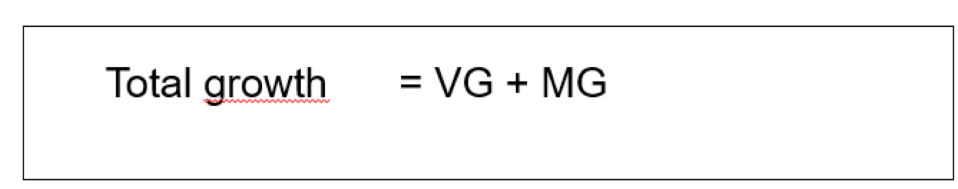Lesson 3: Dynamic Demography
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What does dynamic demography study?
Dynamic demography studies the changes that occur over time in the size, structure and geographical distribution of human populations, and also describes the laws that determine these changes
What simple phenomena govern population dynamics?
Birth and death rates, and migratory movements.
What consequences do population dynamics have?
They affect population size and structure, available resources, socio-economic disruptions, and health status.
Why is knowledge of population dynamics essential?
Because it enables estimations and projections of future population changes in size and structure, which must be considered to modify and prioritise public health actions.
What is birth rate?
The term birth rate refers to all live births in a community during a specific period of time.
What is the source of data for birth rate?
Civil Record.
How are newborns registered statistically?
Children born alive but dying in the first 24h are included in the statistical bulletin of births as abortions. Children who survive at least 24h are officially included in the statistical bulletin of births.
What is the formula for the raw birth rate?
Raw birth rate = number of children born alive during 1 year × 1000 / total average population.

Factors affecting birth rate
Biological, social, economical, cultural, religious, small houses
What biological factors affect birth rate?
Age of woman, breast feeding.
What social factors affect birth rate?
Marriages, size of families.
What economic factors affect birth rate?
Unemployment, women in professional life, economical recession.
What other factors affect birth rate?
Cultural factors, religious factors, small houses (viviendas poco espaciosas).
Fertility
Fruchtbarkeit
What is fertile age?
Women aged 15–49 years.
What is the general fertility rate (GFR)?
Number of children born alive during a year, divided by the female population aged 15–49 at mid-year, multiplied by 1,000.
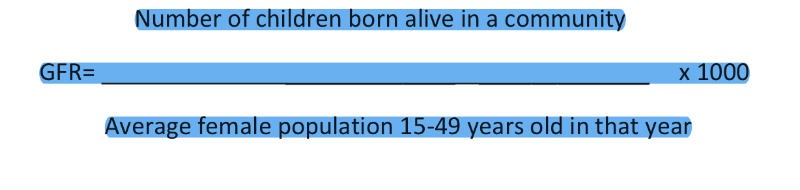
What is an Age-Specific Fertility Rate (ASFR)?
The annual number of births to women in a particular age group per 1000 women in that age group.
What is ASFR used for?
Comparisons in fertility behaviour at different ages, fertility at different ages over time, and fertility across countries or populations.
What is the Total Fertility Rate / Synthetic fecundity index?
The average number of children each woman would have by age 50 if she were subject to the specific fertility rates during her fertile life (15–49 years).
What value should the synthetic index exceed for population renewal?
It should be above 2.
What is Spain’s current synthetic fertility index?
Previously 1.5, currently down to 1.2.
What is the raw reproduction rate?
The average number of daughters per fertile woman.
What is the net reproduction rate?
Average number of daughters per fertile woman if women would fulfill specific fecundity rate by age and specific mortality rate.
Mortality
Sterblichkeit
What is the raw mortality rate?
The number of deaths that occur in a population in one year.
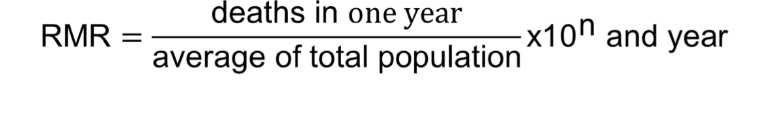
What is the Swaroop Index?
An index that expresses the proportion of deaths among people aged 50 and over out of the total number of deaths, used to avoid age influence.
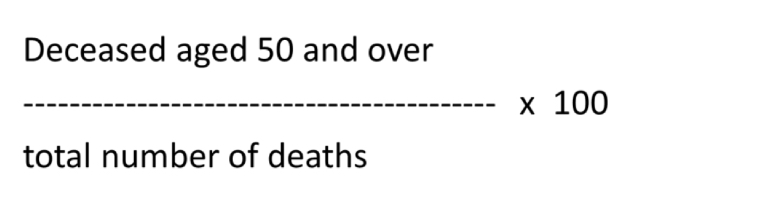
How is the infant mortality rate calculated?
Number of children under one year old who died during one year / born alive × 1000.

How is the neonatal mortality rate calculated?
Number of live newborns who die before 1 month of life / born alive × 1000.

How is the postneonatal mortality rate calculated?
Number of children who die after living more than 1 month but less than one year / born alive × 1000.

What are Years of Potential Life Lost (YPLL)?
An indicator of premature mortality that calculates the total number of years of potential life lost up to an arbitrary age limit due to premature deaths.
What is the commonly used age limit for YPLL?
70 years, but life expectancy may also be used.
What is the migration balance formula?
Migration balance = immigrants − emigrants / total population × 1000

What is the growth rate formula?
Growth rate = (born alive + immigrants − (died + emigrants)) / total population × 1000.

What are the consequences of immigration?
– Population growth
– Increasing birth rate
– Rejuvenation due to average age of immigrants (25–35 years)
What happens when immigration is excessive?
– Unbalance between size and structure of the population
– Increased resource needs
– Economic disturbances
– Impact on the health level, because the same resources must serve more people
Population growth:
Natural or vegetative growth

Population growth:
Migratory growth

Population growth:
Total growth