anat3022 lectures 1-11
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/458
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 6:23 AM on 9/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
459 Terms
1
New cards
Structural organisation of NS
central nervous and peripheral nervous system
2
New cards
Functional organisation of NS
somatic and autonomic systems (becomes sympathetic and parasympathetic systems)
3
New cards
Cellular organisation of NS
neurones and glial cells
4
New cards
Glia
Non-neuronal cells that provide support and protection for neurons in the nervous system
5
New cards
Astrocytes
A type of glial cell that provides trophic, metabolic and structural support and nourishment to neurone. Part of BBB.
6
New cards
Oligodendrocytes
A type of glial cell that produces myelin, which insulates and protects neurones. Dysfunction indicated in MS
7
New cards
Microglia
The immune cells of the central nervous system that remove cellular debris and bacteria via phagocytosis and release of cytokines/chemokines. Indicated in Alzheimer’s
8
New cards
neurocranium
comprised of cranial vault and cranial base. brain is held via anterior, middle, and posterior cranial fossa (ditches)
9
New cards
hole in cranial base
foramen magnum
10
New cards
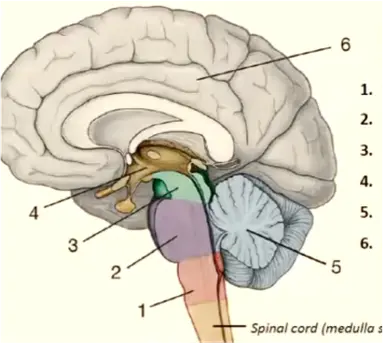
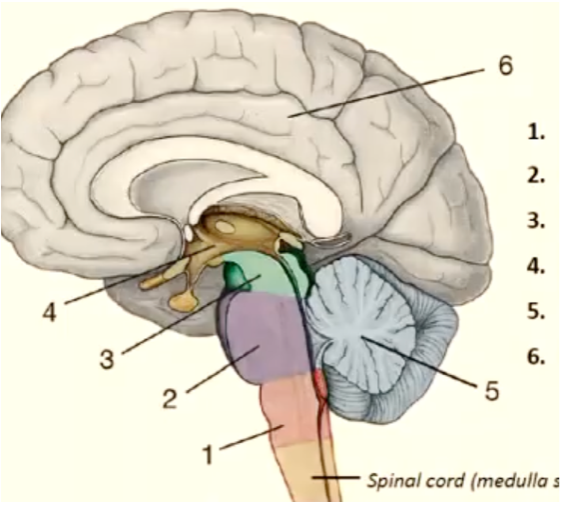
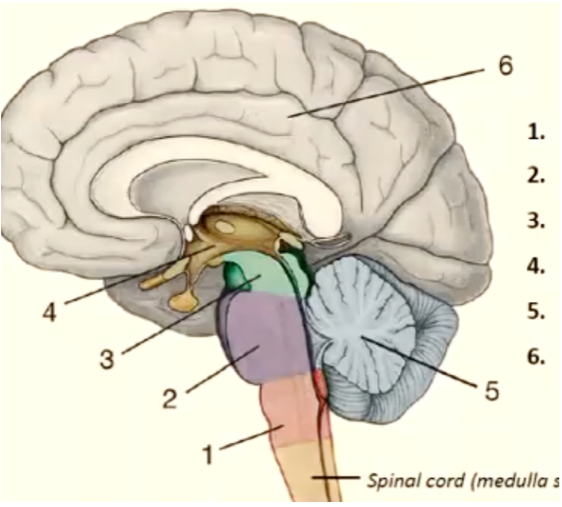
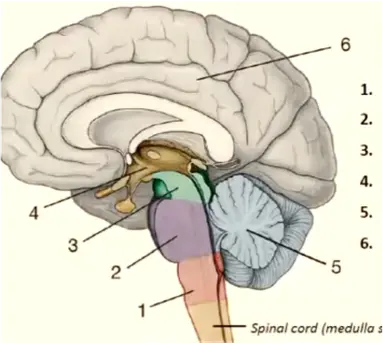
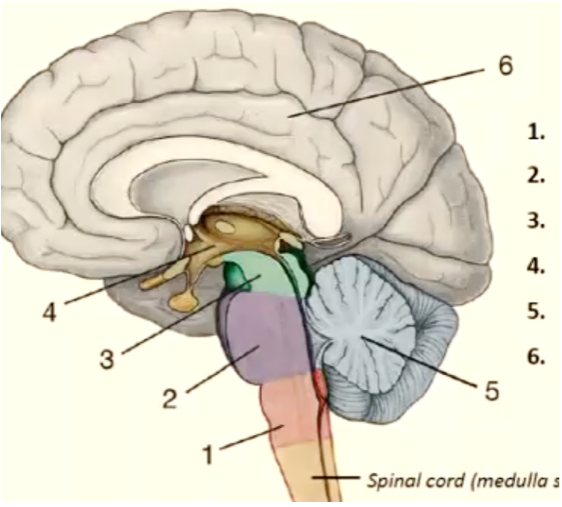
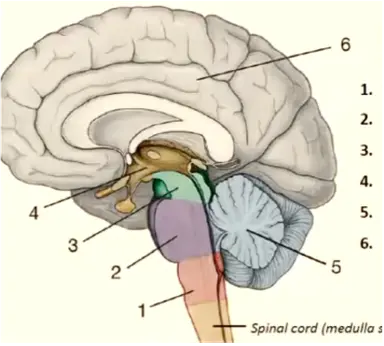
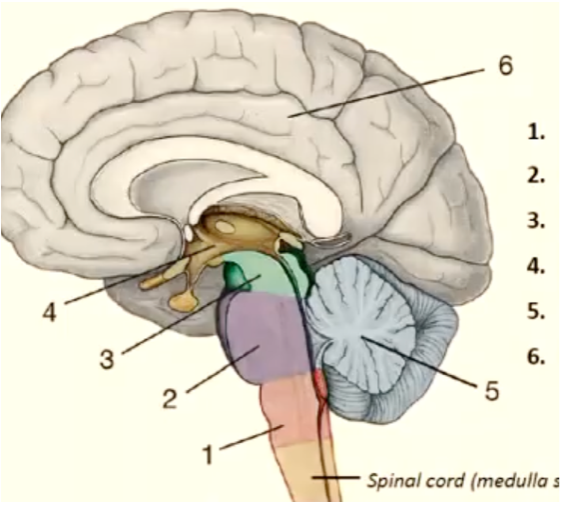
1
medulla oblongata
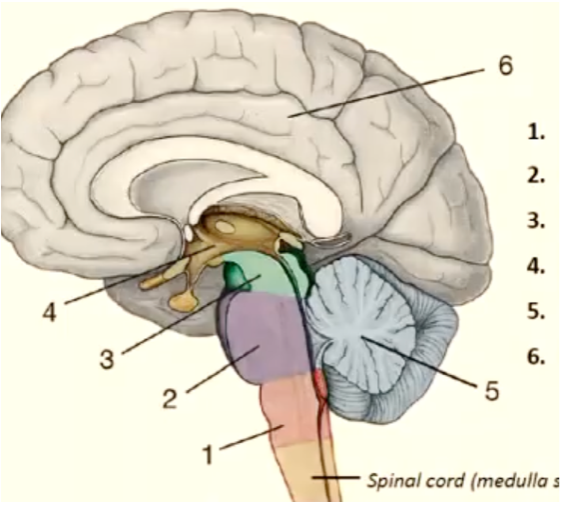
11
New cards
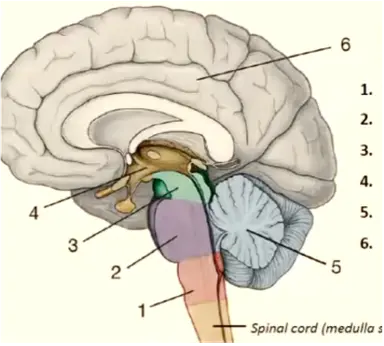
2
pons
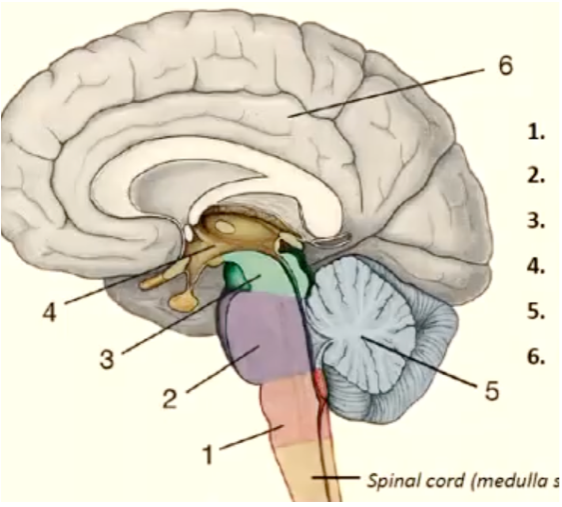
12
New cards
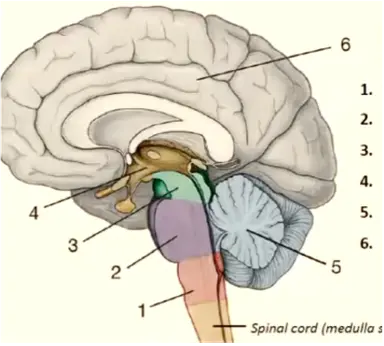
3
mesencephalon
13
New cards
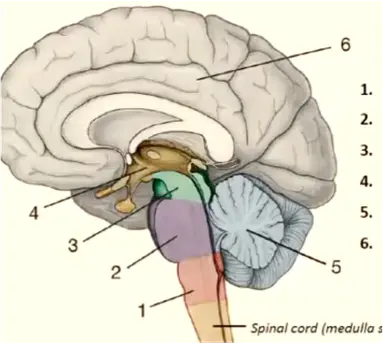
4
diencephalon
14
New cards
5
cerebellum
15
New cards
6
telencephalon
16
New cards
gastrulation
formation of 3 germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
17
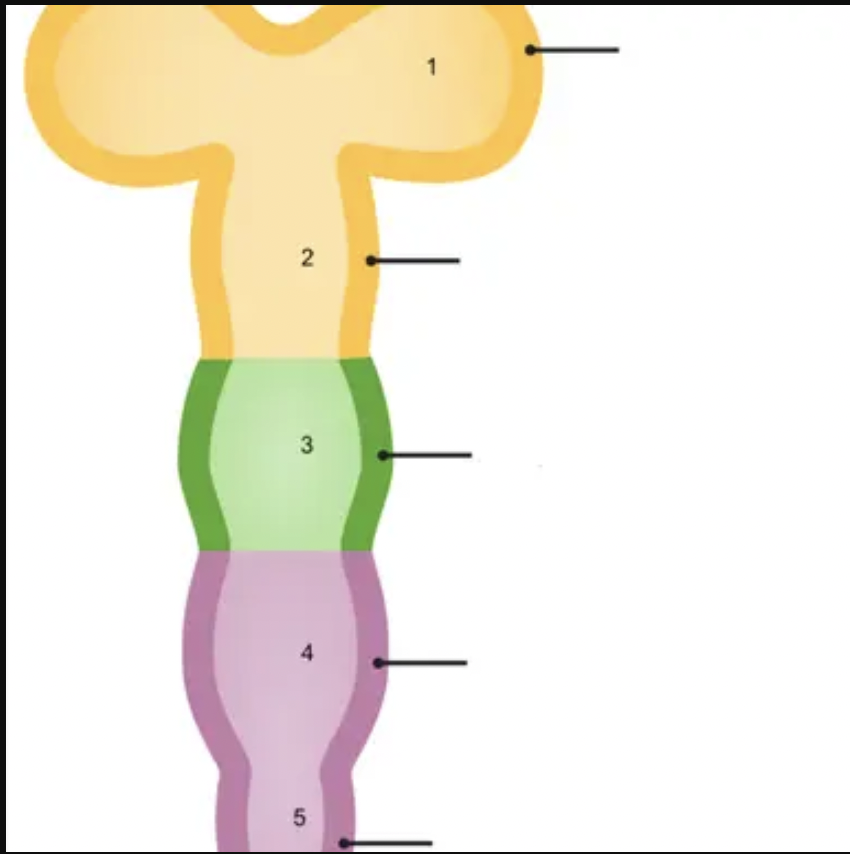
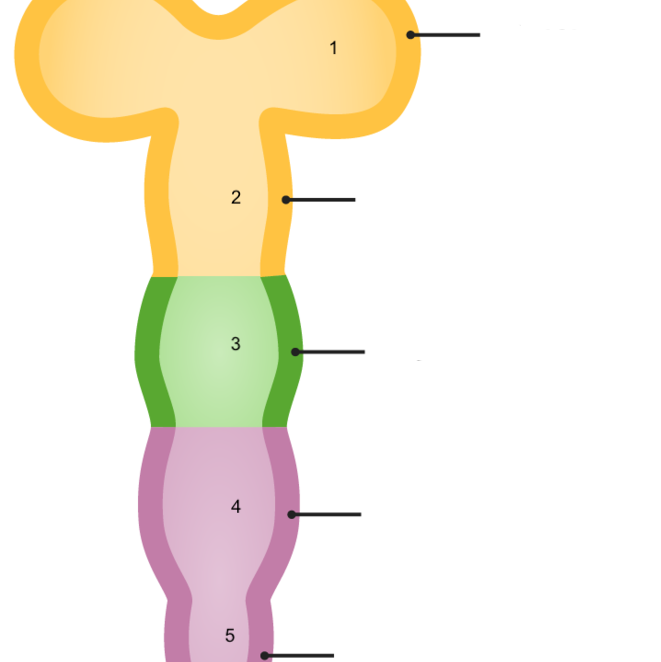
New cards
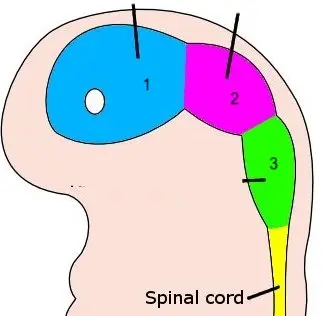
1
prosencephalon
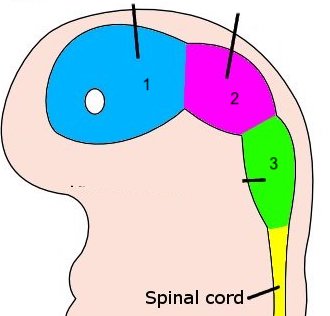
18
New cards
2
mesencephalon
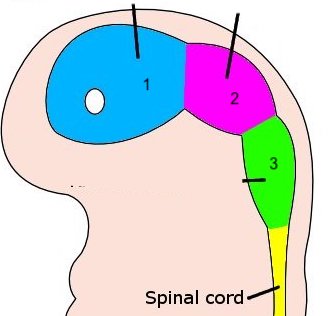
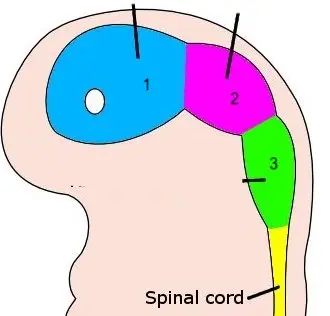
19
New cards
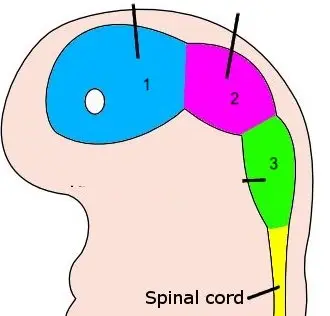
3
rhombencephalon
20
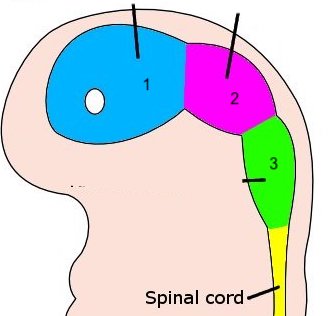
New cards
1
telencephalon
21
New cards
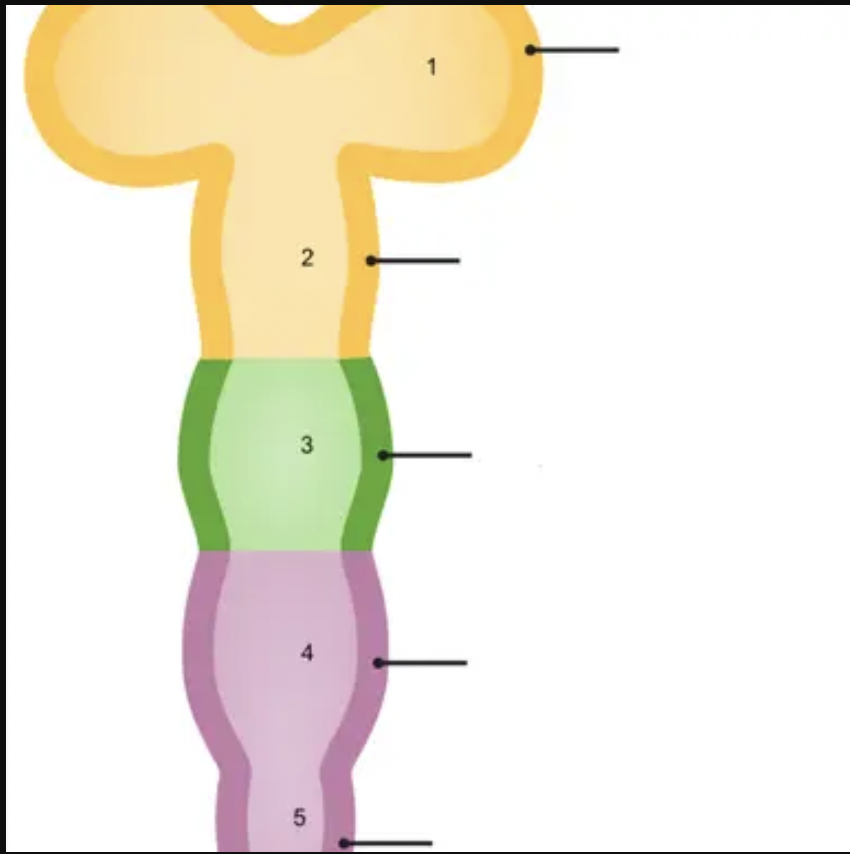
2
diencephalon
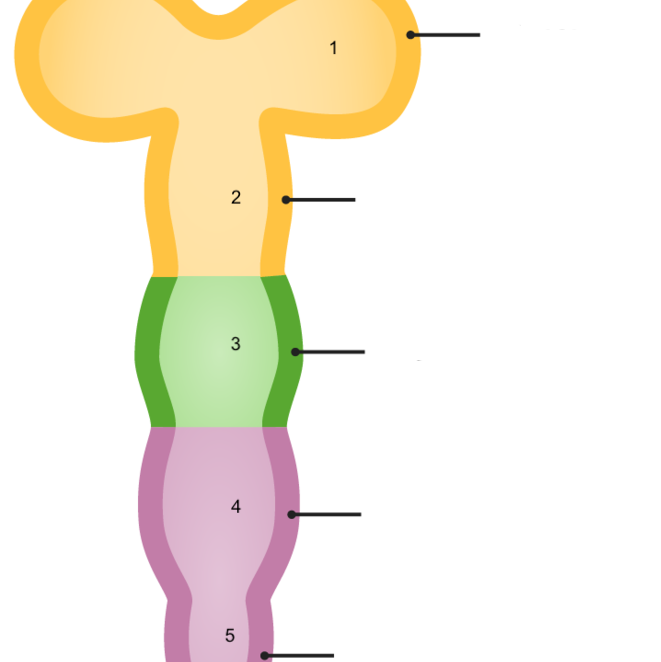
22
New cards
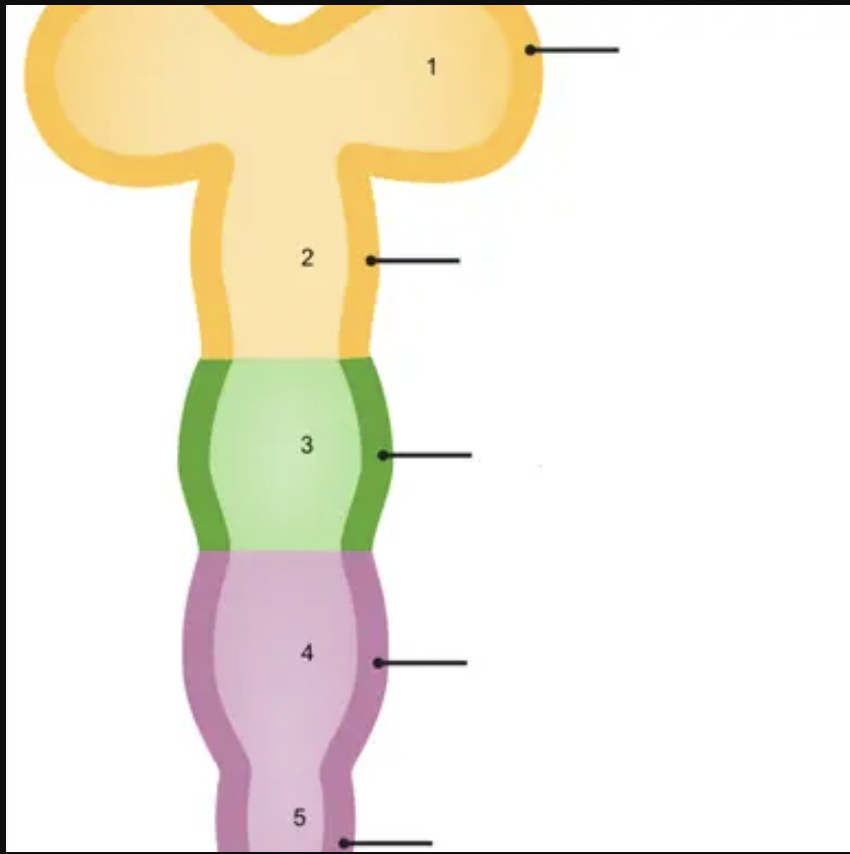
3
mesencephalon
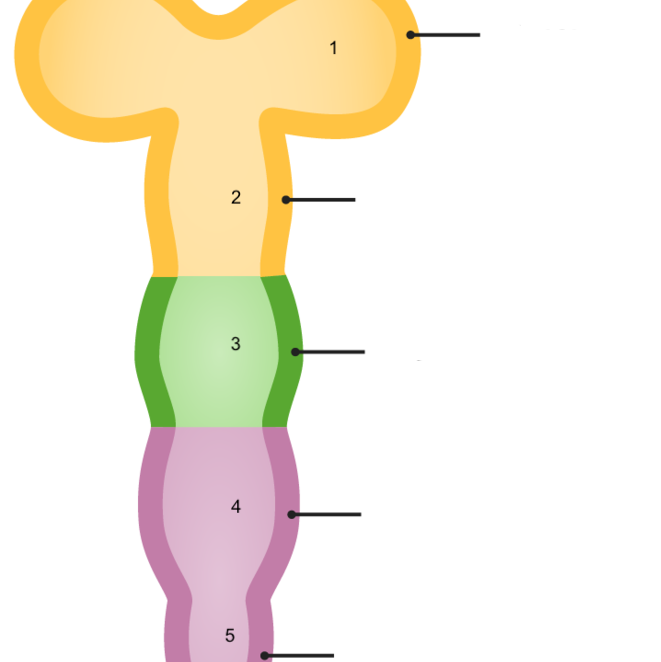
23
New cards
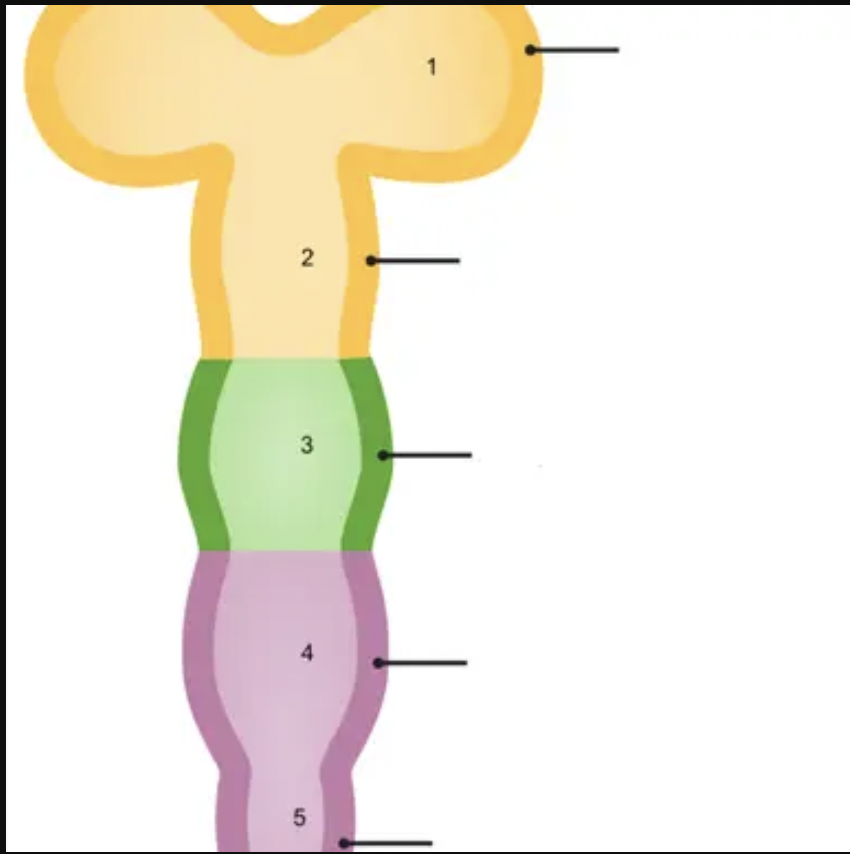
4
metencephalon
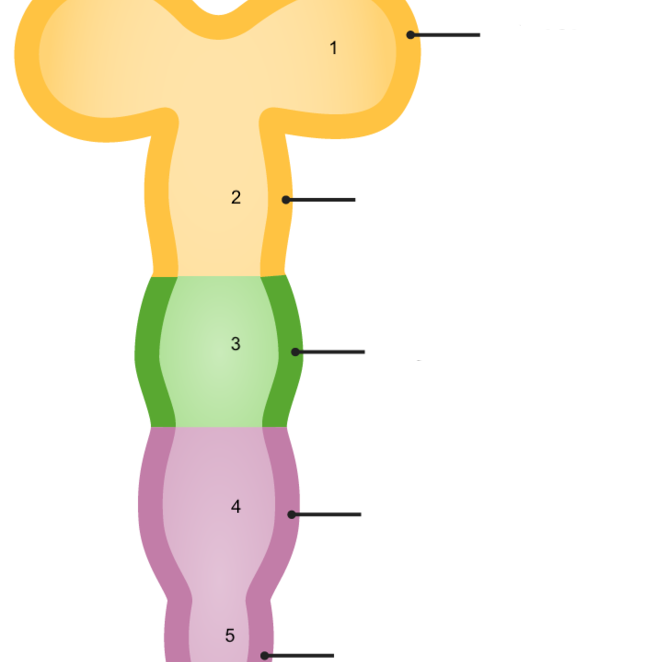
24
New cards
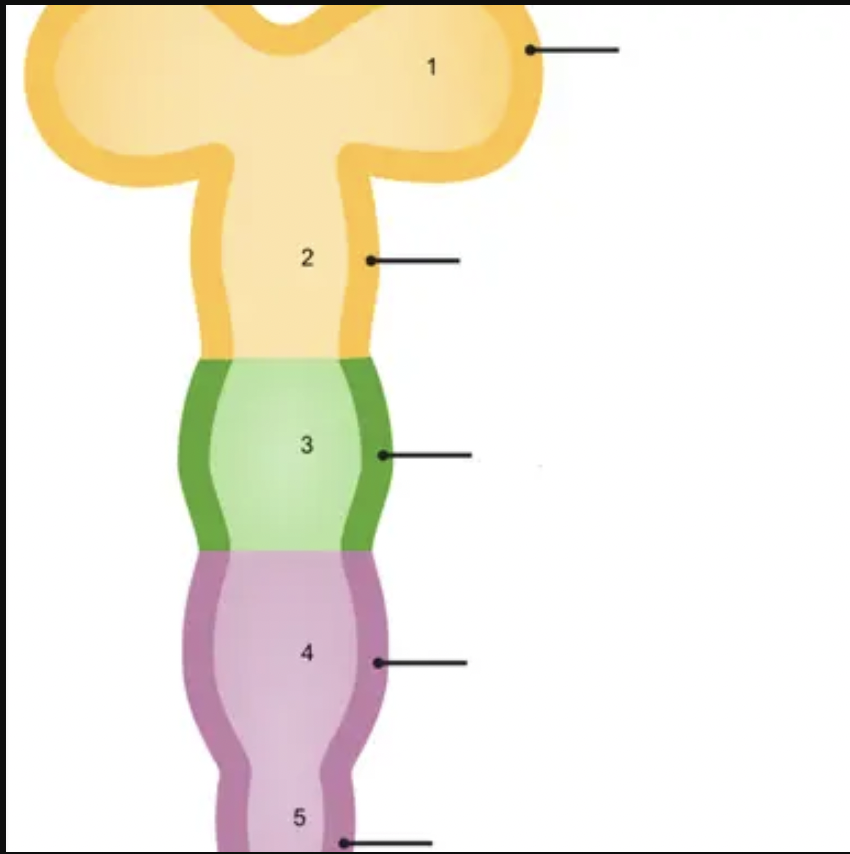
5
myelencephalon
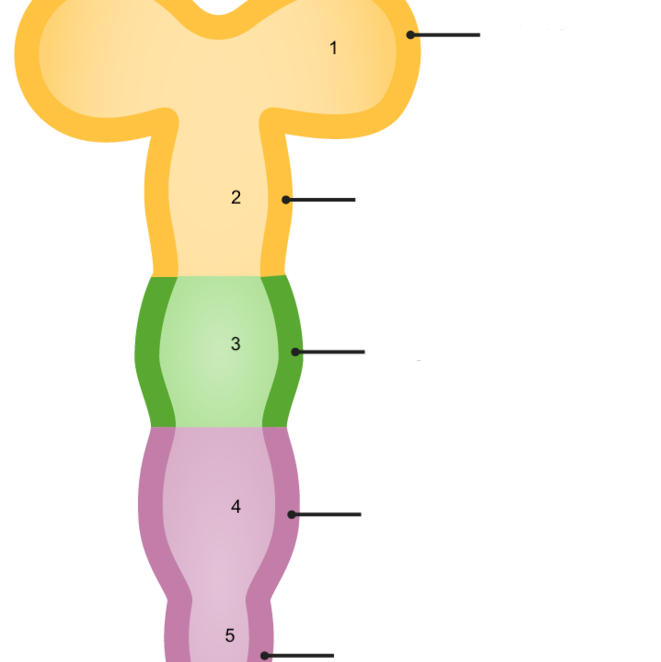
25
New cards
metencephalon is comprised of
pons and cerebellum
26
New cards
prosencephalon is comprised of
telencephalon and diencephalon
27
New cards
brainstem is comprised of
medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain
28
New cards
medulla oblongata function
The lower part of the brainstem that controls breathing and blood pressure.
29
New cards
pons function
The part of the brainstem that works with the cerebellum to coordinate movement.
30
New cards
mesencephalon/midbrain structures and functions
peduncles, tegmentum, tectum. sensory and motor functions.
31
New cards
diencephalon/interbrain structures and functions
pituitary, thalamus and hypothalamus. involved in hormone secretion and autonomic regulation (homeostasis)
32
New cards
cerebellum functions
motor learning, coordination, balance
33
New cards
telencephalon structures and functions
cerebrum; executive functions, memory, perception
34
New cards
brainstem structures and functions
medulla oblongata, pons, mesencephalon.
control of head/neck via cranial nerves, consciousness via reticular formation, supraspinal reflexes
control of head/neck via cranial nerves, consciousness via reticular formation, supraspinal reflexes
35
New cards
multipolar neurone
one of most abundant
‘classic neurone’
projecting neurones
motor and pyramidal neurones
‘classic neurone’
projecting neurones
motor and pyramidal neurones
36
New cards
unipolar neurone
exocrine glands and smooth muscle
37
New cards
bipolar neurone
senses, smell, sight
38
New cards
pseudo-unipolar neurone
sensory neurones, e.g. dorsal root ganglia
39
New cards
eminence
prominent protrusion
40
New cards
folia
cerebellar gyri
41
New cards
blue plane
coronal/frontal
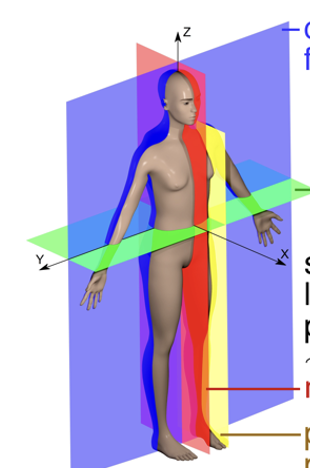
42
New cards
green plane
horizontal/axial/transverse
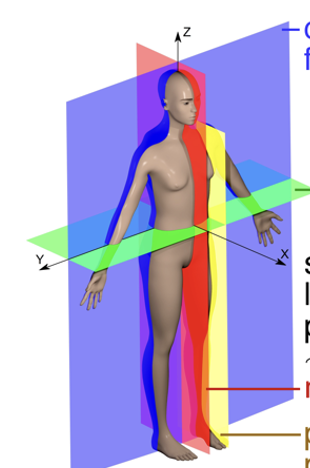
43
New cards
red plane
sagittal/longitudinal
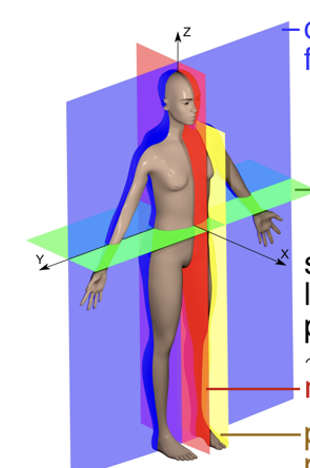
44
New cards
peduncle
prominent stalk attaching part to brain, interconnecting regions
45
New cards
meninges
membranous connective tissue
dura mater, leptomeninges (arachnoid and pia mater)
dura mater, leptomeninges (arachnoid and pia mater)
46
New cards
meninges inside longitudinal fissure
falx cerebri
47
New cards
meninges between base cerebrum and cerebellum
tentorium cerebelli
48
New cards
gyri/sulci of frontal lobe
3 horizontal: superior, middle, inferior
1 vertical: precentral
1 vertical: precentral
49
New cards
gyri/sulci of temporal lobe
superior, middle, inferior
transverse temporal (Heschl gyrus) (auditory cortex), found inside lateral sulcus
transverse temporal (Heschl gyrus) (auditory cortex), found inside lateral sulcus
50
New cards
commissural fibres of corpus callosum
connects frontal, occipital, parietal lobes (300m axons)
51
New cards
commissural fibres of anterior commissure
connects temporal lobes (5m axons)
52
New cards
association fibres
connect intra-hemispherically
53
New cards
short arctuate fibres
connect neighbouring gyri
54
New cards
long arctuate fibres
connect distant gyri
55
New cards
superior longitudinal fascicle
connects ipsilateral occipital and frontal lobes
56
New cards
inferior occipitotemporal fascicle
connects occipital and temporal lobes
57
New cards
cingulum and uncinate fascicle
connect limbic cortices of frontal and temporal lobes
58
New cards
arcuate fasciculus
connects Broca’s and Wernicke’s areas
59
New cards
projection fibres
efferent and afferent fibres connecting cerebral cortex with deep cerebral nuclei (e.g. basal ganglia), brainstem, and spinal cord
all projection fibres pass through corona radiata
all projection fibres pass through corona radiata
60
New cards
meninges
Membranous connective tissue covering the brain
61
New cards
3 layers of meninges
dura mater
arachnoid mater
pia mater
arachnoid mater
pia mater
62
New cards
dura mater
Thickest layer with 2 sub-layers: periosteal layer and meningeal layer. dura septa prevents brain displacement.
63
New cards
arachnoid mater
Middle layer with many blood vessels and contains the subarachnoid space filled with CSF.
64
New cards
pia mater
Innermost and thinnest layer that directly contacts the brain.
65
New cards
how CSF from the brain is returned
drains into sinuses of dural septa, which are large veins formed by meningeal layers, such as the superior sagittal sinus, inferior sagittal sinus, and sinus rectus/straight sinus.
From sinuses, CSF is drained into the jugular vein and re-enters the bloodstream
From sinuses, CSF is drained into the jugular vein and re-enters the bloodstream
66
New cards
superior sagittal sinus
on top of falx cerebri
67
New cards
inferior sagittal sinus
ventral to falx cerebri
68
New cards
sinus rectus (straight)
in middle of tentorium cerebelli
69
New cards
dura septa
where layers of dura mater split. prevents brain from moving around
70
New cards
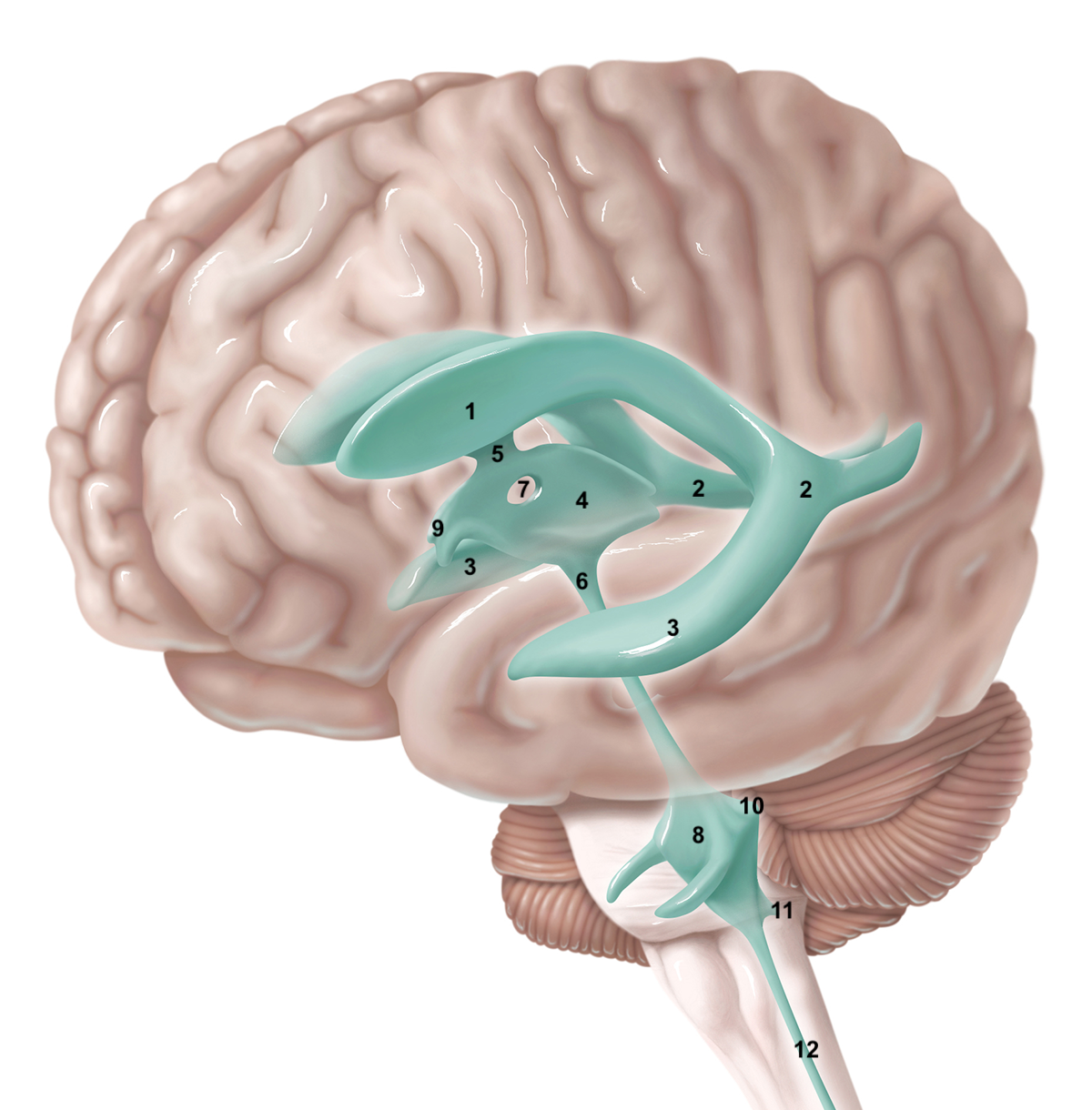
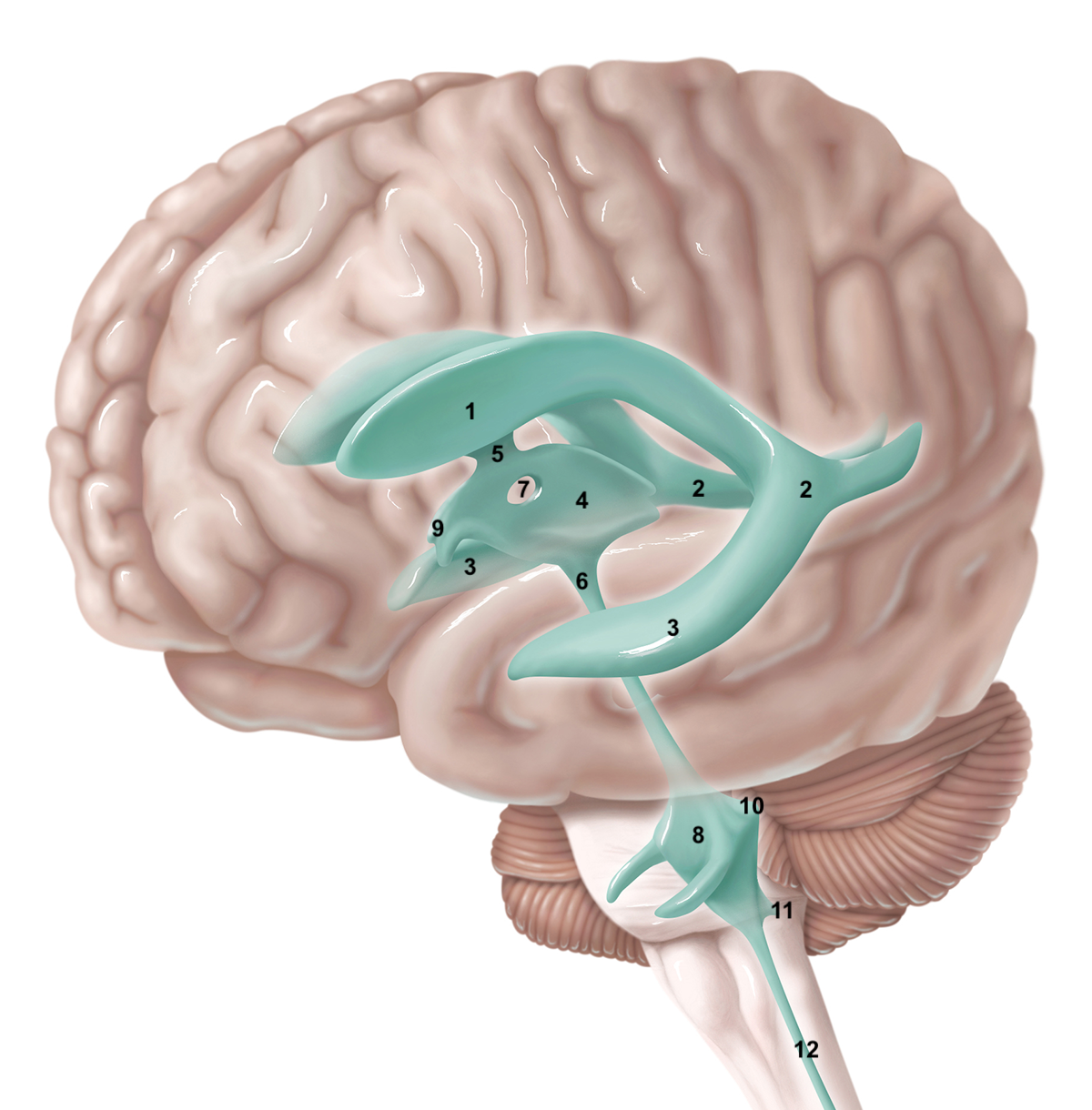
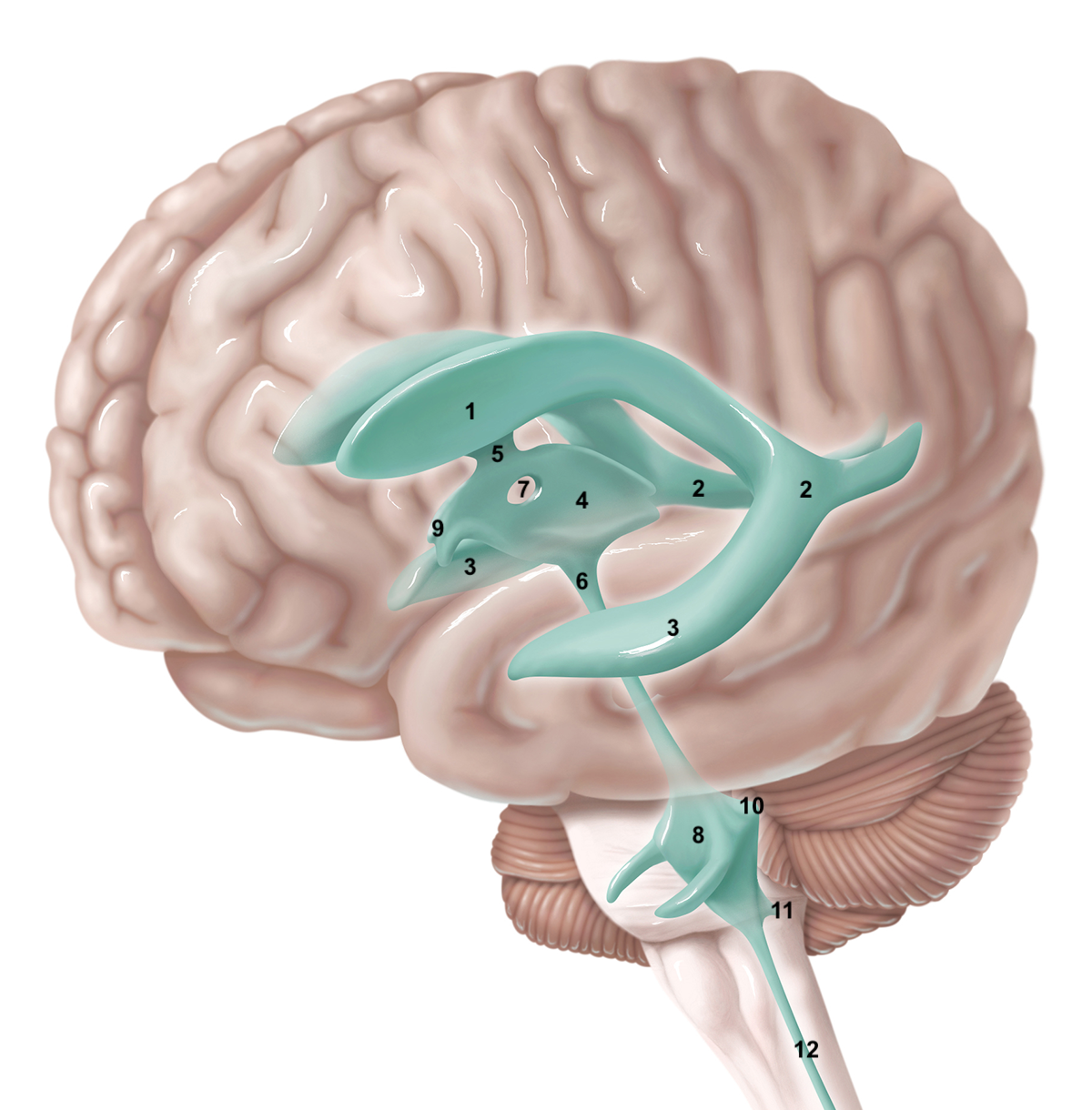
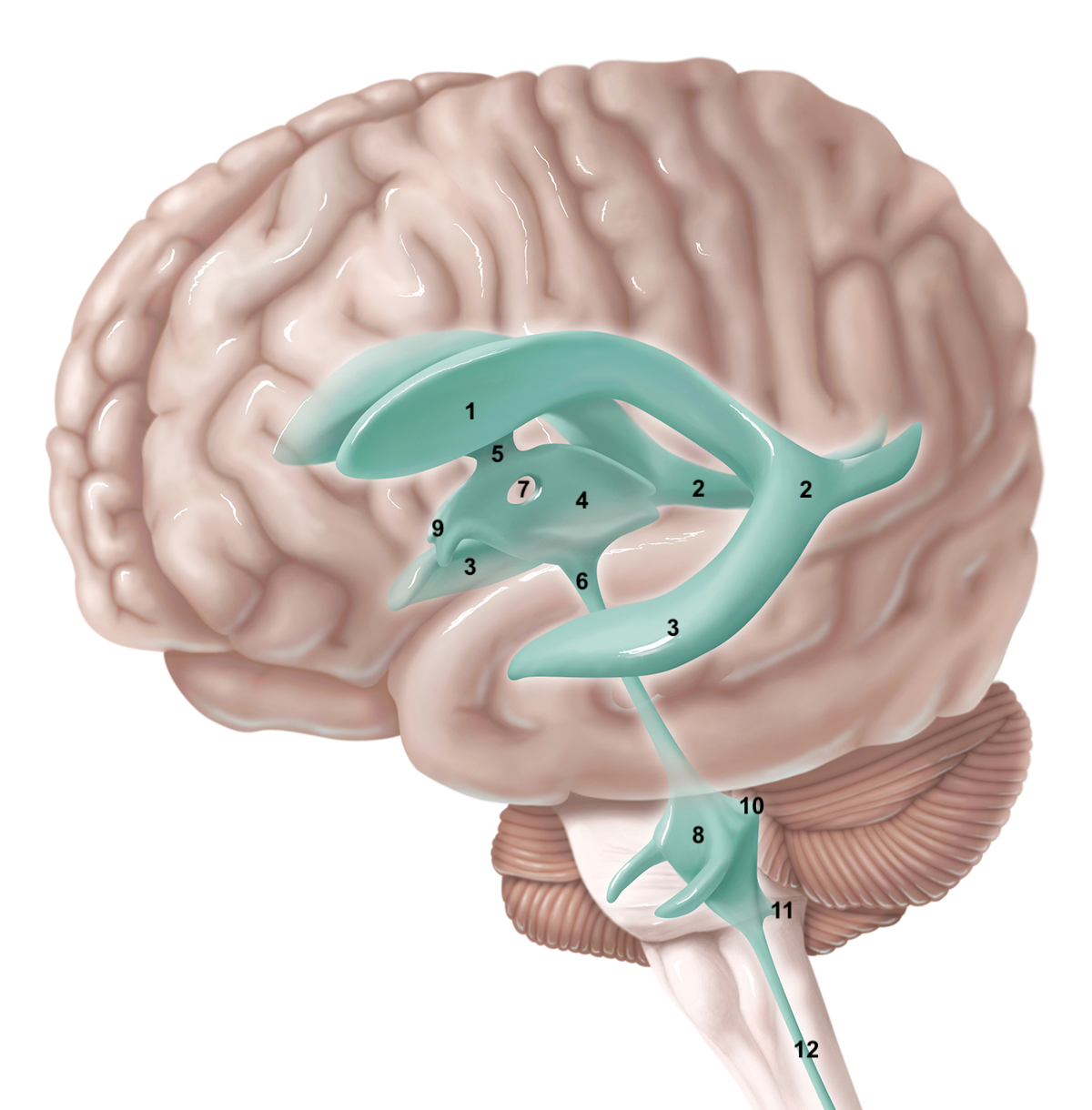
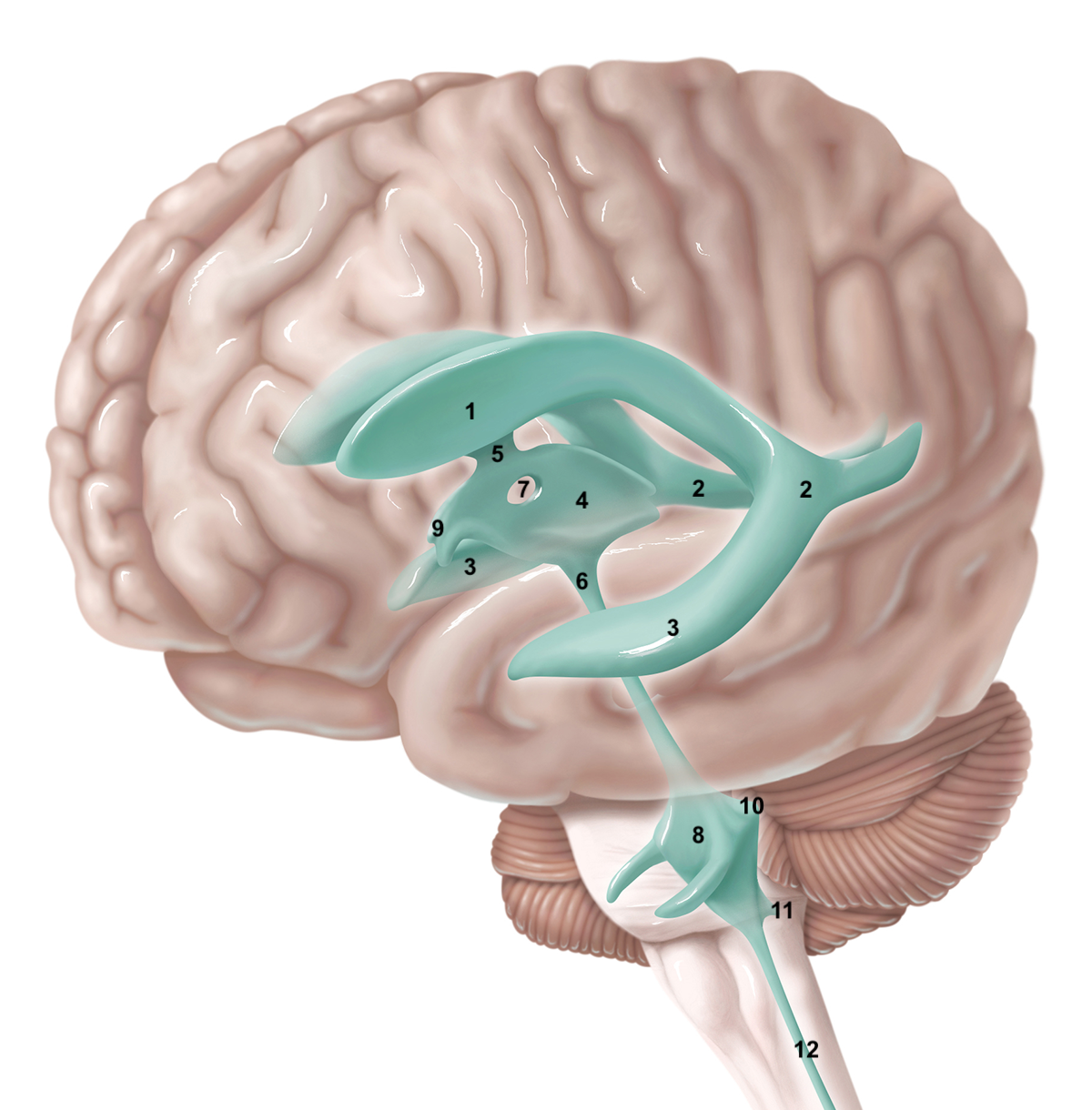
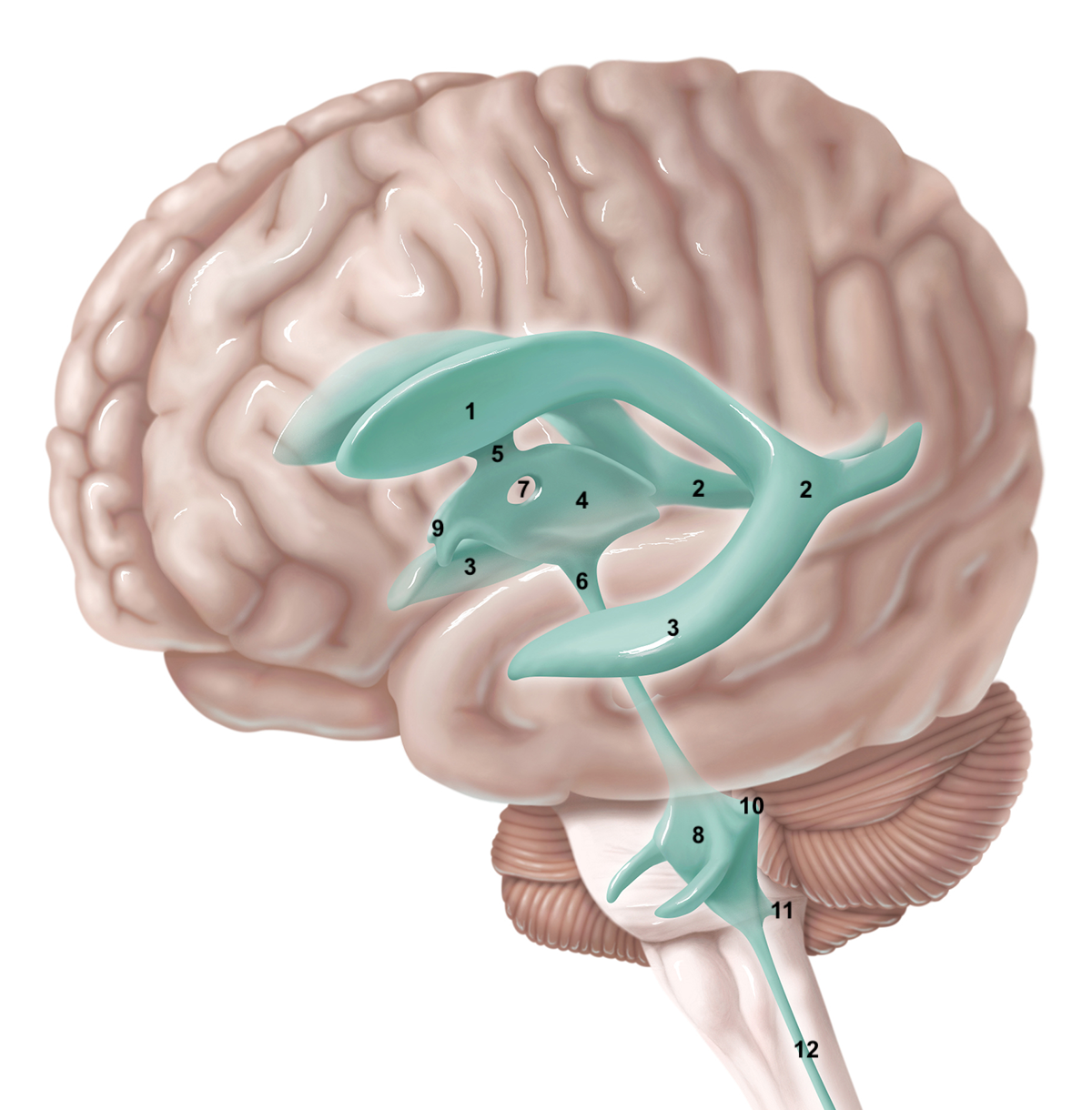
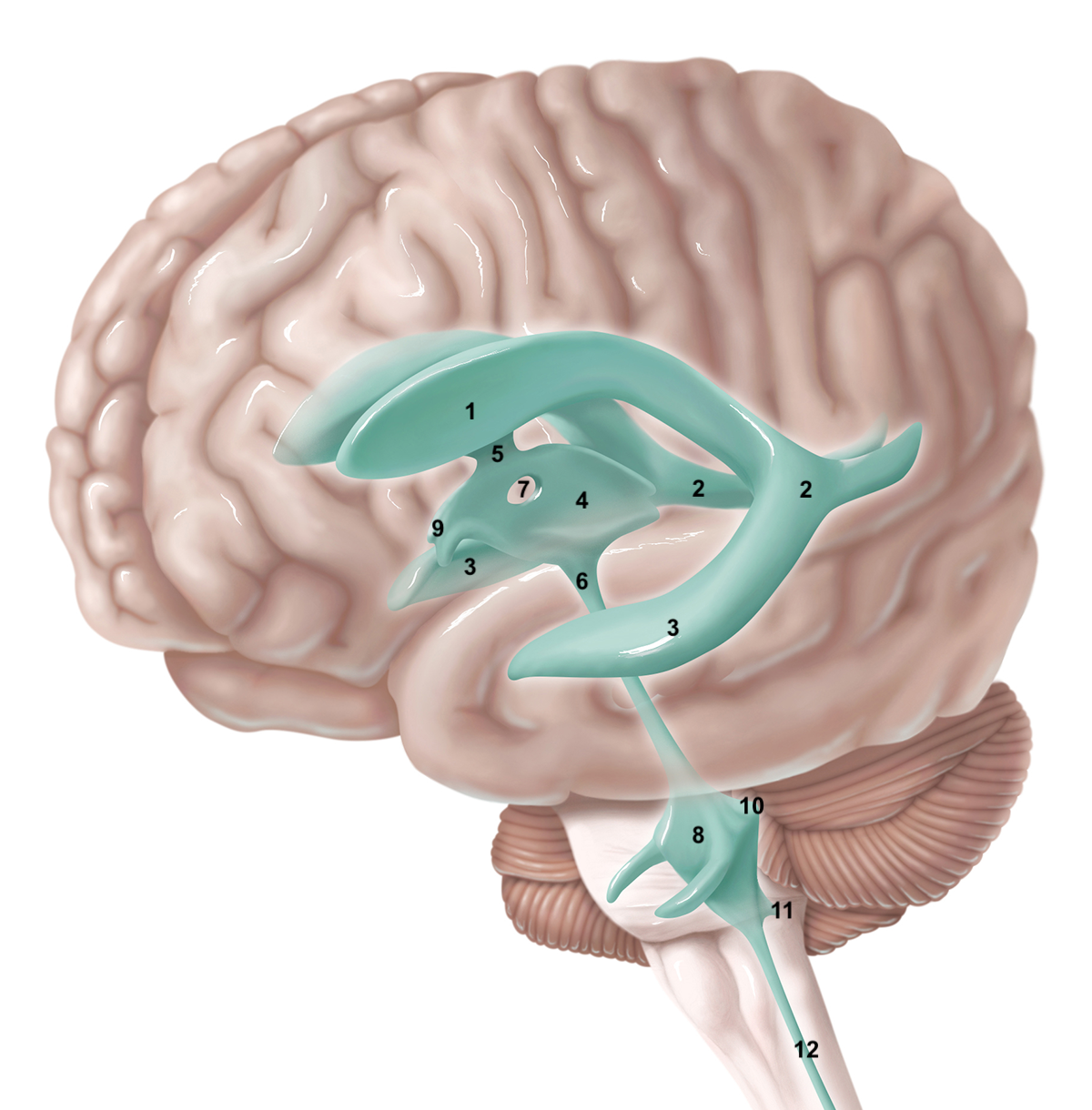
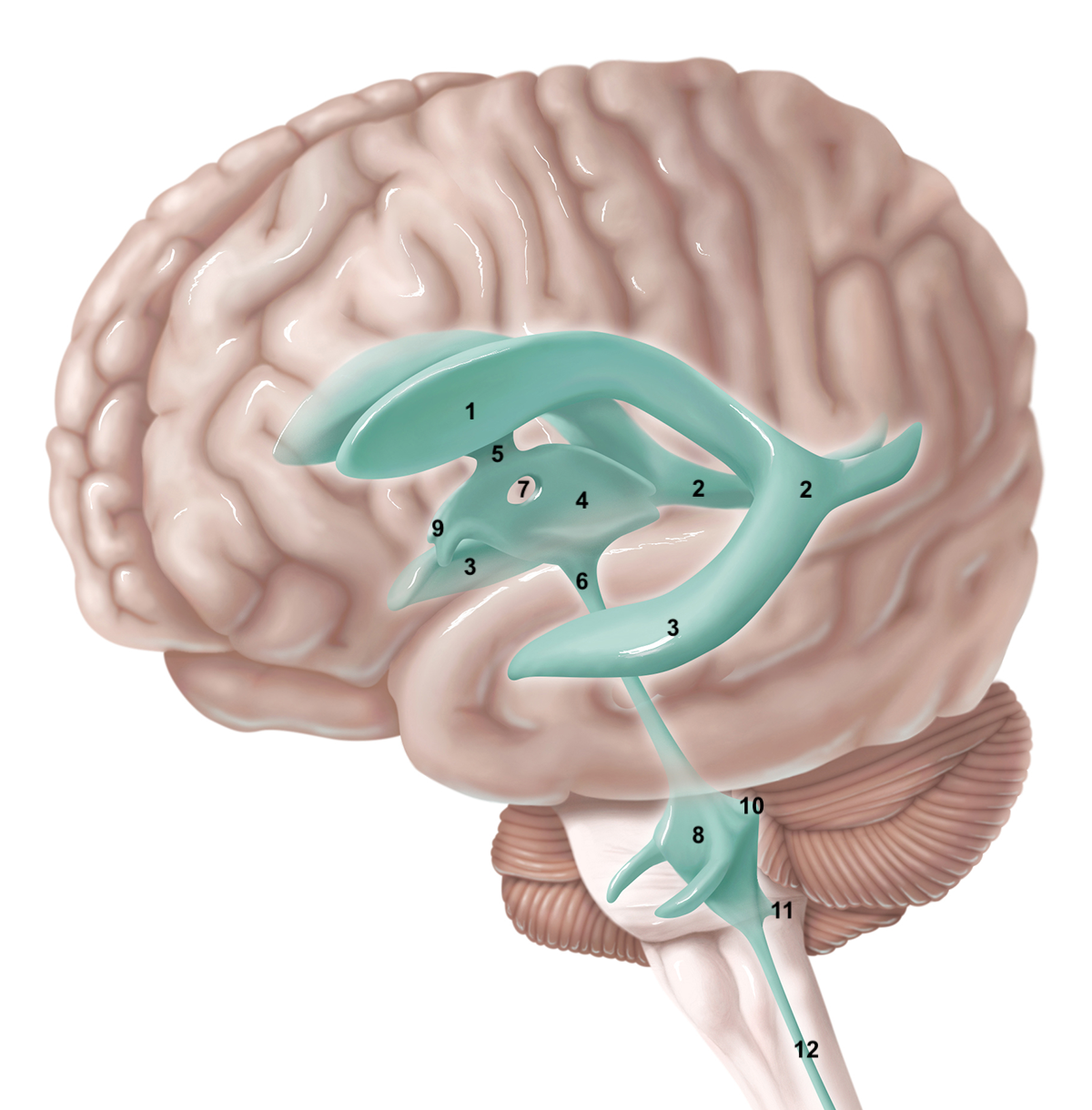
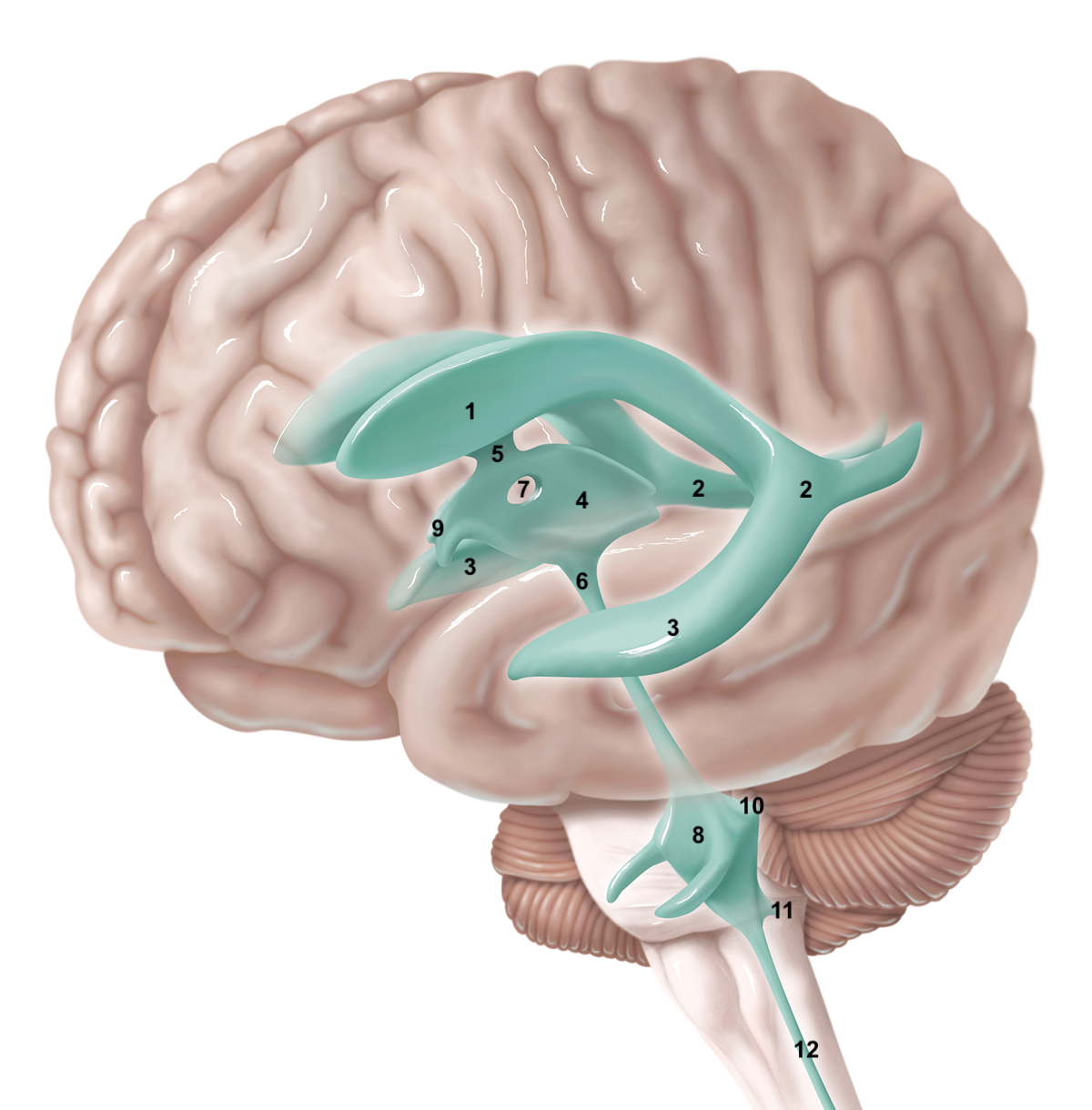
1
anterior horn of lateral ventricle
71
New cards
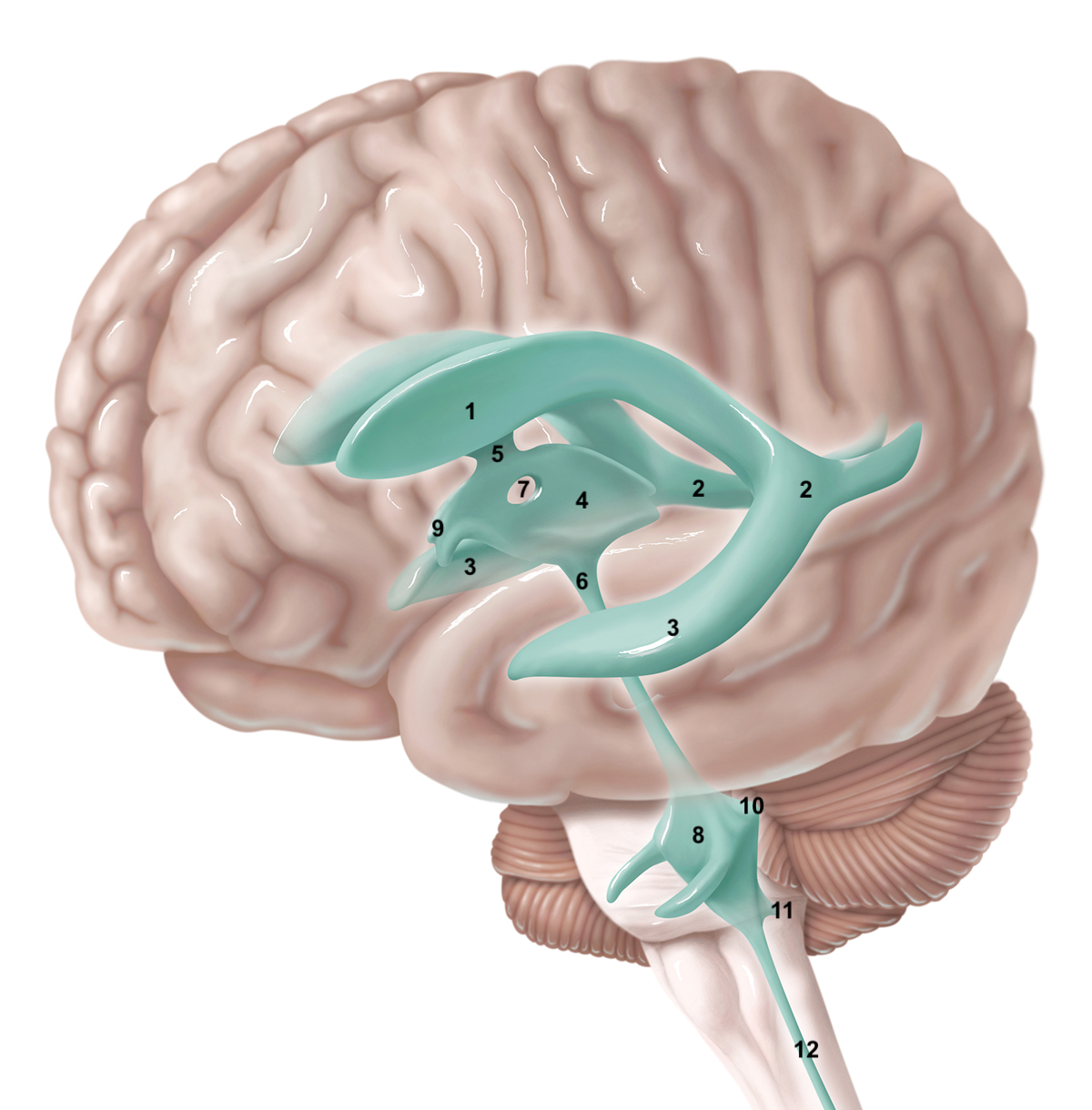
2
posterior horn of lateral ventricle
72
New cards
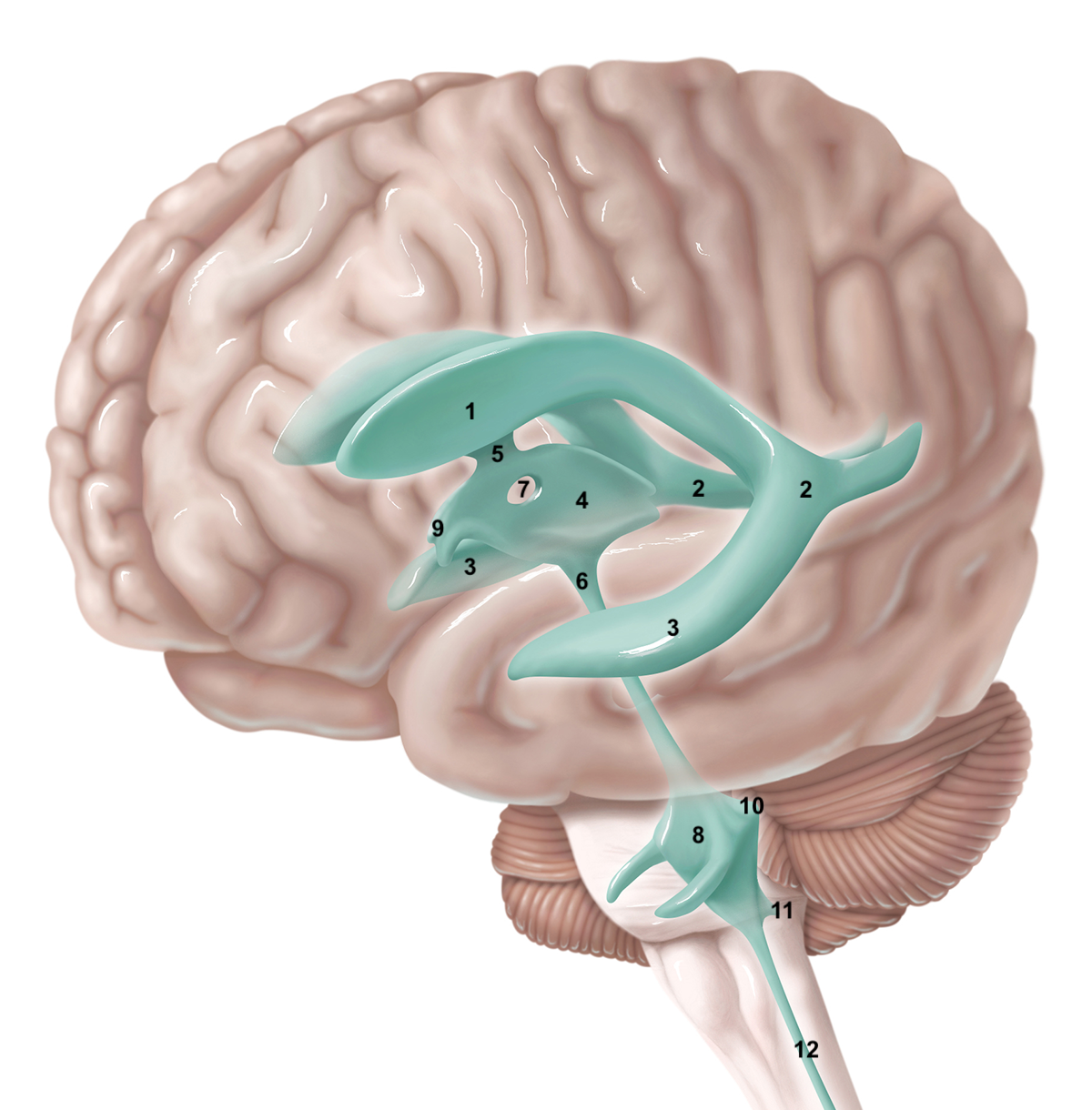
3
inferior horn of lateral ventricle
73
New cards
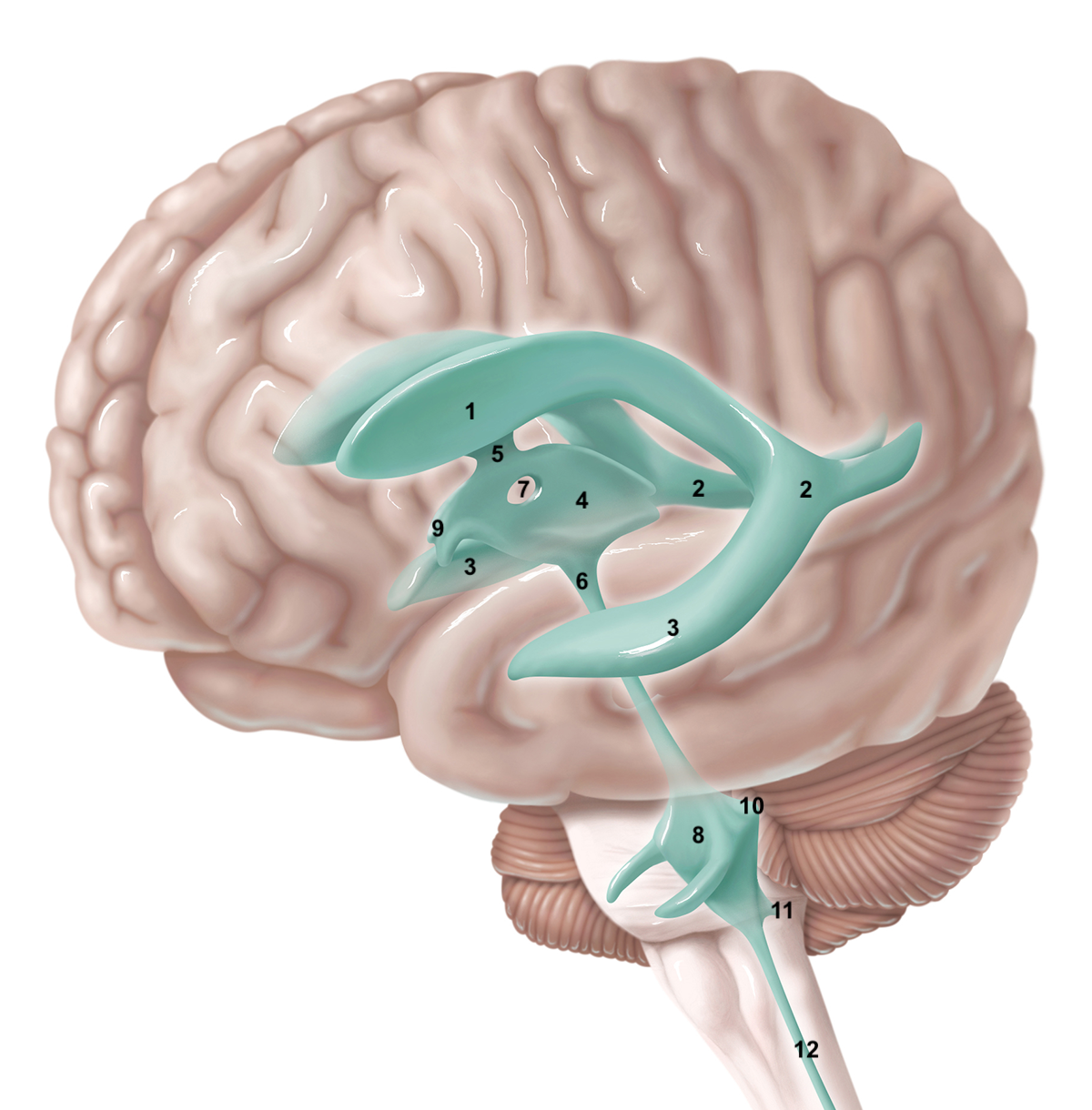
4
3rd ventricle
74
New cards
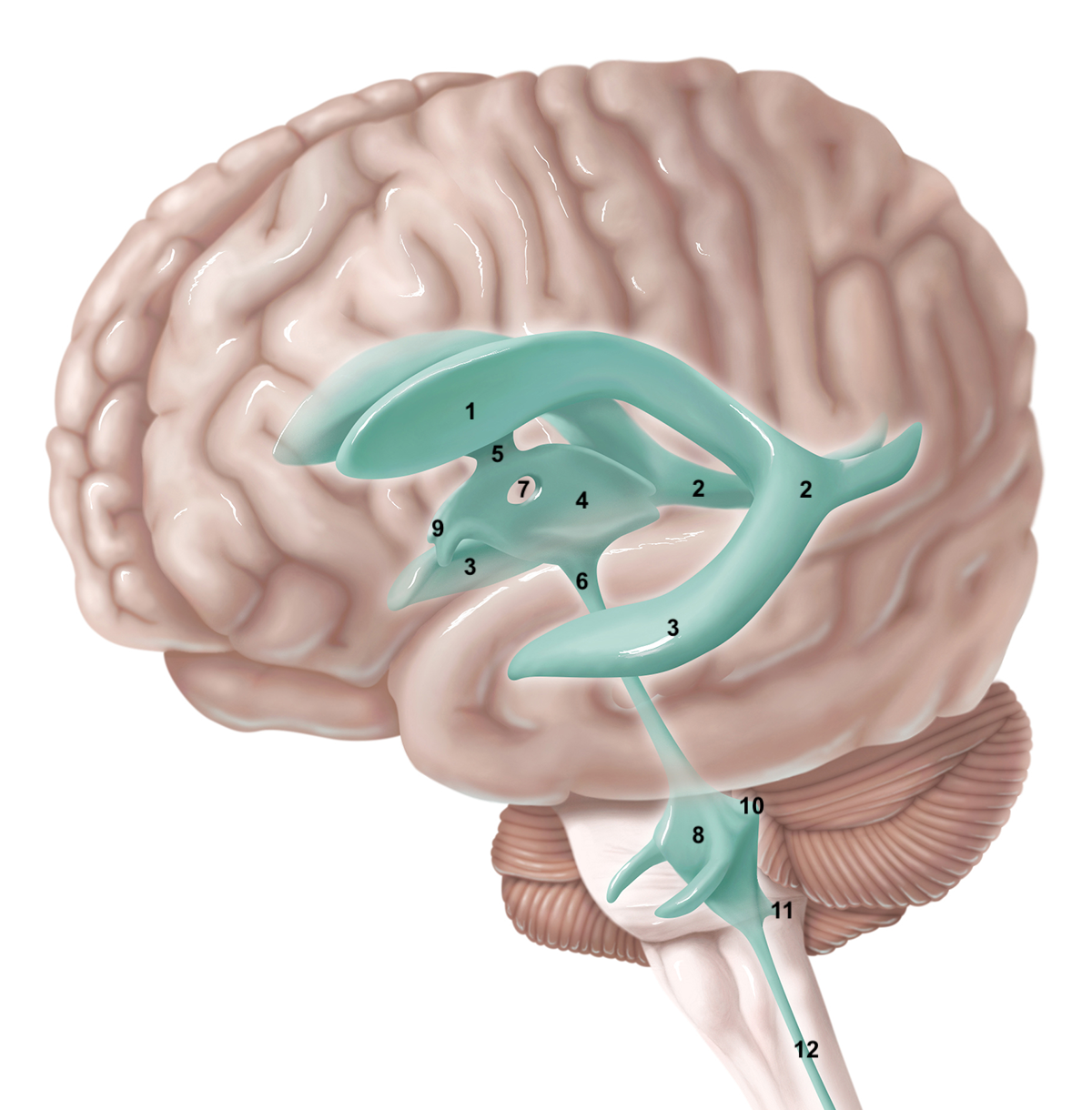
5
intraventricular foramen
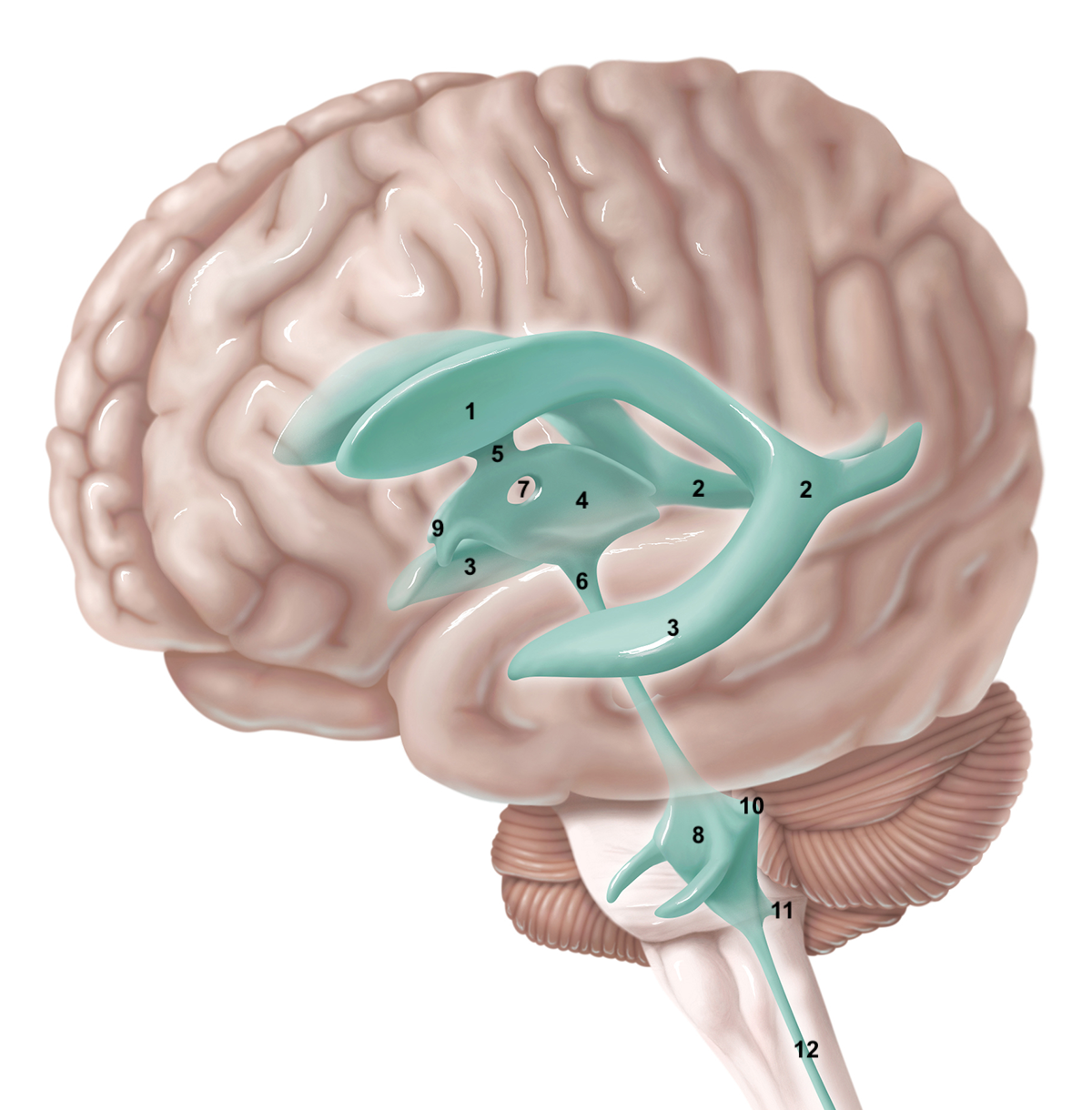
75
New cards
6
cerebral aqueduct / aqueduct of sylvius
76
New cards
7
interthalamic adhesion
77
New cards
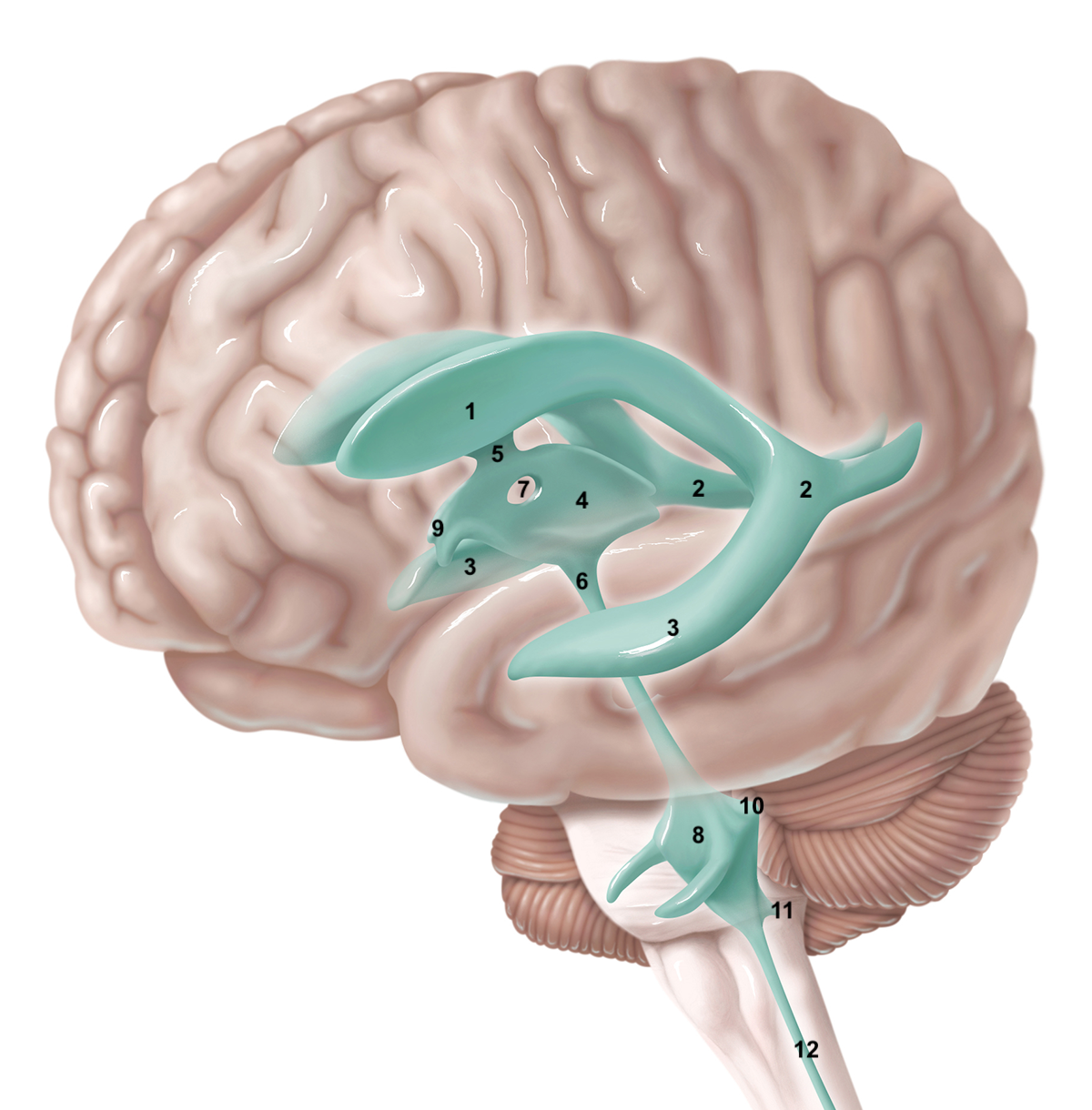
8
4th ventricle
78
New cards
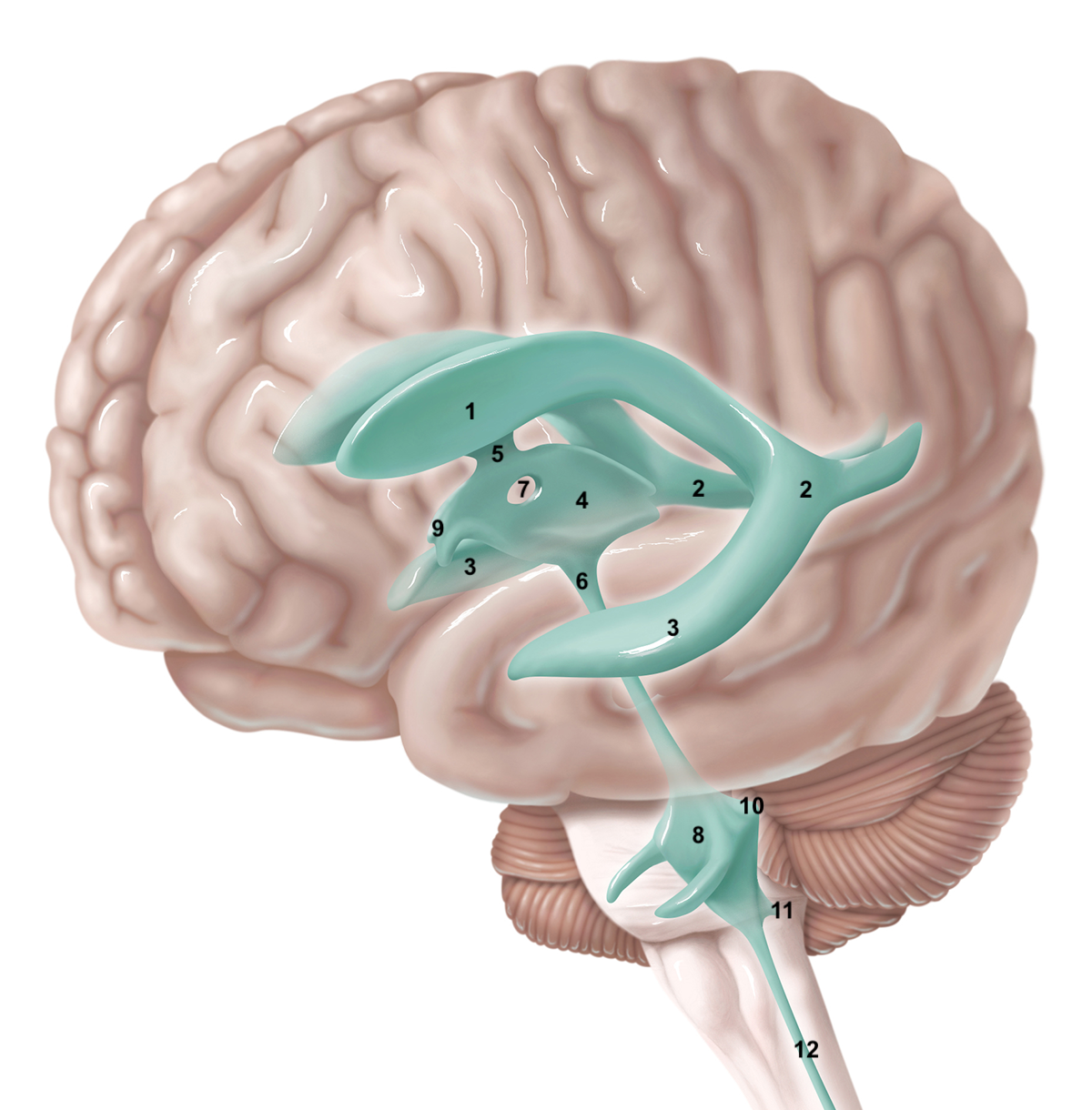
9
intraventricular foramen of Monro / lateral aperture
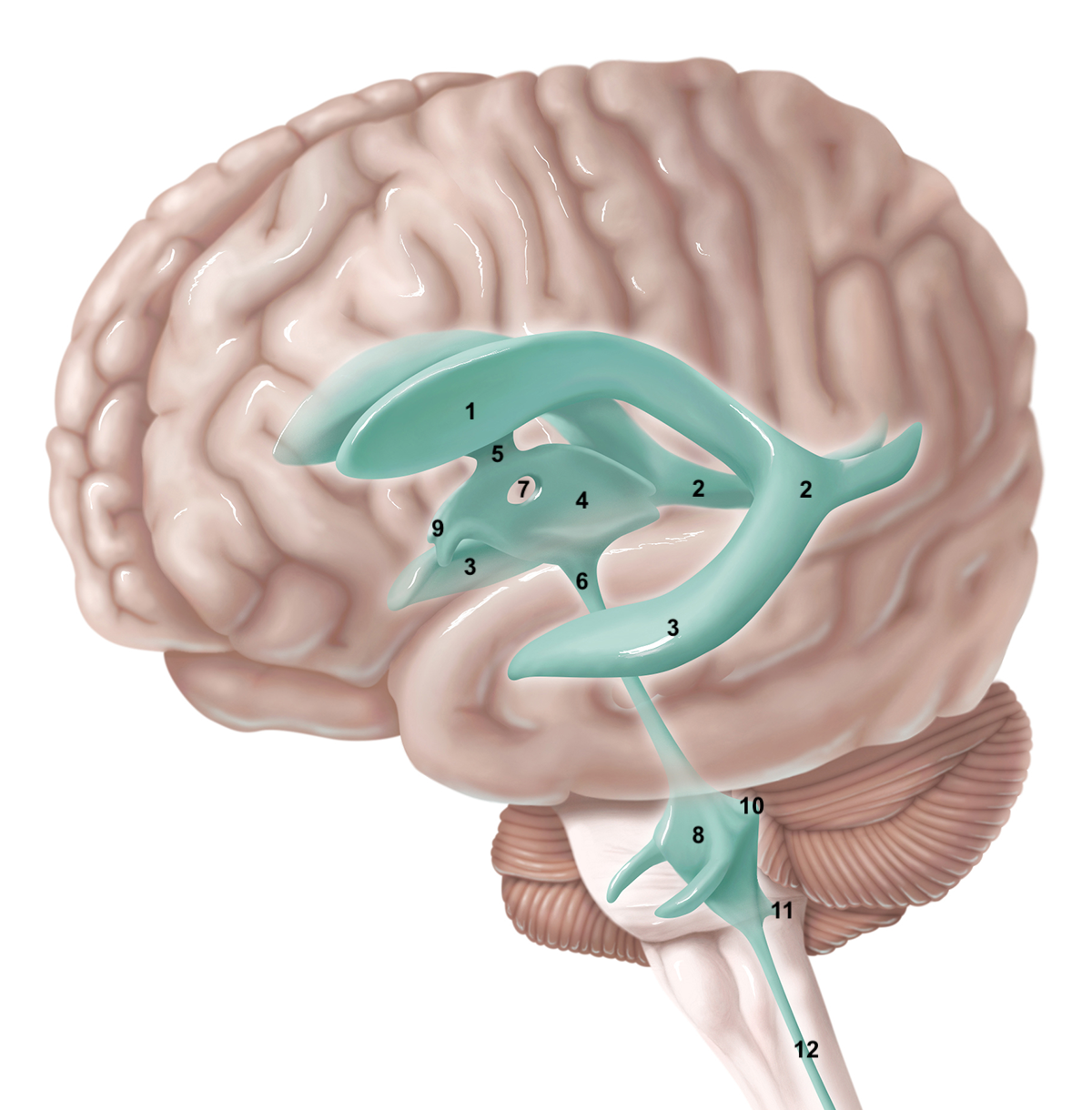
79
New cards
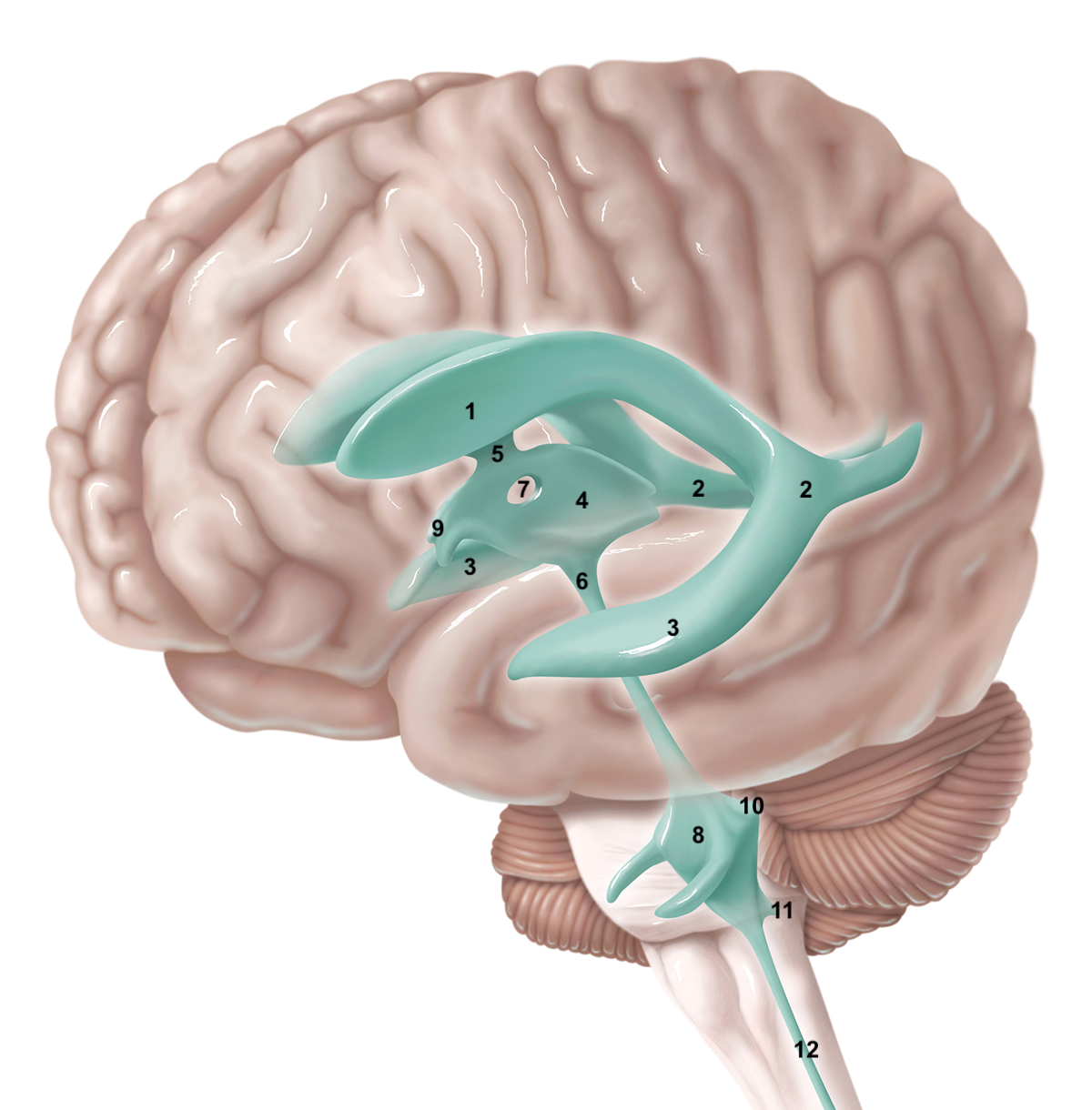
10
foramen of Luschka / lateral aperture
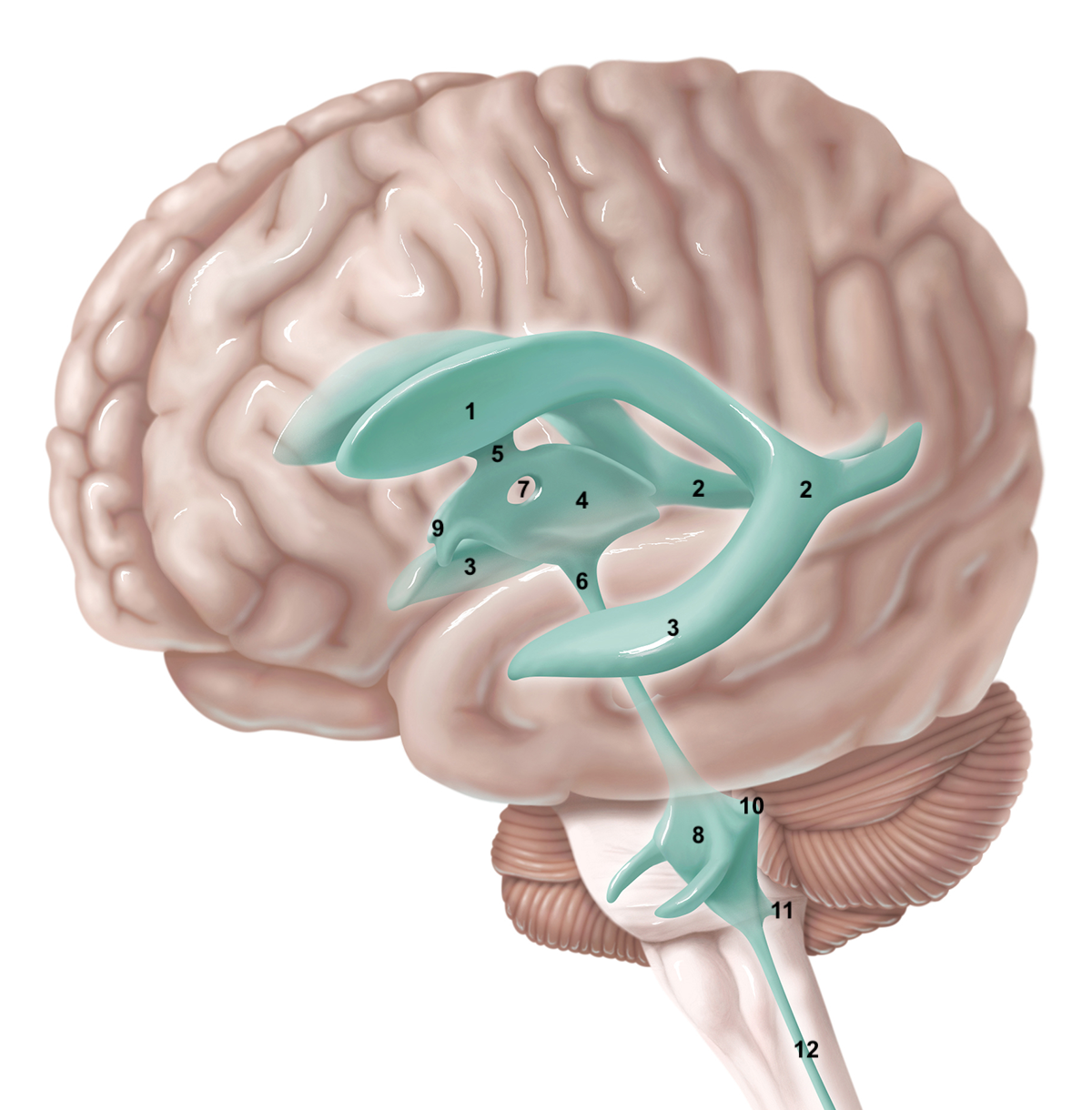
80
New cards
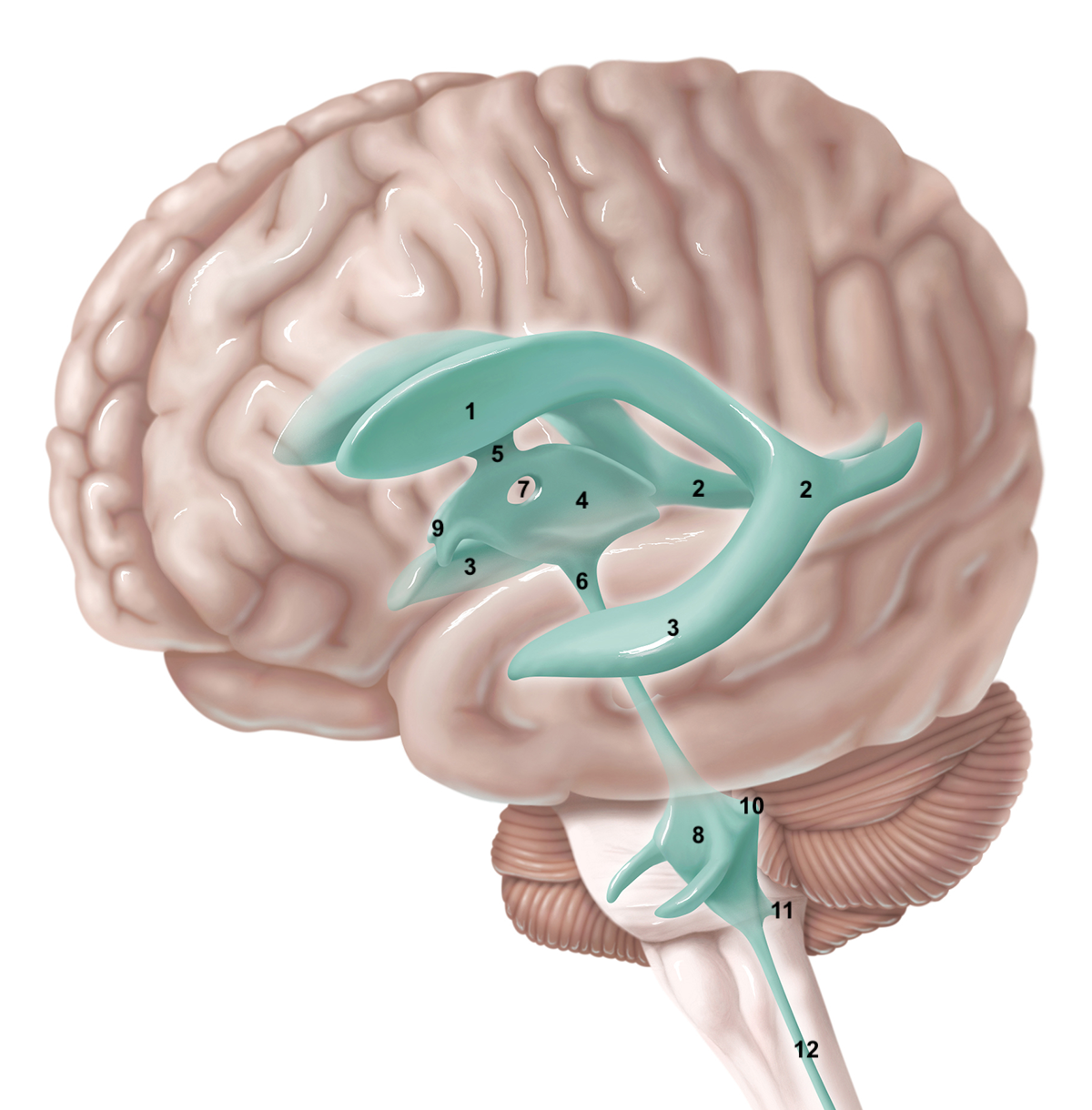
11
foramen of Magendie / median aperture
81
New cards
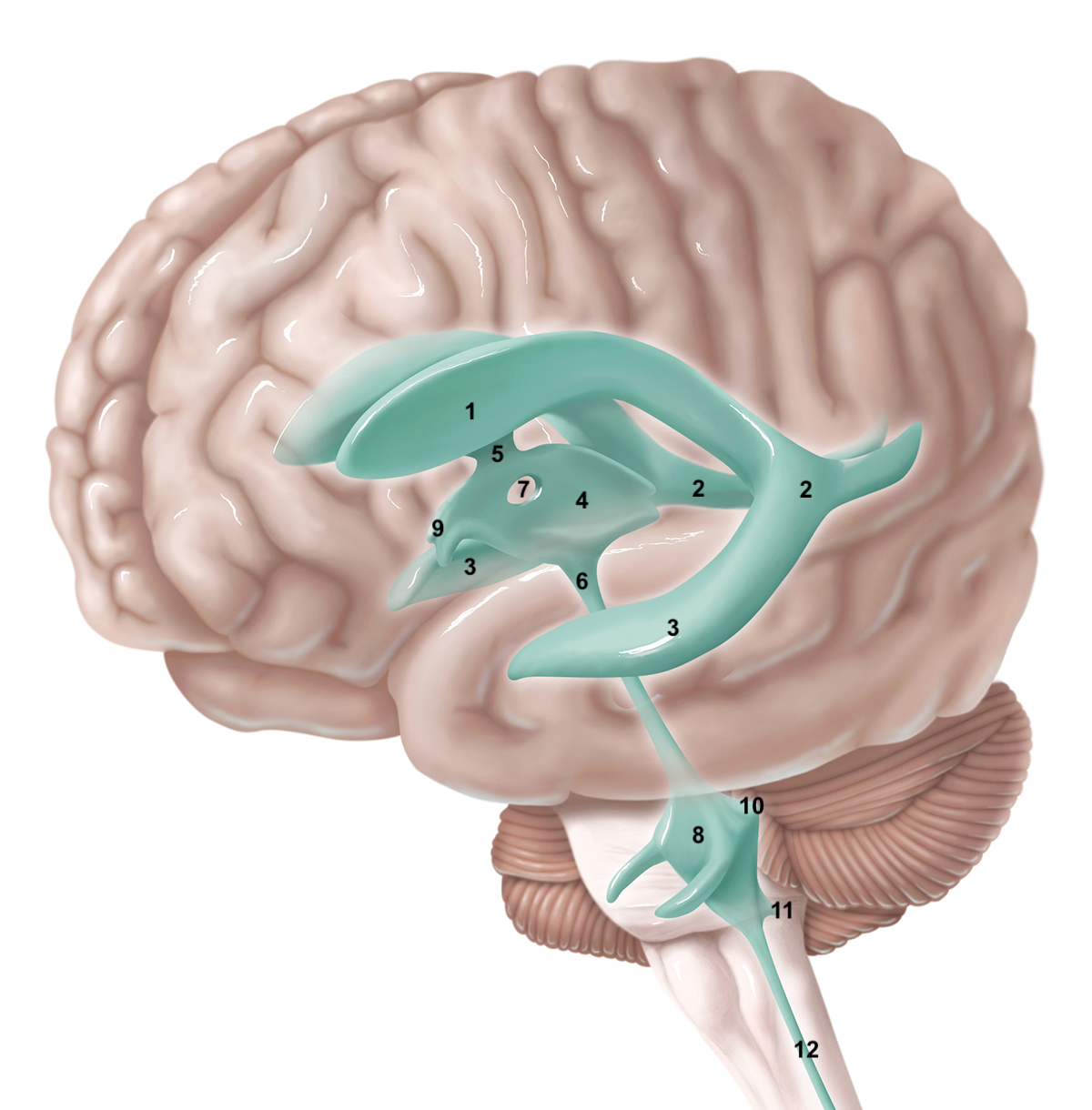
12
central canal
82
New cards
CSF production
mainly from the choroid plexus, located in the ventricles
83
New cards
choroid ependymal cells
tight junctions with choroid epithelial cells, BBB, control CSF composition via tight junctions and active ion transport
84
New cards
CSF circulation
CSF produced in the lateral ventricles, travels through the intraventricular foramen, joins the 3rd ventricle, goes down the aqueduct of Silvius, and enters the 4th ventricle
85
New cards
CSF release
CSF exits the 4th ventricle via two apertures, the median aperture (foramen of Magendie) and the lateral aperture (foramen of Luschka), goes into the subarachnoid space
86
New cards
CSF filtration
CSF circulates around the brain and is filtered at the arachnoid granulations before entering the superior sinuses and returning to the bloodstream via the jugular vein
87
New cards
purpose of CSF
physical support to brain (cushion)
buoyancy (reduces net weight from 1.4kg to \~25g)
waste excretion
nourishment and communication (chemical messenger distribution through CSF)
buoyancy (reduces net weight from 1.4kg to \~25g)
waste excretion
nourishment and communication (chemical messenger distribution through CSF)
88
New cards
perivascular drainage pathways
how ISF leaves the brain
flows from intramural perivascular drainage system to cervical lymph nodes
flows from intramural perivascular drainage system to cervical lymph nodes
89
New cards
glymphatic system
glial-dependent
astrocytes allow exchange of CSF and ISF from brain parenchyma and drainage directly into vessels via aquaporin-4 channels on feet of astrocytes
astrocytes allow exchange of CSF and ISF from brain parenchyma and drainage directly into vessels via aquaporin-4 channels on feet of astrocytes
90
New cards
CSF circulation
acts as sink for waste, exogenous solutes/compounds
91
New cards
meningeal lymphatic routes
specific for meninges
important for immune surveillance
important for immune surveillance
92
New cards
4 lymphatic drainage pathways of brain
perivascular drainage pathways, glymphatic system, CSF circulation, meningeal lymphatic routes
93
New cards
main arterial blood supply to brain
vertebral and carotid artery
94
New cards
vertebral artery
supplies posterior circulation
branches into PICA, posterior spinal artery, AICA, and fuses into the basilar artery
branches into PICA, posterior spinal artery, AICA, and fuses into the basilar artery
95
New cards
basilar artery
branches into superior cerebellar artery and posterior cerebral artery, supplying various brain regions
96
New cards
internal carotid artery
supplies anterior circulation (80% of blood flow). Branches into ophthalmic artery, then anterior cerebral artery, supplying the frontal and parietal lobes.
97
New cards
deep veins
great cerebral vein receives from internal cerebral veins and basal veins, draining into the sinus rectus and returning to the jugular vein
98
New cards
superficial veins
superior cerebral veins drain into the superior sagittal sinus, and the middle cerebral vein drains into the superior sagittal sinus and pernicular sinus
99
New cards
ischaemic stroke
caused by artery blockage from clot or plaque, leading to reduced blood flow to a brain region
100
New cards
middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO)
most common stroke type. affects the M1 (primary motor cortex), leading to hemiplegia, aphasia, and neglect