1.5 Eukaryotes
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
eukaryote
cell with a defined nucleus and organelles
fungi and parasites (protozoa and helminths)
can be unicellular or multicellular
protozoa cellularity
unicellular
fungi
either
helminths
multicellular
Flagella
motility— thicker and more structurally complex than bacterial flagella. Covered by an extension of cell membrane (protozona
Cilia
motility- shorter and more numerous than flagella. Beat in coordination
cell wall
present on fungi, protozoa and helminths do not (parasites need flexibility to function as a worm so they dont have a cell wall)
gives structure and shape
inner layer of chitin or cellulose, outer layer of glycans (no peptidoglycan)
cell membrane
phospholipid bilayer (semi permeable)
intermixed with cholesterol to give the membrane structure
nucleus
nuclear envelope and chromatin (linear DNA wound around histones to form chromosomes)
Lysosome
contains variety of enzymes that break down food
mitochondria
generates energy (ATP) for the cell
types of fungi
yeasts- round/oval shape, asexual reproduction
hyphae (mold)- long, threadlike cells

dimorphic
some fungi are dimorphic and can transition between forms depending on the growth conditions
medically important fungi- yeasts at body temperature and hyphae at room temperature
saprobes
most fungi are saprobes and obtain nutrients from dead plants and animals
parasite
some fungi are parasites and live in/on the body of a living host
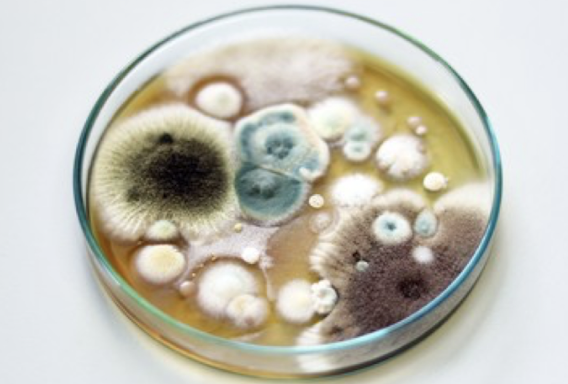
colonies
growth of fungi in associations
appear soft, hairy, velvety
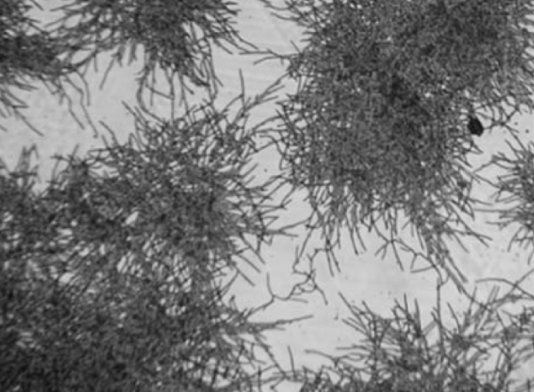
mycelium
the intertwining mass of hyphae that makes a colony
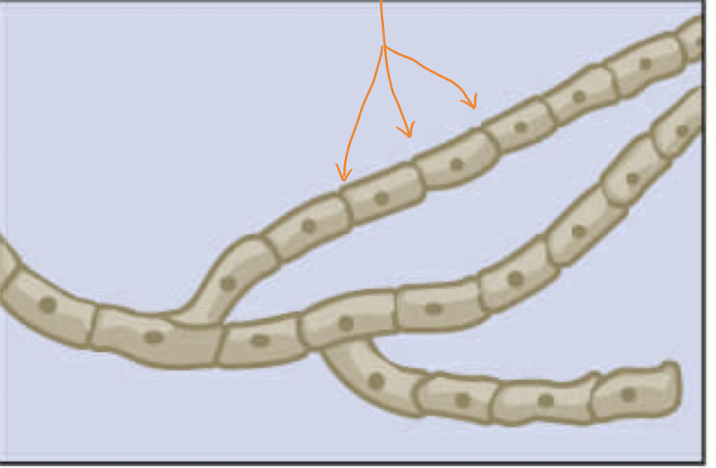
septate hyphae
segmented branches with breaks
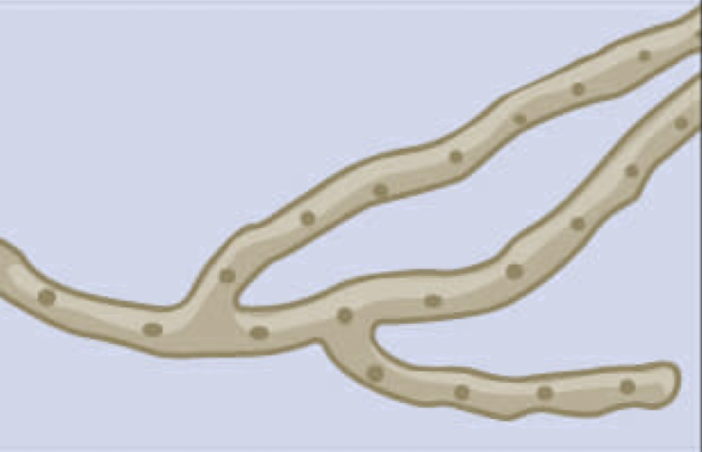
non-septate hyphae
continuous cell without breaks
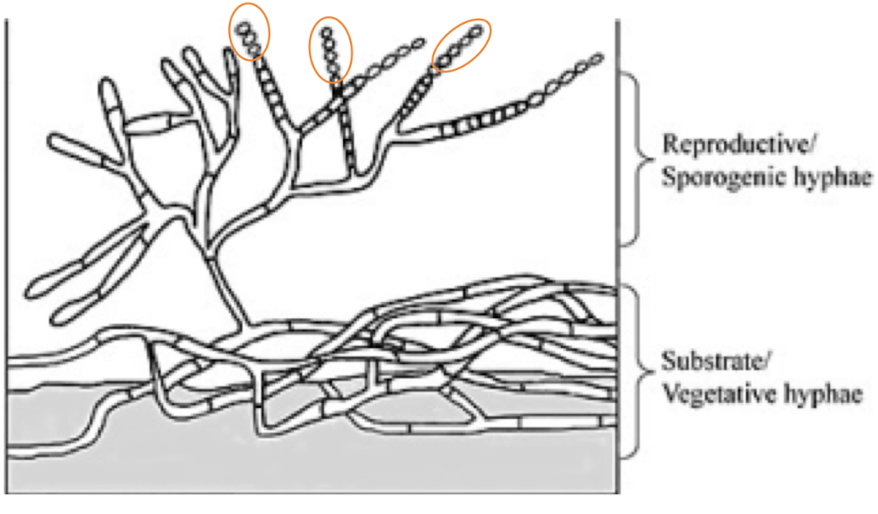
vegetive hyphae
growth phase, absorb nutrients from substrate (like roots)
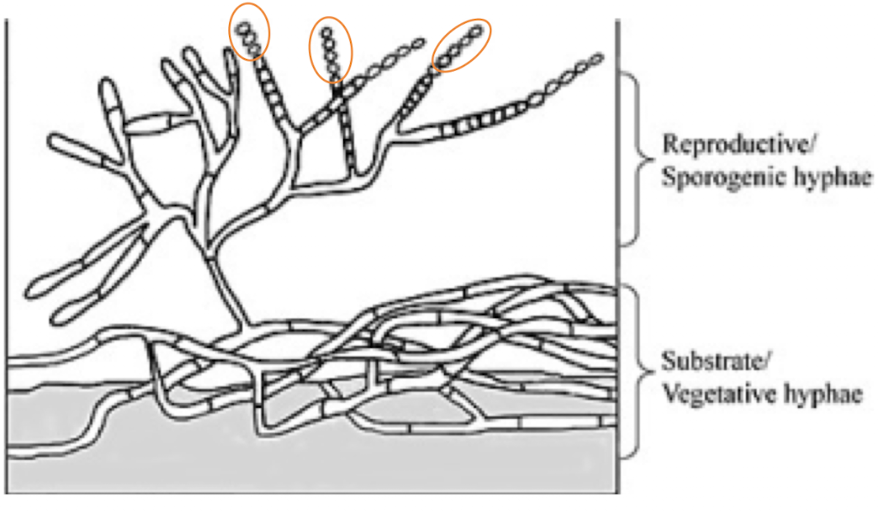
reproductive hyphae
branches from vegetive hyphae, forms fungal reproductive bodies called spores
Protozoa
diverse and not necessarily genetically related, but they share similar physical characteristics
form and function of protozoa
move through fluid with pseudopods, flagella, cilia
no cell wall
cyst
dormant, resting stage that occurs when environment changes
helminths
flatworms- cestodes, trematodes
round worms-

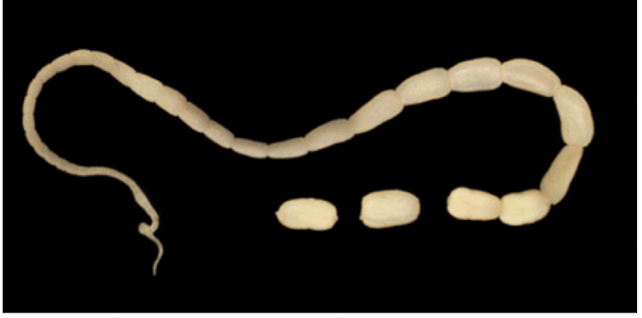
cestodes
long, ribbonlike arrangements (tapeworm)
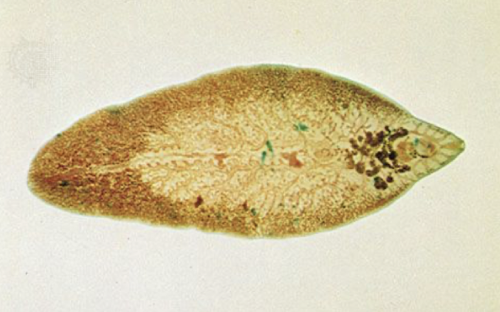
trematodes
flat, ovoid bodies
life stages of helminths
fertilized egg (infect humans), larval (infect humans), adult (pathogenesis occurs)
intermediate (secondary) host
host in which larval development occurs
definitive (final) host
host in which adulthood and mating occur