Medical Interventions unit 2
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Denaturation
94°C
Strands separate
Annealing
64°C
Primers attach
Extension
72°C
TAQ polymerase adds bases
What gene were we testing for in the lab?
TAS2R38
How many bands for a nontaster? Dominant or recessive?
1 band
recessive
How many bands for a taster? Dominant or recessive?
2 bands
Dominant
CVS
Chorionic villus sampling
Sample taken from placenta
Weeks 10-12
Trans-cervical or trans-abdominal
Amniocentesis
Low risk but invasive
Amniotic fluid contains fetal cells
Weeks 16-20
Waste and metabolites give information on fetal health
Low risk
Gene therapy
alteration of the genes of a person afflicted by a genetic disorder
Vector
An agent that contains modified genetic material and can be used to introduce new genes
Genome editing
uses tools in the cell to cut DNA and replace mutated genes
can alter the DNA in stem cells
3 strategies of gene therapy
Insert
A functional gene is inserted so the body can make a functional protein (defective gene is still present but its effects are masked)
Disable
a dysfunctional gene is disabled
Repair
dysfunctional gene is repaired
Plasmid
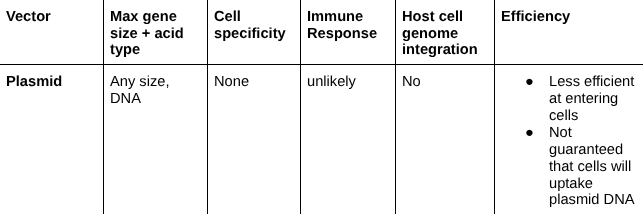
Liposome
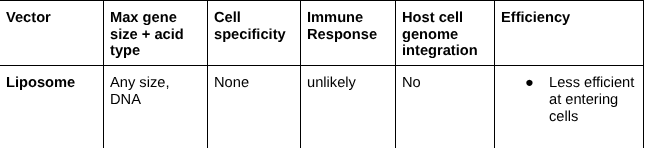
Herpes Virus
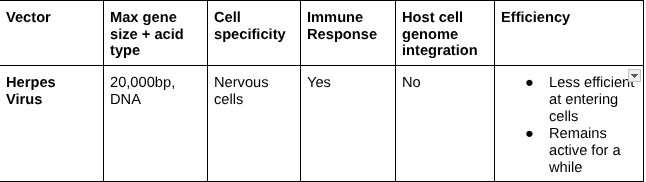
Adeno-associated virus
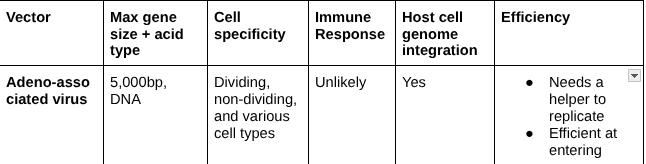
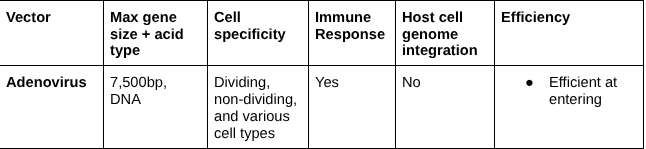
Adenovirus
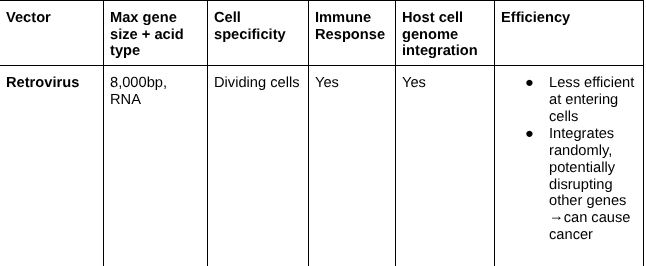
Retrovirus
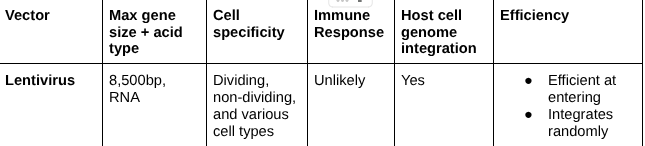
Lentivirus
in vivo
Taking place inside a living organism
in vitro
Performed in a lab, outside a living organism
in vivo: Pros and cons
Pros
patient receives benefits more readily
Cons
more chance of immune response
vector may enter non-affected cells
cells cannot be easily tested to check progress
in vitro: Pros and cons
Pros
less likely to cause immune response
target cells can be harvested to ensure the vector entered
cells can be tested before reintroduction
Cons
patient has to wait to receive benefits
What gene causes CF and where is it?
CFTR gene, chromosome 7
What does a functional CFTR protein do?
Transports chlorine ions.
Preimplantation Genetic diagnosis
screens the embryo for potential mutations before being implanted following in vitro fertilization
What maternal serums can be tested for during first trimester? Second trimester?
First: hCG & PAPP-A
Second: Quad screen →hCG, AFP, DIA, uE3
What is hCG? What do low and high levels mean?
A pregnancy hormone produced by the placenta.
Low: ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage
High: Pregnant with multiple babies, Tumors, down syndrome
What is PAPP-A? What do low and high levels mean?
A protein produced by the placenta →provides oxygen and nutrients to baby
Low: Down syndrome, Edwads syndrome
High: lower risk of preeclampsia
What is a quad screen?
a blood test during pregnancy that tells you if the fetus is at increased risk for having certain genetic disorders →16-21 weeks (not diagnostic)
What is AFP? What do low and high levels mean?
Fetal protein-A, Large role in fetal development
Low: chromosomal abnormalities
High: Neural tube defects (defects of the brain, spine, or spinal cord)
What is UE3? What do low and high levels mean?
estriol →a form of estrogen
Low: high risk of down syndrome
What is DIA (inhibin-A)? What do low and high levels mean?
regulates cell division and differentiation in fetus
High: risk for down syndrome increases
What does cell free DNA screenings test?
Fetal DNA circulating through the mothers blood.
Anatomy ultrasound
18-22 weeks
examine babies anatomical development, heart rate, etc
NT (Nuchal transluscency) ultrasound
11-14 weeks
ultrasound that focuses on the back of the childs neck to examine developmental milestones of the brain and spinal cord
Usually paired with serum screening
Higher than 3.5mm = increased chance of chromosomal abnormality
Cystic fibrosis gene and location.
CFTR on chromosome 7
Cystic fibrosis causes and symptoms
CFTR cannot transport Chlorine ions to mucus ducts so mucus builds up. It also causes an influx of water into cells which makes mucus sticky and thick →trap pathogens
Can block respiratory passageways and pancreatic ducts
What does CRISPR stand for?
Clustered
Regularly
Interspaced
Short
Palindromic
Repeats
What is Cas-9
A restriction enzyme that cuts the DNA at a target sequence.
How does CRISPR target the gene of interest?
It uses the guide RNA and identifies the matching sequence
Which diseases are candidates for treatment for the CRISPR-Cas9 system?
Huntigtons
CF
Sickle cell
Spacer DNA
Segments of viral DNA that previously infected the bacteria.
Interspaces palindromic repeats
What happens in a bacteria when a virus enters?
CAS protein and guide RNA are produced →form a complex
Complex locks onto a sequence called PAM and begins to unzip DNA
Looks for a match to guide RNA and cas9 cuts viral DNA at this point
How is the CRISPR-CAS9 system modified for humans?
Use only CAS 9
Connect Guide RNA and tracrRNA (holds Guide RNA in place)
Can modify the Guide RNA to target many genes
DNA feeds into complex and CAS9 cuts DNA at target sequence