GCSE Physics - Waves & Sound
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
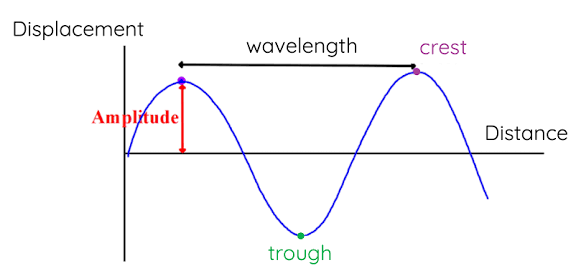
Amplitude
The maximum distance from the rest position to the wave. Measured in m.
Frequency
The number of oscillations per unit time. Measured in Hz.
Wavelength
The distance between a point on one wave to the same point on the next. Measured in m.
Time Period
The time taken for one complete wave. Measured in s.
What is the equation for frequency?
Frequency = number of waves/ time taken
Unit : Hz
What is the equation for time period?
Period = 1/ frequency
Unit : s
What is the equation for wave speed?
Wave speed = frequency x wavelength
Unit : m/s
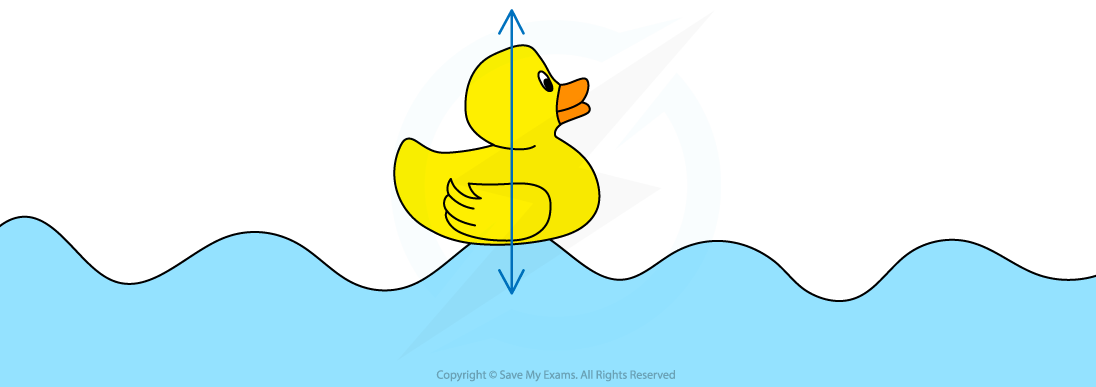
What is the method for finding the frequency of waves? (method of finding speed of water waves passing a duck)
Use a stopwatch to measure the number of waves passing the duck in a given time
Repeat and average to make sure the results are repeatable
Find the frequency using the equation: f = n/t
What do waves do?
Waves transfer energy or information without mass
What are the two types of waves?
Longitudinal and transverse waves
Transverse waves
Oscilante perpendicular to the direction of energy transfer
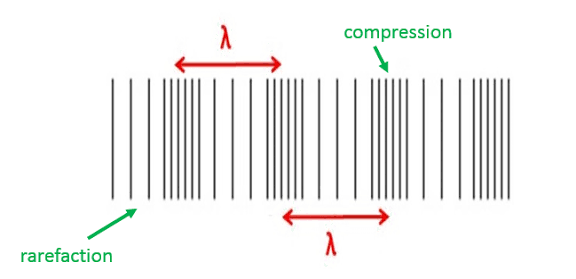
Longitudinal waves
Oscillate parallel to the direction of energy transfer
Give three examples of transverse waves
Light waves, S-earthquake waves, water(surface) waves
Give three examples of longitudinal waves
Sound waves, P-earthquake waves, pressure waves
What are the parts of a transverse wave?
• crest
• trough
• wavelength
•amplitude
What are the parts of a longitudinal wave?
• compressions
• rarefactions
• wavelength
What do longitudinal waves need?
Longitudinal waves like sound need a medium to transfer energy - longitudinal waves cannot travel through a vacuum.
Describe how a floating duck illustrates that waves transfer energy without mass.
Waves move in one direction.(1) Duck moves up and down about a fixed point.(1)
How can we use the speeds of sound and light to measure distance?
Light travels much faster than sound( 3×10^8 m/s > 340 m/s)
If the time delay from observing the flash to hearing the sound is timed using a stopwatch, the distance can be found
Using s = d/t
How sound waves travel?
The particles oscillate back and forth and collide with each other, transferring kinetic energy. The particles oscillate in the same direction as the energy travels, so are longitudinal.
Human hearing range
The typical human hearing range is between 20 Hz and 20 KHz.
Ultrasound
Frequencies over 20 KHz and are above the human hearing range.
Infrasound
Frequencies under 20 Hz and are below the human hearing range.
What does the volume of a sound depend on?
The volume of a sound depends on the amplitude of the wave. The higher the amplitude the louder the sound.
What does the pitch of a sound depends on?
The pitch of a sound depends on the frequency. The higher the frequency, the higher the pitch.
Sounds in solids, liquids and gases
• sound travels when particles collide
• the closer the particles are packed together, the more frequently this happens and the faster the sound travels.
• as v = f x lambda, when f is constant v is proportional to lambda
• the frequency of the sound produced doesn’t change. So when the wave speed increases the wavelength increases.
What is the clapper used for in the speed of sound in air practical?
Used to create a sound visually.
What is the trundle wheel used for in the speed of sound in air practical?
To measure longer distances.
Accuracy
How close a result is to the true value
Precision
How close the results are to each other
How can we improve accuracy in the speed of sound practical through time and distance measurements?
Time : use microphones or sound sensors to start and stop the stopwatch
Distance : make the distance between the students larger
What is the formula for uncertainty?
% Uncertainty = (uncertainty/measured value) x 100%
What is an echo?
A sound caused by the reflection of sound waves from a surface back to the listener.
How do ultrasounds work?
• gel used to stop reflection at skin
• ultrasound emitted into person
• reflected at foetus, bone
• measure time taken and halve it
• speed of sound in human body is known
• rearrange the formula s = d/t into d = st
• computer builds up pictures using distances
Uses of ultrasound
• medical scanning
• navigation by animals
• finding ocean depth(sonar)
• crack detection
Uses of infrasound
• animal communication over long distances
• monitoring volcanoes
• detecting meteors in the atmosphere
What is the build up of the earth?
Th crust(solid), the mantle(solid), the outer core(liquid) and the inner core(solid).
Primary waves
• longitudinal waves
• oscillate parallel to direction of energy transfer
• can travel through liquids and solids
• fast
• causes push-pull
Secondary waves
• transverse waves
• oscillate perpendicular to direction of energy transfer
• can travel through solids only
• slow
• causes shaking
How do s-waves and p-waves give us evidence of the Earth’s structure?
• the density changes with depth in our Earth - shown by the waves refracting
• the outer core is liquid - S waves are not detected by seismometers in the shadow team as they are absorbed
• the inner core is solid - p waves travel faster through the centre of the Earth as there are more particles to transfer the energy
What parts of the ear are in the outer ear?
The outer ear(pinna) and ear canal.
What parts of the ear are in the middle ear?
The ears drum and the hammer, anvil and stirrup(ossicles).
Why parts of the ear are in the inner ear?
The cochlea and auditory nerve.
How does the ear work?
Sound waves are collected by the outer ear
Then channeled by the ear canal towards the ear drum
The ear drums vibrate at the same frequency
The ossicles amplify these vibrations
These vibrations are converted into electrical impulses by the cochlea
They travel down the auditory nerve to the brain.
How do louder sounds affect the vibrations of the ear drum?
Louder sounds result in higher amplitude vibrations. This affects how much the ear drums vibrate moves.
How do higher pitch sounds affect the vibrations of the ear drum?
Higher pitch sounds result in higher frequency vibrations. The frequency influences the speed of vibration.
What are some causes of hearing loss?
• exposure to loud sounds
• age
• injury
• infection
What is the method for the speed of wave in fluid practical?
Measure the distance with a ruler
At one end of the tray, move dipper up and down without it leaving the water; start stop clock at the same time.
Stop the stop clock when the wave reflects off end of tray and has returned to the dipper. Record the time.
Repeat 3 times and take an average to improve the accuracy.
Calculate the speed with the formula s = d/t; make sure to double the distance.
What is the method for the speed of wave in a solid practical?
Set up the equipment.
2. Measure the length of the rod from end to end using a ruler
Set the stop clock to record and tap one end of the rod with the hammer
Record the time measured for the wave to travel along the rod
Repeat three times and calculate the average to improve accuracy.
What is the ripple tank method?
Measure the length of 10 waves using a metre rule.
Divide by 10 to calculate the wavelength
Count number of waves passing a point in 10 seconds, measuring the time with a stop clock
Divide by 10 to calculate the frequency
Calculate wave speed using v = f x lambda
Why is the ripple tank more accurate than the speed of wave in liquid practical?
• measurements of wavelength and frequency are measured more accurately:
The time in the first method is hugely affected by human reaction time which produces a large percentage error on small measurements