Historical Illustration Quiz 1
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
relief carving
shallowly carved narrative sculpture
hierarchical scale
the importance of subjects is based on their size and/or position
stele
stone or wooden slab, generally taller than it is wide. commemorative.
hellenism
admiration for / imitation of the ideas, style, or culture of classical greek civilization
iconography
religious images were believed to have miraculous origins, so the jin of the artist was to copy them as closely as possible. deviation and innovation was heretical.
silk road
4000 mile network of trade routes that connected eastern and western eurasia, allowing transfer of goods, ideas, and aesthetics from 200 BCE - 1500s AD
arabesque
rhythmic linear patterns of scrolling and interlacing lines in Islamic art — repetition shows the infinite nature of god
renaissance
triangular, stable compositions
first oil paintings and mathematical perspective
often commissioned by the church
scientific revolution
man is not so special
comparative anatomy (man vs animal)
earth moves around the sun
isaac newton, laws of physics + gravity
baroque
dark and scary
reflects religious tensions at the time
catholic church in rome trying to reassert dominance after protestant reformation
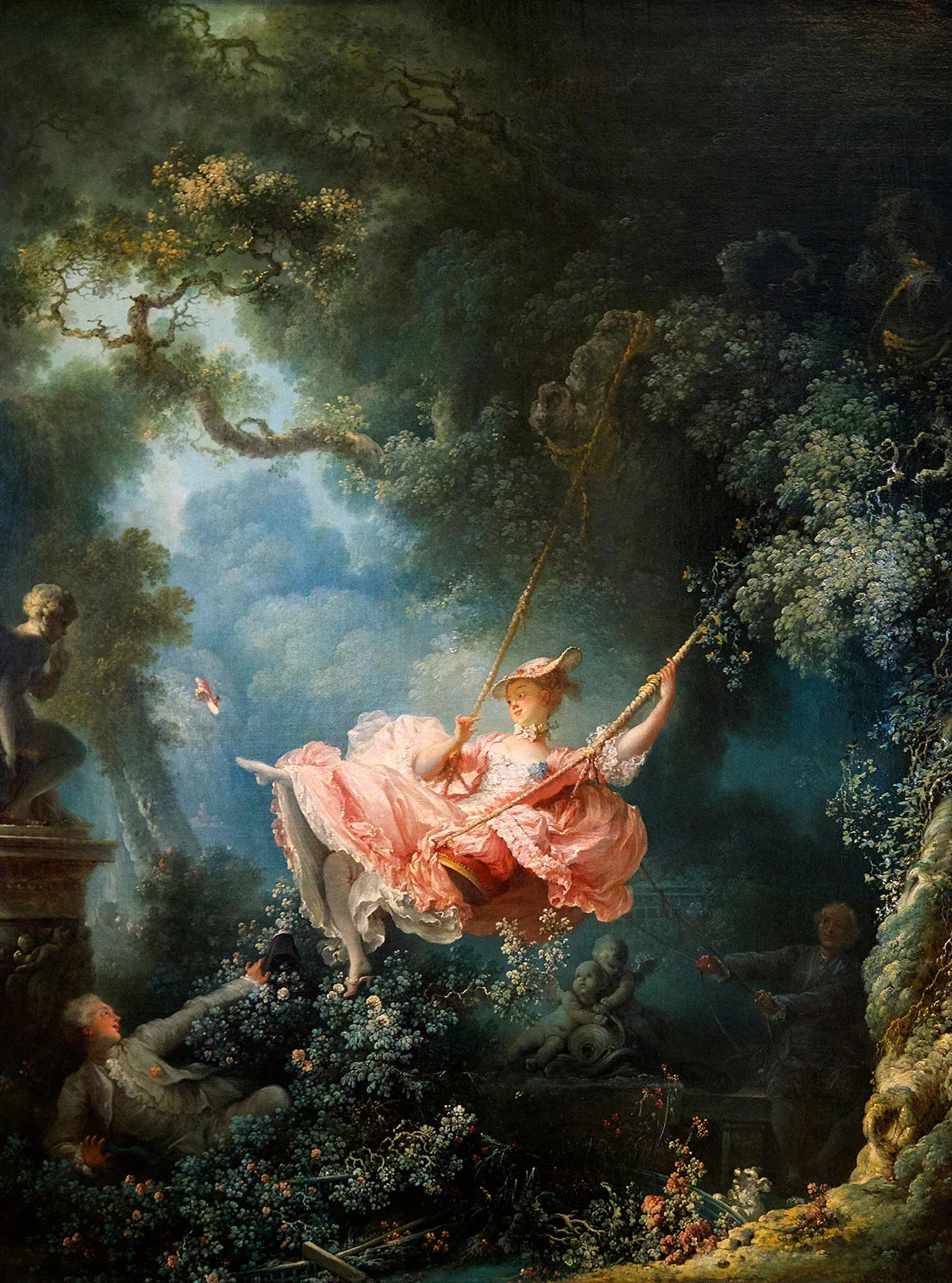
rococo
cultural center is now france
frivolous, fanciful, decorative, focused on leisure of aristrocrats
reaction to religious agenda of baroque
enlightenment
reason, liberty, and order valued above all else. classical antiquity is seen as the height of civilization.
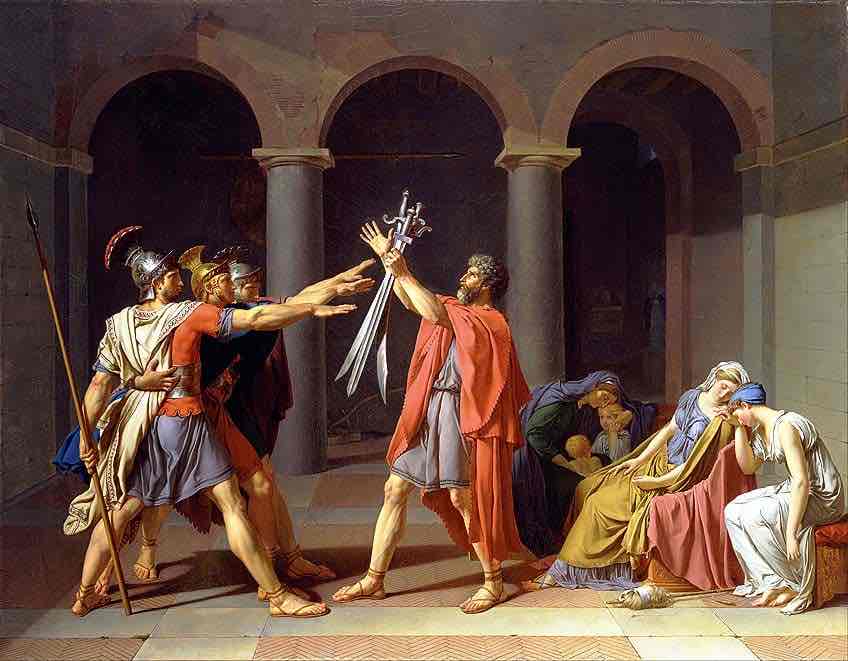
neoclassicism
reaction to frivolity of rococo, aligned with the values of the enlightenment
moral stories demonstrated the ethical “superiority” of antiquity
partly stimulated by the discovery of roman ruins at herculaneum and pompeii
mandala
a chart, diagram, or geometric pattern that represents the universe
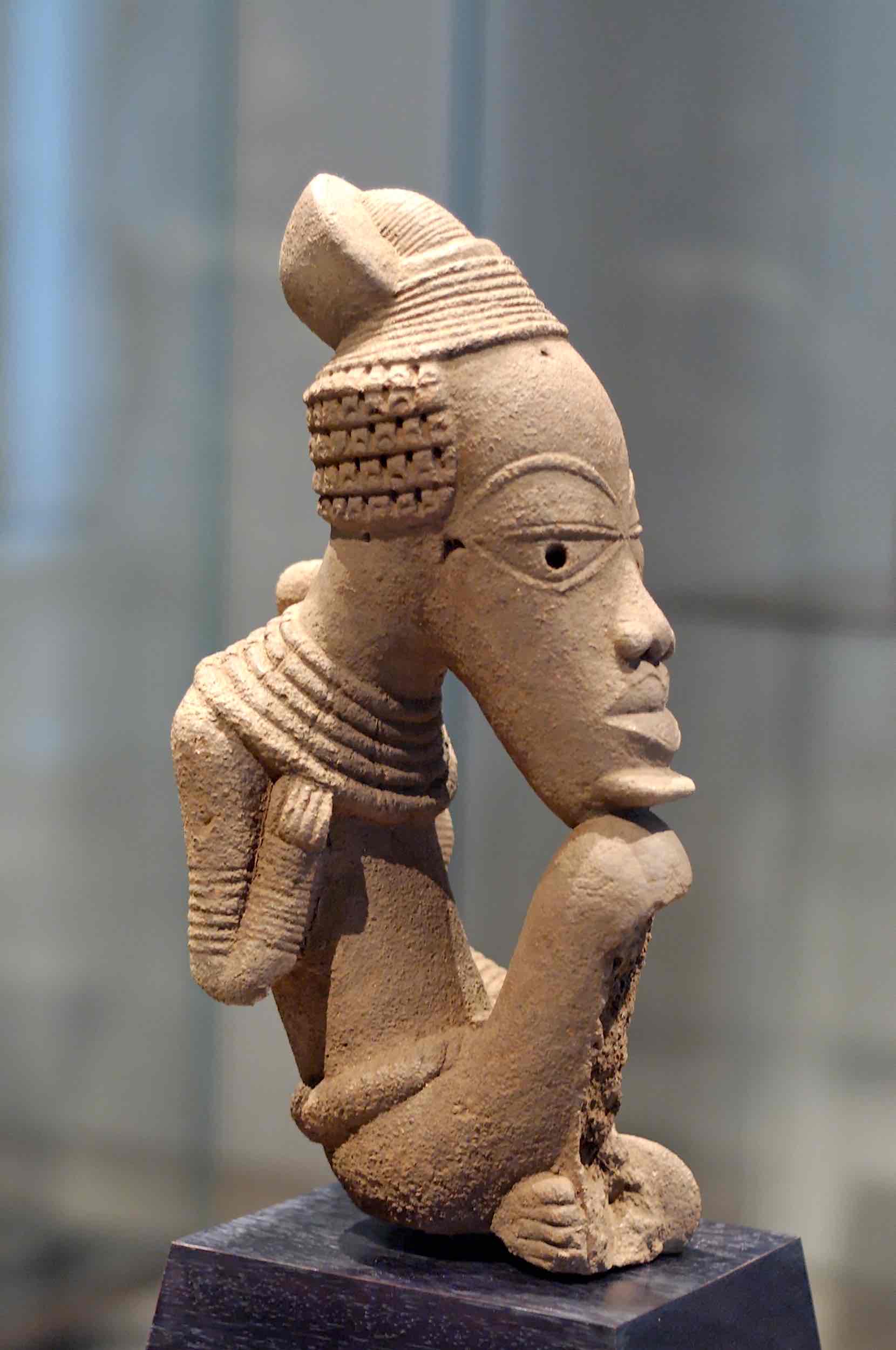
african art
power, imagination. disregard for anatomy. design > realism
logogram
a sign or character representing a word or phrase, used in Mesoamerican art
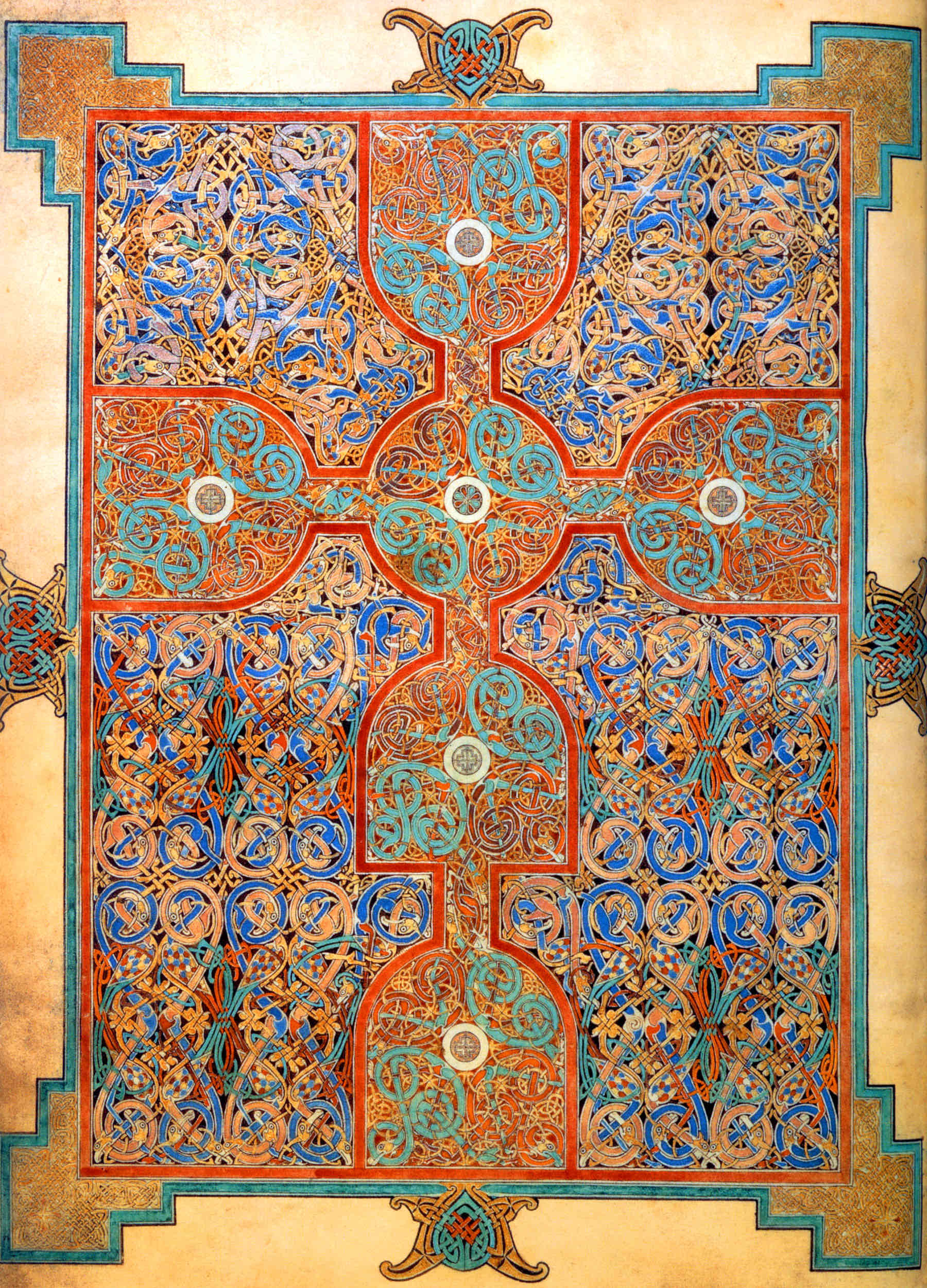
carpet page
an illuminated manuscript page covered entirely in decoration
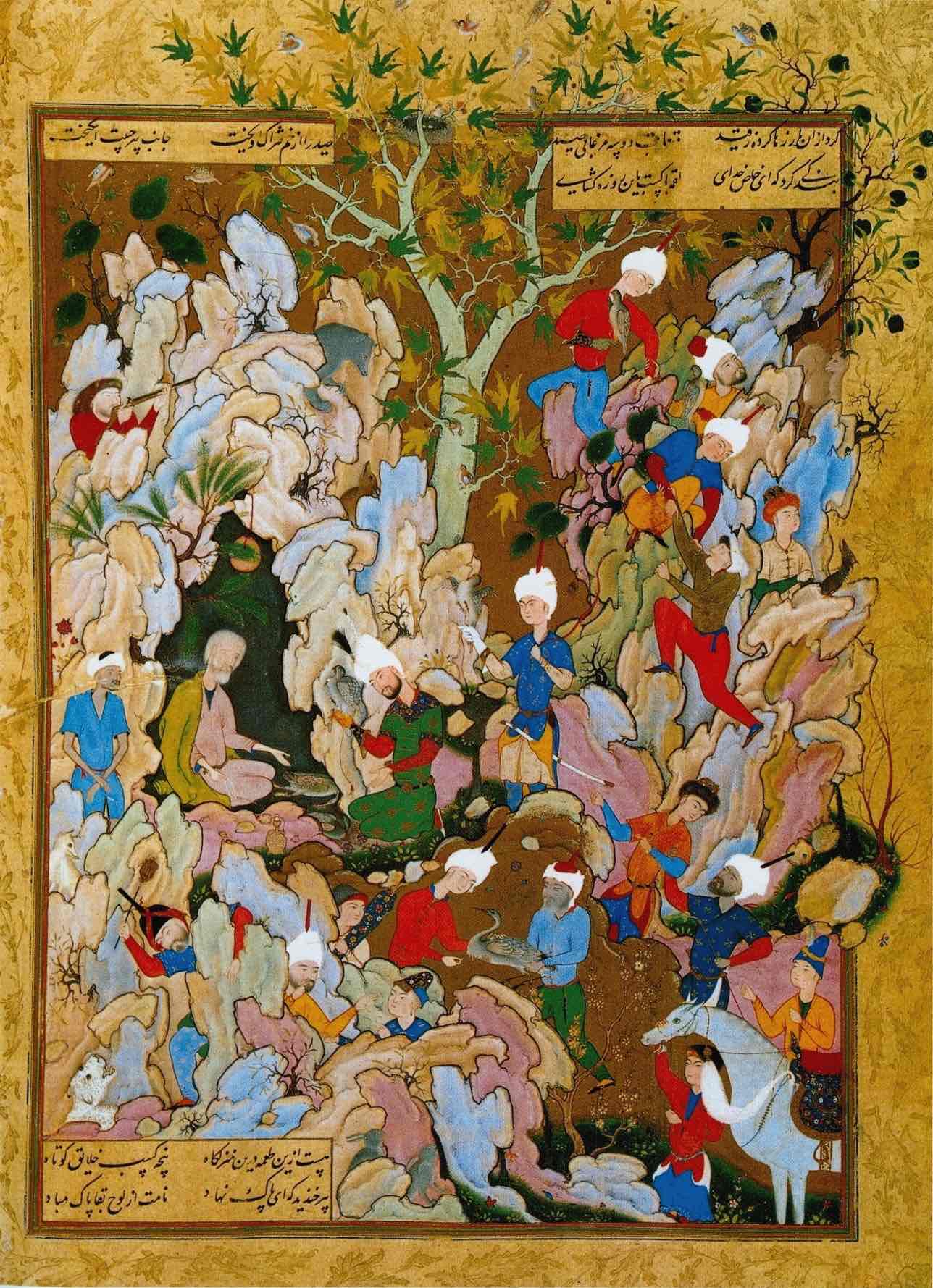
persian miniatures
islamic art that did not forbid the human figure
gutenberg press
developed in 1440, dramatically sped up reproduction time for books; beginning of the end of illuminated manuscripts
wood and copperplate engraving
main illustration technique for 500 years
industrial revolution
1850
beginning of life based on commerce, mass production, and materialism instead of spiritual and natural beauty
the industrial revolution…
prompts several stylistic reactions
romanticism
realism
the pre-raphaelite brotherhood
the arts and crafts movement
Japan Opens for Trade
1850
japanese woodblock prints, with flat, graphic depictions, open space, planar perspective, and high horizons spread around the west
western cultural influence spreads through japan
romanticism
reaction to industrial revolution
a longing for the days of antiquity
mythological and legendary subject matter with particular regard for the hero and heroine
same time period as neoclassical art, but very different stories and focus
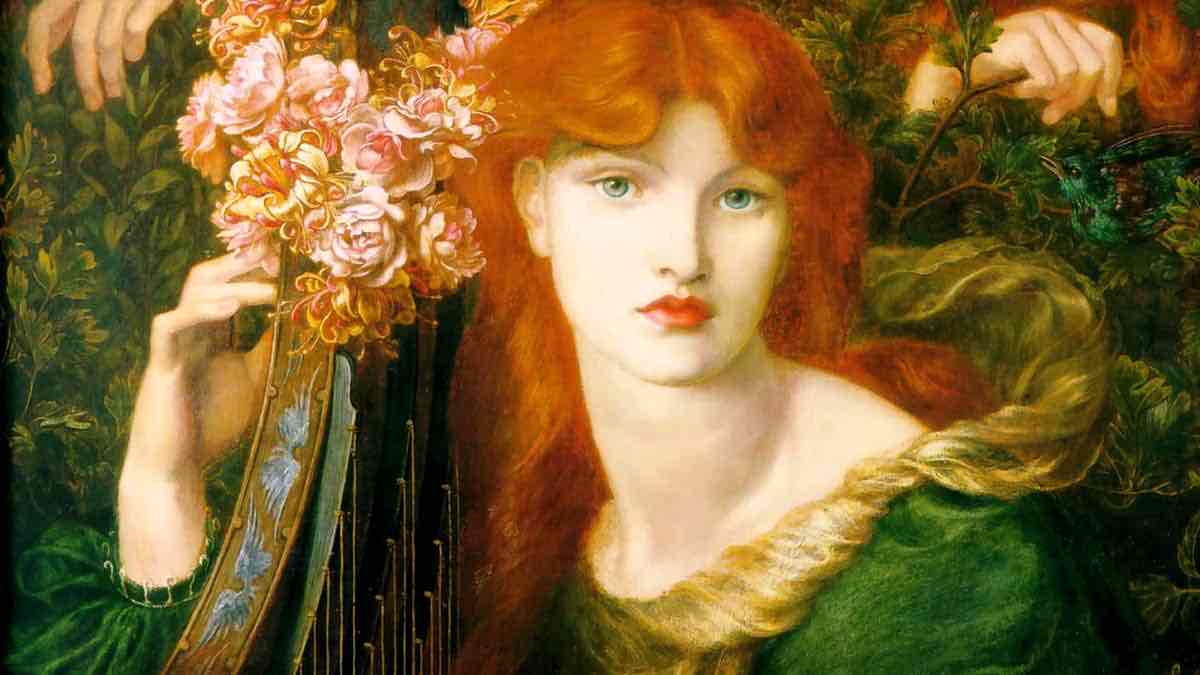
preraphaelite brotherhood
dismissing the requirements of “fine” art that dominated since Raphael (renaissance)
natural detail, every single leaf on a plant
observation and photographic reference
full picture plane, as if the image will be engraved
love ophelia, tragic romantic stories
arts and crafts movement
believed that hand crafted objects were superior to those made by machine and that the rural craftsman had a superior lifestyle to those who slaved in the urban mills and factories
currier and ives
lithographic print producing company that chronicled life in the 19th century
revolutionary war
documentation and political cartoons founded American published artwork
Reading Industry
1800s
the decreasing cost of publishing and the increased capacity for travel via the invention of tracks, engines, and the corresponding railway distribution
cheaper and faster to print large quantities
ad revenue decreased costs to the consumer
ability for literature to be circulated on a large scale
increased literacy due to easier access
penny press
new printing technology dramatically sped up the printing process = increased newspaper circulation. cheap, interesting literature = increased literacy = larger market
as revenue
gave newspapers autonomy — not reliant on personal wealth to start production
fewer socioeconomic barriers to publication = more differing viewpoints were published
Hogarth’s Act
Engravers Copyright Act (1735) — the first copyright law to deal with visual works as well as the first to recognize the authorial rights of an individual artist
two major competing illustration heavy newspapers:
Harper & Brothers
Frank Leslies Illustrated News
special correspondents
civil war artists who mailed their work to publications via special delivery — worked for two major newspapers, Harper’s or Leslie’s
penny dreadful
late 1800s — cheap popular serial horror stories
precursor to pulp fiction, along with story papers
1890 Photomechanical Reproduction
allowed illustration to be directly reproduced in print
killed engraving
opened way for individual illustration styles
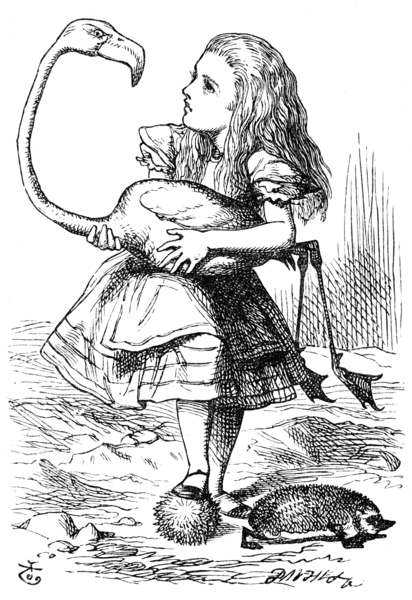
John Tenniel

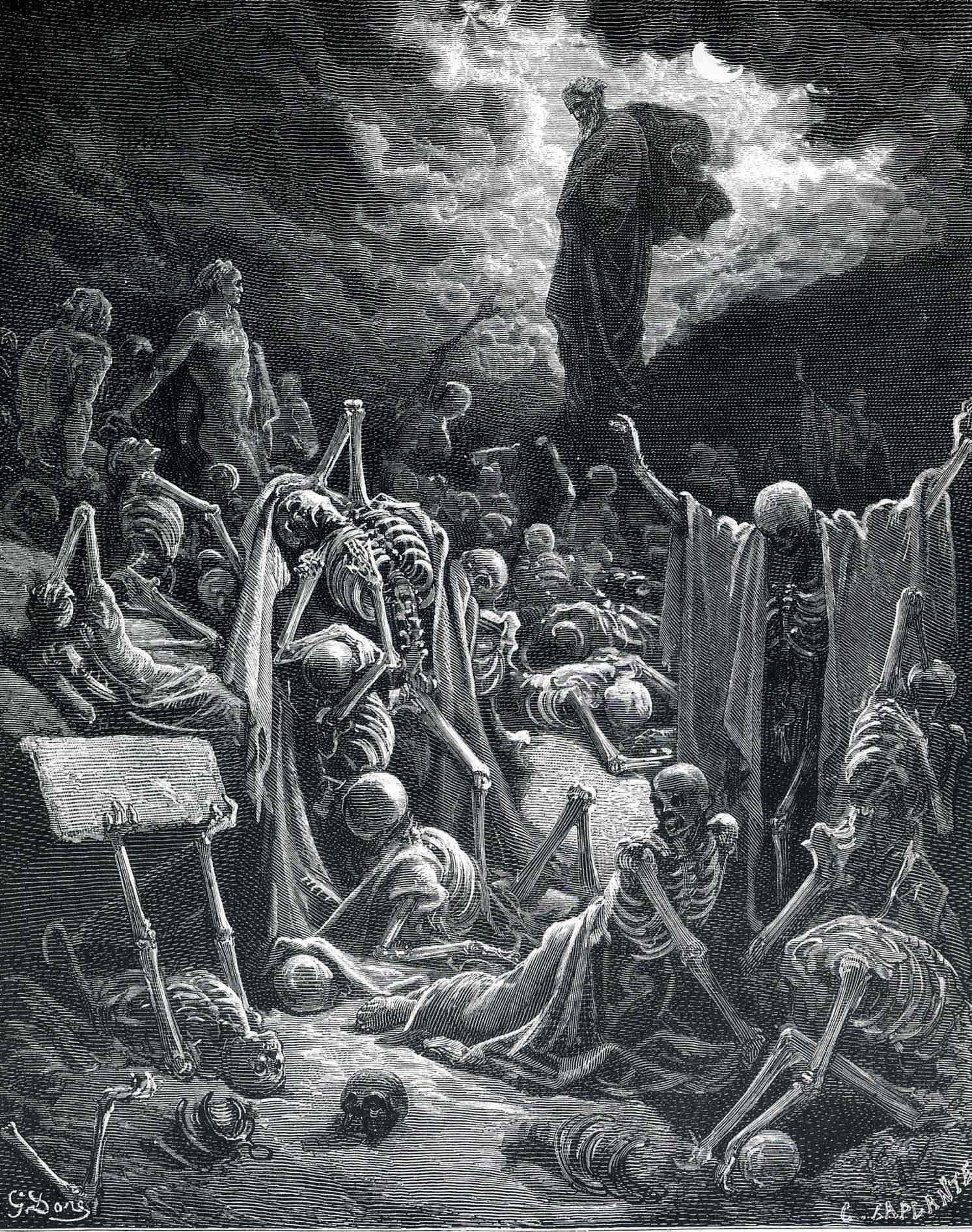
Gustav Dore

John James Audubon

Dante Gabriel Rosetti

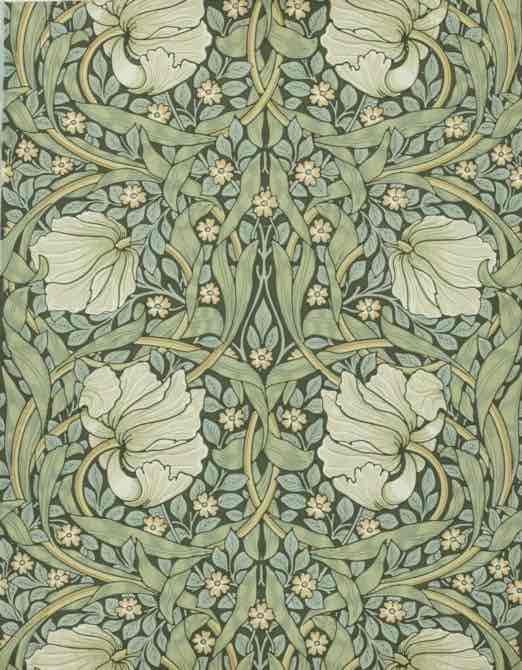
William Morris

J.J. Grandville

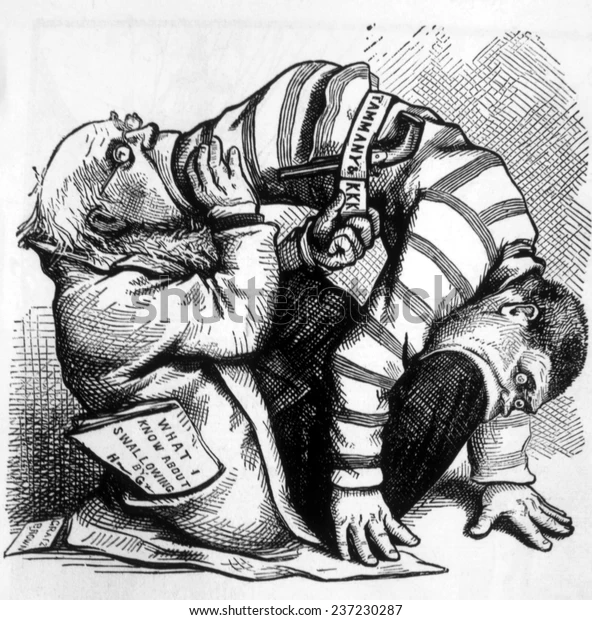
Thomas Nast

Aubrey Beardsley

Egyptian Art
Nok Sculpture

Celtic Art

Illuminated Manuscript

Illumination - Carpet Page

Persian Miniature

Gothic

Renaissance
Mannerism

Baroque

Rococo

Neoclassism


Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood
Special Correspondents

Lithograph

Woodcut
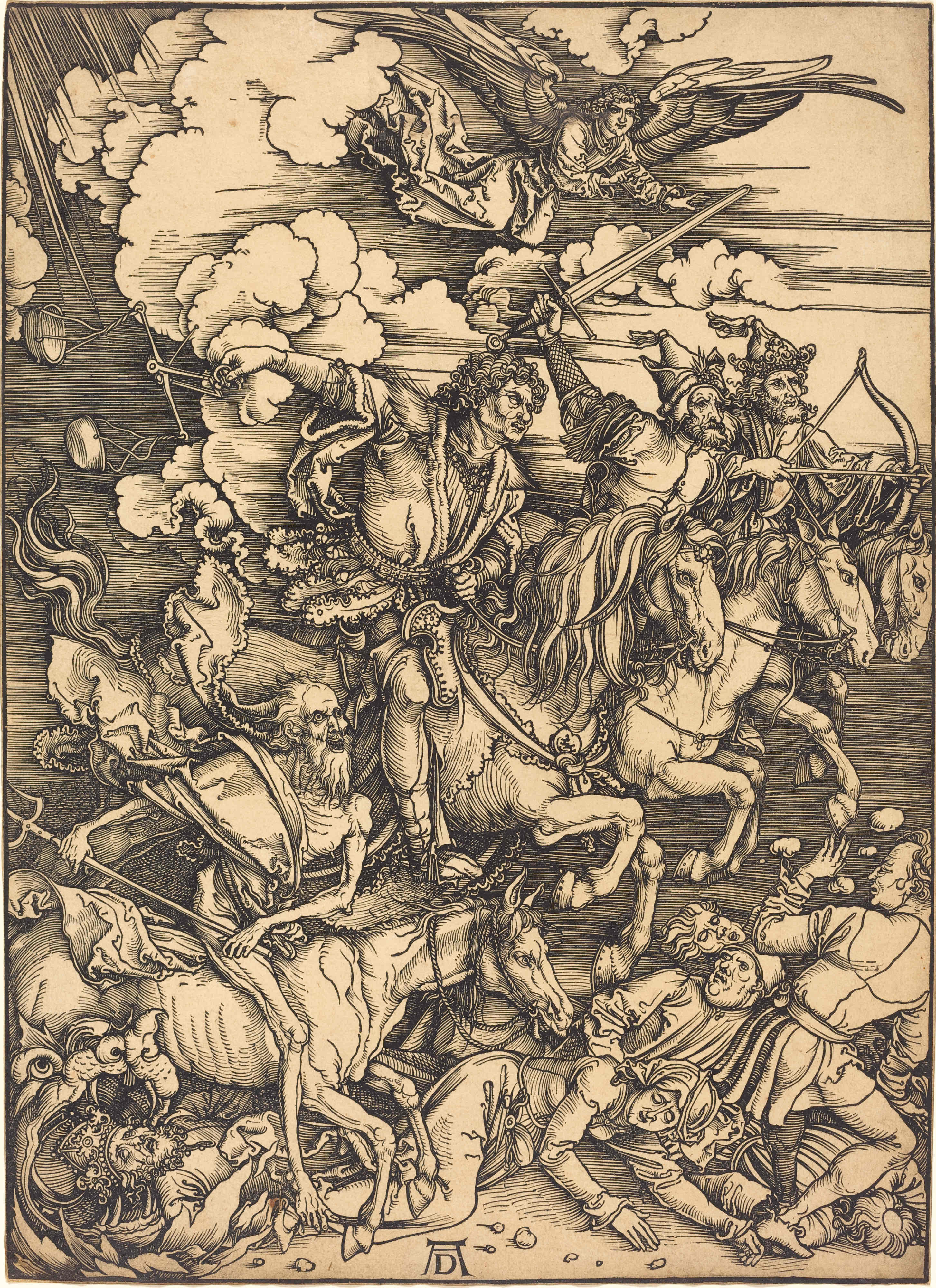

Copperplate
