Covalent Bonding
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
state which elements form covalent bonds:
non - metal + non - metal
Define covalent bond:
The strong electrostatic forces of attraction between two nuclei and the shared pair of electrons between them
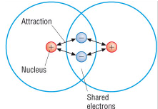
Define bond length:
The distance between the two covalently bonded nuclei (at positions of maximum attraction)
How does bond length influence bond strength?
As bond length decrease, bond strength increases
State 3 factors that bond length depends on:
atomic radii
shielding
attraction
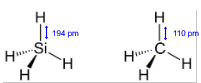
Explain why the Si-H and C-H bond lengths are different:
silicon has a larger atomic radius than carbon
so has more shielding
which reduces the attraction for the bonded electrons
What is a “lone pair”?
a pair of electrons in the outer shell which are not used to form a covalent bond
What period can the expansion of the octet occur in and why?
Period 3 and beyond - they have a 3d subshell
What is a dative bond?
When an atom uses a lone pair of electrons to form a covalent bond
What condition a dative bond can form in?
the acceptor atom must be electron deficient (there are available orbitals for the electron to occupy)
Do shorter or longer bond lengths require more energy to break?
Shorter
because there is greater attraction between nuclei and electron