Homeostasis
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What is homeostasis?
The state of balance in the body when the temperature and other conditions are stable for cells and enzymes to work.
The regulation of internal conditions of a cell or organism to maintain optimum conditions for function in response to internal and external changes.
Why does the temperature near the brain decrease when consuming cold water?
The blood is cooled in the mouth
Which flows to the brain
What should a runner do to reduce dehydration?
Drinks lots of water
To replenish water lost through sweating
What are the main internal conditions?
Body temp
Water levels
Blood glucose levels
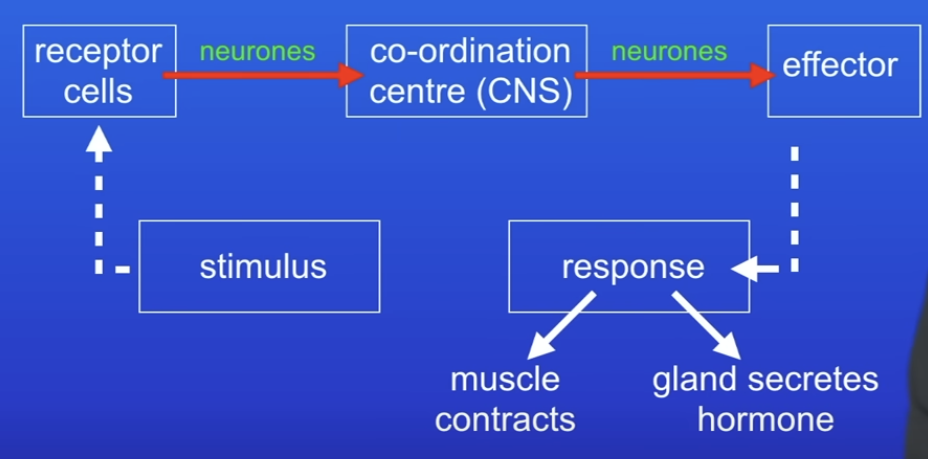
What are the features of the automatic control system?
What is the Nervous system?
CNS - central nervous system (brain & spinal chord)
Other nerves which run to and from CNS
What is a reflex arc?
Stimulus is detected by receptor
Electrical impulses travel along sensory neurones to the CNS
Reaches the synapse where a chemical is released
Diffuses to a relay neurone and triggers an electrical impulse which travels across relay neurone.
Reaches another synapse & another chemical released
Chemical triggers an electrical impulse in a motor neurone.
Electrical impulse travels down motor neurone to an effector
E.g. hand touches heat, skin (receptor) senses heat, effector (muscle) contracts and pulls hand away from heat (response).
What is a reflex?
No decision making from the conscious part of the brain
Automatic & rapid
Protect us from danger
E.g. removing hand from heat, protect face from object in flight
Reaction time Required Practical method
Person 1 sits on stool with dominant hand over table
Person hold meter ruler with 0 mark between P1 thumb and first finger
P2 drops ruler at random time
P1 must catch the ruler as fast as possible
Measure cm spot that the ruler was caught
Record on a table and repeat 10 times to calculate mean
Repeat with different people
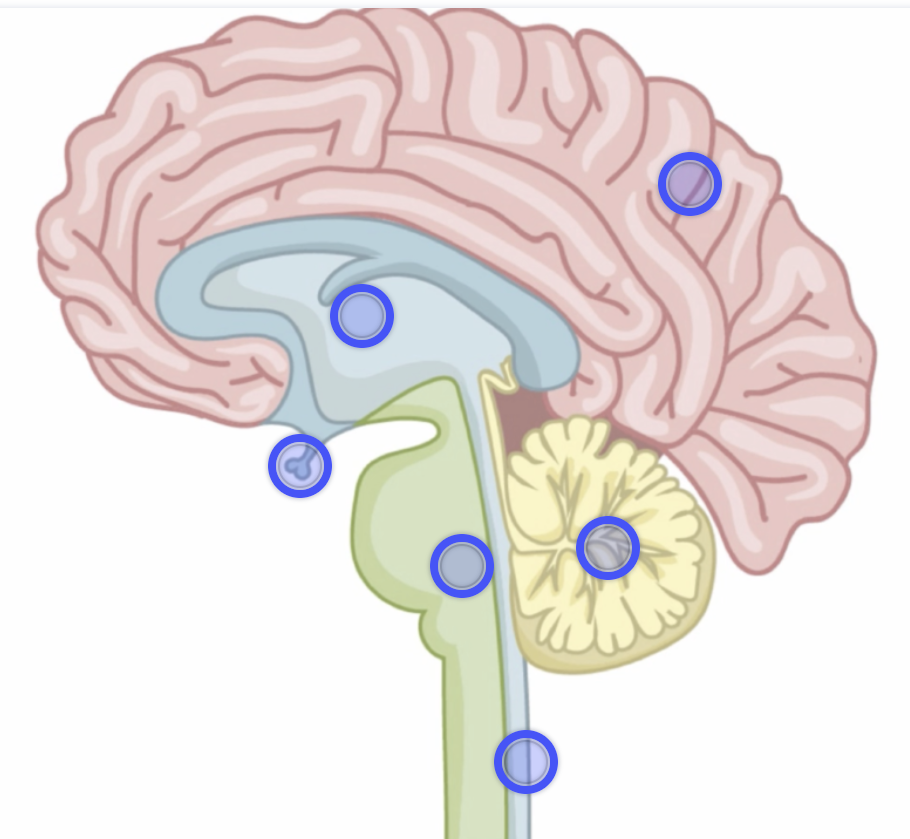
Label this diagram of the brain
What are the functions of the different parts of the brain?
Cerebral cortex - language, memory and consciousness
Cerebellum - balance, co-ordinates movement
Medulla - Heart & Breathing rate
Hypothalamus - Thermoregulatory centre
Pituitary gland - coordinates many hormones
Why is it difficult to study the brain
Tricky to access (skull)
Complex structures (don’t know which parts do what)
Extremely delicate (Easy to damage)
How do scientists study the brain?
Study patients who have brain damage (where damage is can be linked to its function)
Electrically stimulate brain and watch effects of peoples behavious (narrow down regions to functions)
MRI scan to see what part of brain is active during different activities
Label this diagram of the eye
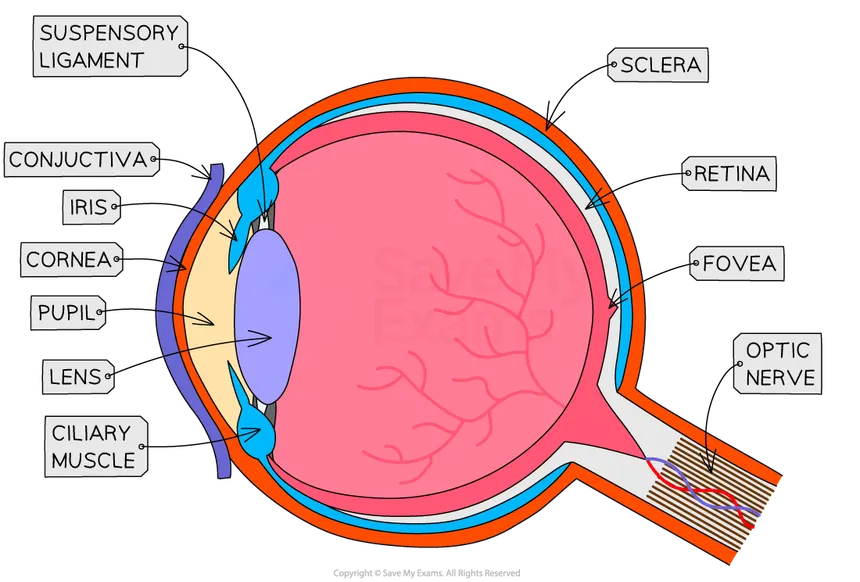
What are the functions of different parts of the eye?
Cornea - Start focussing of light rays
Iris - Coloured part, controls pupil size
Pupil - Allows light into eye
Lens - Focus light rays onto back of the eye
Retina - receptor cells for light intensity & colour
Optic nerve - electrical impulses from eye to brain
Ciliary muscle & Suspensory ligaments - Work with lens to focus on near or far objects
Sclera - white part protects eye
How does the eye focus?
Accommodation - The lens allows focus on near or far objects by changing its shape.
The lens is surrounded by Circular (ciliary) muscles and fibres (suspensory ligaments.
The ciliary muscle can contract or relax to change the thickness of the lens.
When ciliary muscle contracts, suspensory ligaments loosen and the lens is now thicker and refracts light rays more strongly (close focus) vice versa.
How is long or short sightedness treated?
Hyperopia / Long sighted (Eyeball is too short, light focuses at point behind retina) - glasses with convex lens
Myopia / Short sighted (Lens too thick or eyeball is too long & light focuses at point in front of retina - Concave glasses lens
Laser surgery - changes shape of cornea
Or replace lens inside eye with artificial one.
Contact lenses
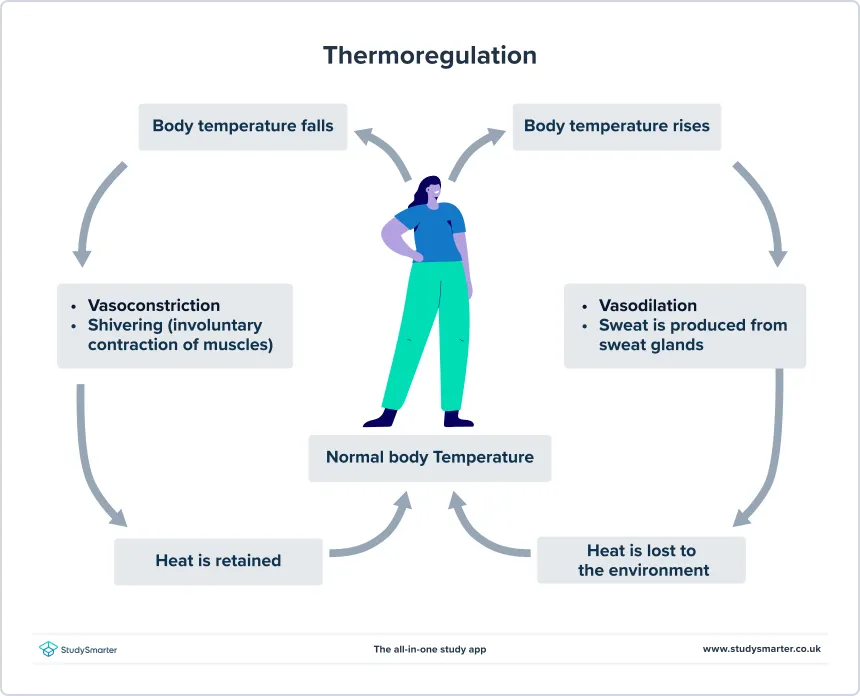
What is Thermoregulation? How is it done?
Thermoregulatory centre is in the brain and controls body temp
Contains receptors sensitive to temp of blood
Skin also contains temp receptors and sends electrical impulses through sensory neurones to the thermoregulatory centre.
Too hot:
Sweat glands release sweat onto surface of skin, sweat evaporates and takes energy from body.
Flushing - Blood vessels supplying capillaries dilate (get wider / Vasodilation) so more blood flows and heat can transfer out of blood.
Too cold:
Blood vessels constrict (narrower/ vasoconstriction) So less heat is lost through blood.
Shiver - skeletal muscles contract, generate energy by muscles cells increasing rate of respiration.
Stop sweating
What is the Endocrine system?
Number of glands which secrete hormones into blood stream. Blood carries hormones around body.
Slower and longer lasting effect than nervous system
Label this Endocrine system diagram
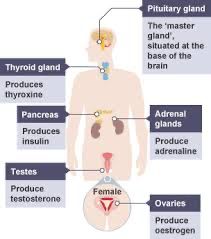
What are the functions of the glands?
Pancreas - Blood glucose concentration
Ovaries & Testes - Puberty & reproduction
Thyroid - Growth & Basal metabolic rate (How fast chemical reactions happen)
Adrenal glands - release adrenaline when stressed
Pituitary gland - Releases different hormones depending on conditions and act on other glands.
How is blood glucose concentration controlled?
Carbs cause blood glucose concentration to rise.
Pancreas senses this and produces hormone insulin.
Triggers body cells to take glucose from blood.
Triggers liver and muscle cells to store it as glycogen
If blood glucose concentration falls too low, glucagon triggers liver cells to turn glycogen back into glucose into blood.
What is diabetes?
Type 1 - Pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin. When carbs are consumed, the blood glucose rises but doesn’t go back down as far as it needs to
Type 2 - Body stops responding to the insulin produced. Must avoid carbs and exercise.
How does the body lose water?
Via lungs when we exhale
Sweat via skin (+ ions & urea)
Via kidneys in urine (+ ions & urea)
What do the kidneys do?
Blood containing urea enters kidneys by arteries
Removes excess ions, urea and water
Leaves the kidneys as urine in bladder
Blood leaves kidney through a vein
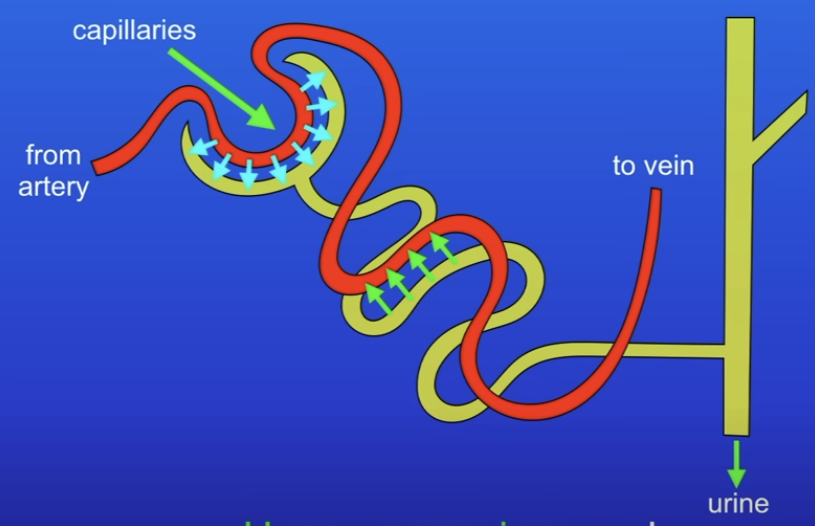
Explain this diagram
From kidneys to bladder
Blood passes through capilleries
Small molecules are filtered out (Urea, ions & water, glucose)
Pass into tube (yellow)
(Green arrows) Some of the molecules (not urea) are reabsorbed into blood (Selective reabsorption)
Urea, excess ions & excess water are released as urine.
How does the body deal with excess amino acids?
Amino acids go into blood during digestion
Liver breaks down excess amino acids into ammonia (Deamination)
Ammonia is toxic so it it converted into urea
How does the body maintain water levels in blood?
Increase water levels: The pituitary gland releases hormone ADH
so more water can pass out of the kidney tubules to be reabsorbed into blood & less urine is produced
Pituitary gland stops releasing ADH as water levels increase
Decrease water levels: Pituitary gland stops releasing ADH, less water reabsorbed, more urine produced
What is kidney dialysis
Kidney failure means blood contains too much urea, ions and water
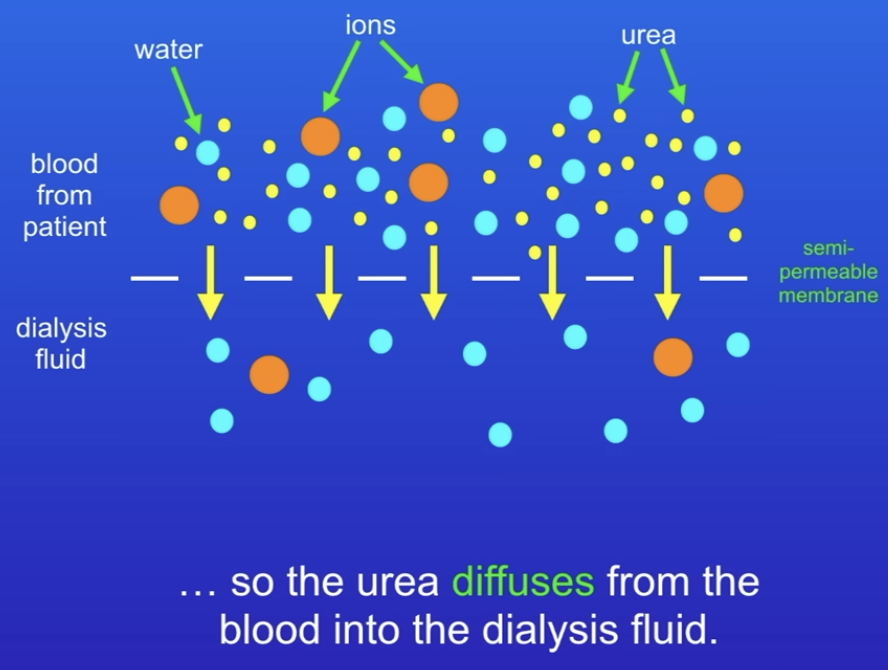
Kidney dialysis: patients blood passes over a semi-permeable membrane which allows smaller molecules through
Dialysis fluid on other side of membrane - controls normal concentration of water and ions but no urea
Steep concentration gradient lets smaller molecules pass through.
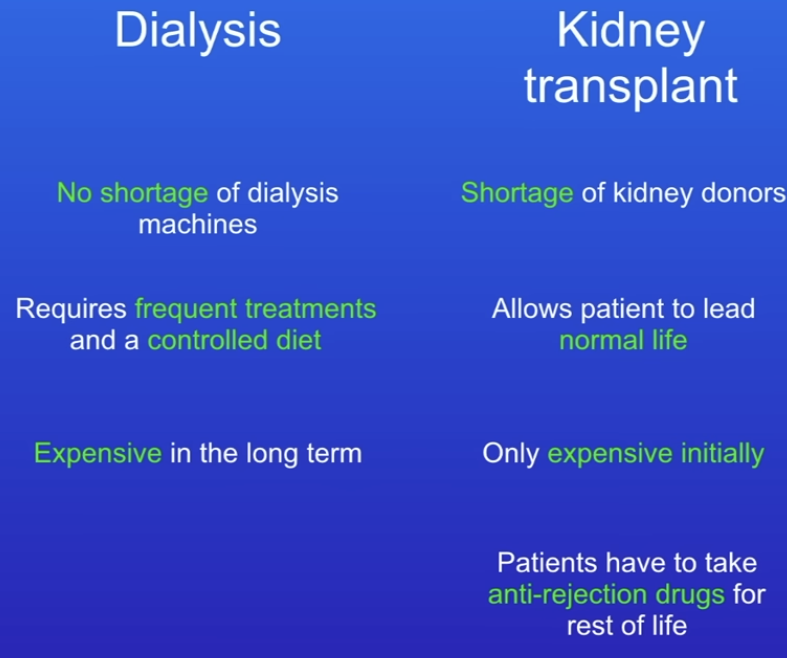
What are disadvantages of Kidney Dialysis and what is a better alternative?Compare them.
Inconvenient - have to go to hospital several times a week
Must eat a controlled diet
Kidney transplant - Diseased kidney replaced with healthy kidney, but may be rejected.
The menstrual cycle
Ovulation (release of egg) every 28 days
To prepare, uterus lining becomes thick and spongy
Egg goes to uterus and can be fertilised if sperm is present, then implant into uterus wall, develop into a baby
If not fertilised, egg and uterus lining is released (period)
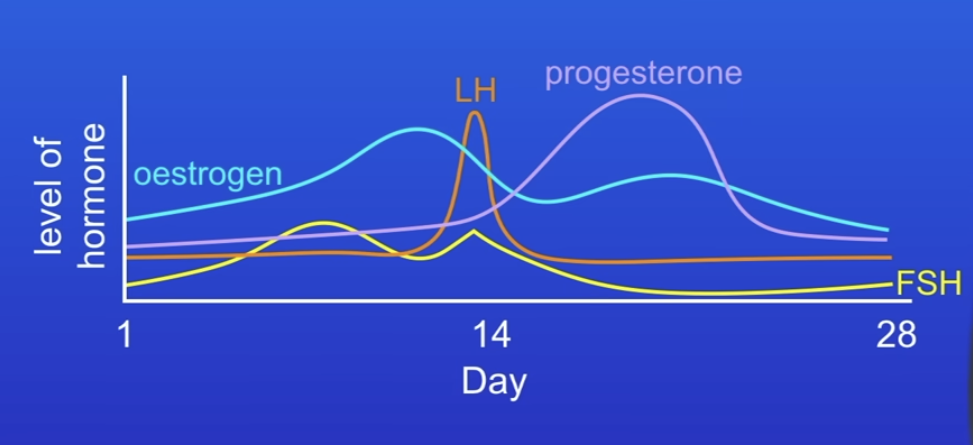
Hormones during the menstrual cycle
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) causes egg to mature in ovary
Luteinising hormone (LH) causses ovulation
Oestrogen (Produced by ovary) and progesterone maintain uterus lining incase egg is fertilised and implants.
How do the hormones interact with the menstrual cycle?
Pituitary gland releases FSH
FSH travels in blood to ovaries, causing egg to mature
FSH triggers ovaries to produce oestrogen, causing lining to become thick & stops pituitary gland releasing FSH
Pituitary gland release LH, triggers ovulation
Ovaries now produce progesterone, stops pituitary gland releasing LH and FSH to stop anymore eggs maturing or being released.
Progesterone also causes lining to become thick. progesterones falls if not fertilised, uterus lining and egg are released (period)
What is an IUD?
Intrauterine device (IUD) ‘coil’
Prevents embryo from implanting
Can release hormones to reduce risk of fertilisation
Highly effective and can prevent pregnancy for up to 10 years
DOesn’t protect agains STI’s
How does the pill work?
The pill - contains hormones which prevent the production of FSH which stops any eggs maturing. Highly effective if taken correctly (everyday)
Side effects: Risk of breast cancer, blood clots
What other hormone methods can a woman use for contraception?
Implant / Skin Patch / Injection, contains progesterone stopping the egg maturing or being released.
More convenient than taking a daily pill, has side effects
These don’t prevent STI’s or STD’s
What barrier methods are there?
Condom/Diaphragm: Barrier method stops sperm reaching egg, effective if used correctly.
Adv: no side effects
Disadv: condoms can break or slip off
More effective if used with a spermicide gel which kill or disable sperm.
What are surgical forms of contraception?
Sterilisation
Prevent women’s eggs reaching uterus
Men: Prevents sperm leaving the penis.
Difficult to reverse, be certain they don’t want children.
Don’t protect against STI’s
What is the natural form of contraception?
Abstain from sex after ovulation
Hard to tell when ovulation occurs
Doesn’t protect against STI’s
Opinions on contraception
Some religions see it as unethical
Some people think everyone should be able to choose for themselves.
Condoms reduce risk of STI’s
What options are there to treat infertility?
Fertility drug - injection of LH & FSH, ovulate more than usual
IVF - fertilisation outside of body. First administer FSH & LH, eggs mature, collected, collect sperm and fertilise eggs in lab. Develop into embryos which are inserted into the womb.
Not high success rates
Emotionally stressful & Physically demanding on mum
Lead to multiple births (risky for mum and babies)
Ethical views: Destroying unwanted embryos
Expensive
What is adrenaline?
Adrenal glands (On top of kidneys) release adrenaline in fear or stress. Released into blood. Increases heart rate to deliver more oxygen and glucose to body (Fight or flight)
What is thyroxine?
Thyroid gland in base of neck
Releases Thyroxine
Stimulates the basal metabolic rate (makes bodys chemical reactions take place faster)
Role in growth and development
What is a negative feedback loop?
What is phototropism, how was it investigated?
When plants grow towards the light.
Shine light onto shoots from one side
The shoots lean towards the light
When the tips of the shoot were cut off, they didn’t grow towards the light.
Suggested that the tips produce plant hormone auxin
Covered tips with foil, again didn’t grow to light so the tips are sensitive to light.
Covered bottom with foil and the tip still grew towards the light, so the bottom isn’t sensitive to light
How does a plant use auxin?
For Photopism:
Auxin produced at tip
Triggers cells growth
Light causes auxin to concentrate on darker side of shoot tip
Auxin spreads down the shoot
Cells on darker side grow faster than cells on light side, so tip towards the light.
For Gravitropism/Geotropism
Root grow towards force of gravity
Auxin produced in roots
Gravity causes auxin to concentrate on lower side
Auxin inhibits cell growth in roots.
Lower side grows slower than the upper side, so grow towards force of gravity
WHat other chemical are used in plants?
Gibberellins - germination of seeds
Ethene - controls cell division and fruit ripening
Plant Response RP (light) and variables
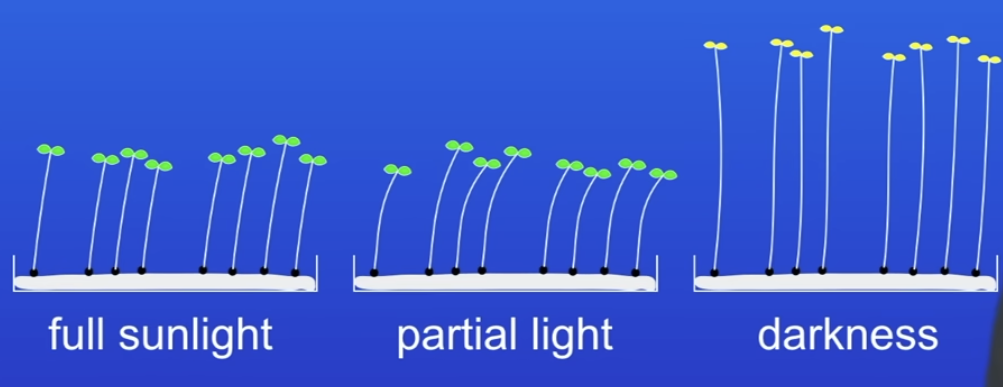
Investigate light intensity on height of seedlings
IV - light intensity
DV - Height
CV - Water volume
The full and partial light seedlings have similar heights because the chlorophyll is very efficient at absorbing light energy. They don’t need full light to grow
They tilted towards the light - phototropism
Darken ess - grew longest, when the seeds germinate, they grow rapidly to reach the light and in the darkness they continued grow rapidly to try and reach the light. Small yellow leaves, no energy for photosynthesis
Plant responses (light) RP Method
Cotton wool in 3 petri dishes, filled with equal volume of water
Place 10 mustard seeds in each dish
Leave in warm place to germinate
Water every day with same volume
Seeds will germinate
Ensure each sample has the same amount of germinated seeds
Measure height with ruler, hold stem to measure accurately.
Place one dish in full sunlight, one in partial light, one in darkness
Measure heights everyday for 5 consecutive days
Record results on table
Calculate mean seedling height per day
Plant responses (gravity) RP Method
Dish of seedlings placed on its side in the dark
Shoot grows upwards against direction of gravity
Roots grown down following direction of gravity
How are hormones used in agriculture and horticulture?
Auxins - weed killers, rooting powders, promoting growth in tissue culture
Gibberellins - Force a seeds to germinate before it normally would (end seed dormancy), encourage plants to flower, make fruit grown larger
Ethene - Ripen fruits just before sale.