L3: Respiratory Component
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
what is the difference between the thoracic cavity and thoracic cage?
-thoracic cage is just the skeleton
consider: stomach
within the rib cage (thoracic cage) but in abdominal cavity, not thoracic
what should you note about the pleura?
-small amounts of serous fluid
which cells of the pleura are simple squamous?
-mesothelial cells (1 cell thick)
what is the biggest fx of the pleura?
lubrication
when are the pleural sacs important?
-embryologically - the pleura sacs line thoracic cavity and lungs grow into them
which pleural sac is larger?
R (more lung tissue on R side (consider: more lobes)
space between pleura sacs?
-mediastinum
-where the pleural sacs push against each other
space inside pleural sac?
-pleural cavity
what is found in mediastinum?
-bascially everything, in thoracic cavity, except lungs
-trachea
-esophagus
-heart
-vessels
which part of the respiratory system forms first?
-trachea
explanation:
lungs and pleura while forming
-as lungs push into pleural space already covered in pulmonary viseral pleura
- pulmonary visceral pleura then forms up against the parietal pleura
-space between pulmonary visceral pleura and parietal pleura is called pleura space
-small amounts of serous fluid in pleural space
Location:
Coastal pleura
-against ribs (inside rib cage) location
location:
Diaphragmatic pleura
– Against diaphragm
Location:
Mediastinal pleura
– Against mediastinum
(3) types of parietal pleura
-costal
-diaphragmatic
-mediastinal
What is pleural exudate?
-too much pleural fluid
Why is plural space fluid so important? (Lungs)
– Lungs do not have muscles, only mm thorax
– Fluid allows for a vacuum; lungs to stick to the thoracic cavity so as that increases bigger, the lungs move with it and expand
What is important to note about the surface tension of the plural space and lungs?
– Is what causes the lungs to stick to the thoracic cavity
– based on the tension of pleural fluid
– Note: not suction because there is no change in pressure
-as the lungs and thorax expand allows for the lungs and thorax to rub against each other and not cause irritation and information
Why is the plural space so important for lung and thorax movement
– There is no physical (like membronous) connection between the lungs and the thorax; need the serous fluid
How are the mediastinum parts described?
– Based on location by the heart
Which structure will you see in every mediastinal part?
Esophagus
When do you see the thymus in the cranial mediastinum?
– In young animals
What structure is dominated in the cardiac mediastinum?
-heart
how does the L phrenic n run?
-drops down and runs to L side of heart
what is the plica VC?
-outpouching of mediastinum (not mediastinum proper)
-holds CaVC, R phrenic n
what is the pulmonary ligament?
-no strength
-not an actual membranous ligament
-area where mediastinal pleura becomes visceral pleura push against each other
-mediastinum to lungs
where does the pulmonary ligament extend?
caudally from principal bronchi → caudal part of lung
what is very important to note about the mediastinum?
-perforated
NOT CLOSED
what is the clinical significance of the holes in the mediastinum ?
-so the R and L sides can communicate
-but if there is a problem on one side it will affect both sides
definiton:
cupulae pleurae
pleural cups
-cranial part of pleural sac
-by thoracic inlet
definition:
costo-diaphragmatic recess
-”open” space between diaphragmatic and costal pleura
-lung does not go here
-during inspiration, diaphragm flattens and recess enlarges
allows for some movt of lungs into space
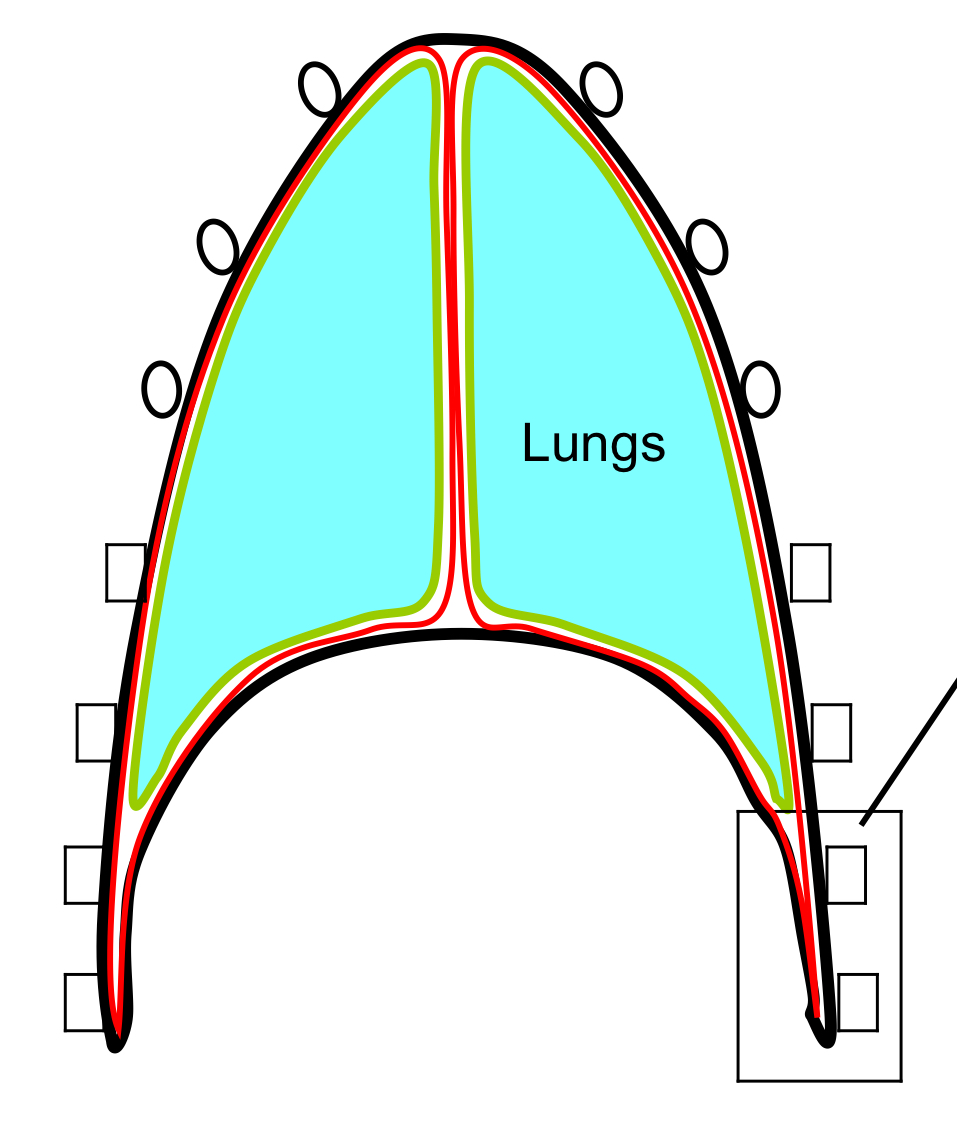
costo-diapragmatic recess
what are the first two structures that come off trachea to lungs?
-principal bronchi
what structure comes off each bronchi and then to lung?
-2ndary bronchi OR lobar bronchi
what is the basic lung lobe pattern across all species?
-4 lobes on R
-2 lobes on L
which lung BORDER may extend into costo-diaphragmatic rececess?
-basal/diaphragmatic
what is the pluck view?
-if you were to hold the trachea, how the lungs fall into place
-view from dorsal
in terms of pluck:
location of dorsal border
-inside
pluck:
ventral border location
outside
pluck:
basal border location
costo-diaphragmatic recess
why do pigs and ruminants have an additional tracheal bronchus?
-R cranial lobe is quite large
-to support and allow more air need another tube
what is the general pattern of the lungs as animals get bigger?
(excluding eq)
-lungs get larger and more complex
which animal has the most complex lung?
-ruminants
which animal has a similar lung to ox?
-sheep
which animal does not have a middle lobe?
-horses
why is there a cardiac notch?
-during inspiration, the lungs expand
-need an area where lungs won’t crush heart
-sternal side
-heart will never touch sternum but close
definition:
hilus of lung
-root
-where everything attaches to mediastinum
-anchors lunch to trachea & heart