ESCI 274 Lecture 2: Population and Globalization
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:45 PM on 2/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
1
New cards
Absolute Population
* The magnitude of the increase or decrease in population for a defined period
* ex; if last year the population of a city was 3,000 and this year the population has changed to 5,000, then the absolute increase in population is 3,000
* ex; if last year the population of a city was 3,000 and this year the population has changed to 5,000, then the absolute increase in population is 3,000
2
New cards
Population growth rate
* Population in the world is, as of 2022, growing at a rate of around 0.84% per year (down from 1.05% in 2020)
* The current population increase is estimated at 67 million people per year
* The current population increase is estimated at 67 million people per year
3
New cards
Spatial distribution
* The spatial pattern due to dispersal of population, formation of agglomeration, linear spread etc
1) 1 B in 1800 (Ag Rev)
2) 2 B in 1930
3) 3 B in 1960
4) 4 B in 1975
5) 5 B in 1987
6) 6 B in 1999
7) 7 B in 2011
8) 8 B in 2022
1) 1 B in 1800 (Ag Rev)
2) 2 B in 1930
3) 3 B in 1960
4) 4 B in 1975
5) 5 B in 1987
6) 6 B in 1999
7) 7 B in 2011
8) 8 B in 2022
4
New cards
Impact of human population on climate
* More people = more polluters
* Population growth isn’t necessarily causing climate change, it's the amount each person consumes
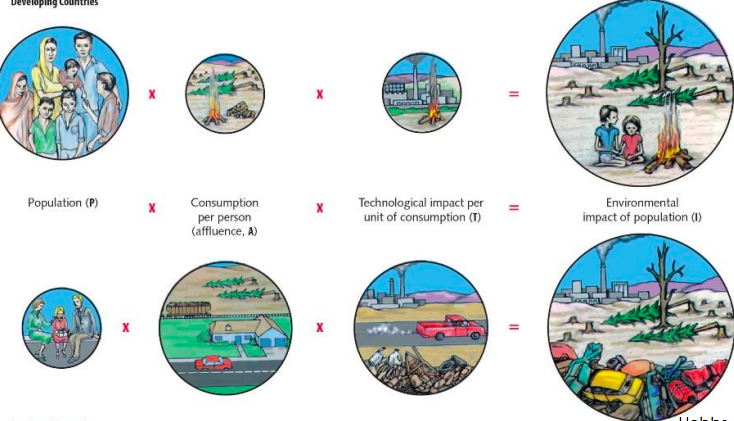
* Population (P) x consumption per person (affluence, A) x technological impact per unit of consumption (T) = environmental impact of population (I)
* Population growth isn’t necessarily causing climate change, it's the amount each person consumes
* Population (P) x consumption per person (affluence, A) x technological impact per unit of consumption (T) = environmental impact of population (I)
5
New cards
Major events in human development that have impacted climate
1) **Palaeolithic tool making** - Stone and wool tools
2) **Neolithic agriculture** - More advanced tools like soil turners dragged by horses
3) **Industrial Revolution** - Factories, etc
4) **Currently in the modern medical technological revolution**
2) **Neolithic agriculture** - More advanced tools like soil turners dragged by horses
3) **Industrial Revolution** - Factories, etc
4) **Currently in the modern medical technological revolution**
6
New cards
Malthusian vs Technocentric views of resources
* **Malthusian** scenario resources and population collide (overlap) and humanity returns to a subsistence level of living because population outpaces production
\
* **Technocentric** scenario resources and population are independent. Population increase is a cause of changes in agriculture.
\
* **Technocentric** scenario resources and population are independent. Population increase is a cause of changes in agriculture.
7
New cards
Globalization impact in the environment/climate
1) New diseases
2) Increasing obesity (and associated health impacts)
3) Disasters in one area may impact resources in another (exports/imports)
4) Overdevelopment or exploitation of resources (i.e. fish, water)
5) Pressure on food supplies
6) Degradation of land and water
7) Depletion of resources
8) Ecosystem disturbances
9) Disruption of bio geophysical systems (e.g., climate system)
2) Increasing obesity (and associated health impacts)
3) Disasters in one area may impact resources in another (exports/imports)
4) Overdevelopment or exploitation of resources (i.e. fish, water)
5) Pressure on food supplies
6) Degradation of land and water
7) Depletion of resources
8) Ecosystem disturbances
9) Disruption of bio geophysical systems (e.g., climate system)
8
New cards
Linkages between wealth and environmental/climate impact
Wealthy people consume more energy and, consequently, are responsible for more greenhouse gas emissions than less wealthy people
9
New cards
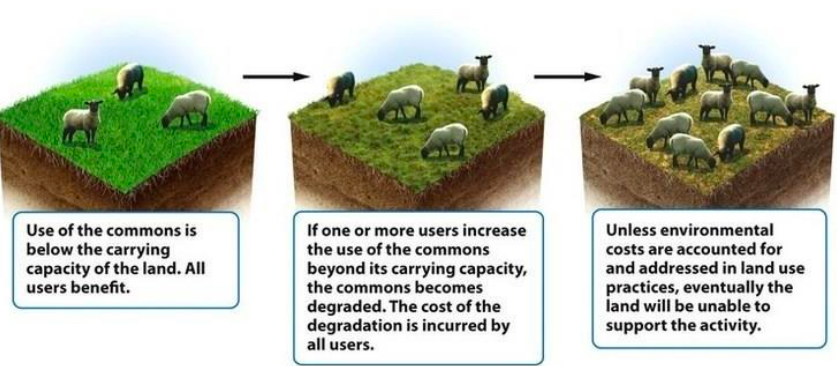
Tragedy of the commons diagram
10
New cards
Humans/ Climate change developing countries vs developed countries diagram
11
New cards
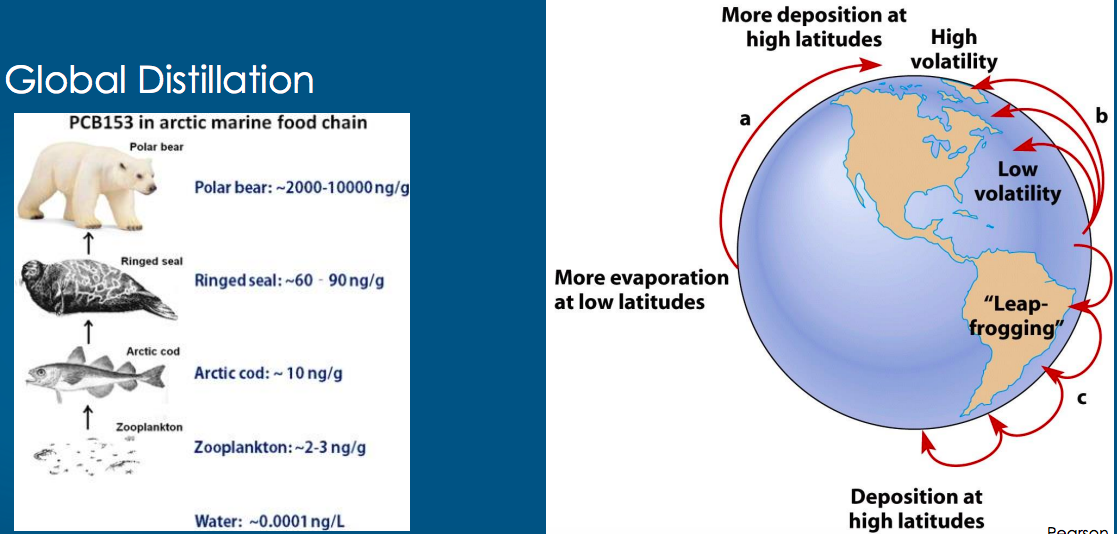
Our impact on others diagram
12
New cards
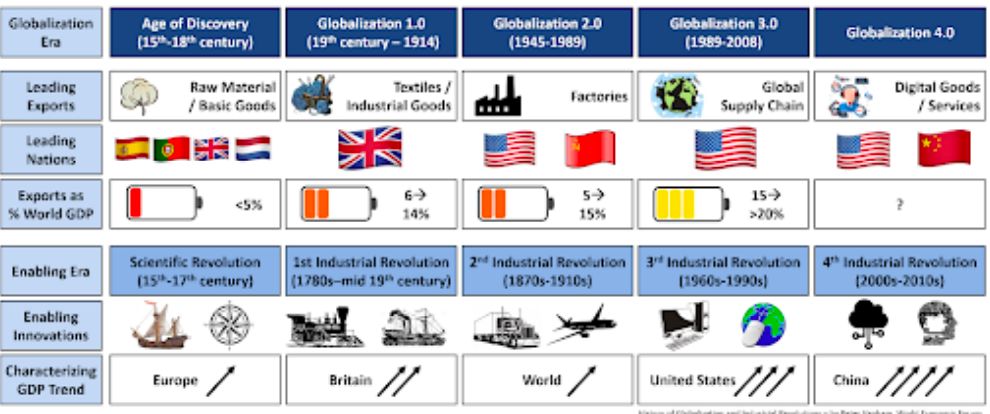
Globalization over time diagram