INTECH 1100 ( 2ND TERM)
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
1
New cards
An integer n is ____ if, and only if, n equals twice some integer. Symbolically, if n is an integer, then n is
even
2
New cards
what do you call this type of symbol?
∃ an integer k such that n = 2k.
∃ an integer k such that n = 2k.
even
3
New cards
An integer n is ____ if, and only if, n equals twice some integer plus 1
odd
4
New cards
what do you call this type of symbol?
odd ⇔ ∃ an integer k such that n = 2k + 1
odd ⇔ ∃ an integer k such that n = 2k + 1
odd
5
New cards
An integer n is ___ if, and only if, n > 1, and for all positive integers r and s, if n = rs, then either r or s equals n
prime
6
New cards
what do you call this type of symbol?
∀ positive integers r and s, if n = r s then either r = 1 and s = n or r = n and s = 1.
∀ positive integers r and s, if n = r s then either r = 1 and s = n or r = n and s = 1.
prime
7
New cards
An integer n is ___ if, and only if, n > 1 and n = rs for some integers r and s with 1 < r < n and 1 < s < n.
composite
8
New cards
what do you call this type of symbol?
∃ positive integers r and s such that n = r s and 1 < r < n and 1 < s < n.
∃ positive integers r and s such that n = r s and 1 < r < n and 1 < s < n.
composite
9
New cards
In proving existential statements are called___?
constructive proofs of existence
10
New cards
what do you call in Disproving Universal Statements
Counterexample
11
New cards
what do you call in Proving Universal Statements
proof by exhaustion
12
New cards
To show that every element of a set satisfies a certain property, suppose x is a particular but arbitrarily chosen element of the set, and show that x satisfies the property
Method of Generalizing from the Generic Particular
13
New cards
a step-by-step method for
performing some action.
performing some action.
ALGORITHM
14
New cards
used to refer to a specific storage location in a computer’s
Memory.
Memory.
Variable -
15
New cards
indicates the set in which the the variable takes its values, whether the set of integers, real numbers, character strings, and so forth
Data type -
16
New cards
gives a value to a variable.
x:= e
x:= e
Assignment statement -
17
New cards
allow this natural order to be overridden by using the current values of program variables to determine which algorithm statement will be executed next
Conditional statements -
18
New cards
Conditional statements are denoted either: ( give the form)
a. if (condition)
then s1
else s2
b. if (condition) then s1
then s1
else s2
b. if (condition) then s1
19
New cards
Often the condition is called a ___because it is stationed before s1 and s2 and restricts access to them.
guard
20
New cards
____ used when a sequence of algorithm statements is to be executed over and over again.
Iterative statements
21
New cards
two types of iterative statements?
while loop
for-next
for-next
22
New cards
where the condition is a predicate involving algorithm variables. The word while marks the beginning of the loop, and the word end while mark its end.
while loop
23
New cards
A while loop has the form?
while (condition)
[statements that make up the body of the loop]
end while
[statements that make up the body of the loop]
end while
24
New cards
A for-next loop has the following form:
for variable:= initial expression to final expression
[statements that make up
the body of the loop]
next (same) variable
[statements that make up
the body of the loop]
next (same) variable
25
New cards
This discussion can be summarized in a table and it shows the current values of algorithm variables at various points during execution.
Trace table -
26
New cards
The founder of set theory
Georg Cantor -
27
New cards
Cantor used the letter M because it is the first letter of the German word for set:?
Menge
28
New cards
The founder of set theory, Georg Cantor, suggested imagining a set as a “___________"
collection into a whole M of definite and separate objects of our intuition or our thought. These objects are called the elements of M.
29
New cards
A set may be specified using the ______ by writing all of its elements between braces.
set-roster notation
30
New cards
(The symbol ....... is called an ____ and is read "and so forth.")
ellipsis
31
New cards
The ____ says that a set is completely determined by what its elements are—not the order in which they might be listed or the fact that some elements might be listed more than once.
axiom of extension
32
New cards
Another way to specify a set uses what is called the___?
set-builder notation
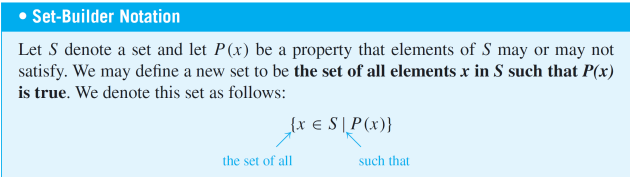
33
New cards
It follows from the definition that for a set A not to be a subset of a set B means that there is at least one element of A that is not an element of B.
Subsets
34
New cards
A _____of a set is a subset that is not equal to its
containing set.
containing set.

35
New cards
We have known that by the axiom of extension, sets A and B are equal if, and only if, they have exactly the same
Elements.
Set Equality
36
New cards
If sets A and B are represented as regions in the plane, relationships between A and B can be represented by pictures, called _____
Venn Diagrams
37
New cards
Venn Diagram was introduced by the British mathematician named _____ in ___ (year)
John Venn in 1881
38
New cards
A is a subset of B in venn diagram
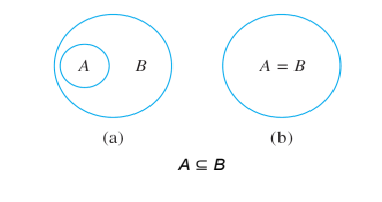
39
New cards
A is not sub set of B in venn diagram
40
New cards
these operations are the union (∪), intersection(∩), complement
(′), difference (−), and the Cartesian or cross product (×).
(′), difference (−), and the Cartesian or cross product (×).
Operations on Sets
41
New cards
The ___operation combines all elements of two sets. Any element that occurs in both sets only occurs once in the new set.
union (∪)
42
New cards
The union of A and B, denoted___, is the set of all elements that are in at least
one of A or B.
one of A or B.
A U B
43
New cards
the intersection of A and B, denoted ___, is the set of all elements that are common to both A and B.
A ∩ B
44
New cards
The difference of B minus A (or relative complement of A in B), denoted ____
, is the set of all elements that are in B and not A.
, is the set of all elements that are in B and not A.
B - A
45
New cards
The complement of A, denoted ___, is the set of all elements in U that are
whined
whined
A‘
46
New cards
Venn diagram representations for union,
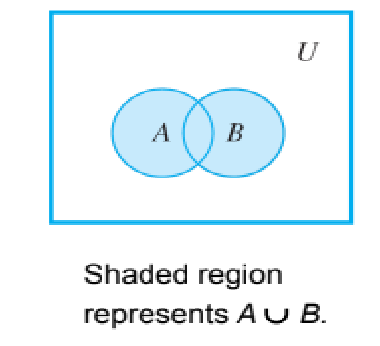
47
New cards
Venn diagram representations for intersection
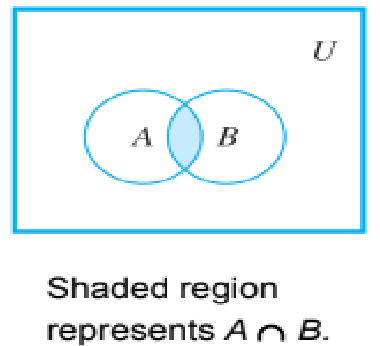
48
New cards
Venn diagram representations for difference
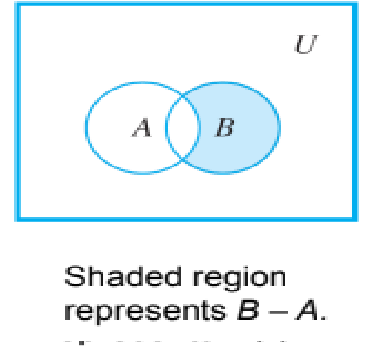
49
New cards
Venn diagram representations for complement
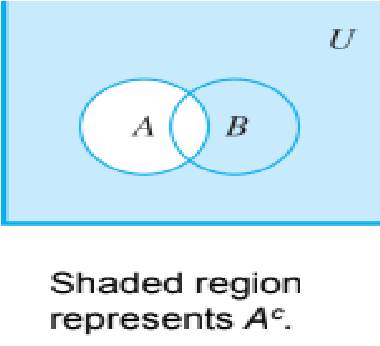
50
New cards
what do you call to a set that has No element and denote it by the symbol __?
The Empty Set or null set
Ø
Ø
51
New cards
sets are divided up into nonoverlapping (or disjoint) pieces. Such a division is
called a ___.
called a ___.
partition
52
New cards
Two sets are called disjoint if, and only if, ______.
they have no elements in common

53
New cards
Sets A1, A2, A3... are ____(or pairwise disjoint or nonoverlapping)
if, and only if, no two sets Ai and Aj with distinct subscripts have any elements in
common.
if, and only if, no two sets Ai and Aj with distinct subscripts have any elements in
common.
mutually disjoint
54
New cards
The _____guarantees that this is a set.
power set axiom