Forces and Newtons 1st Law`
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
How do you calculate Normal Force?
kg x 9.8
How do you calculate Friction Force?
M (coefficient of friction) x Fnorm
If the free body diagram is balanced, the net force is always ___
zero
weight is the same thing as…
normal force
How do you find the coefficient of friction (M)?
Ffric / Fnorm
the amount of stuff present in an object. Metric unit (kg), doesn’t depend upon location, the same object has the same mass on all planets
mass
the force of gravity acting upon an object. Metric unit (N), does depend upon location, the same object weighs differently on different planets
weight
how do you calculate weight
weight = Fgrav = mass x gravitational field
what does a 15kg box weigh on earth
147 N (15kg)(9.8)
a push or pull acting on an object, forces include gravity, friction, and applied force. causes changes in the speed or direction of motion. these changes are called acceleration. a vector because it has both size and direction.
force
if tow forces act on an object in opposite directions, the _______ is the sum of the two forces. the _____ is always greater than or equal to zero but less than either of the individual force
net force
states that an object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion with a constant speed in a straight line unless the object is acted on by an unbalanced force
Newtons 1st Law
objects with greater mass have greater ___
inertia
to change the motion of an object _____ must be overcome by an unbalanced force acting on the object
inertia
when an object is at rest, forces are ___
balanced
when an object moves with constant velocity, forces are
balanced
when an object speeds up, slows down, or changes direction, forces are
unbalanced
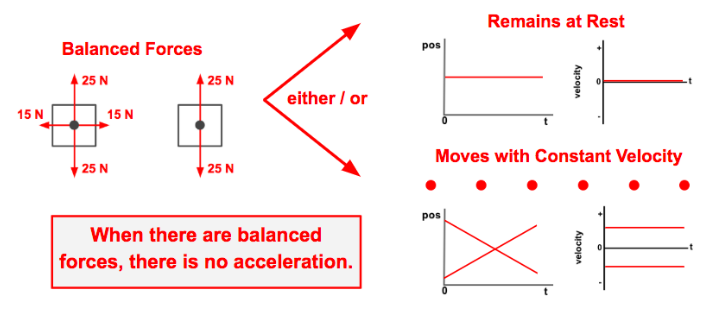
the following image is an example of a _____ force
balanced
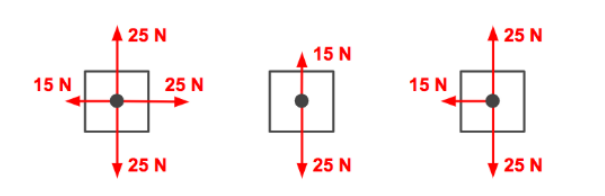
the following image is an example of a _____ force
unbalanced
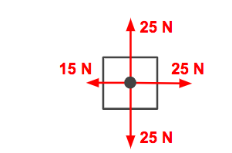
the following image is an example of a _____ force
rightward unbalanced (rightward acceleration)
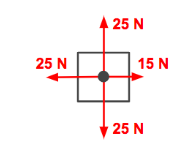
the following image is an example of a _____ force
leftward unbalanced (leftward acceleration)
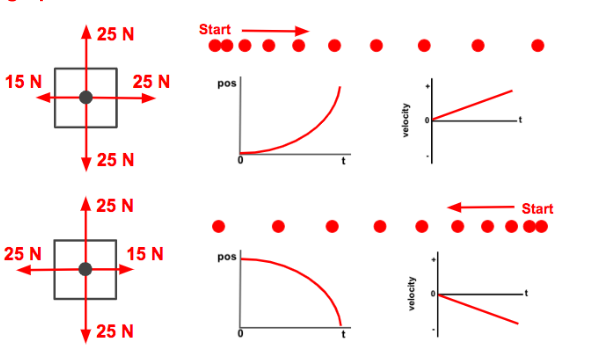
the following image represents _____ motions
speeding up
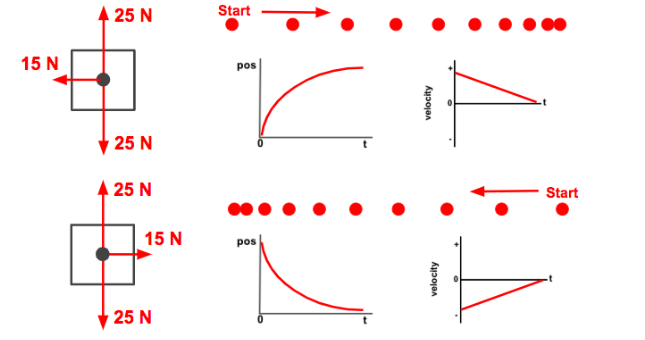
the following image represents _____ motions
slowing down
ALWAYS PRESENT. The non-contact force acting between any two objects with mass; most significant when one or both objects are very massive. Always acts downwards on objects. ex. The Earth pulls downward upon any object that is near it.
Gravity force (Fgrav)
RESULTS FROM TWO SURFACES PRESSING AGAINST EACH OTHER. The force resulting when an object presses against another object. This force is often observed to be a support force from a stable surface upon which or against which an object rests. ex. . A person stands on the floor. The floor pushes up on the person with an Fnorm. 2. Book at rest on a table. The table pushes up on the book with an Fnorm.
Normal Force (Fnorm)
FORCE FROM STRING, ROPE, WIRE, CABLE, ETC. The force transmitted through a string, rope, cable, or wire that is pulled tight. The rope pulls with a tension force on both objects. ex. A box hangs from the ceiling by a cable. The cable exerts an upward tension force on the box. 2. A dog chain pulls a dog. The chain exerts a force upon the dog.
tension force (Ftens)
FORCE FROM COMPRESSED/STRETCHED SPRING. The force exerted upon an object by a stretched or compressed spring. ex. A mass is suspended from the ceiling by a spring. The spring exerts an upward pull upon the mass.
Spring Force (Fspring)
TWO SURFACES SLIDING ACROSS EACH OTHER. The force between two surfaces that are sliding (or attempting to slide) across each other. Friction opposes the motion of the sliding object. ex. A truck skids to a stop along a road. Friction exerts a backward force upon the truck. 2. A baseball player slides across the infield dirt. There is a backward friction force on the player
Friction Force (Ffrict)
OBJECT MOVES THROUGH SURROUNDING AIR. A force acting upon an object that is moving through air. Air resistance is greatest for high speed objects that have poor aerodynamics. ex. . A skydiver is falling. Air resistance acts upward on the skydiver. 2. A truck is moving at high speed. Air resistance acts backward on the truck.
Air resistance Force (Fair)
A PERSON PUSHING/PULLING ON AN OBJECT. The force exerted upon an object by a person (usually) or thing. This force is usually a “catch-all” type of force to account for any force not covered by the other types. If you’ve already counted the crate-worker interaction by another type (such as normal force), don’t count it again. ex. A worker pushes a crate up a hill. There is an applied force on the crate (by the person).
Applied Force (Fapp)
the friction force that resists the sliding of two moving surfaces past one another
kinetic friction
a property of matter which keeps stationary objects at rest and moving objects in motion at constant velocity. All objects have ____. A more massive object has more _____ than a less massive object
inertia
The standard metric unit of is _____ the kilogram. _____ depends on how much matter is present in an object. If all other variables are equal, then an object with a greater _____ would have a more difficult time accelerating.
mass