NEcon Week 4- Rewards
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
what is the behaiovral definition for a reward
increases frequerncy (lilihood) and intensity of behaivors that precede or lead up to the reward (in other words encourages reinforced learning)
Increases motivarted behaivors like approach (seeking) and consummatory (eating) responses, typically in presence of reward-predictive cues.
Elicits feelings of pleasure or positive emotions
primary vs secondary reinforcers
primary reinforcer = (food, water, etc.) innately rewarding stimuli that satisfy biological needs and are inherently assocaited with a positive feeling of satisfaction/pleasure and that motivates behavior.
secondary reinforcer = Things not inherently rewarding but come to acquire value and become rewarding.
Medals, money, points
true or false, we have sensory receptors but no value/ reward sensors
true , sensory receptors throughout the body but no value/reward sensors.
mechnical : pressure and distortion in the finger tips
chemical: photons; photonreceptors in the eyes
thermal: sensory receptor sensitive to heat
electromagnetic
proprioception - muscle spindles, golgi tendon organs
how do we study rewards? explain the rat video shown in class
we need to study behaivor and learn about how the brain gets what it wants
the full rat is sedentary and is laying down while the starved rat is constantly searching for fod, until he finds when he presses down on a lever bar he will get food
explain the cocnept of sensory in, reward out
input: sensory information from the external word like sushi is presented
the sensory information is assocaited with some internal information like sight, smell, touch or past memories and
output: expections determine something is rewarding
who published one of first papers on the study of reward processing> (1950’s)? What they do and conclude?
James Olds & Peter Milner – Positive reinforcement produced by electrical stimulation
they set up a lever that when pressed stimulated the septal area of the rat brain (no food involved) > the rats has 285 presses/hour of presses each time the electrode stimluated part of the brain that brought satisfaction > extinction eventually occured
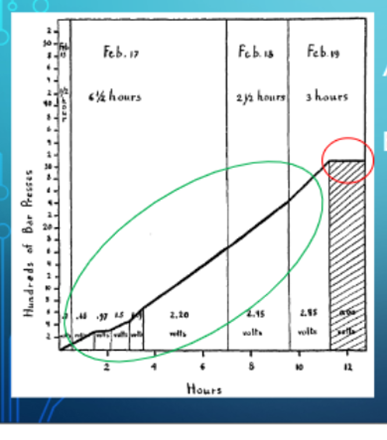
conclusion: septal nuclei stimulation leads to the greatest time spent responding, rats can be made to gratify drives of hunger, thrift, and sex by self-stimulation of their brains and electricity.
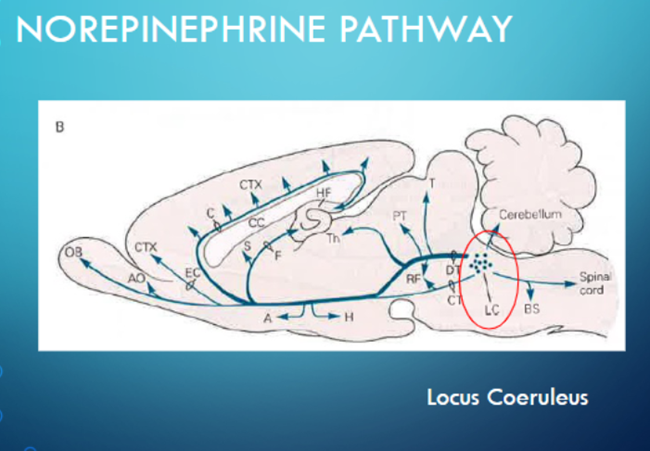
what is the significance of the medial forebrain bundles?
later studies show exciations of medial forebrain bundles within the Pons (where the NE center is) coorelating to increased lever pressing
scientsits looking at NE pathways as this was a time where tranquilizers and anti-psycholotics were big > these drugs block NE transport (no excitation)
NE center
what is Chlorpromazine
what is Reserpine
o Locus Coeruleus in Pons = NE center
o Chlorpromazine: blocks NA receptors.
o Reserpine > depletes brain NE by blocking its transport back into synaptic vesicles
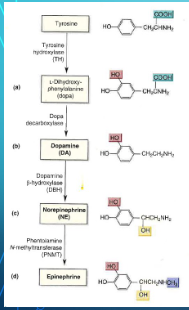
synthesis of NE steps
Tyrosine <TH> Dopa <Dopa decaryboxylase> Dopamine <DBH> NE <PNMT> Epinephrine
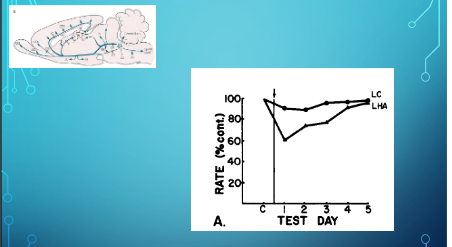
Wise & Stein (1969) - Facilitation of Brain self-stimulation by NE
gave animals Disulfiram which blocks synthesis of NE by blocking DBH (dopamine B-hydroxylase)
and the animal did not press lever anymore, administering dopamine did not reinstate lever pressing but administering NE did

what did Roll (1970) argue about Wise et Stein (1969) results?
Roll say that NE is important for general wakefullness and arousal (response to stimuli in general) not directly connected to reward behavior.
Roll 1970 - Intracrianila Self-stimulation adn wakefulness, effect of maniuplatring ambient brain catecholamines
Roll gave rats disulfiron like Wise to block NE synthesis, the animals paused in bar pressing but looked asleep and sedated, disulfiron blocking NE more impacts wakefulness NE is not the neurotransmitter for reward, the results of the studies which claim to show this effect are accounted for by variation in wakefulness and activity level
Corbett et al. (1977) – Dorsal NA bundle lesion fail to disrupt self-stimulation from region in locus coeruleus
lesions to noadrenergic fibers in the NA center in the medial forebrain does not stop the self-stimulating lever pressing rates > decrease in lever pressing doesnt seem to be related to locus coeruleus and NE release.
okay if not NE, then what?
medial forebrain stimulation activates dopamine release by neurons
ventral tegmental area
substantria nigra parts compacta
substantis nigra pars reticulata
coronal slices for TH staining (enzyme that makes DOPA from tyrosine) show TH expression in the SN, SNc, VTA.
Dopamine: Anhedonia Hypothesis (Wise et al. 1978)
what is Anhedonia?
Chlorpromazine in context to dopamine dysregulation.
what is the hypothesis exactly?
anhedonia > inability to feel pleasure
Chlorpromazine (aka thorazine) > is a dopanine antagonist and antipsychotic drug that blocks dopamine receptors, people (schzophrenics) on this drug dont feel pleasure and people with Parkinsons disease (loss of dopamine in the brain) suffer from depression
anhedonia hypothesis: Dopamine mediates pleasure; blocking dopamine causes inability to feel pleasure.
Wise (2004) - dopamine, learning, and motivation
experimental set up and conclusions
administered Pimozide to rats, it dopamine (D2) receptor antagonist with high affinity
experimental set-up: rats press lever for food reward
Control
acquisition phase: with every lever press the rats given food, cotnrol mice learned fas
extinction phase: no more food given with lever press, lever press died down over the days
rats who were on Pimozide
acquisition phase: lever presses decrease over the days ( no learning)
extinction phase: lever presses decrease over the days like control rats

pimozide build up effects leaning
no
they also gave pimozide over days without testing, then tested and lever pressing still decreases over the days, 4 days of drug does not impact day 1 behaivor, lever pressing still the same
food is devalued with pimozide
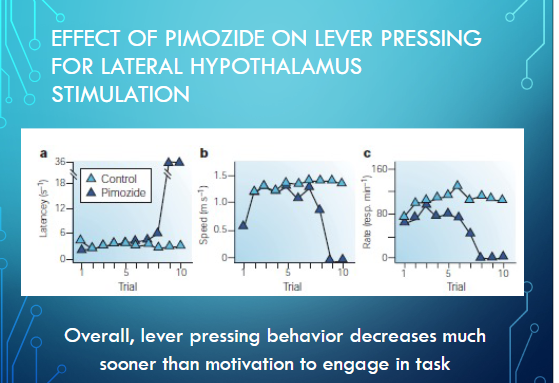
how does pimozide impact lever pressing for lateral hypothalamus stimulation
pimozide does not immediately impact latency or speed to begin approach the lever, they are initially engaged then over the days lose motivaiton to approach
but pimozide immdeiately impacts rate of lever pressing > animal decides lever pressing is not leading to reward quickly by trial 4. overall, lever pressing behavior decreases alot sooner than motivation to engage in task
lever acquires value but pimozide leads to lever being devalued and animal stops engaging
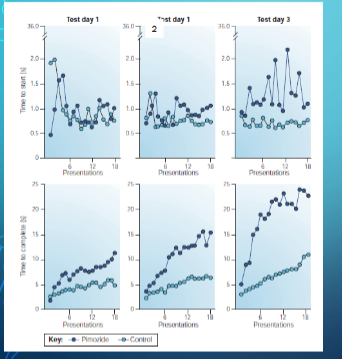
pimozide and free feeding
rats presented with a bowl of food and multiple times throughout a session, its not until day 2 that the animal starts picking up the food pellet despite being just as hungry.
motivation to approach the food takes a while to be impacted, but desire to consume the food is impacted almost immediately (the pimozide rats take longer to comsume)
role of dopamine
plays a role in valuation of rewards
plays a role in motivatroin
valutaion and motivation are distict and dont imapct motor function.