The Microeconomy Today: 16th Edition Exam Guide for Chapters 1-4
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Scarcity
Lack of enough resources to satisfy all desired uses of those resources.
Factors of Production
Resource inputs used to produce goods and services, e.g, land, labor, capital, and entreprenuership.
Capital
Final goods produced for use in the production of other goods, such as equipment and structures.
Entreprenuership
The assembling of resources to produce new and improved products and technologies.
Economics
The study of how best to allocate scarce resources among competing uses.
Opportunity Cost
The most desired foods or services that are forgone in order to obtain something else.
Production Possibilities
The alternative combinations of final goods and services that could be produced in a given period with all available resources and technology.
Efficency
Maximum output of a good from the resources used in production.
Economic Growth
An increase in output (real GDP); an expansion of production possibilities.
Laissez Faire
The doctrine of "leave it alone," of nonintervention by government in the market mechanism.
Mixed Economy
An economy that uses both market signals and government directives to allocate goods and resources.
Market Failure
An imperfection in the market mechanism that prevents optimal outcomes.
Government Failure
Government intervention that fails to improve economic outcomes.
Macroeconomics
The study of aggregate economic behavior, of the economy as a whole.
Microeconomics
The study of individual behavior in the economy, of the components of the larger economy.
Ceteris Paribus
The assumption of nothing else changing.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The total market value of all final goods are services produced within a nation's borders in a given time period.
Per Capita GDP
The dollar value of GDP divided by total population; average GDP.
Economic Growth
An increase in output (real GDP); an expansion of production possibilities.
Human Capital
The knowledge and skills possessed by the workforce.
Capital-Intensive
Production processes that use a high ratio of capital to labor inputs.
Externalities
Costs (or benefits) of a market activity borne by a third party; the difference between the social and private costs (benefits) of a market activity.
Monopoly
A firm that produces the entire market supply of a particular good or service.
Income Quintile
One-fifth of the population, rank-ordered by income (e.g. top fifth).
Factor Market
Any place where factors of production are bought and sold.
Supply
The ability and willingness to sell (produce) specific quantities of a good at alternative prices in a given time period, ceteris paribus.
Demand
The willingness and ability to buy specific quantities of a good at alternative prices in a given time period, ceteris paribus.
Demand Schedule
A table showing the quantities of a good a consumer is willing and able to buy at alternative prices in a given time period, ceteris paribus.
Demand Curve
A curve describing the quantities of a good a consumer is willing and able to buy at alternative prices in a given time period.
Law of Demand
The quantity of a good demanded in a given time period increases as its rice falls, ceteris paribus.
Substitute Goods
Goods that substitute for each other; when the price of good x rises, the demand for good y increases, ceteris paribus.
Complementary Goods
Goods frequently consumed in combination; when the price of good x rises, the demand for good y falls, ceteris paribus.
Cetreis Paribus
The assumption of nothing else changing.
Shift in Demand
A change in the quantity demanded at any (every) given price.
Market Demand
The total quantities of a good or service people are willing and able to buy at alternative prices in a given time period; the sum of individual demands.
Law of Supply
The quantity of a good supplied in a given time period increases as its price increases, ceteris paribus.
Equilibrium Price
The price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied.
Market Mechanism
The use of market prices and sales to signal desired outputs (or resource allocations).
Price Floor
Lower limit set for the price of a good.
Market Surplus
The amount by which the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded at a given price; excess supply.
Market Shortage
The amount by which the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied at a given price; excess demand.
Price Ceiling
An upper limit imposed on the price of a good.
Optimal Mix of Output
The most desired combination of output attainable with existing resources, technology, and social values.
Antitrust
Government intervention to alter market structure or prevent abuse of market power.
Natural Molopoly
An industry in which one firm can achieve economies of scale over the entire range of market supply.
Transfer Payments
Payments to individuals for which no current goods or services are exchanged, like Social Security, welfare, and unemployment benefits.
Merit Good
A good or service society deems everyone is entitled to some minimal quantity of.
Unemployment
The inability of labor force participants to find jobs.
Inflation
An increase in the average level of prices of foods and services.
Progressive Tax
A tax system in which tax rates rise as income rises.
Proportional Tax
A tax that levies the same rate on every dollar of income.
Regressive Tax
A tax system in which tax rates fall as income rises.
Public Choice
Theory of public sector behavior emphasizing rational self-interests of decision makers and voters.
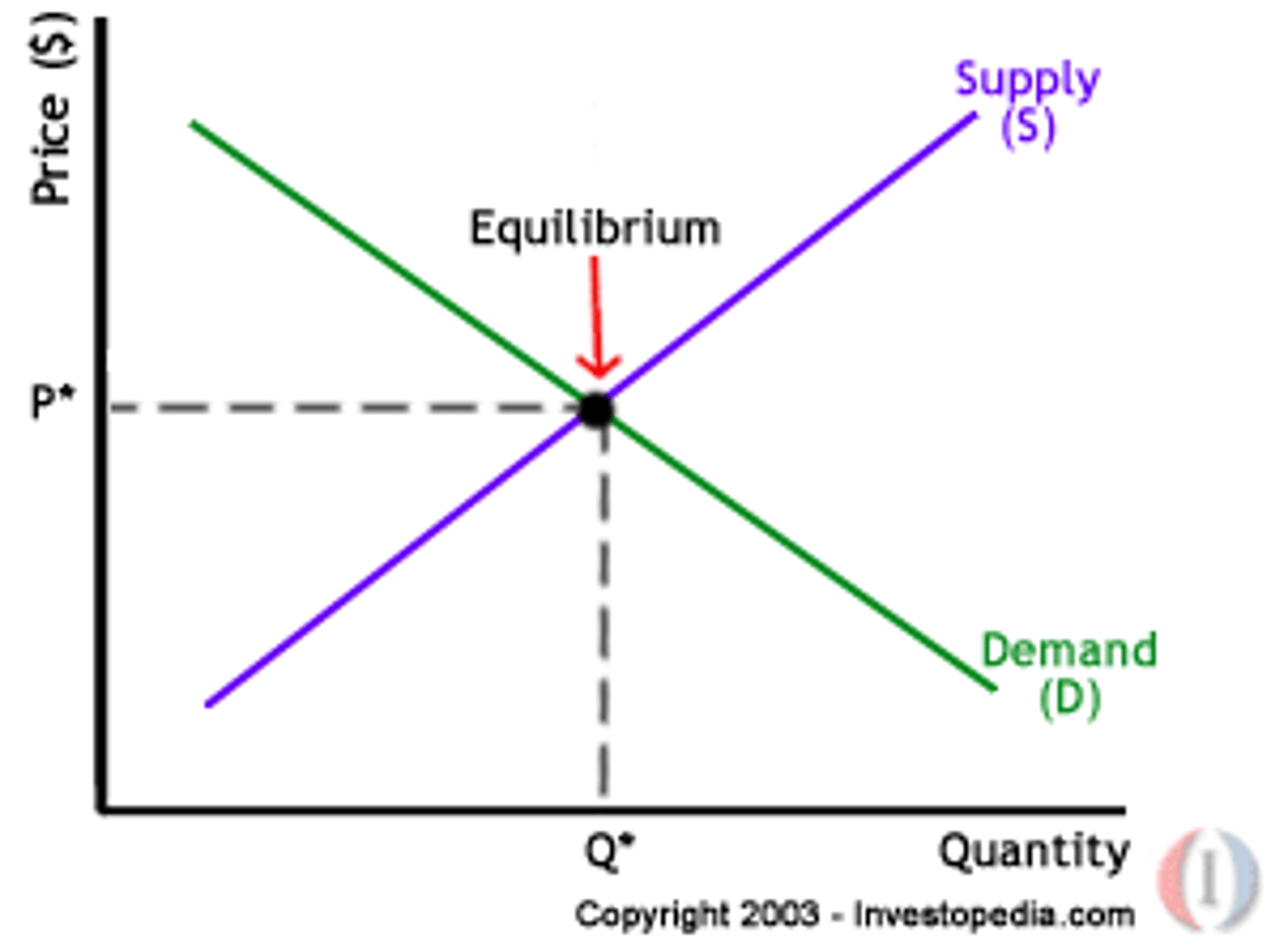
Supply and demand curve (must know)
Know how to draw and interpret the graph.
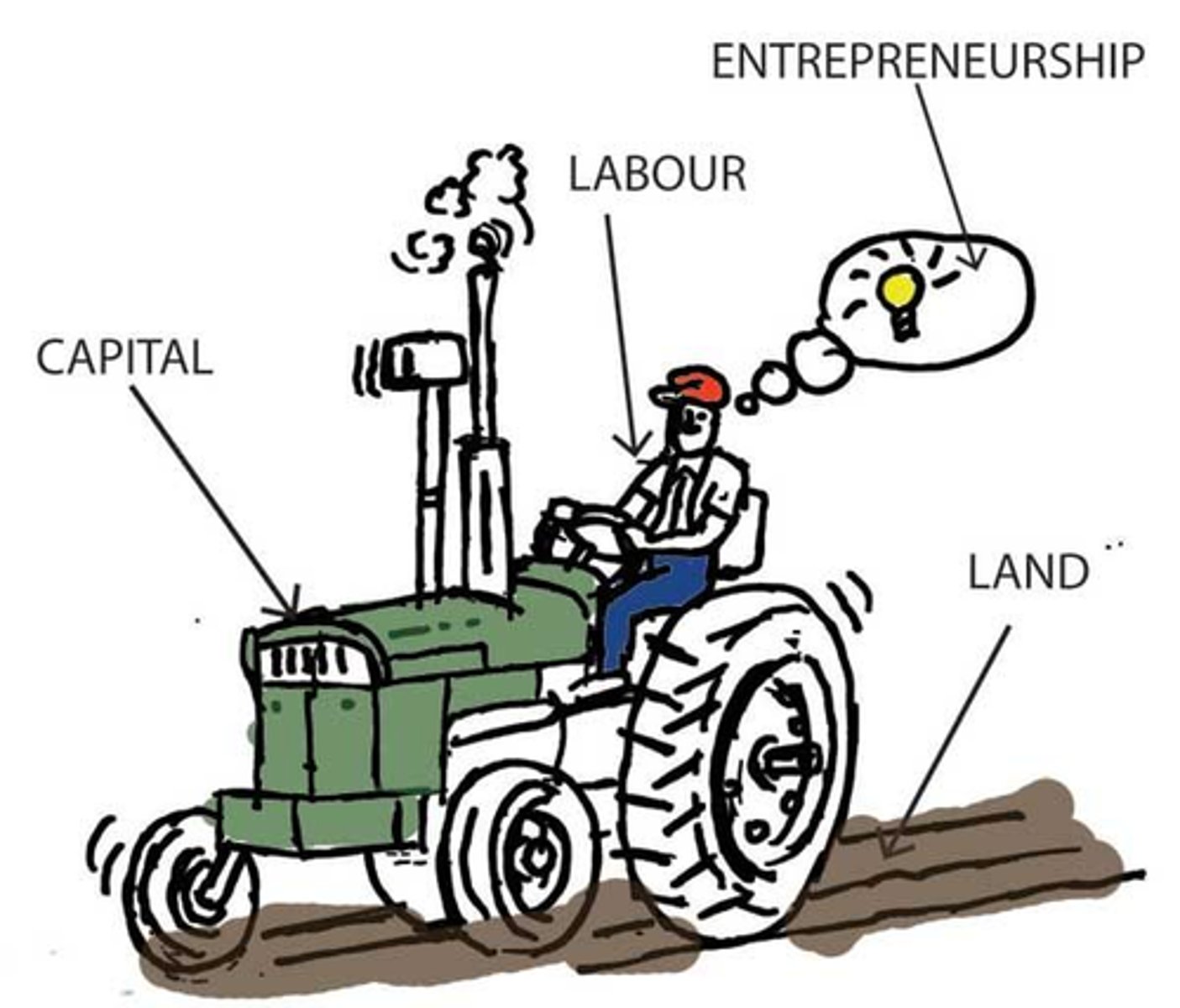
Four Factors of Production and their outputs (must know)
Inputs are land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship... Outputs are rent, wages, interest, and profits.
What is the United State's largest economic sector? (must know)
Now is services, it used to be agriculture.
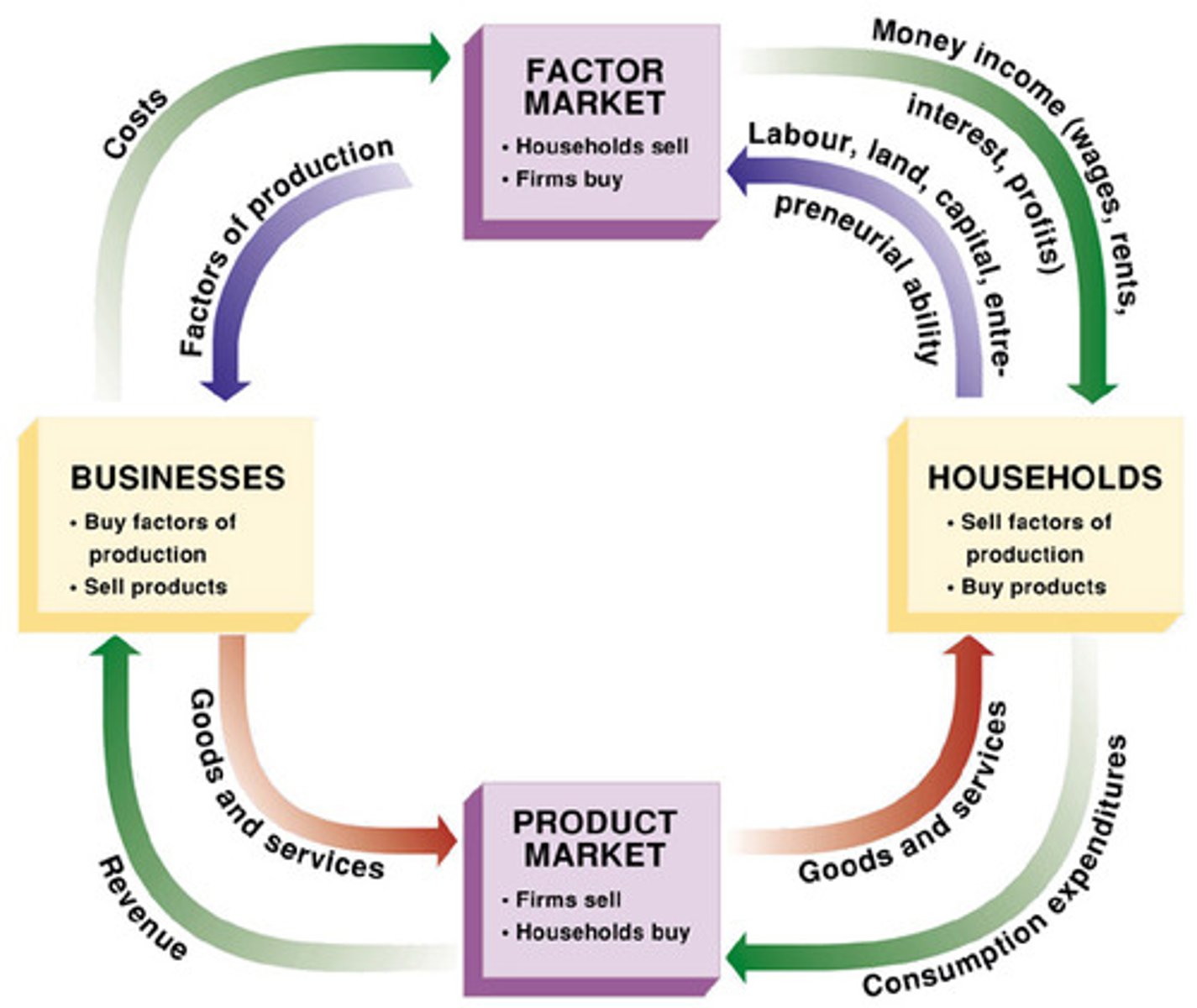
Circular flow diagram (must know how to label and interpret)
a visual model of the economy that shows how dollars flow through markets among households and firms
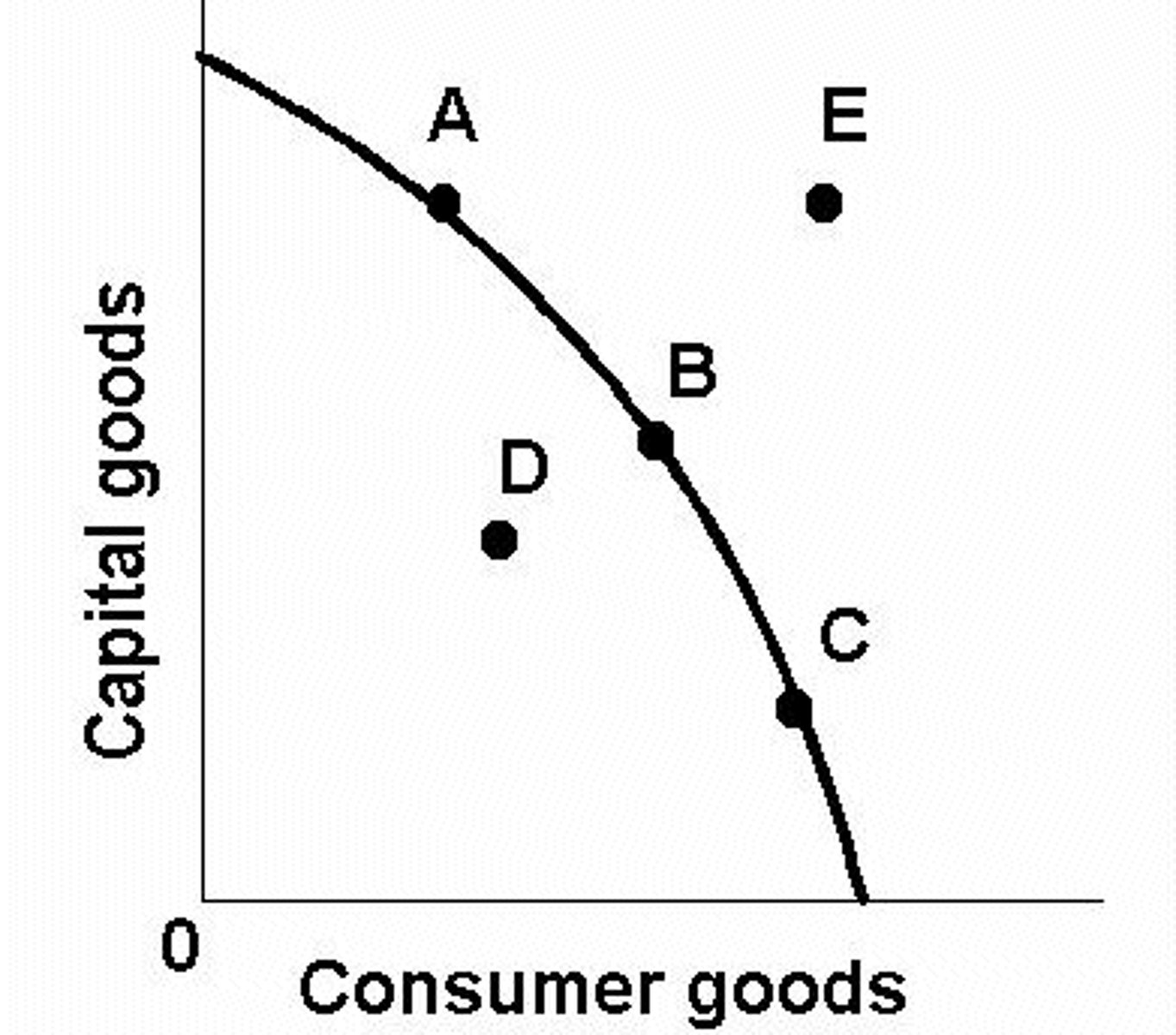
Production possibilities curve/frontier (must be able to graph and interpret)
Point D is possible to manufacture but it is not a good use of all available labor and resources. Point E is not possible to manufacture. All other points along the line are possible to manufacture and are the most ideal.
Three Basic Decisions
What to produce? How to produce? For whom to produce?