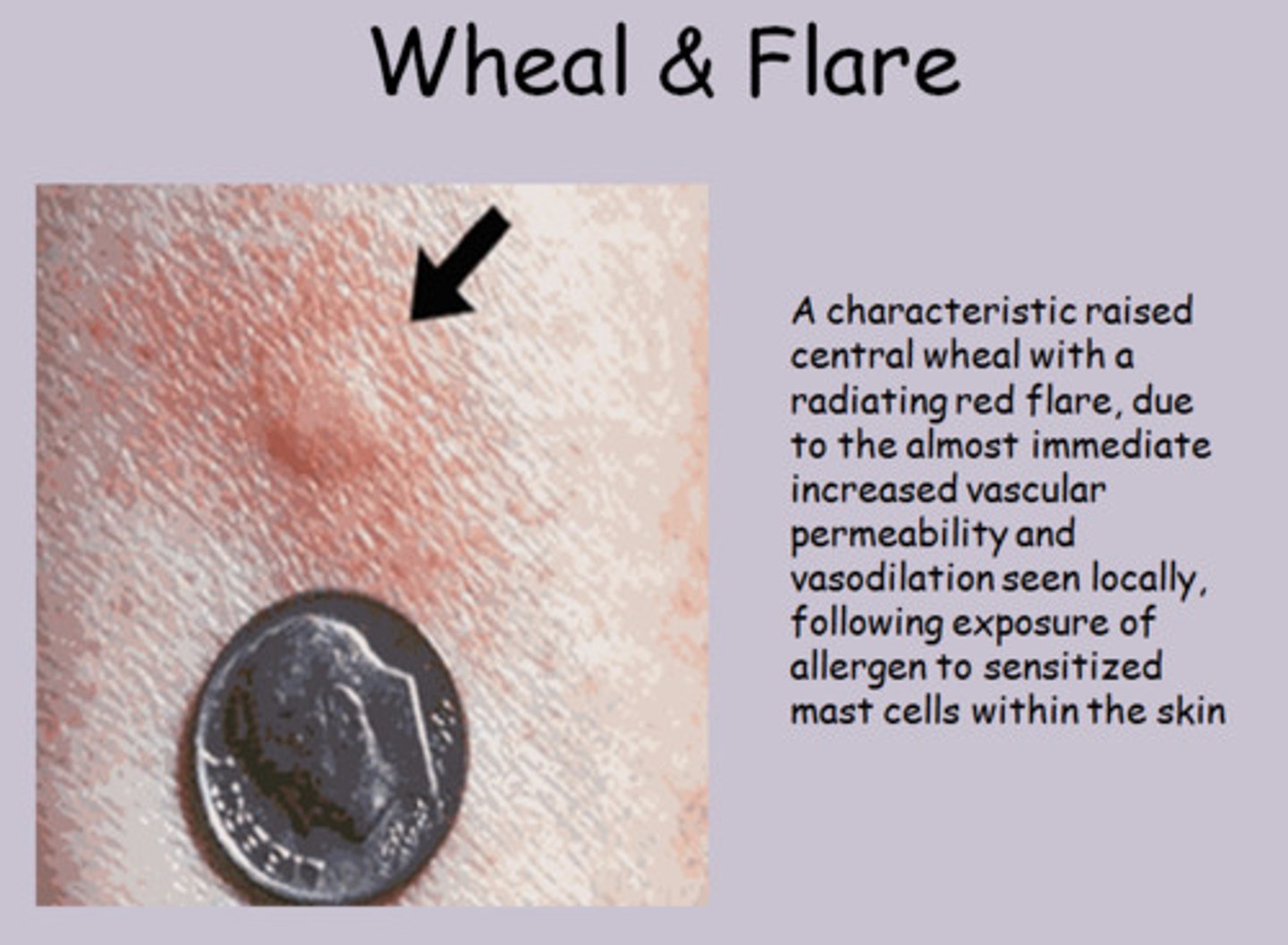
Wheal-and-Flare is characteristic of ____.
Type I Hypersensitivity
Purpose of IgE-mediated Immune Responses
Protect against Parasites