AP Calc Theorems & Rules
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
1
New cards
Limit exists
Limit exists when both the one-sided limits are equal to the same number
2
New cards
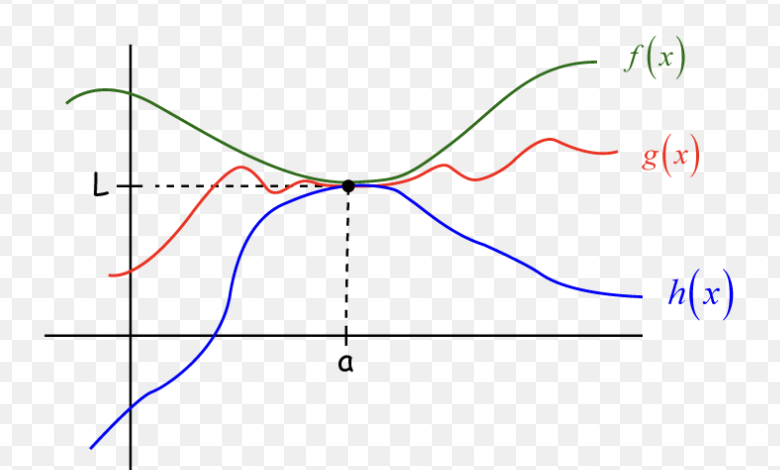
The Squeeze Theorem
if f(x) ≤ g(x) ≤ h(x) and if f(x) and h(x) have the same limit, then g(x) has the same limit
3
New cards
Average Rate of Change
f(b) - f(a)/ b-a
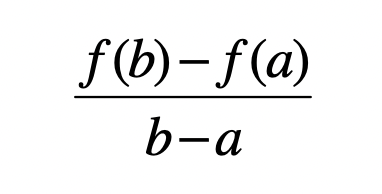
4
New cards
Definition of Derivative (limit)
f’(x) = lim (h → 0) (f(x + h) - f(x))/h
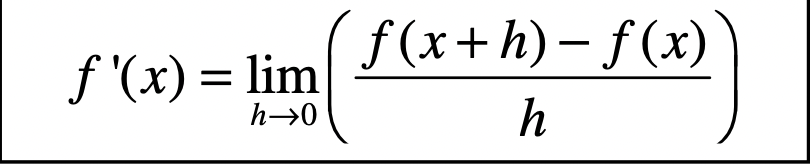
5
New cards
Mean Value Theorem
if f(x) is continuous on \[a,b\], then there exists a value x = c such that (image)
* Rolle’s Theorem is MVT when f(a) = f(b) making f’(c) is 0
* Rolle’s Theorem is MVT when f(a) = f(b) making f’(c) is 0
![if f(x) is continuous on \[a,b\], then there exists a value x = c such that (image)
* Rolle’s Theorem is MVT when f(a) = f(b) making f’(c) is 0](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2ef01b1d6e6348df9913fca6d8226e4c.jpeg)
6
New cards
Average Value
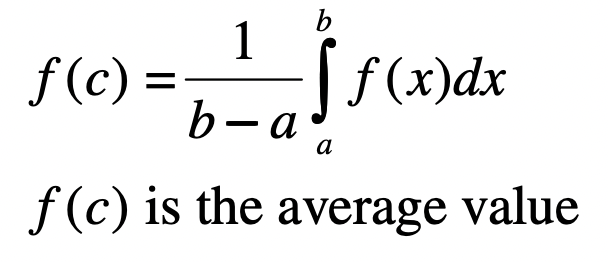
7
New cards
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
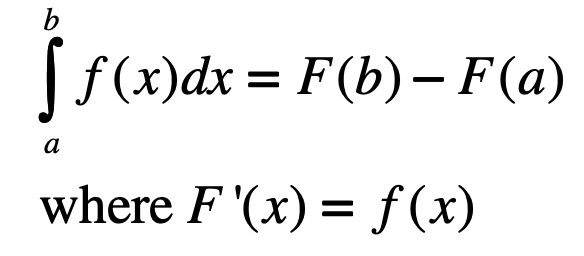
8
New cards
2nd Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
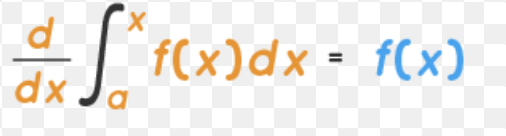
9
New cards
Intermediate Value Theorem (IVT)
if f(x) is continuous on \[a,b\] and m is a number between a and b, then at x=c, there exists f(c) = m
10
New cards
Extreme Value Theorem
If a function *f(x)* is continuous on a closed interval \[ *a, b*\], then *f(x)* has at least one maximum and minimum on \[ *a, b*\]
11
New cards