exam 4- brain + cranial nerves
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
dura mater
the outer layer
strong + fibrous
bi layer:
periostea
meningeal
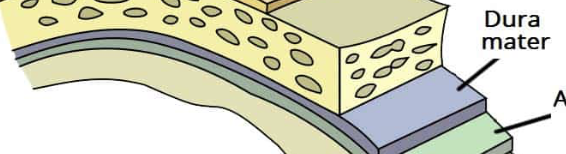
dural septa
inward extensions
fall cerebri + tentorium cerebelli
dural venus sinuses
venous blood
return CSF to blood stream
arachnoid mater
middle layer
spiderweb- like
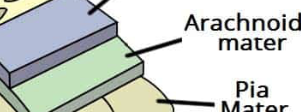
pia mater
innermost layer
lines brain + spinal cords surface
contains blood vessels
filum terminale
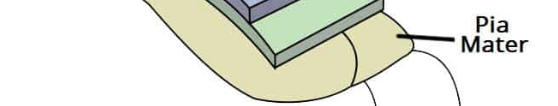
subdural spaces
film of fluid
subdural hematoma
subarachnoid space
cerebrospinal fluid
arachnoid villi/ granulations
CSF function
protection
circulating fluid reservoir
brain monitors CO2
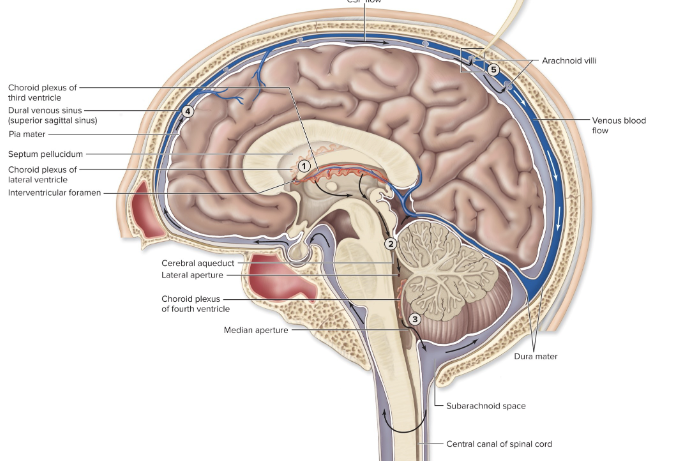
lateral ventricles (2)
in cerebral hemispheres
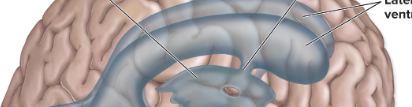
3rd ventricle
thin vertical pocket

4th ventricle
tiny & diamond shaped
continues as central canal of cord
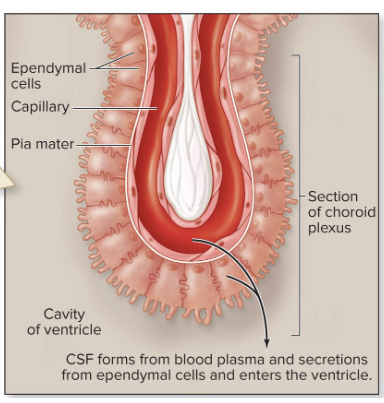
chorioid plexuses
Cerebrospinal formation
capillary networks
projection from Pia mater into ventricles
covered by ependymal cells
plasma separated from blood
CSF- midsagittal view
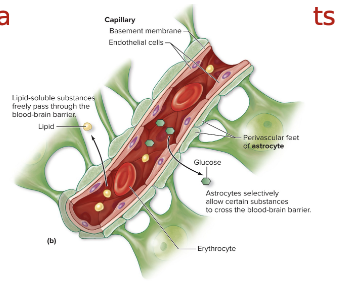
brain capillaries
blood brain barriers
endothelial cells
TIGHT JUNCTIONS
basement membrane
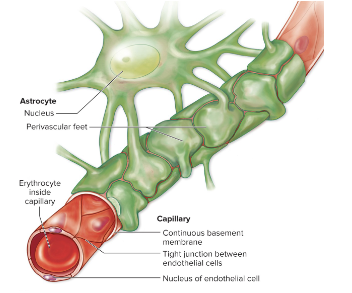
astrocyte feet
stops most substances & all cells
allows diffusion- lipids & gases, ETOH, nicotine, caffeine
allows facilitated diffusion &
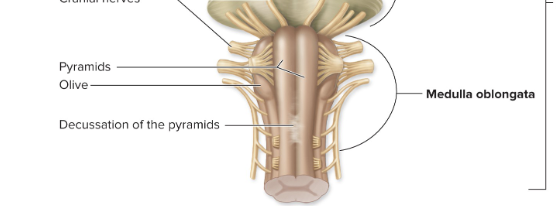
medulla oblongata
pyramids
pyramidal (corticospinal) tracts - DECUSSATE
olives
nuclei for muscle & joint stretch reflexes ( relays to cerebellum)
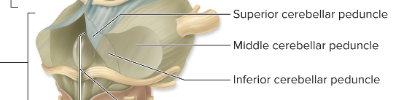
inferior cerebellar peduncles ( tracts to cerebellum_
nuclei
cardiac, respiratory, vasomotor control centers
vomit, sneeze, hiccup, cough, swallow
CNS VIII, IX, X, XI, & XII
pons
“bridge”
conduction tracts connect cerebrum → cerebellum
middle cerebella peduncles
nuclei
CNs V, VI, VII & VIII
pneumotaxic centers- respiration
midbrain- mesencephalon
cerebral peduncles
impulses btw midbrain & cerebrum
CN III-IV

midbrain: superior cerebellar peduncles
impulses from cerebellum
midbrain: corpora quadrigemina
superior colliculi- visual reflex
inferior colliculi- auditory reflex
red nucleus- muscle control
midbrain: substantia nigra (nucleus)
muscle control
dopamine
Parkinson’s disease
brainstorm functions
passageways for spinal tracts
reflex centers
cerebellum
hemispheres
lobes
geri
sulci
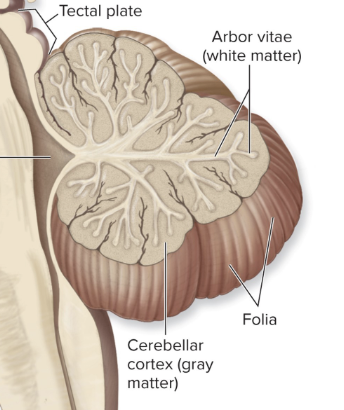
Folia
outer gray matter= Cortex
arbor vitae
inner white matter
long tracts
inferior cerebellar peduncles ← medulla o. & spinal cord
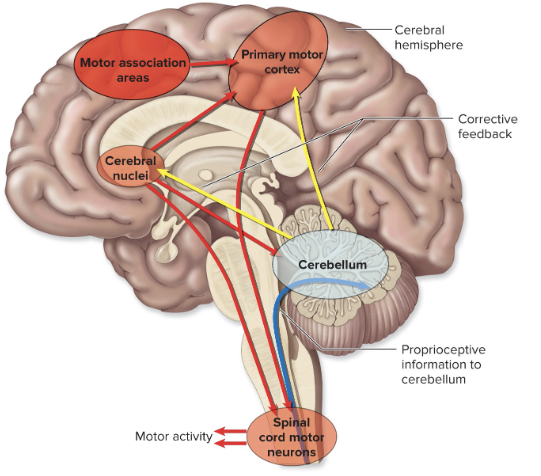
long tracts 2
middle cerebellar peduncles ← pons
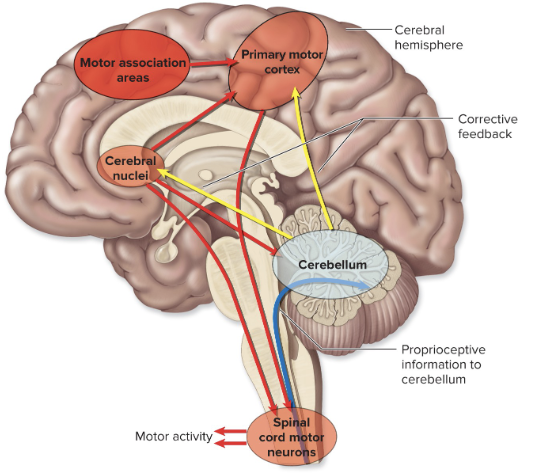
long tracts 3
superior cerebellar peduncles → midbrain
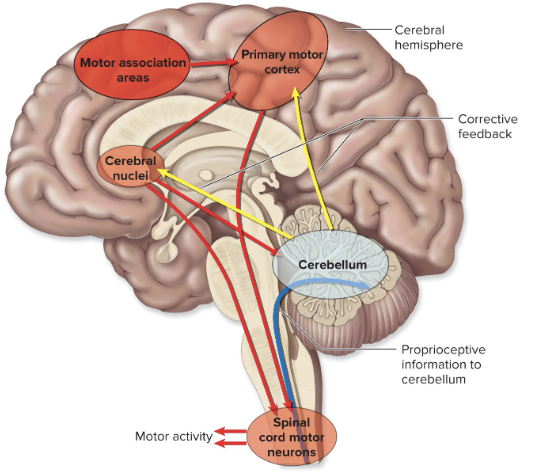
cerebellum functions
movement planning & coordination
posture
balance
sensory data coordination for cerebrum
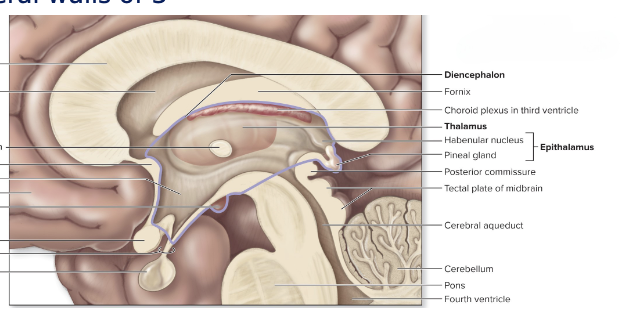
Thalamus
diencephalon
dumbbell shaped
relay station
lateral masses
superolateral walls of 3rd ventricle
interthalamic adhesion - “dumbbell handle”
gray matter- complex arrangement of nuclei
geniculate bodies (nuclei)
auditory relay
visual relay
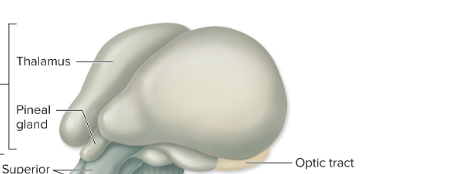
thalamus functions
prioritizes & relays impulse to & from cerebrum
sensation of thalamus
conscious recognition of pain, temperature & touch
relaus extensive sensory impulses to cerebrum
emotional responses
arousal- conscious v. unconscious
complex reflex movements
hypothalamus
diencephalon
inferolateral walls of 3rd ventricle
mamillary bodies
olfactory relays
involved in memories
infundibulum
pituitary gland
hypothalamus- functions
nervous & endocrine
pleasure centers
ANS regulation
relay station btw cerebrum & ANS effectors
mind-body connection
hormone production
water balance & labor (childbirth)
hormone control over anterior pituitary secretion
growth, metabolism, reproduction, water balance, lactation
temperature regulation
appetite regulation
epithalamus
roof of 3rd ventricle
pineal gland
biologic clock regulation
melatonin

cerebral tracts : connective
tracts- white matter
association
protection
commissural: corpus collosum
basal ( cerebral) nuclei
gray matter islands
caudate nucleus
putamen
globus pallidus
amygdaloid body
“filter” or fine-tune
movement
cognition
emotion
cerebral localization
primary cortical areas of specific function
postcentral gyrus
primary somatic sensory area
stimuli ascend for conscious feeling of heat, cold & touch
pre central gyrus
primary somatic motor area
stimuli descend to skeletal muscles
transverse gyrus
primary auditory area
occipital lobe
primary visual area
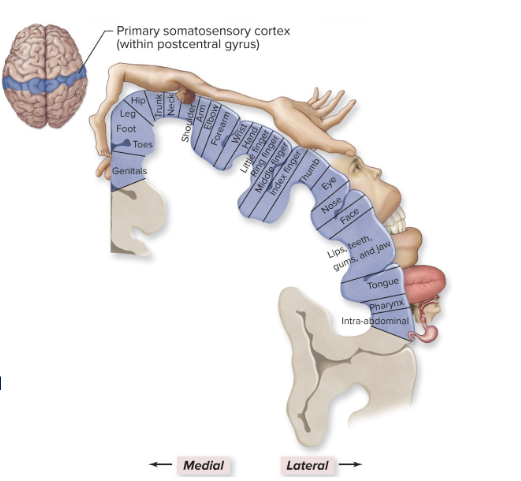
somatic senses: cerebrum function
primary somatic sensory area
post central gyrus
touch, pressure, temperature & body position
register sensations
relay information
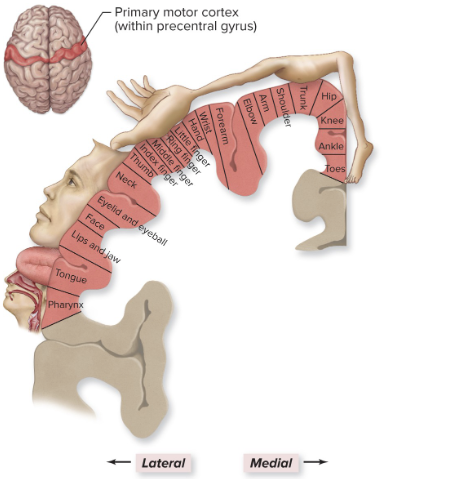
motor control: cerebrum functions
primary somatic motor area
pre central gyrus
control individual muscles
anterior to pre central gyrus
activate muscle groups
integrative functions
sensory reception → integration→ motor output
aspects of integration
consciousness
language
emotions
memories
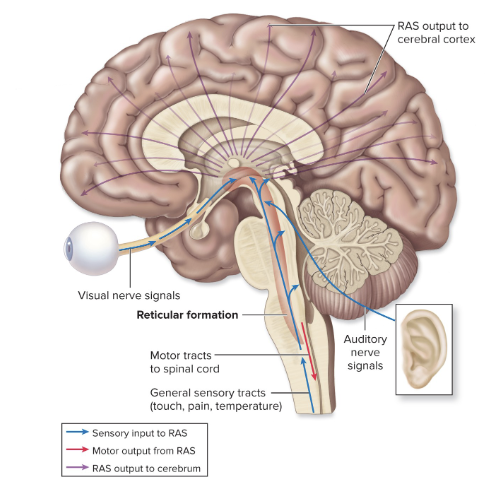
CONSCIOUSNESS = AWARENESS= ALERTNESS
reticular activating system ( RAS)
spinal cord → reticular formation → thalamus → cortex
reticular formation= loose chain of nuclei along brain stem & midbrain
relieves sensory impulses
continuously sends impulses to thalamus
arousal or alert system
filters data
maintains consciousness ( wakefulness)
limbic system emotions
experience & expression
“emotional visceral brain”
around corpus callous & fornix
multiple brain connections
connects higher level cortex & more primitive brainstem
emotion-body connections
regulation of emotions
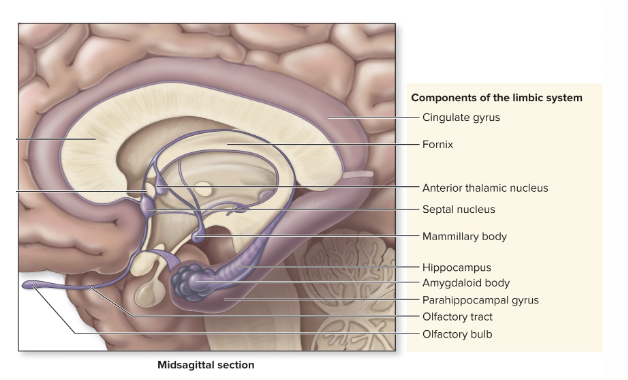
limbic system 2
amygdaloid body
cingulate gyrus
hippocampus
projections to prefrontal cortex
influences hypothalamus activity
linked with smell & memory
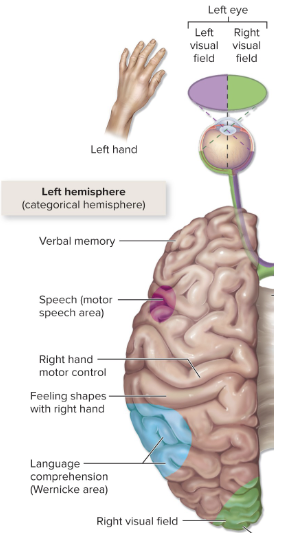
language
acts & interpretation of speaking writing
left hemisphere (90%)
lateralization
broca’s area ( frontal lobe)
expressive aphasia
unable to articulate words
wernicke’s area ( temporal & parietal lobes)
receptive aphasia
unable to understand words
memory
short term (working): secs or minutes
long term- days or years
involves multiple lobes
synaptic structural changes
increase # presynaptic axon terminals '
increase # postsynaptic receptor proteins
increase synaptic neurotransmitter concentration
astrocyte activity
linked to limbic system
“ NEURONS FIRE TOGETHER WIRE TOGETHER!”
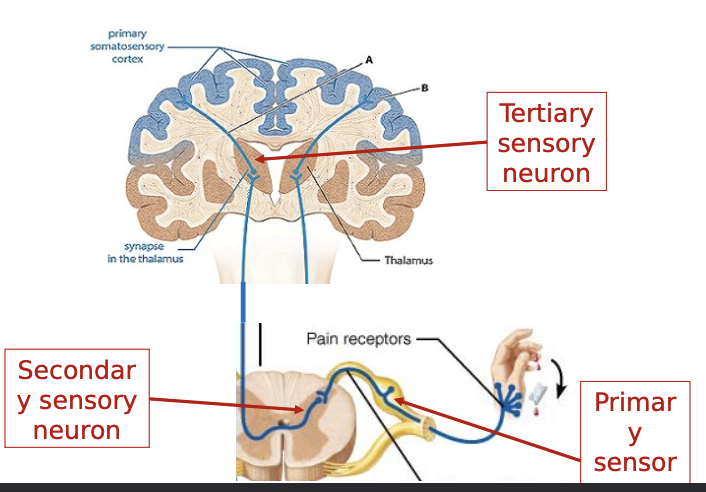
primary sensory neuron: SSP
cell body in DRG
receptor spinal nerve → spinal cord
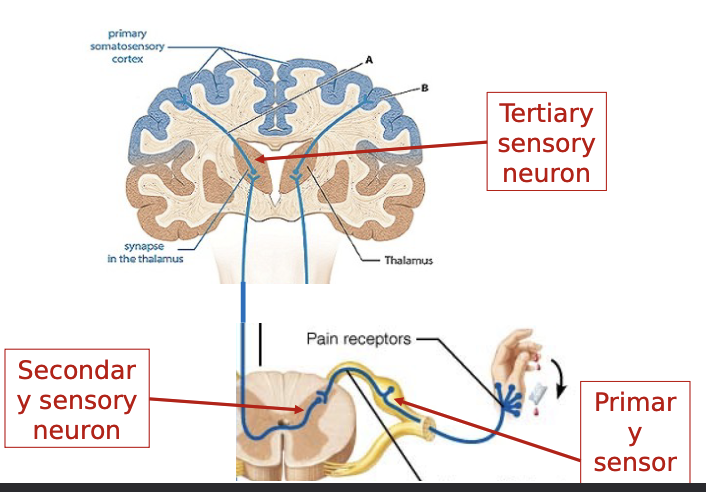
secondary sensory neuron: SSP
cell body in posterior horn
spinal cord ascending spinal tract → thalamus
fibers decussate in spinal cord
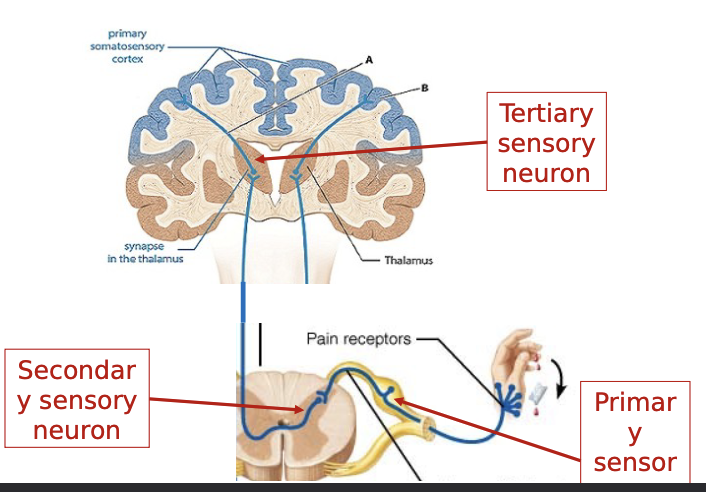
tertiary sensory neuron
cell body in thalamus
thalamocorticar tracts → thalamus postcentral gyrus
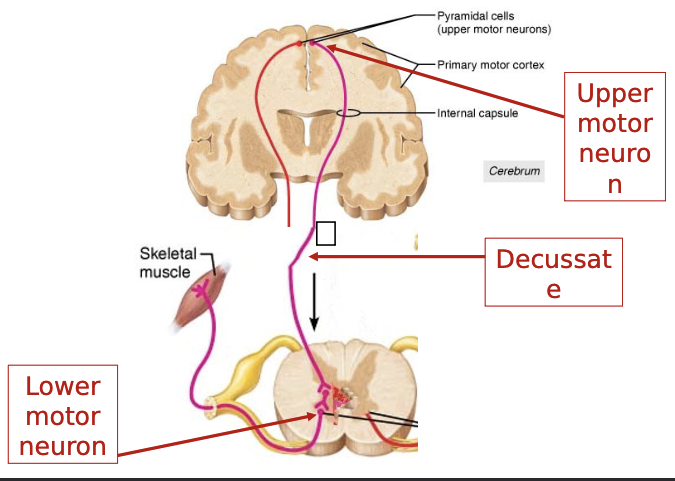
pre central gyrus: SMP
cells in somatic brain
motor upper motor neuron → steam & spinal cord
descending spinal cord tracts
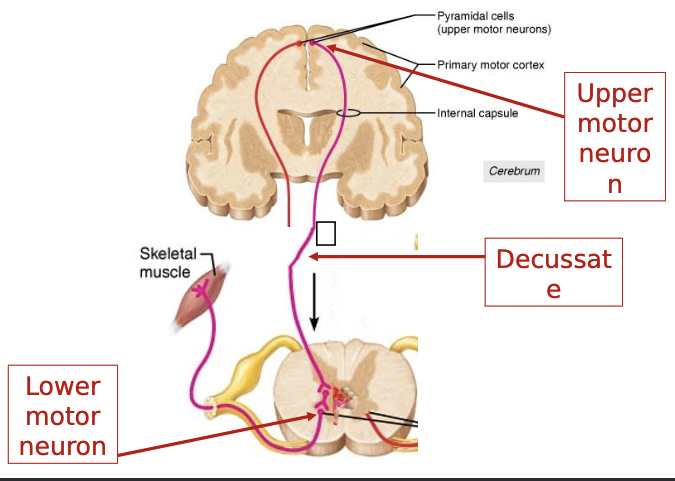
spinal cord
cell bodies in anterior horn
spinal cord → lower motor neuron
muscle fibers (spinal nerve)
usually involve interneurons
functional classification: excitatory v. inhibitory
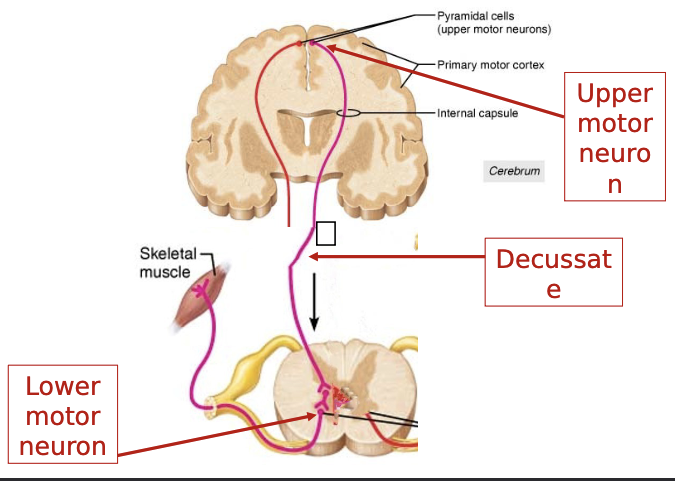
upper motor neuron lesions
CNS damage: control from motor cortex lost
spinal reflexes haphazardly stimulate muscles
“spastic”
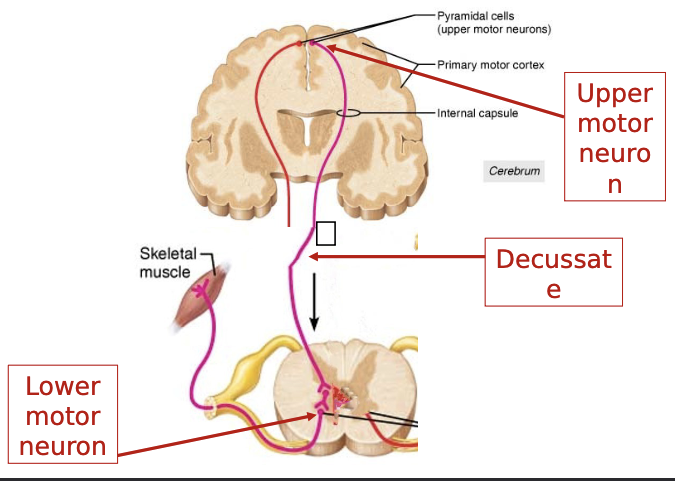
Lower motor neuron lesion
spinal nerve damage
no stimulation to muscle
atrophy
weakness
“flaccid paralysis”
oh no I step on a nail
pain ( SSP) → cry (limbic system) → scream (Broca speech) → pick up foot (SMP) → look at nail in foot (visual cortex) → alarmed (reticular activating system)