ECG Basic
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
In a NORMAL ECG, what do the 12 leads look like
Lead I-III, aVF, V5,V6 are POSITIVE → Lead II should be the MOST positive
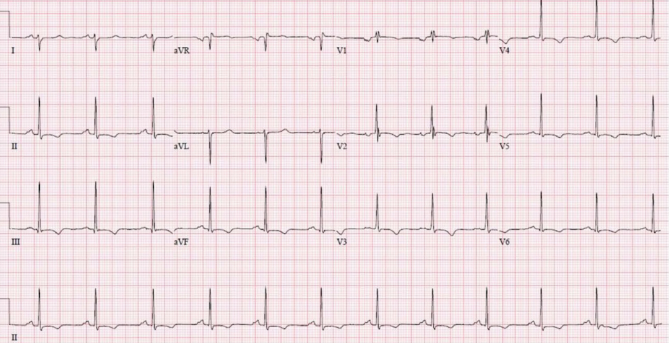
Interpret this ECG
Lead I is negative (normal = positive), aVF positive → RAD

Interpret this ECG
Lead I is positive, aVF is negative (normal is positive) → LAD
What is the normal appearance of P waves
Smooth and round → Small (less than 2.5 small boxes); positive in I,II, aVF, V2-V6, biphasic in VI, inverted in aVR
What is P mitrale
Caused by LA enlargement → Shown by broad, M shape P wave, >120 ms P wave, biphasic V1 has more negative deflection
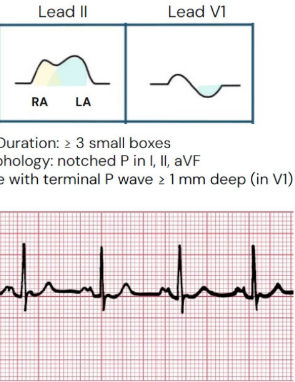
What does this describe
M shape P wave, duration > 3 small boxes → P mitrale
What is P pulmonale
Caused by RA enlargement → Shown by tall peaked P wave in lead II, amplitude > 2.5 mm, biphasic V1 has more positive deflection
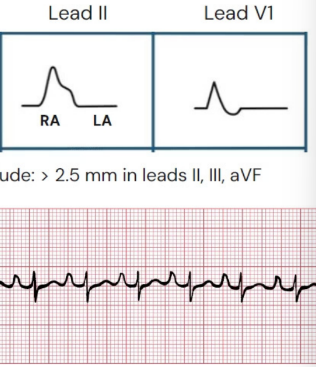
What does this describe
Tall peaked P wave in Lead II → P pulmonale
What is the appearance of the QRS complex on ECG
Q is initial negative deflection, R is first positive deflection, S is negative deflection
What is the 300 method
Regular rhythm: Count the number of large boxes between two R waves → Divide 300 by that number to get HR
What is 6 second method
For irregular rhythm: Count number of R waves in strip then multiply by 10 to get HR
What is 1500 method
More precise than 300 method; count small boxes between R waves and divide 1500 by that number to get HR
What would LVH look like in ECG
S wave in V1 + R in V5/6 >= 35 mm, R in aVL > 11 mm, ST depression and T wave inversion
What could RVH look like in ECG
R wave in V1 > S in V1, R in V1 > 7 mm; ST depression and T wave inversion
What would a RBBB look like in ECG
Wide QRS, rabbit ear or M shape in V1-V2, W shape in V5-6, I and aVL
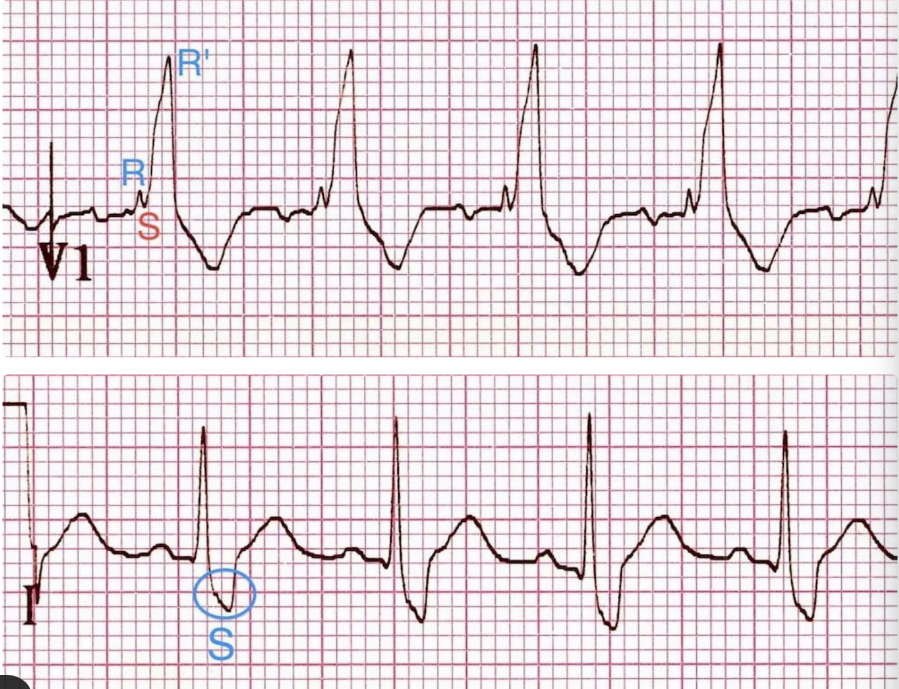
What does this indicate
M shape in V1, W shape in lead I → RBBB
What would a LBBB look like in ECG
Wide QRS complex, dominant S wave in V1, no Q wave in V5-6, aVL
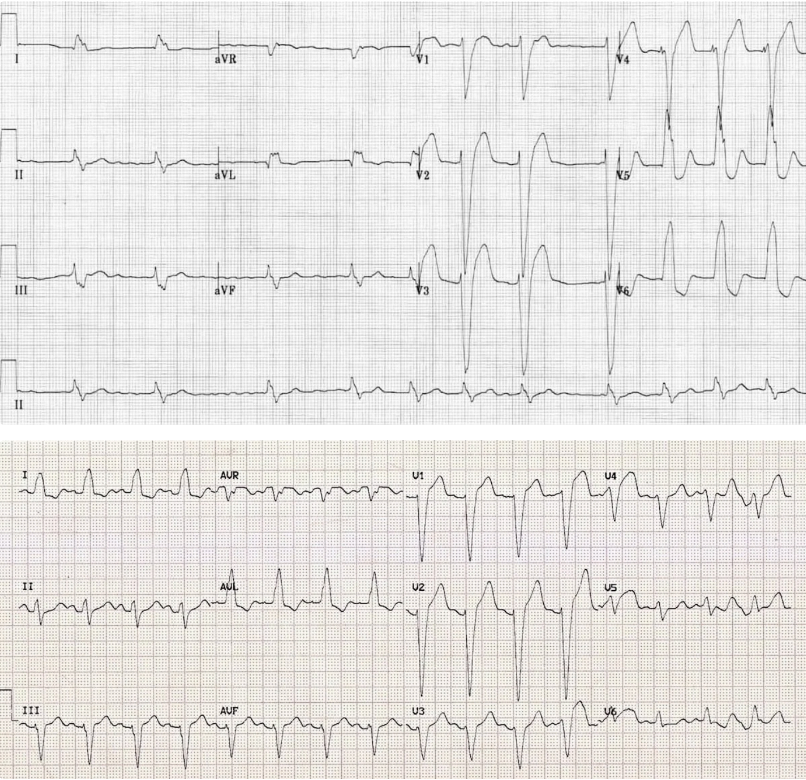
What does this indicate
Wide QRS, dominant S wave in lead V1 → LBBB
What would ECG look like for hyperkalemia
Tall peaked and narrow T wave → Tall peaked T no P wave, wide QRS
What could ECG look like for hypokalemia
T wave is flat or inverted, there are U waves, ST segment has depression
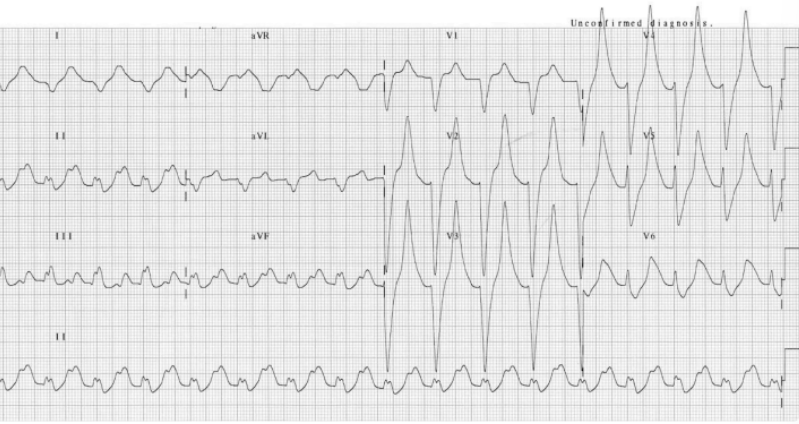
What does this indicate
Wide QRS, tall T wave → Hyperkalemia
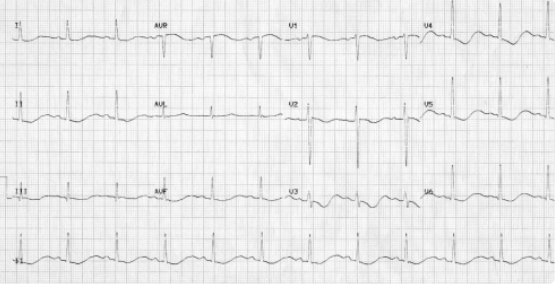
What does this indicate
Inverted T wave, U wave present → Hypokalemia
What is PR interval
Atrial depolarization to ventricular depolarization (normal 3-5 small box) from beginning of P wave to beginning of Q wave
What is QRS duration
Ventricular depolarization (normal < 3 small boxes) → from start of Q to end of S
What is QT interval
Total ventricular repolarization (normal 360-440 ms); from Q wave to T wave
What is ST segment
Flat baseline between QRS end and T wave start; normally at baseline
What is seen in first degree AV block
Prolonged PR interval (>5 small boxes)

What does this indicate
Long PR interval → first degree AV block
What is seen in Mobitz I second degree AV block
Progressive PR prolonged until QRS
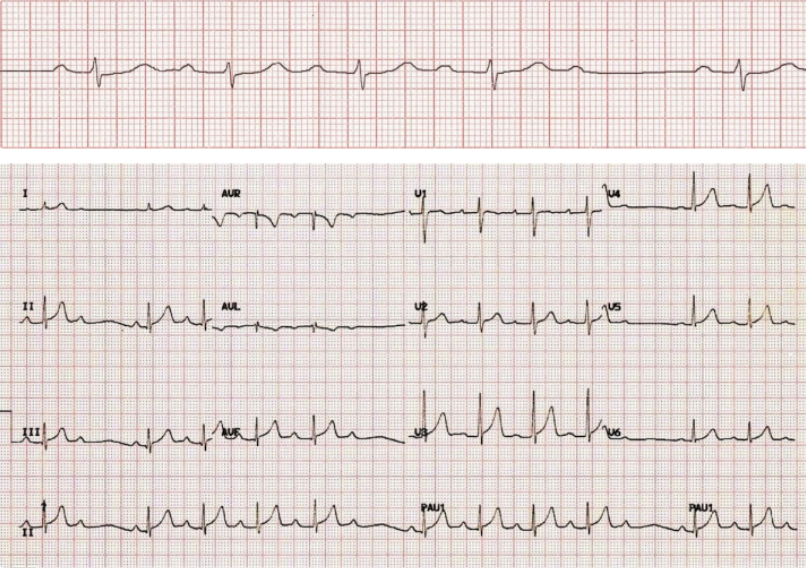
What does this indicate
Long PR until there is QRS → Mobitz I
What is seen in Mobitz II second degree AV block
Constant PR interval with sudden dropped QRS
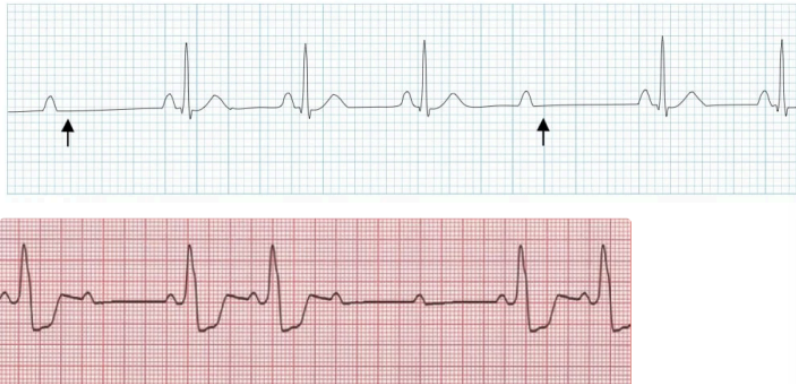
What does this indicate
non conducted P wave without progressive prolongation of PR → Mobitz II
What is seen in third degree AV block
P and QRS complexes are independent
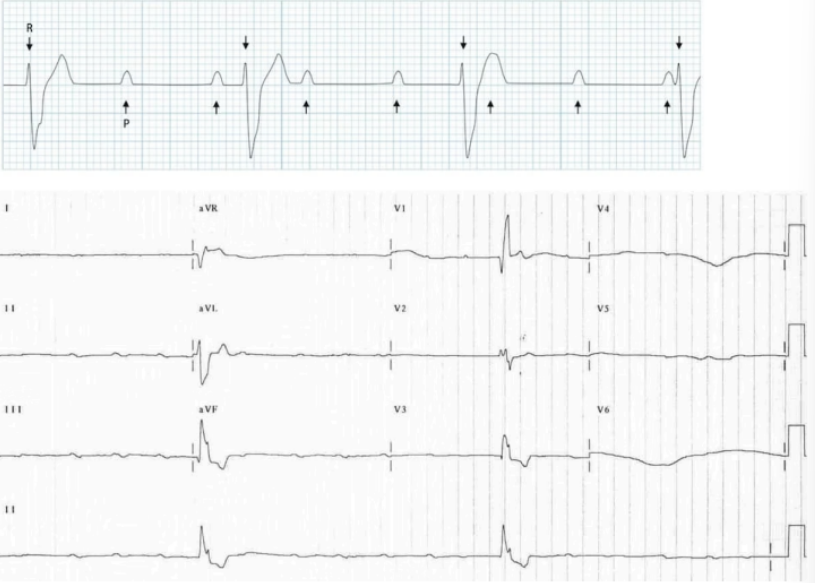
What does this indicate
P and QRS are independent → Third degree AV block
In RCA occlusion, ST elevation is expected in which leads
Inferior wall → II, III, aVF
In LAD occlusion, ST elevation is expected in which leads
Anterior/septal wall → lead V1-4 (V5-6 also possible)
In LCx occlusion, ST elevation is expected in which leads
Lateral wall → lead I, aVL, V5-6
What is the J point in STEMI
Where S wave terminates and ST segment begins → If higher than baseline = ST elevation
What is the characteristic of ST elevation caused by ischemia
Convex, straight up/downslope, straight horizontal
What is the characteristic ST elevation NOT caused by ischemia
Concave shaped
What are common non sinus rhythms
Afib, atrial flutter, ectopic beats, junctional rhythm, heart block
What is the sign of Afib on ECG
Irregularly irregular pattern (no pattern for RR interval), no P wave, narrow QRS

What does this indicate
No P wave, irregular R wave, QRS is narrow → Afib
What is the sign of atrial flutter on ECG
Sawtooth flutter wave (lead II, III, aVF), regular atrial rhythm (very fast but regular)
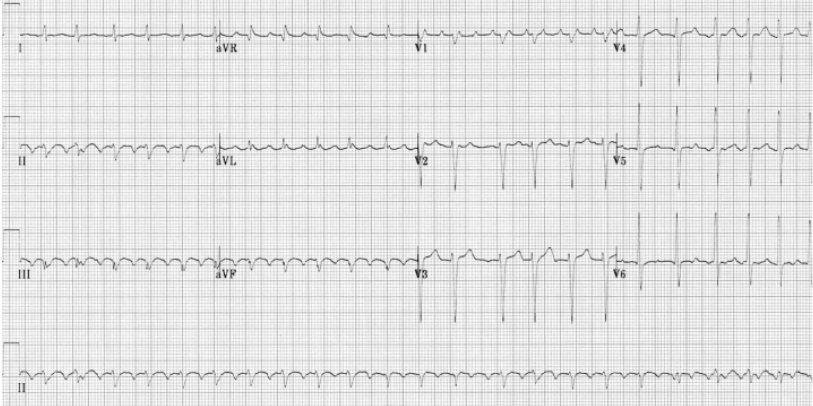
What does this indicate
Sawtooth flutter + very fast atrial rhythm → Atrial flutter
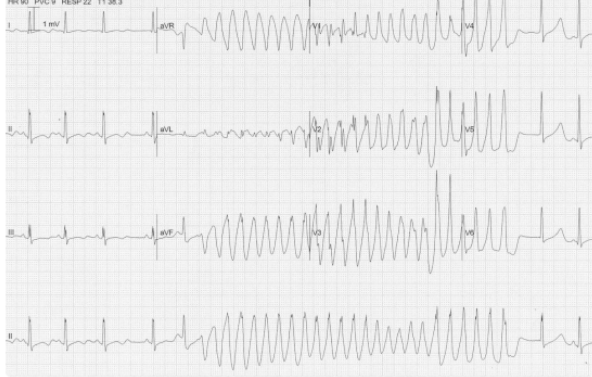
What is sign of ventricular tachycardia on ECG
Wide QRS, rapid rate and regular rhythm, AV dissociation (P and QRS do not beat together)
What is the sign of monomorphic VT
Follows all signs of VT + uniform QRS
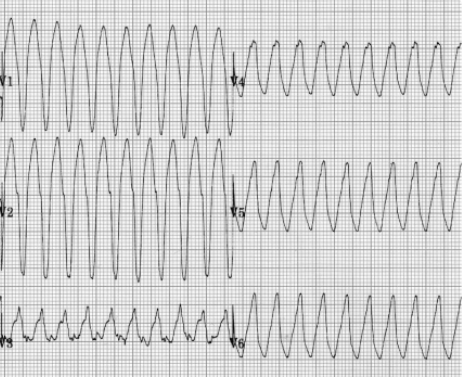
What type of VT is this
QRS is uniform → Monomorphic
What is polymorphic VT
Follows all signs of VT + QRS is variable (all different in shape and amplitude)
What type of VT is this
QRS is not the same → Polymorphic