Global climate change
1/52
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Weather
This refers to the day-to-day changes in the atmosphere
Climate
This refers to the average weather conditions over a long period of time
Climate change
This refers to the long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns
What is the most notable change in the Earth’s climate?
Rising global temperatures
Global temperature anomaly
This is how much warmer or cooler it is than the long-term average, between 0-4°C
What are the six greenhouse gases?
Carbon dioxide
Chlorofluorocarbon
Methane
Nitrous oxide
Ozone
Water vapour
Why are greenhouse gases vital for life on Earth?
They trap enough heat to ensure life on Earth can be sustained, without them the average global temperature would be 18°C
The greenhouse effect
This is a natural process in which greenhouse gases in the atmosphere trap heat from the sun
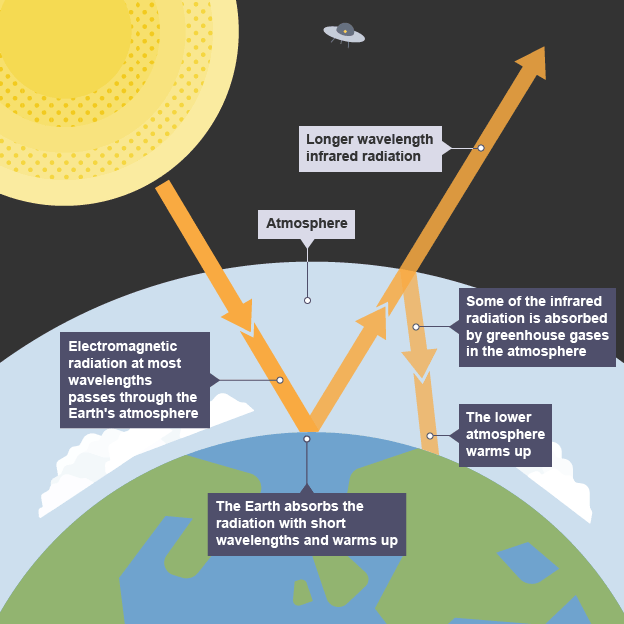
The greenhouse effect
What are the eight human causes of climate change?
Cement
Chemicals
Deforestation
Energy use in buildings
Landfills
Livestock
Rice cultivation
Transport
Cement
Limestone is converted to lime, which releases CO2 that otherwise would have been left in the rock
Chemicals
Chemicals such as ammonia are use in cleaning supplies, which releases CO2 and N2O as a byproduct
Deforestation
This means that there is less vegetation to take in CO2, which reduces how CO2 is stored
Energy use in buildings
Buildings use electricity as a source of power, which uses fossil fuels like CO2 to heat
Landfills
Waste products are sent to landfills, decaying in low oxygen environments, which emits methane
Livestock
Animals kept as livestock produce methane when microbes in their digestive systems breaks down grass, which is released in the atmosphere
Rice cultivation
As the global population increases, the demand for rice increases, which emits methane when the crop dies
Transport
Most transport uses fuels deprived from oil, which releases CO2 and N20 as the engine burns
What are the five physical causes of climate change?
Melting icecaps
Milankovitch cycles
Ocean circulations
Solar variations
Volcanic eruptions
Melting/retreating icecaps
This exposes the land underneath, which reduces the albedo effect and when the permafrost melts methane is released
What are the three Milankovitch cycles?
Axial precessions (axis wobble)
Changes in eccentricity (orbit shape)
Changes in obliquity (axis tilt)
What are the two ocean circulation episodes?
El Niño and la Niña
Solar variations
Sunspots are storms on the sun’s surface that releases intense amounts of magnetic energy, this leads to sun flares that are violent eruptions that can reach temperatures up to 20 million degrees
Volcanic eruptions
Huge amounts of ash, dust, and gases like SO2 are released into the atmosphere which reflects the sun’s energy, this causes the temperature to drop as the sun’s energy is not reaching the Earth’s surface
Solar maximum (solar variations)
This is when the sun is most active, resulting in global warming
Solar minimum (solar variations)
This is when the sun is least active, resulting in global cooling
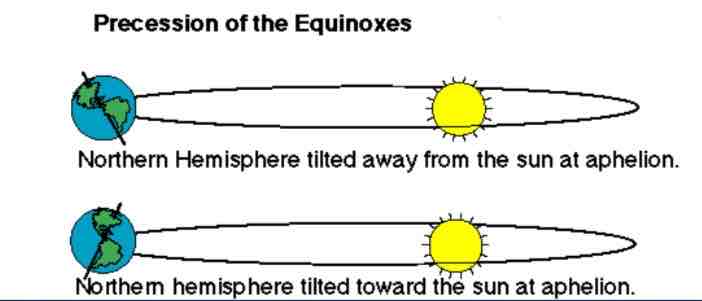
Axial precessions (axis wobble)
The Earth wobbles on its axis, which can change the timings of seasons and affect how big the range in temperatures is
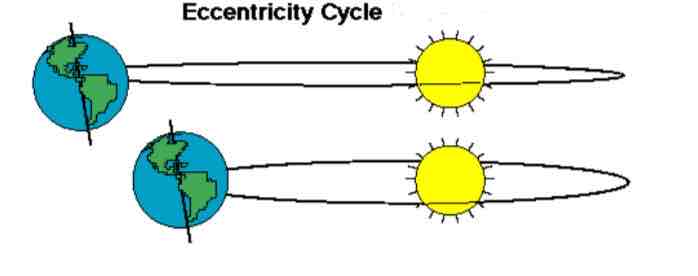
Changes in eccentricity (orbit shape)
The Earth’s orbit stretches, causing changes in how close or far away Earth is to the sun
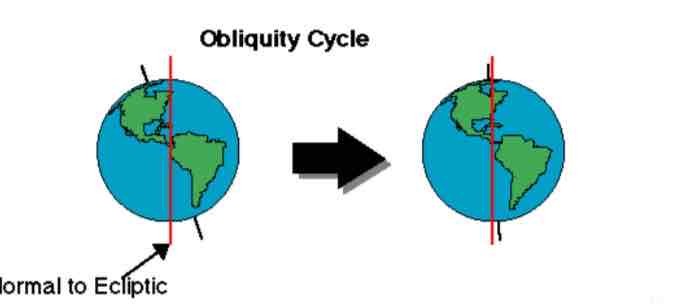
Changes in obliquity (axis tilt)
A greater tilt means more sunlight in the polar regions, which reduces the likelihood of ice building up
Positive feedback loop
When ice melts, the land and oceans absorb the suns energy instead of reflecting it
El Niño
This occurs when there are above-average sea-surface temperatures over equatorial pacific, bringing warmer and wetter weather
What are the eight impacts of climate change?
Air pollution
Conflict and tension
Drought
Falling crop yields and livestock deaths
Flooding of coastal communities
Heat waves
More frequent tropical storms
Reducing fish stocks
Air pollution
Local industry factories are outputting gases, which affects low-middle income countries as they cannot afford to move away
Conflict and tension
Countries that are dependant on other countries imports will loose out on resources, which affects a countries resources as they can no longer make an income from trading
Falling crop yields and livestock deaths
Droughts and/or heatwaves can cause crops to die, which affects a country as they will need to rely on outside help to not starve
Flooding of coastal communities
The surrounding water rises and floods are becoming more likely, which affects smaller countries that live on islands as households become lost due to damage
Heat waves
Rising temperatures can affect already hot countries as the temperatures continue to rise, which affects people who cannot afford air-conditioning or water storages as they become prone to health concerns like heat stroke
Reducing fish stocks
As waters become warmer fish will migrate to cooler waters, which affects communities that rely on fish as a food course as people will go hungry and loose an income
More frequent tropical storms
Rising sea temperatures contribute to an increased risk of tropical storms, which affects countries that live in tropical areas as some communities cannot rebuild as easily as others
Drought
Warming temperatures can cause places to dry, which affects countries that rely on agriculture as they are no longer able to rely on their country to produce food
What two things are required to manage climate change?
Adaptation and mitigation
Adaptation
The response to the impacts that are already occurring because of climate change
Mitigation
The reduce the rising levels of greenhouse gases in our atmosphere
What are the eight mitigation strategies?
Afforestation schemes
Carbon trading
Eating less meat and shopping local
Home energy efficiency grants
Improvements in public transport
Low emission zones
Recycling
Renewable energy
Afforestation schemes and its effectiveness
The Great Green Wall is a mass tree planting scheme spanning from Senegal to Djibouti that aims to reduce desertification and offers sustainable firewood, this is ineffective due to as of 2020 only 4% of the great green wall has been planted
Carbon trading and its effectiveness
Trading systems within countries helps meet the global reduction of the world’s greenhouse gas emissions, this is effective as businesses have been forced to become more efficient and pollute less
Eating less meat and shopping local and its effectiveness
Some people include more plant based foods in their diet, resulting in less methane being emitted, this is effective as between 2019-2020 there has been an increase of 46% people buying vegan meals
Home energy efficiency grants and its effectiveness
Councils provide money to upgrade council housings as to not let energy escape, this is effective as it reduces council housing prices while still heating homes
Improvements in public transport and its effectiveness
Edinburgh city council has come up with a ‘city mobility plan’ which aims to reduce the number of km travelled by cars, this is effective as it has reduced the volume of cars travelling in and out of Edinburgh’s city centre
Low emission zones and its effectiveness
These are designed to reduce emissions by restricting the most polluting vehicles, this is effective because between 2017-2022 CO2 emissions decreased by 46%
Recycling and its effectiveness
This reduces the amount of items going into low oxygen level environments in order to reduce methane levels, this is effective as it helps to control the disposal of large items such as fridges to ensure CFC’S do not go into the atmosphere
Renewable energy and its effectiveness
Investing in wind farms, solar panels, and hydro/geothermal power aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 80% before 2030, this is effective as emissions fell by 57% in 2017
La Niña
This occurs when there are below-average sea-surface temperatures over the Pacific, brining cooler and drier weather