Cell Types ,Cell Theory, Scientists, & Microscopes
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
cell theory
Idea that: 1. ALL living things are composed of cells, 2. cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things, 3. new cells are produced from preexisting cells
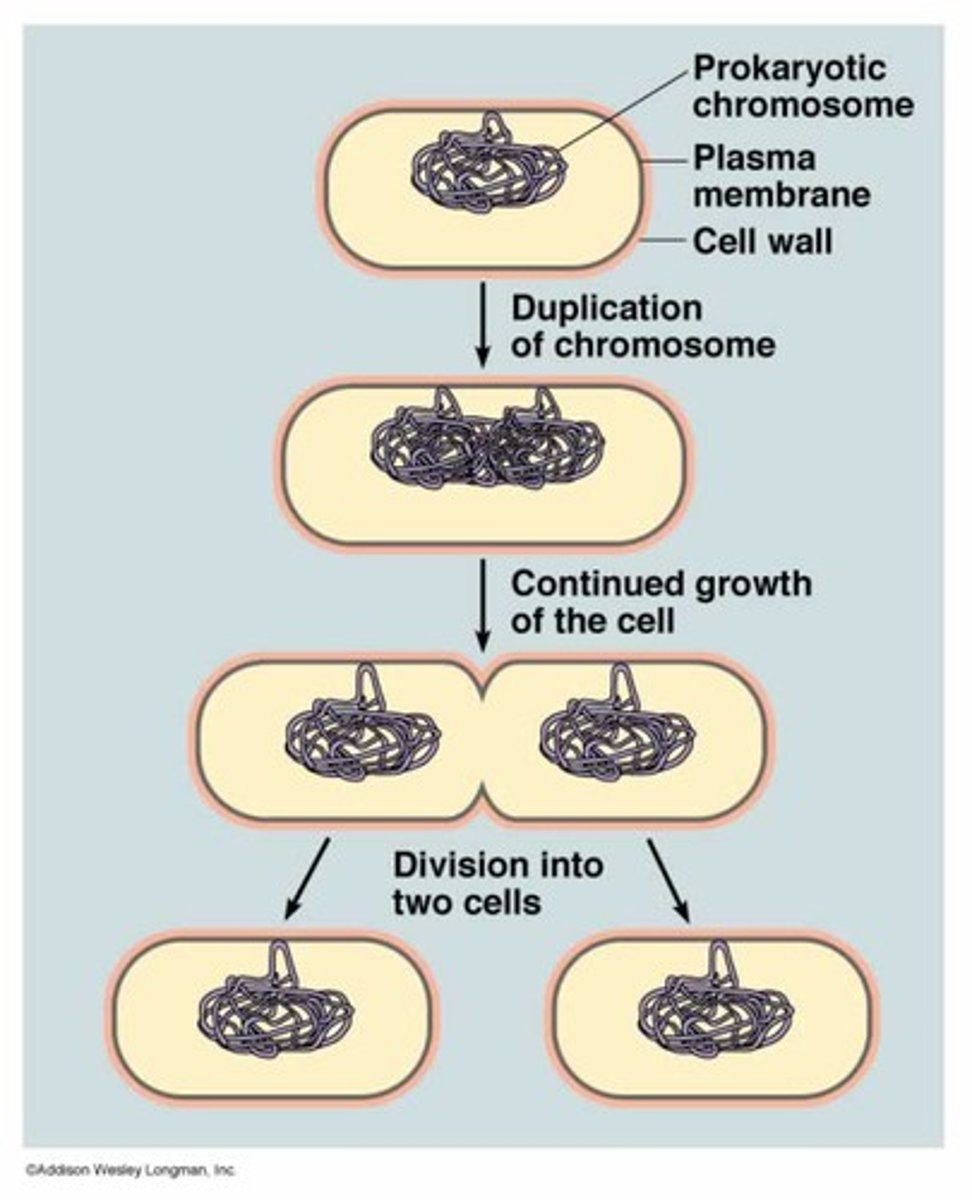
prokaryotic cell
very small simple cell that does NOT have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles ( Kingdoms Archaebacteria and Eubacteria)

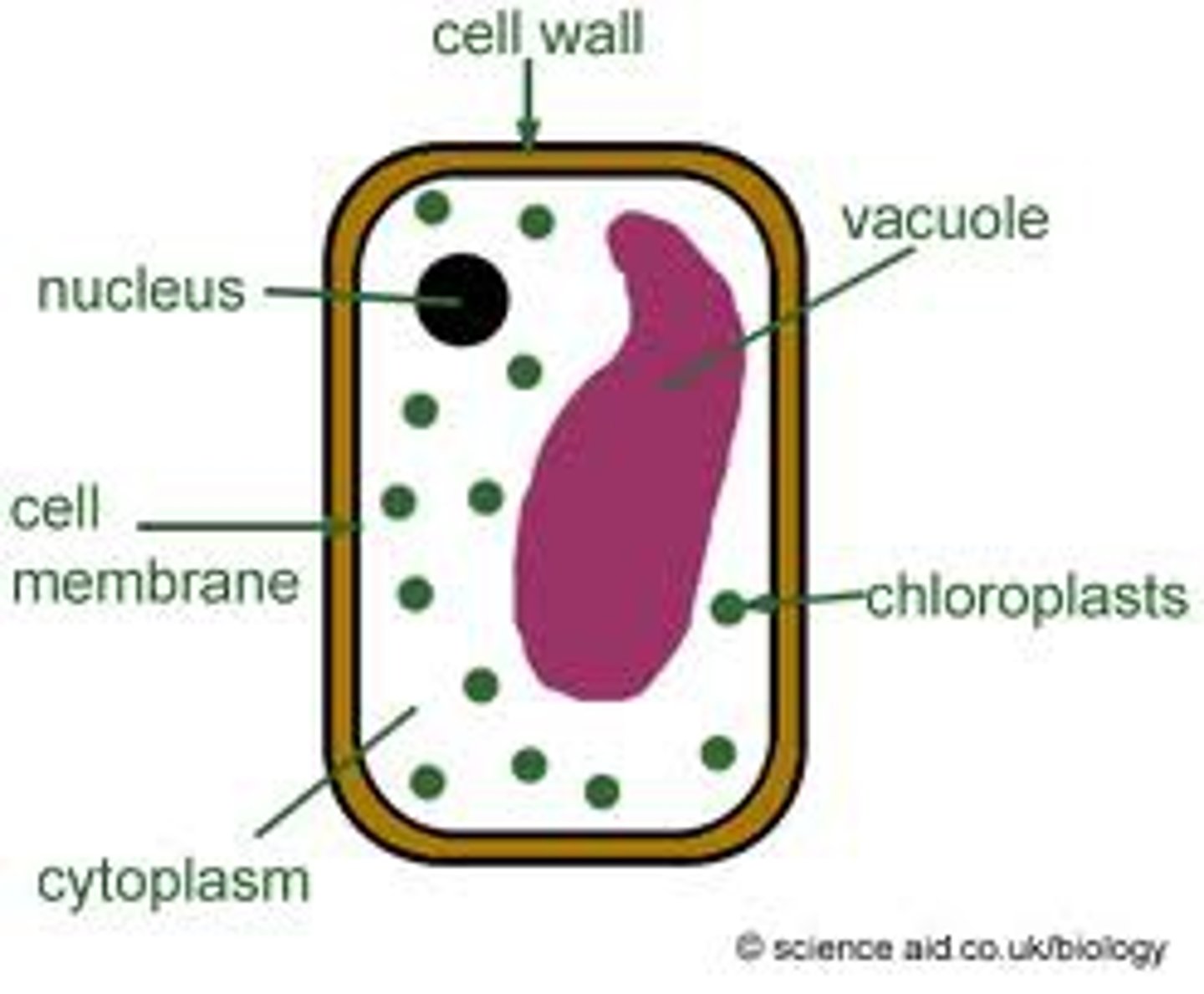
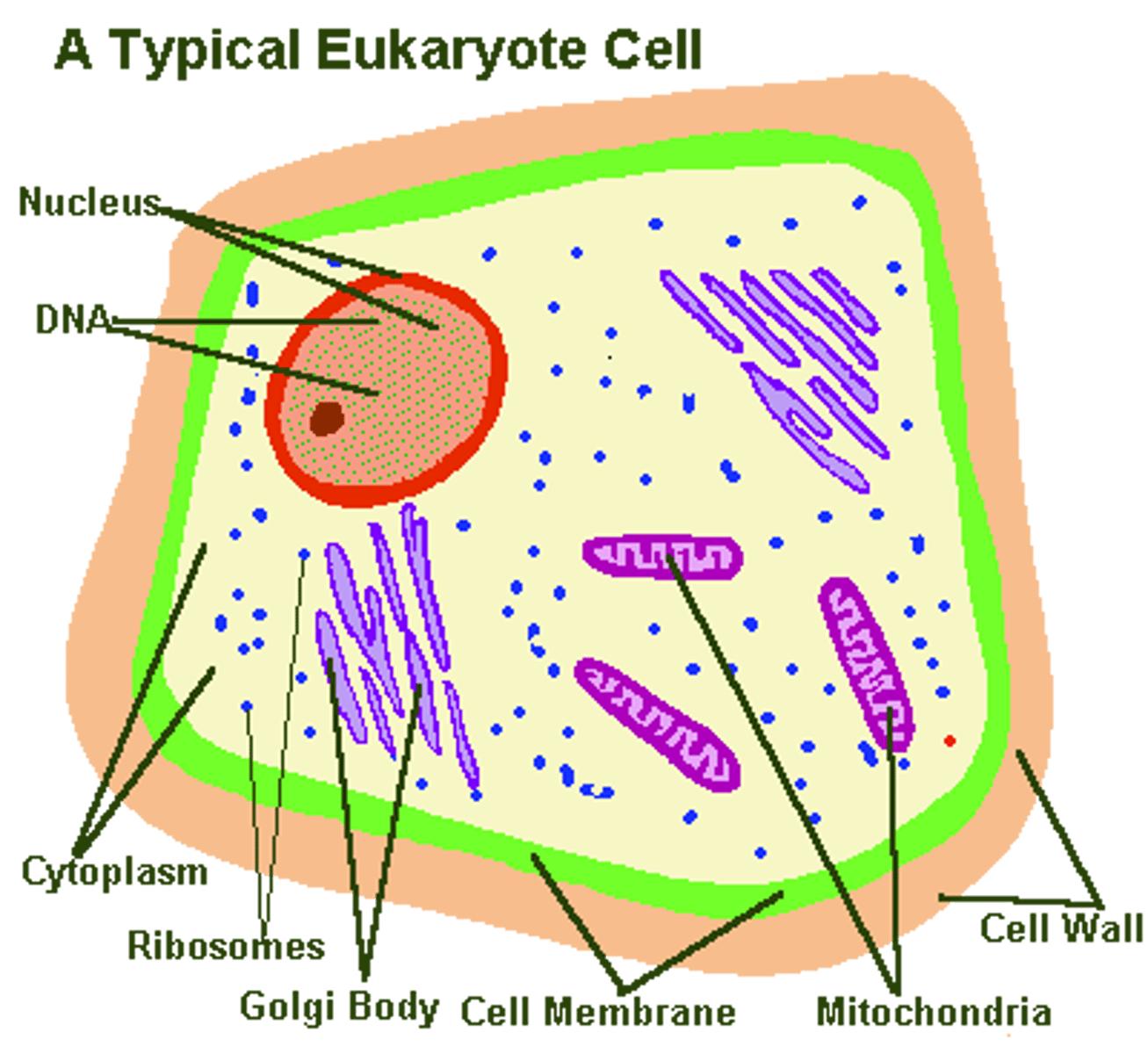
eukaryotic cell
Cell with a nucleus (surrounded by its own membrane) and other internal organelles ( Kingdoms: Fungi, Plantae, Protista, & Animalia)
Robert Hooke
Studied cork under the microscope and and named the structures he saw "cells", discovered cells, 1st to see cells

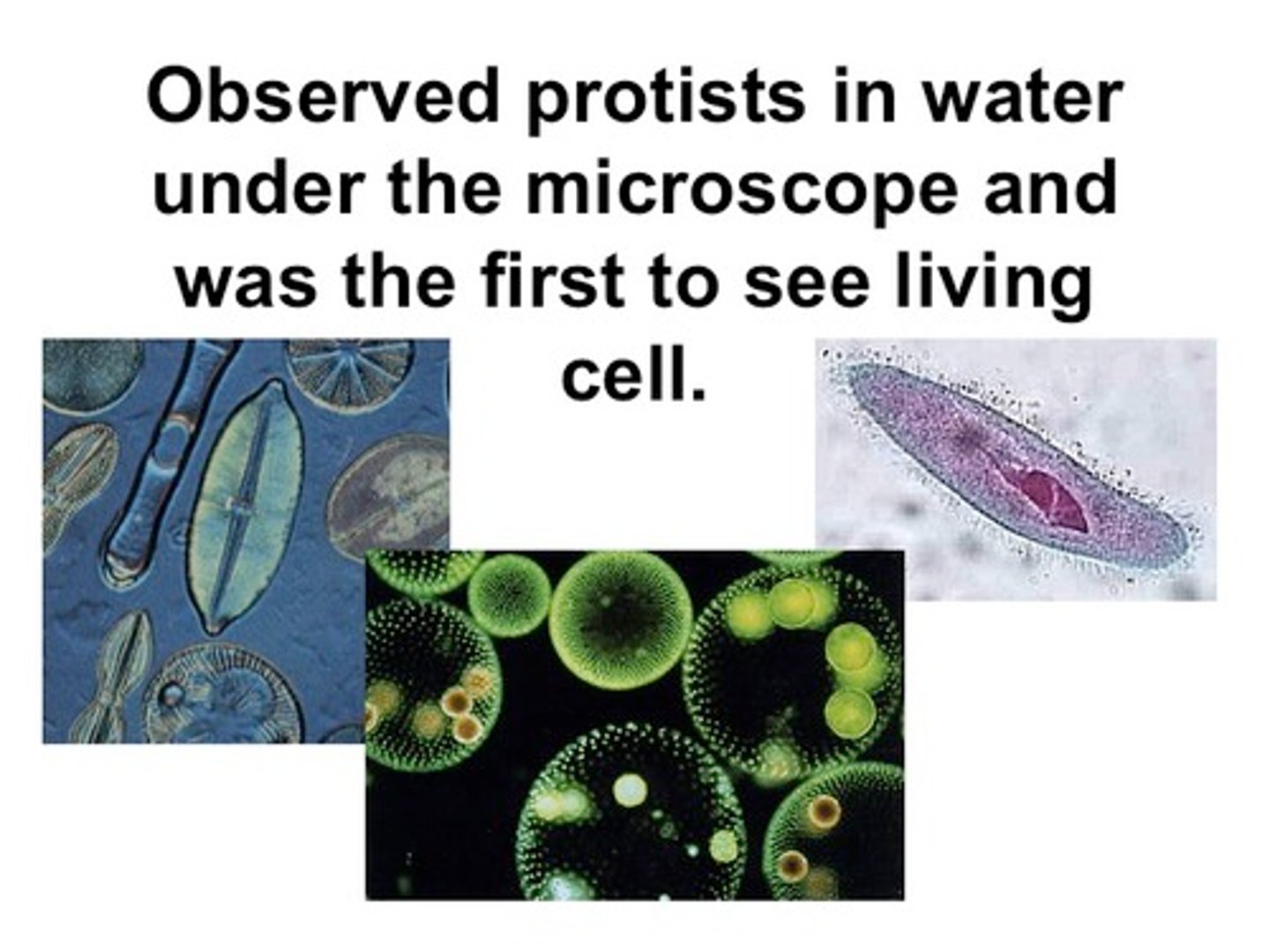
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
Dutch scientist who looked at teeth scrappings and pond water, called the organisms he saw "animicules", further advanced the microscope, 1st to see LIVING cells
Mathias Schleiden
German botanist who studied plant cells, he and Schwann contributed to cell theory by demonstrating that all living things are made of cells AND that cells are the basic structural unit of living things

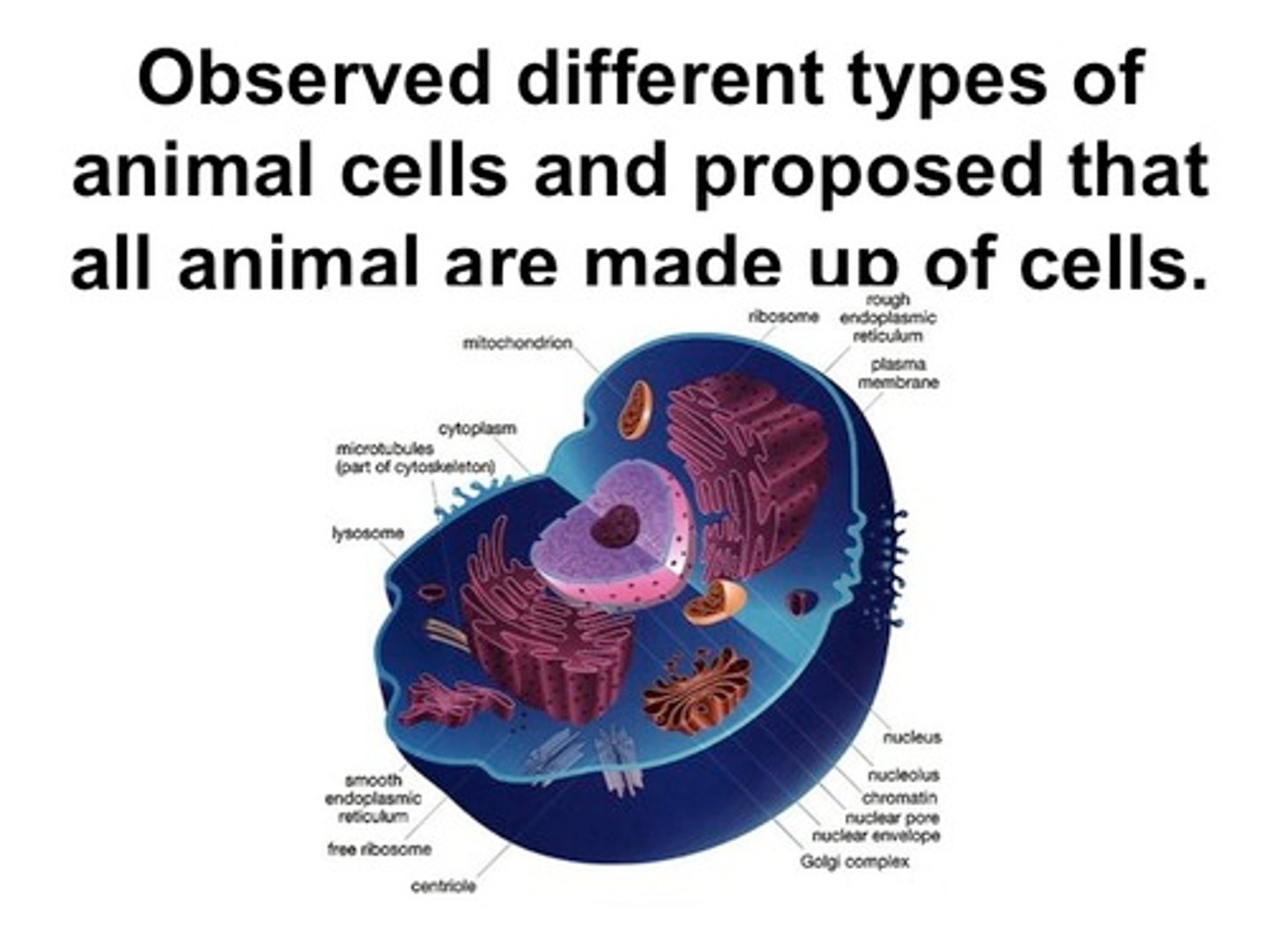
Theodor Schwann
German zoologist who studied animal cells, he and Schleiden contributed to cell theory by demonstrating that all living things are made of cells AND that cells are the basic structural unit of living things
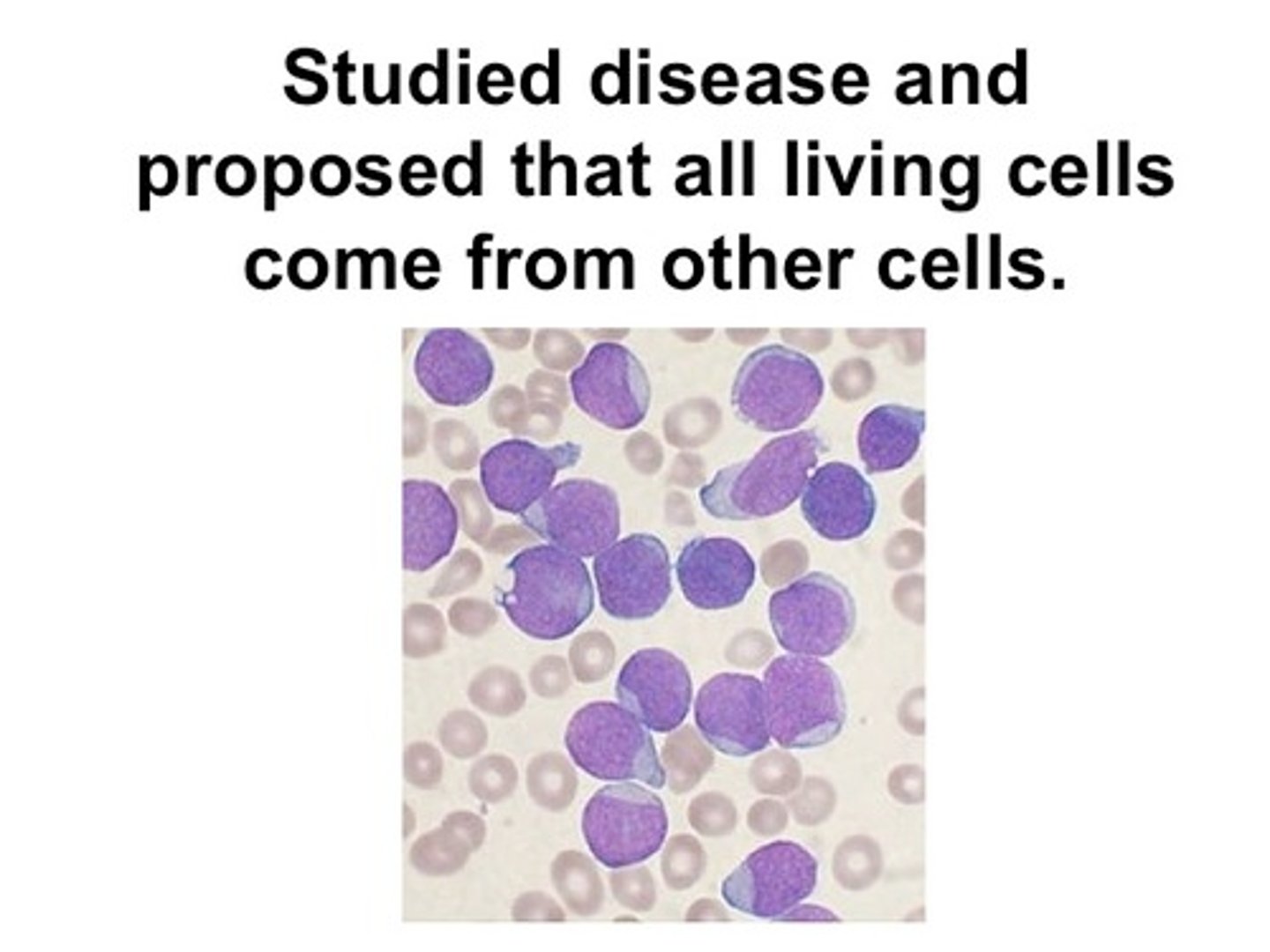
Rudolph Virchow
A German doctor who stated that all living cells come from other living cells (part 3 of the cell theory)
compound light microscope
a microscope that shines light through a specimen and has two lenses to magnify an image
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
A microscope that uses an electron beam to study the surface architecture of a cell or other specimen, expensive and requires training to operate

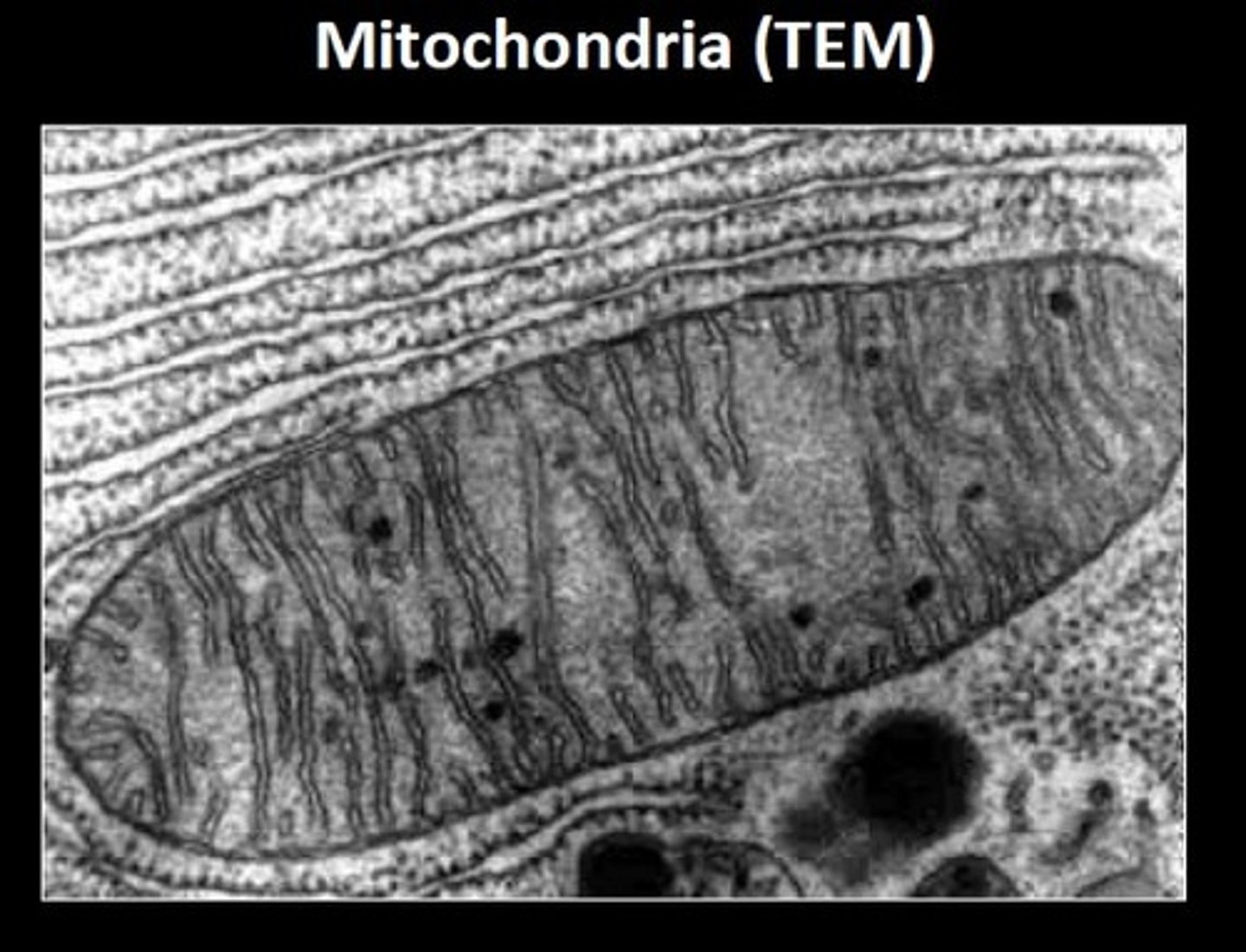
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
a microscope that passes an electron beam through very thin sections stained with metal atoms and is primarily used to study the internal structures of cells, expensive and requires training to operate
nucleus (of a cell)
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction, NOT FOUND IN PROKAYOTIC CELLS
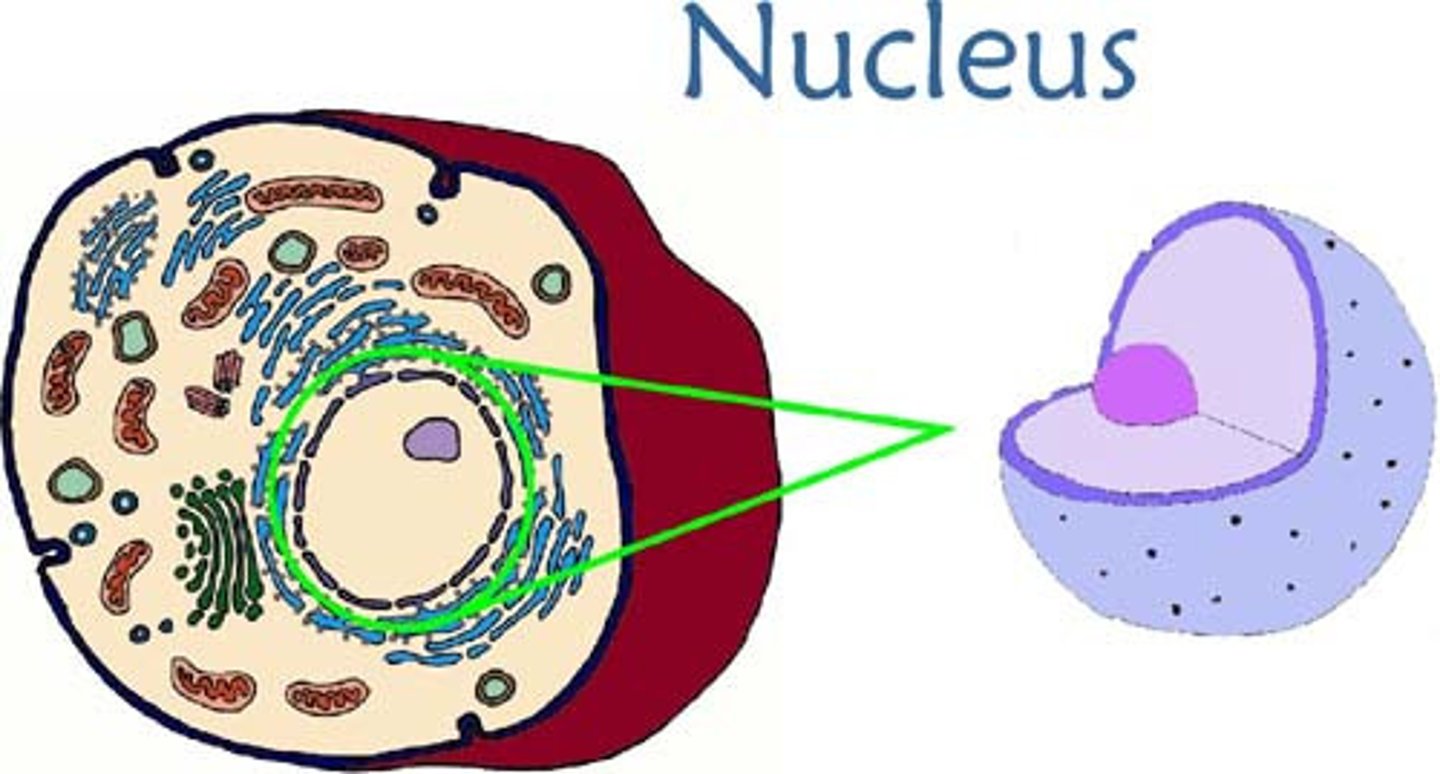
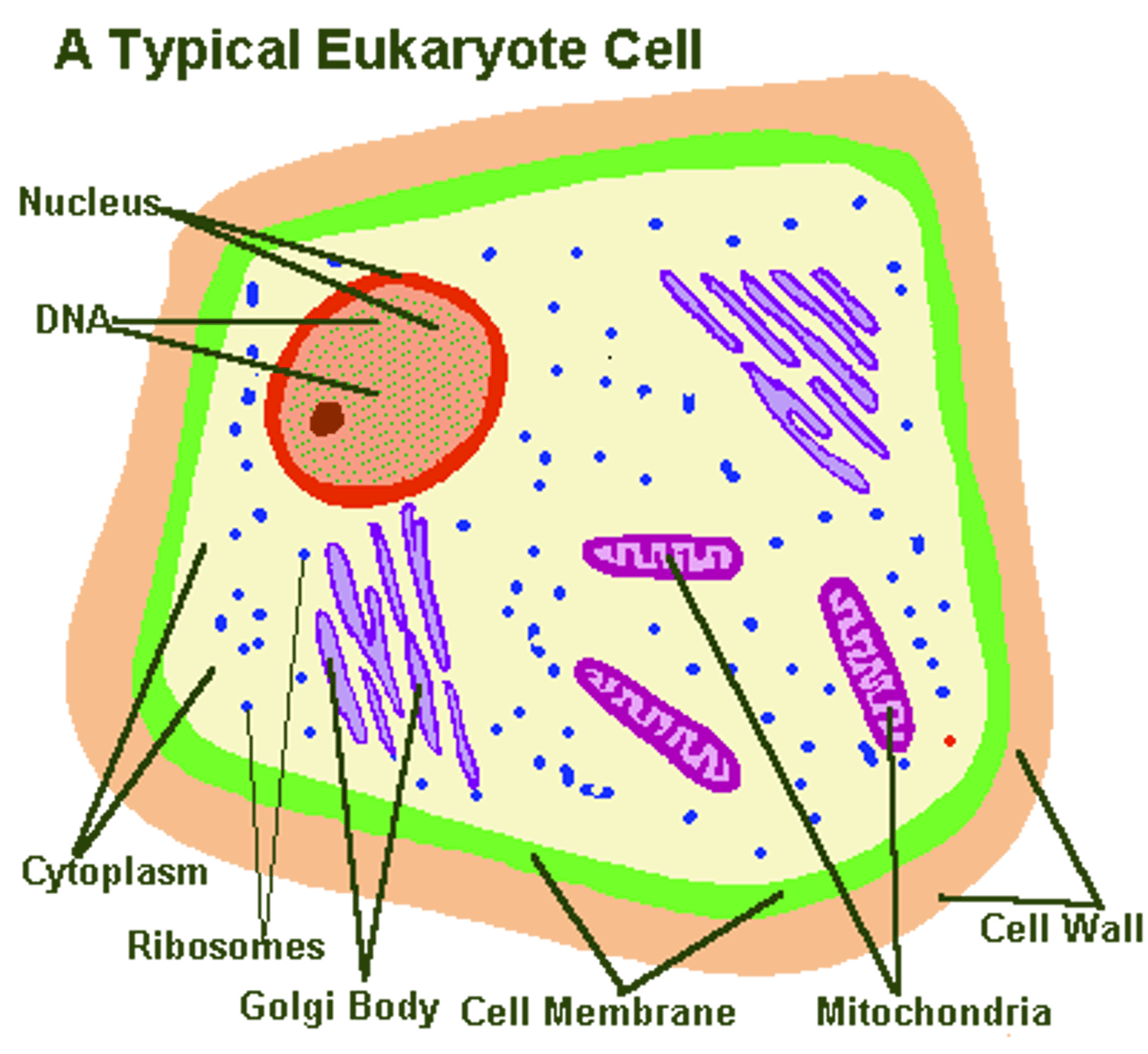
membrane bound organelles
ONLY eukaryotic cells have these, tiny organ like structures surrounded by a membrane
Unicellular
Organism made of a single cell, ALL prokaryotes are unicellular
Multicellular
organisms made of many cells, most eukaryotes are multicellular but many protists are not
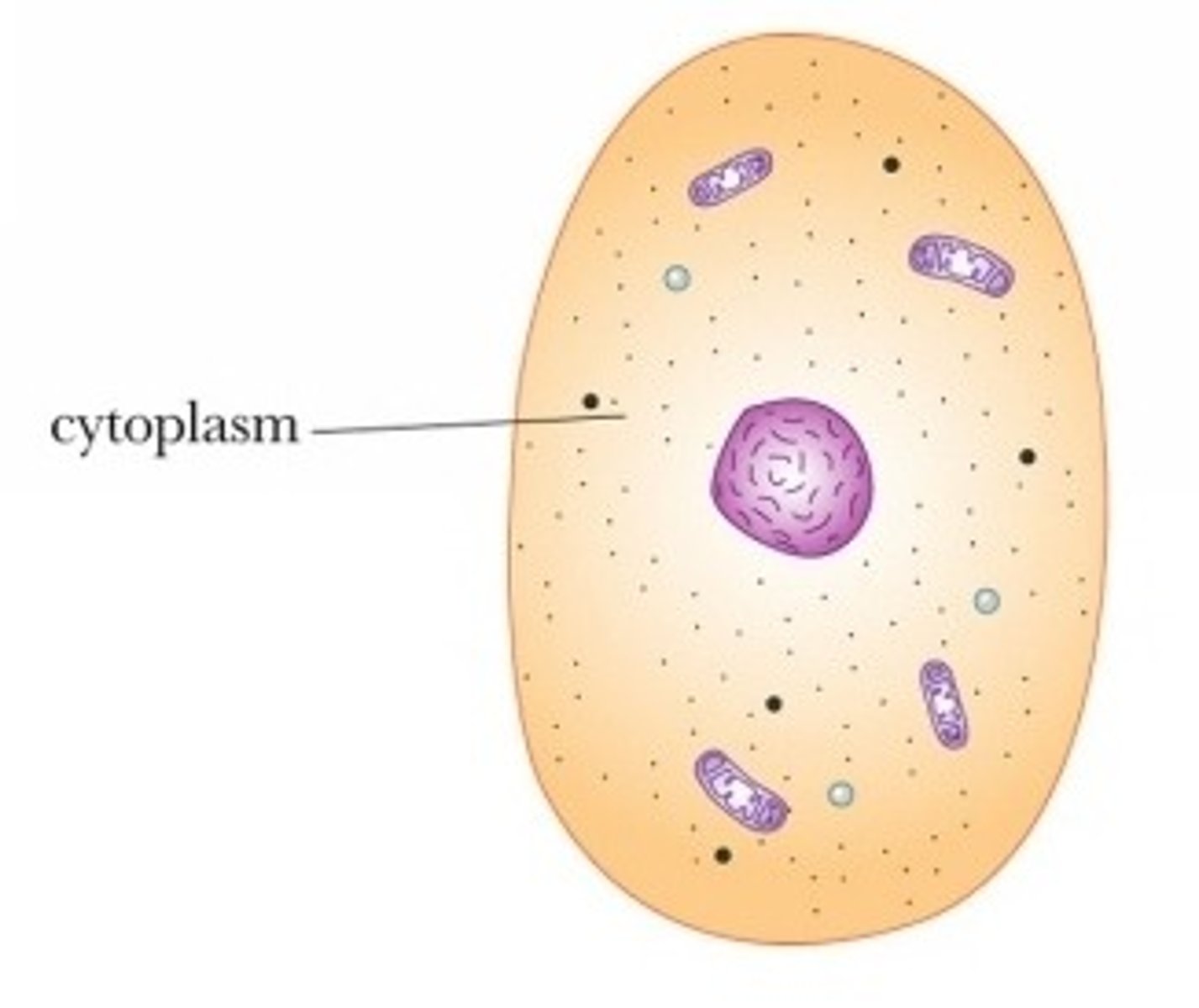
ALL CELLS
have a cell membrane (plasma membrane), cytoplasm, DNA, and ribosomes
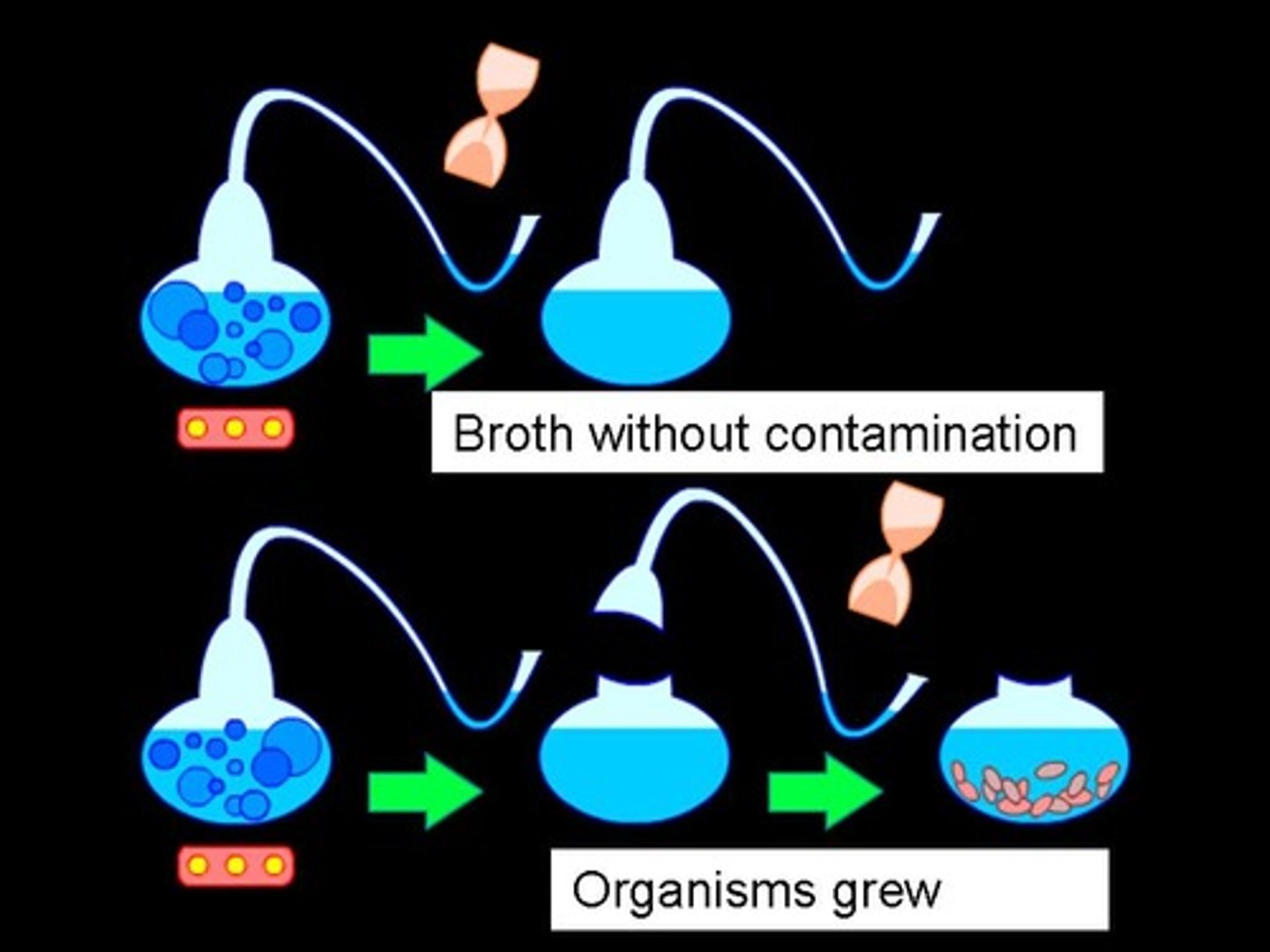
spontaneous generation
the MISTAKEN idea that living things arise from nonliving sources, in direct conflict with 3rd point of Cell Theory ( All cells come from preexisting cells)
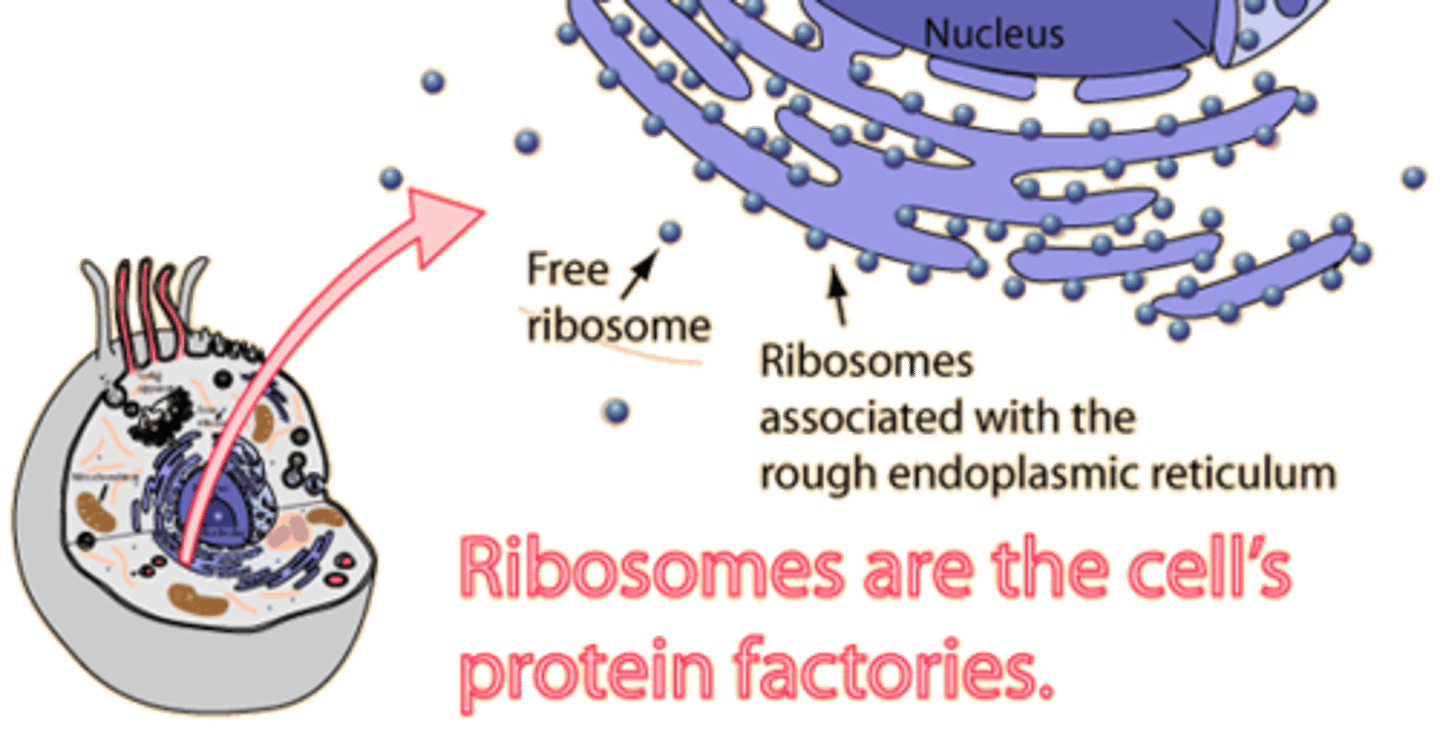
Ribosome
Makes proteins, found in BOTH prokaryotes and eukaryotes
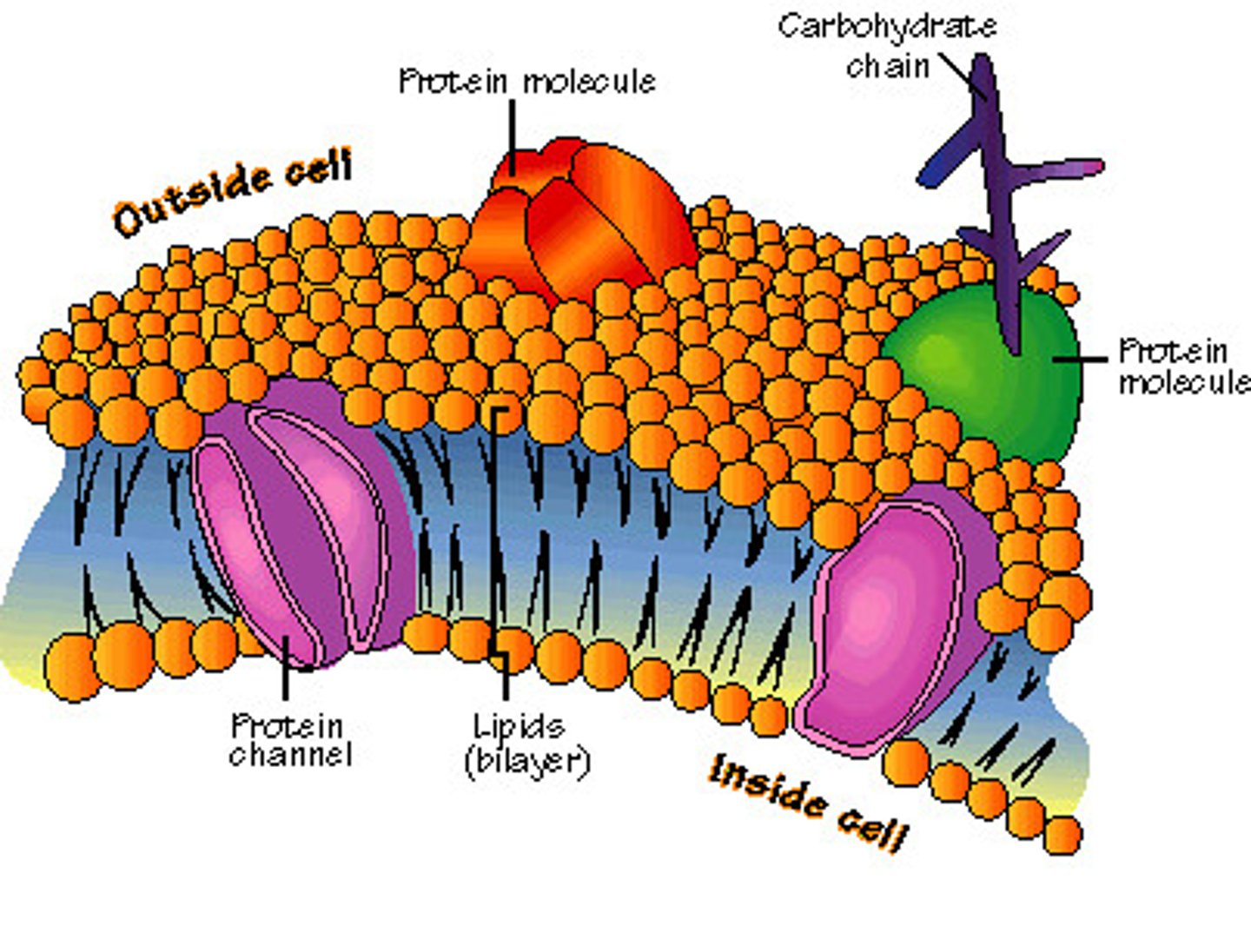
Cell membrane (plasma membrane)
phospholipid bilayer that surrounds ALL cells and regulates what enters and leaves the cell
Pasturization
process in which a liquid is heated to a temperature that kills most bacteria and microorganisms to prevent spoiling of canned goods

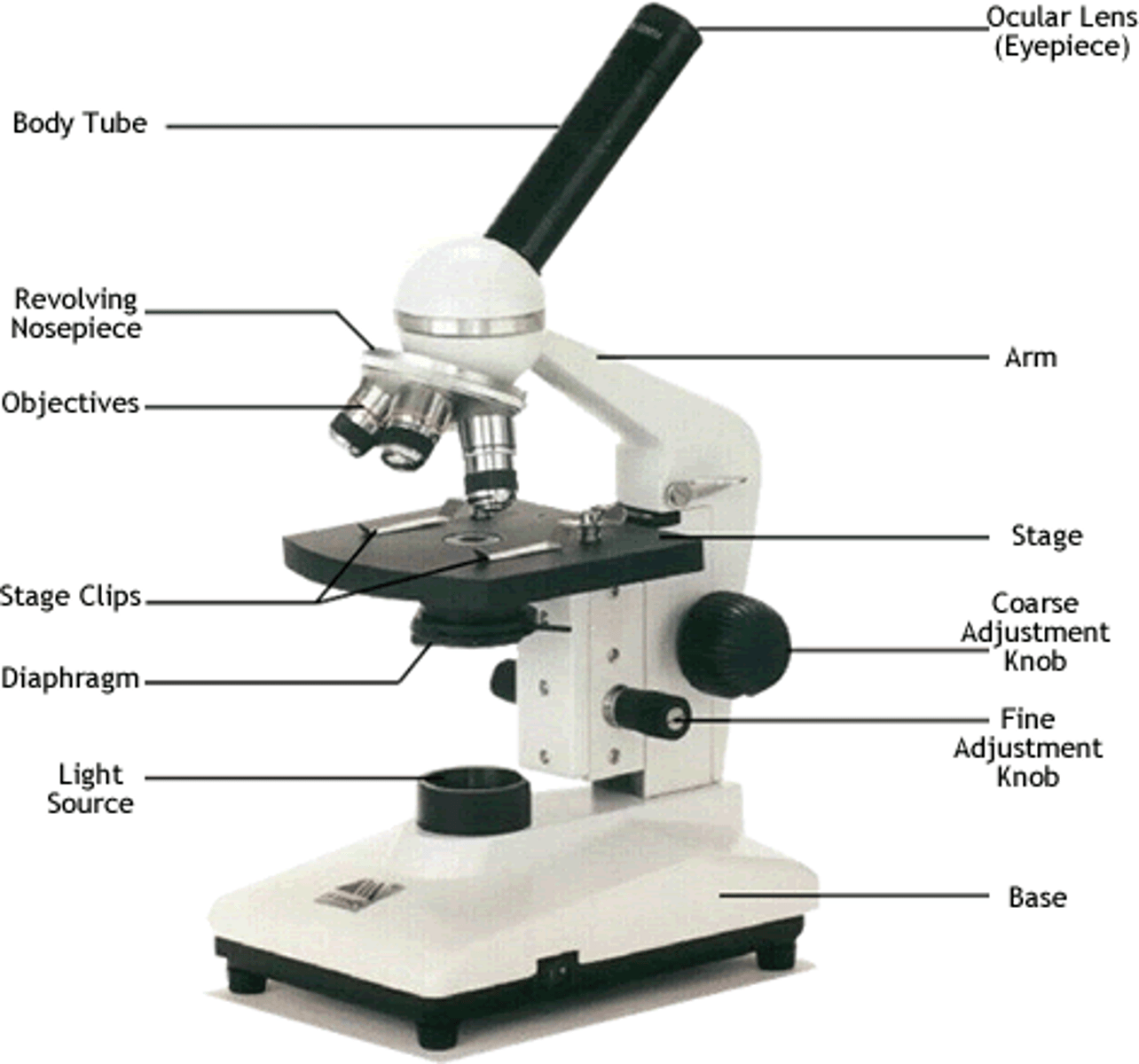
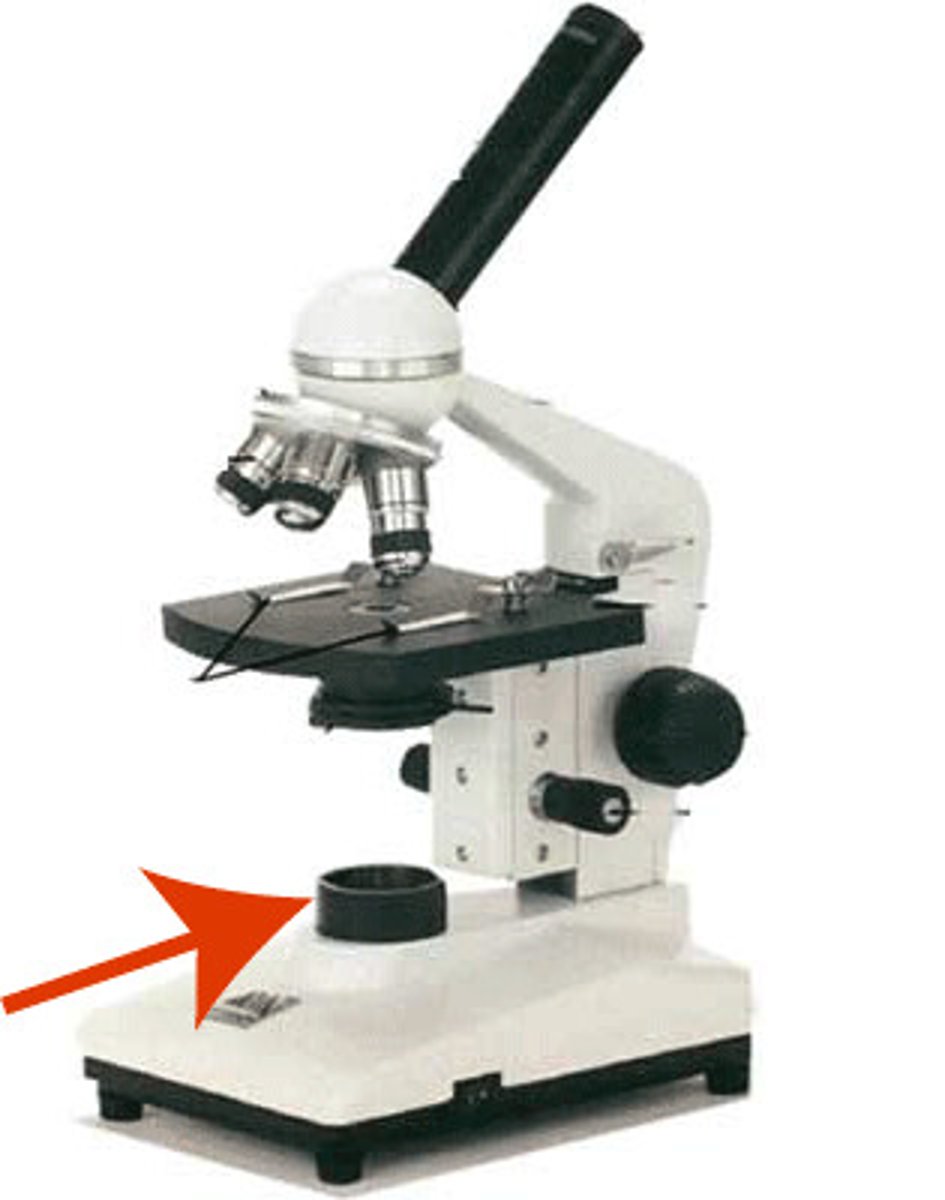
light source of microscope
located in the base
illuminates sample

stage of microscope
Holds the microscope slide in position.
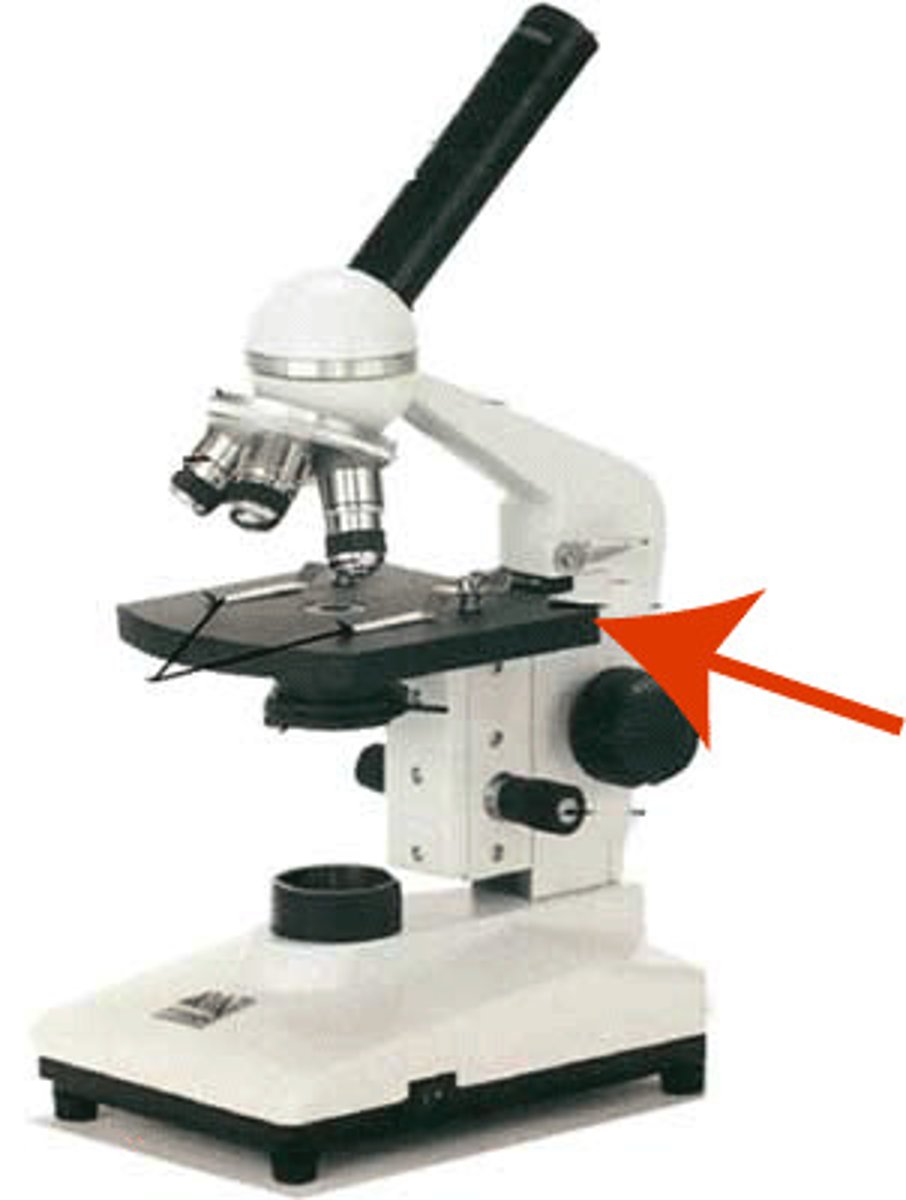
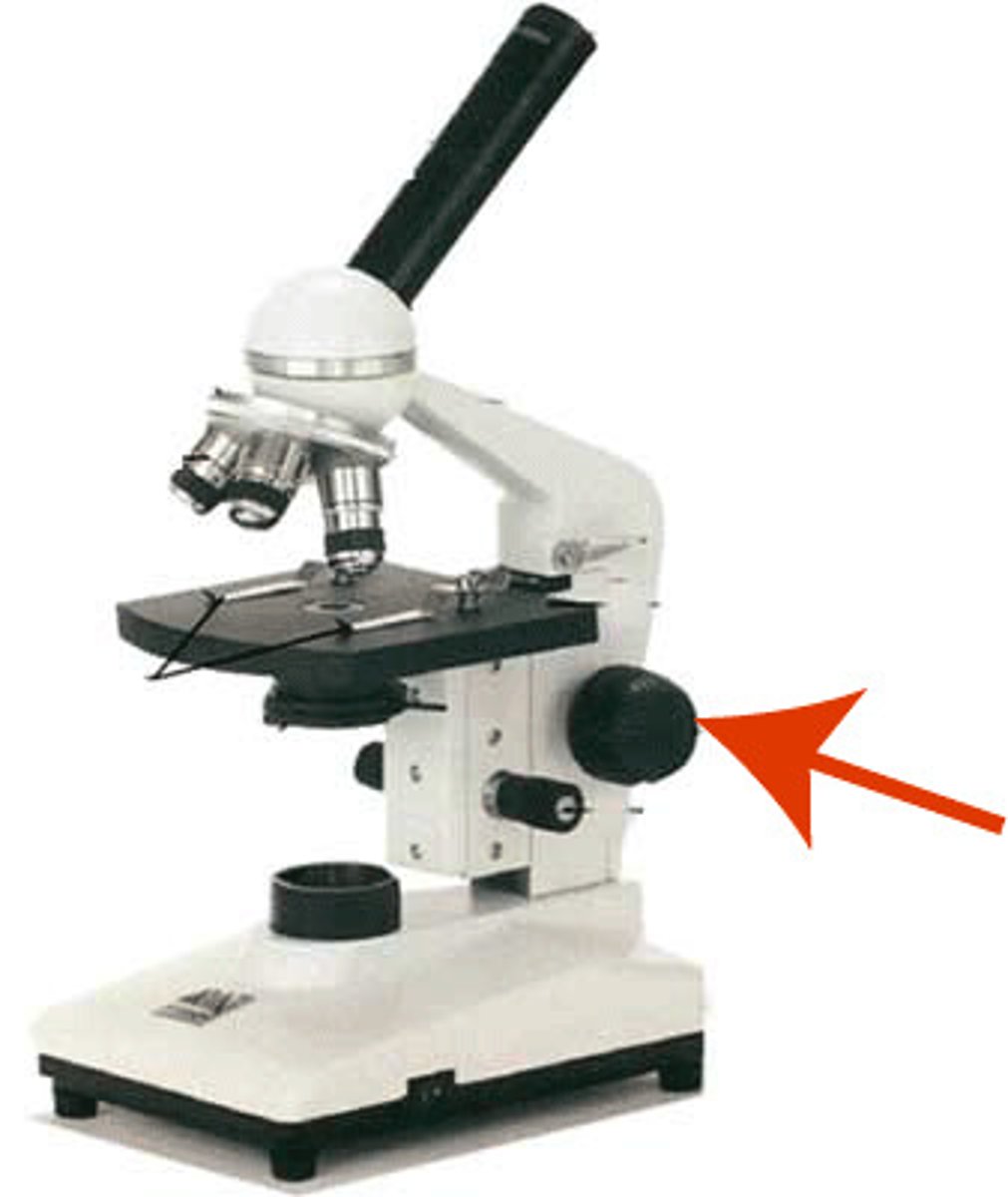
course adjustment knob
used to focus only on low power

revolving nosepiece
Holds and turns the objectives into viewing position
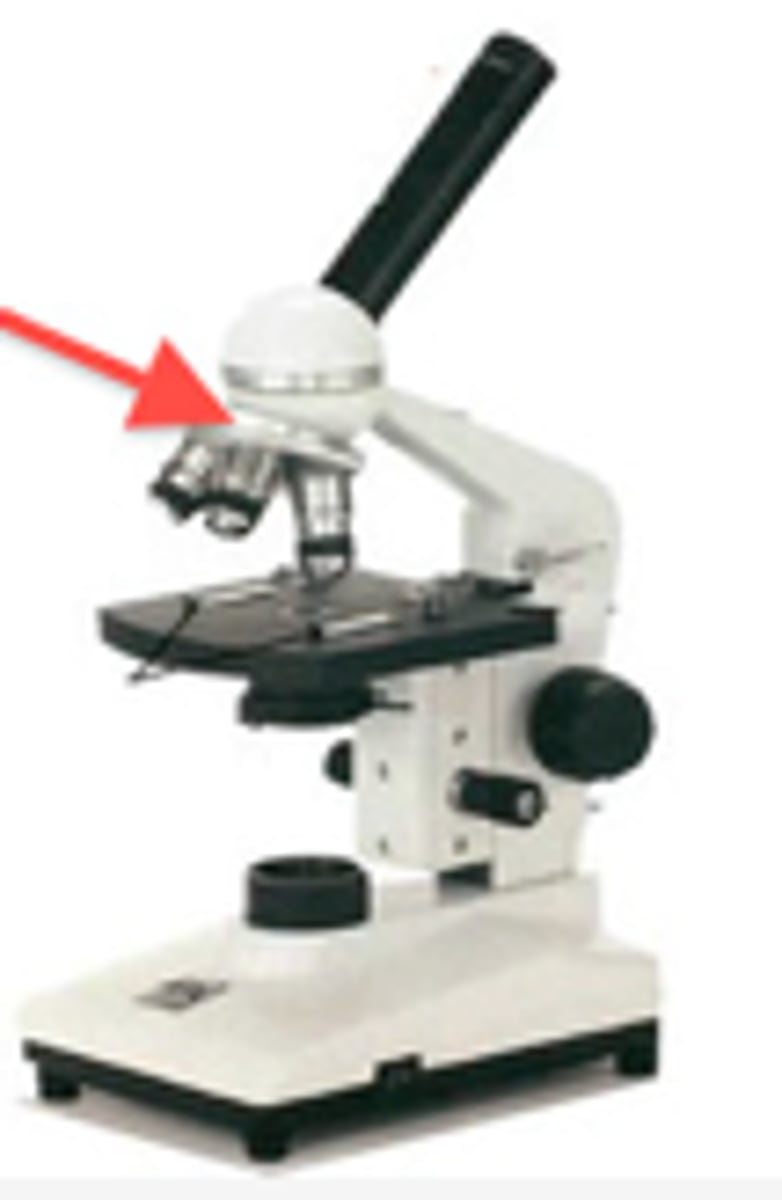
Diaphragm
Regulates the amount of light on the specimen
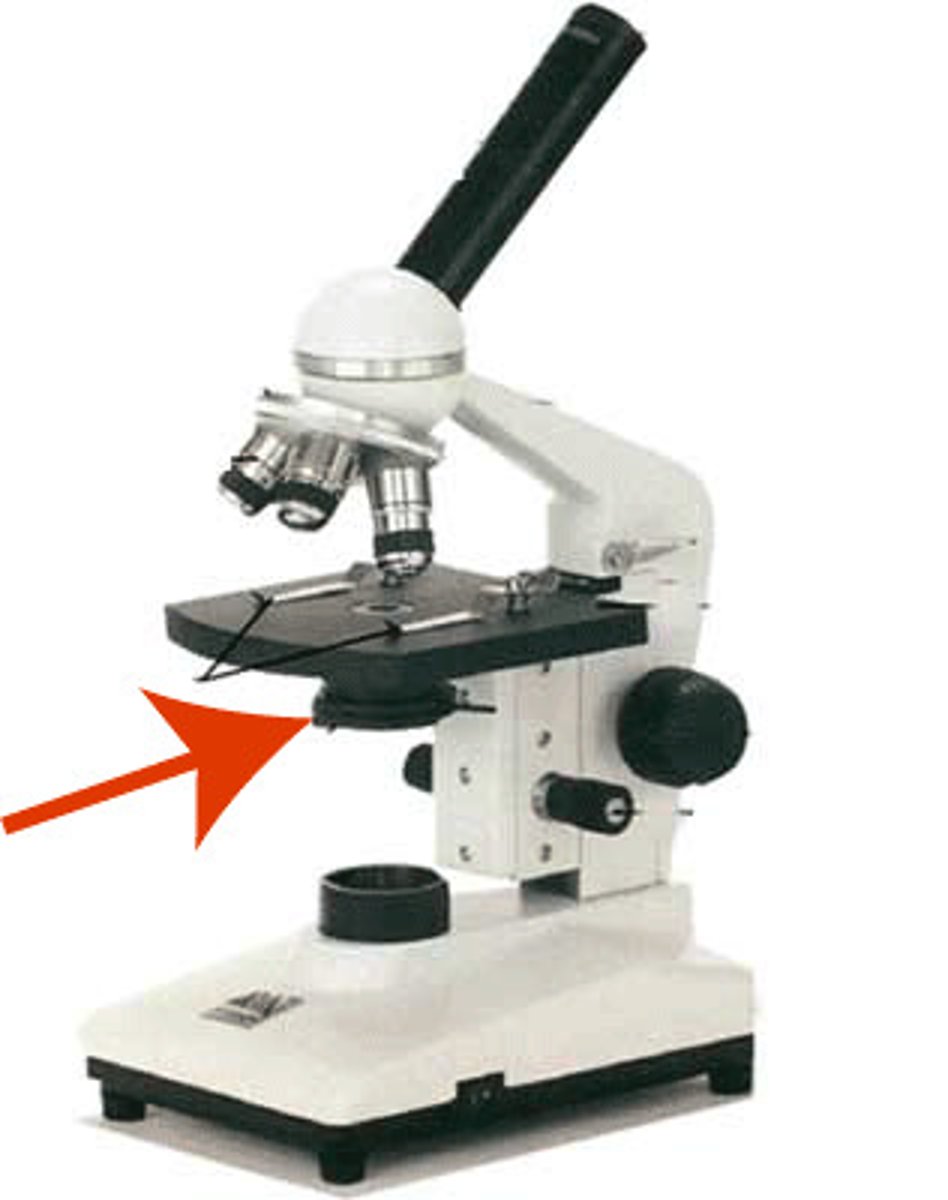
eyepiece lens (ocular lens)
Contains a lens that magnifies about 10x

fine adjustment knob
this part moves the stage slightly to help you sharpen or "fine" tune your view of the specimen
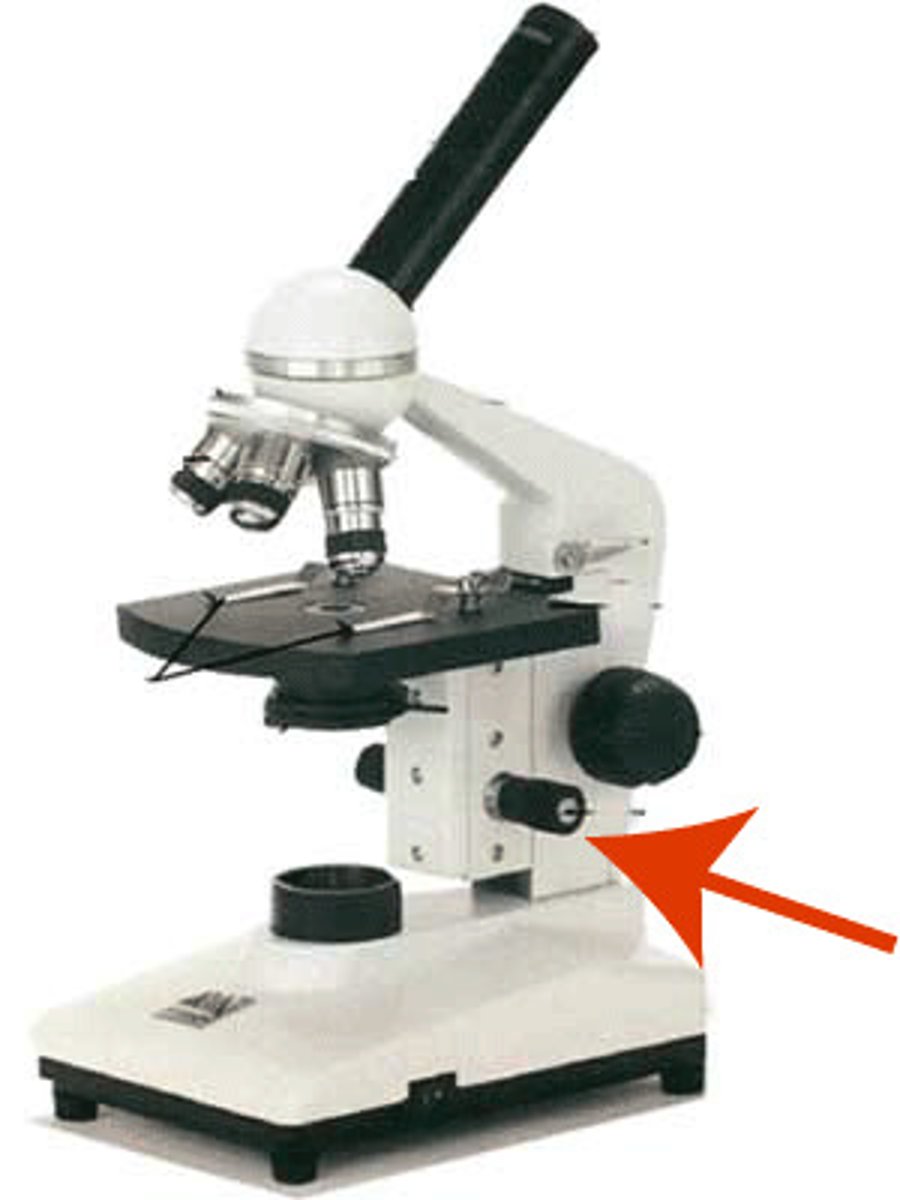
low power objective
a small lens with low magnifying power (4x)
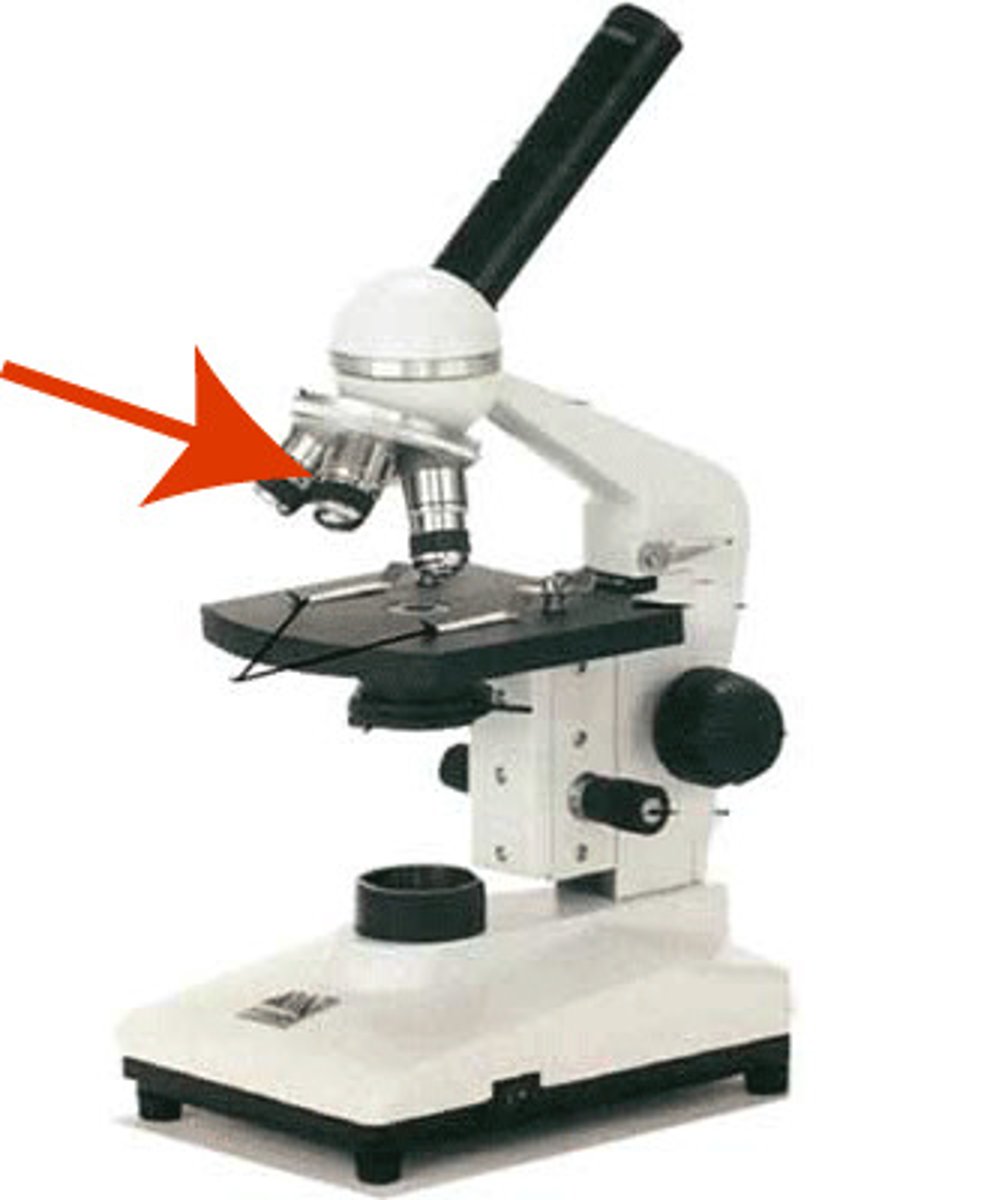

medium power objective
medium sized objective
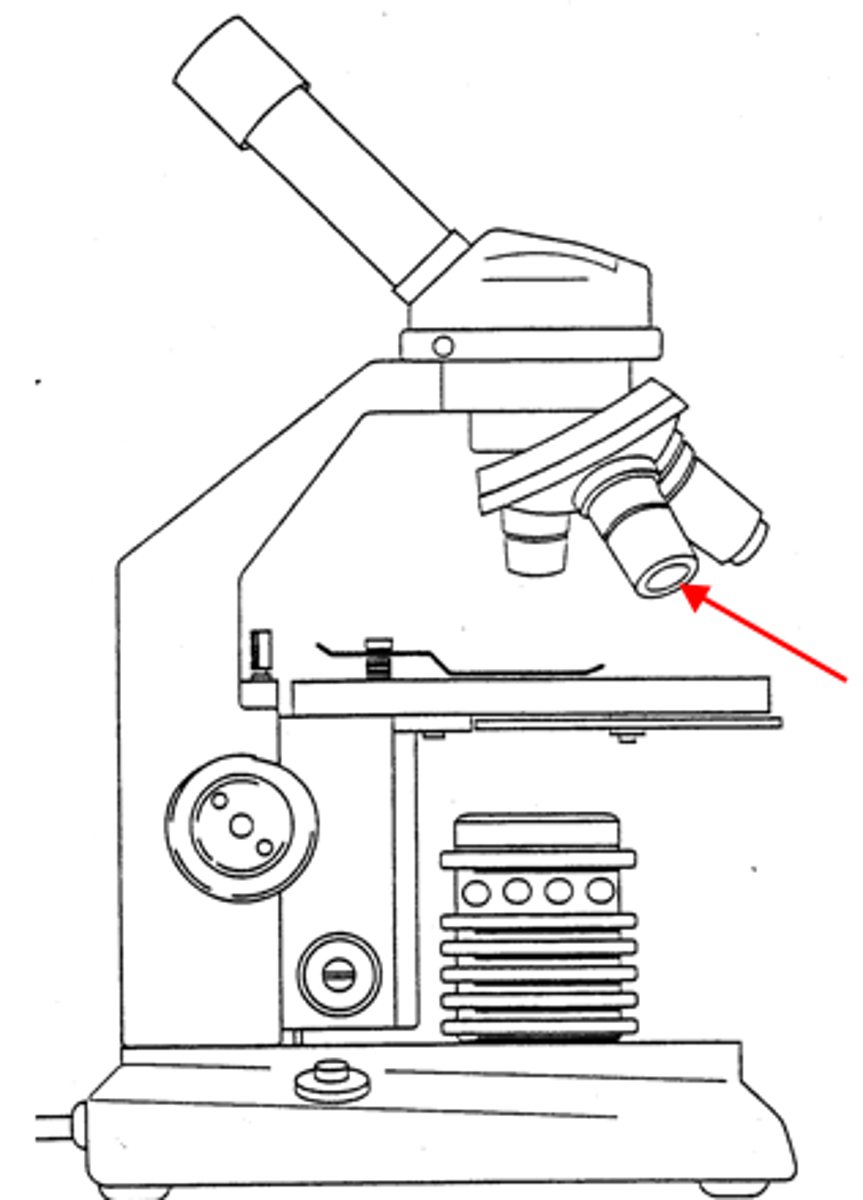
high power objective
a large lens with high magnifying power.
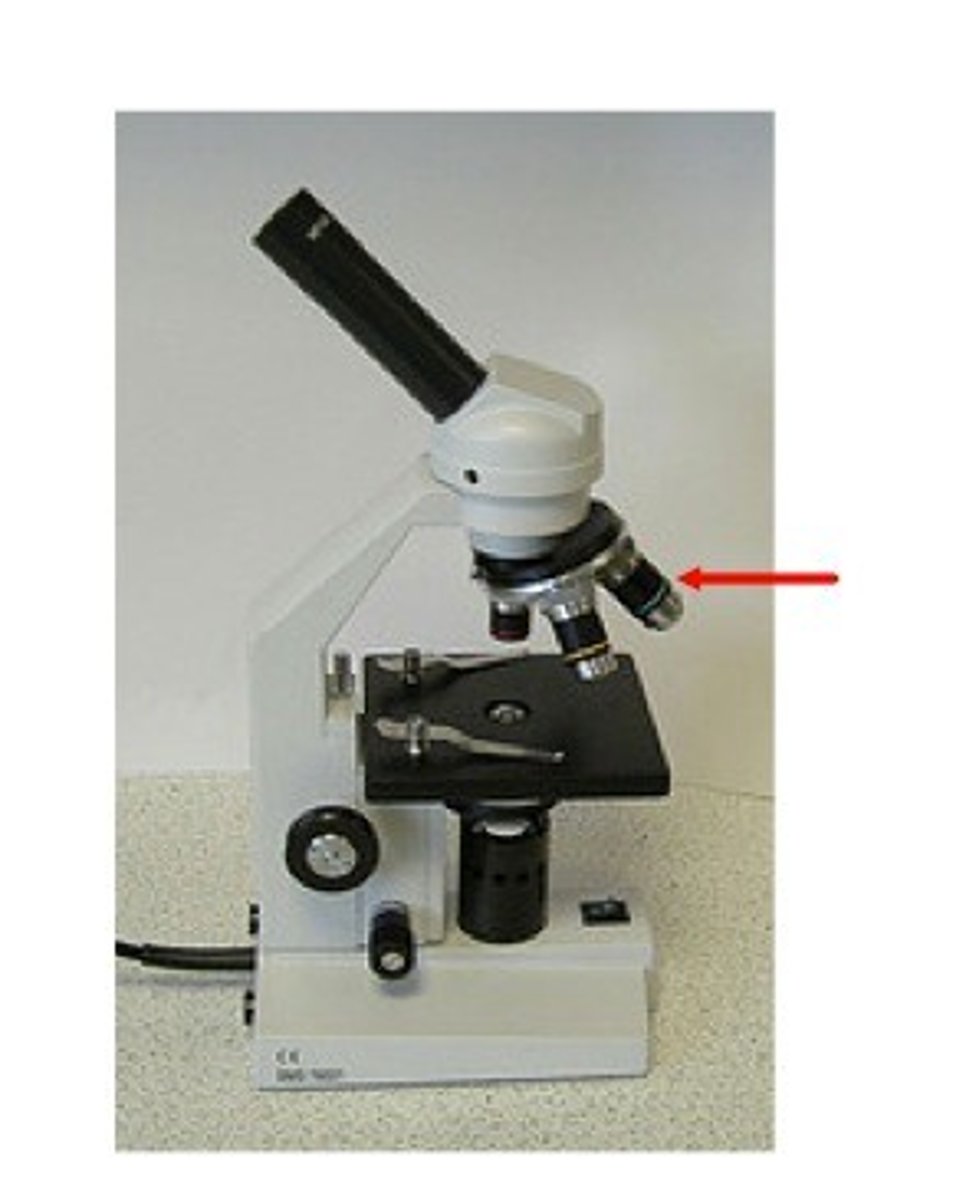
arm
Used to support the microscope when carried
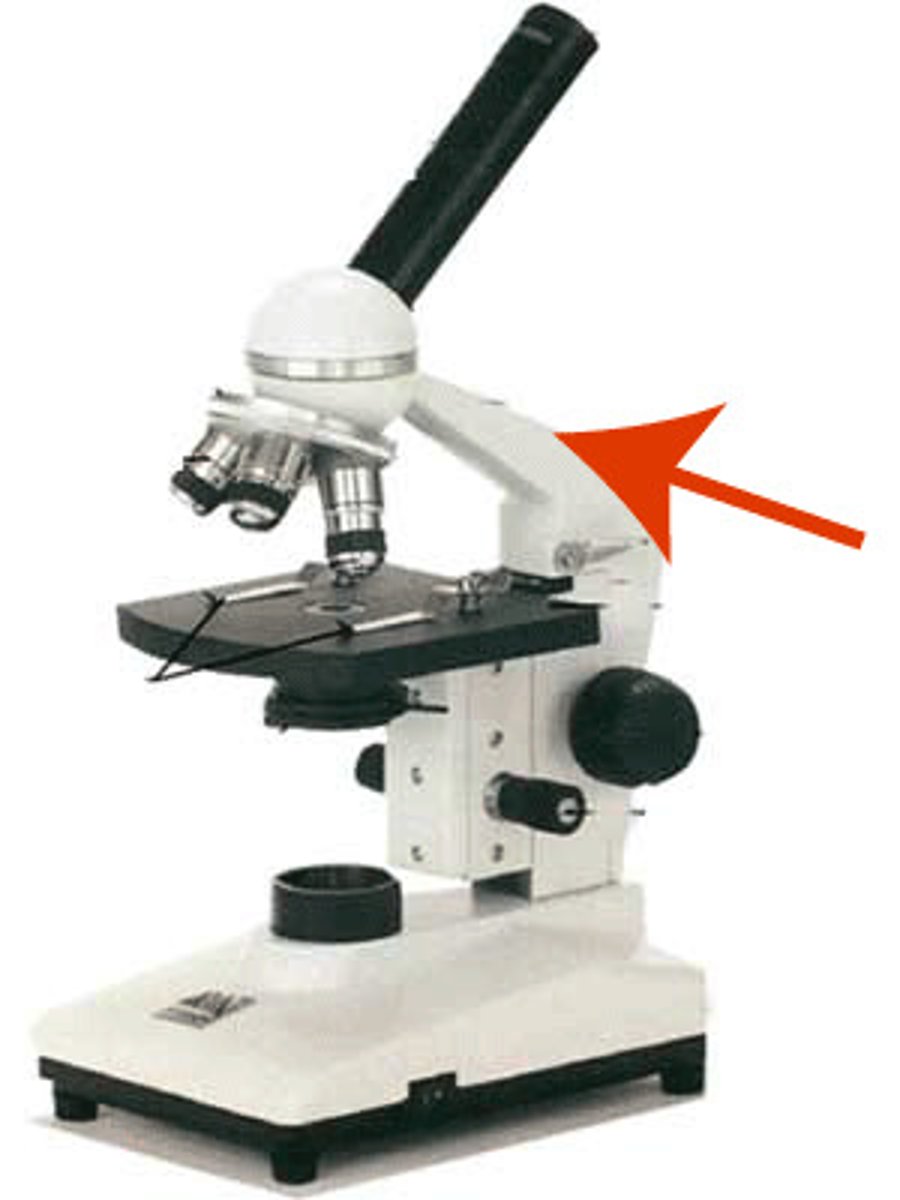
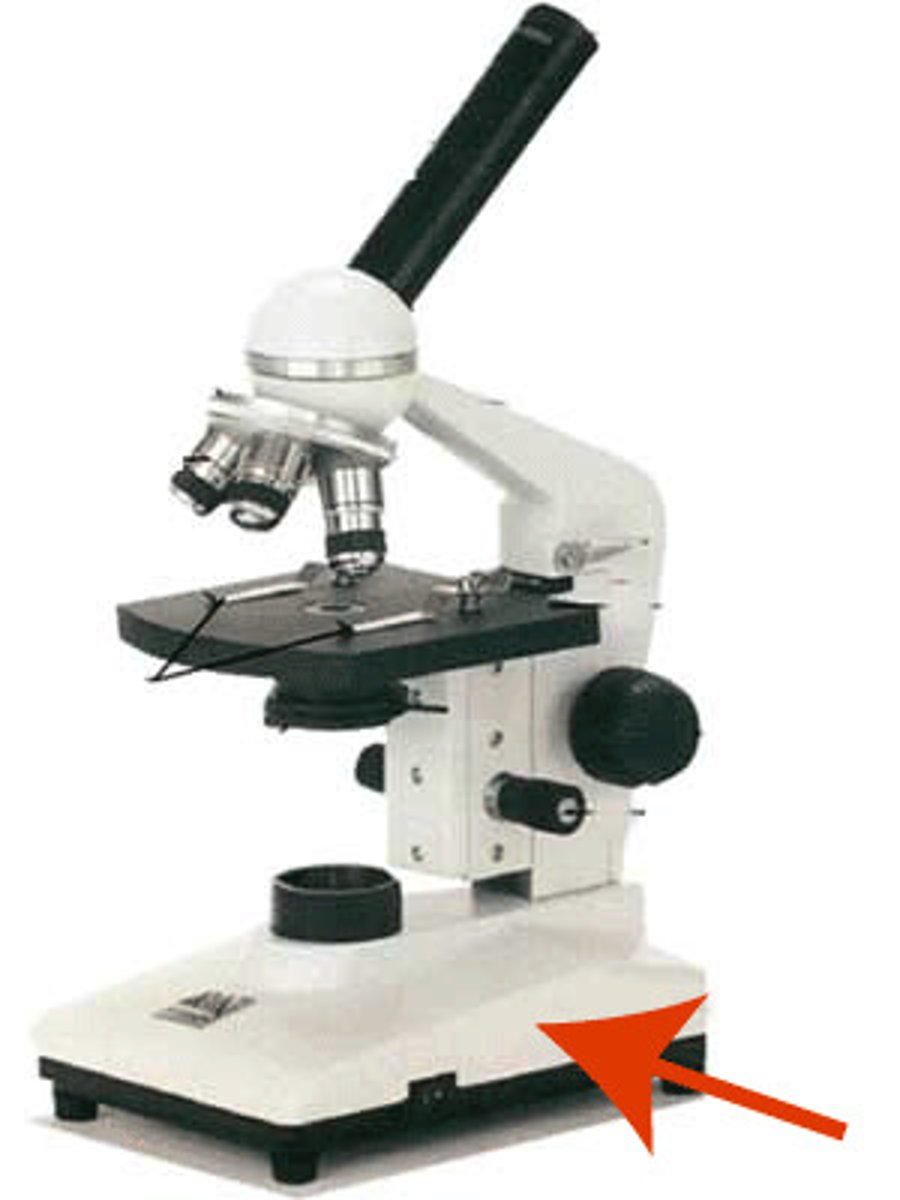
Base
supports the microscope

body tube
Connects the eyepiece to the revolving nosepiece
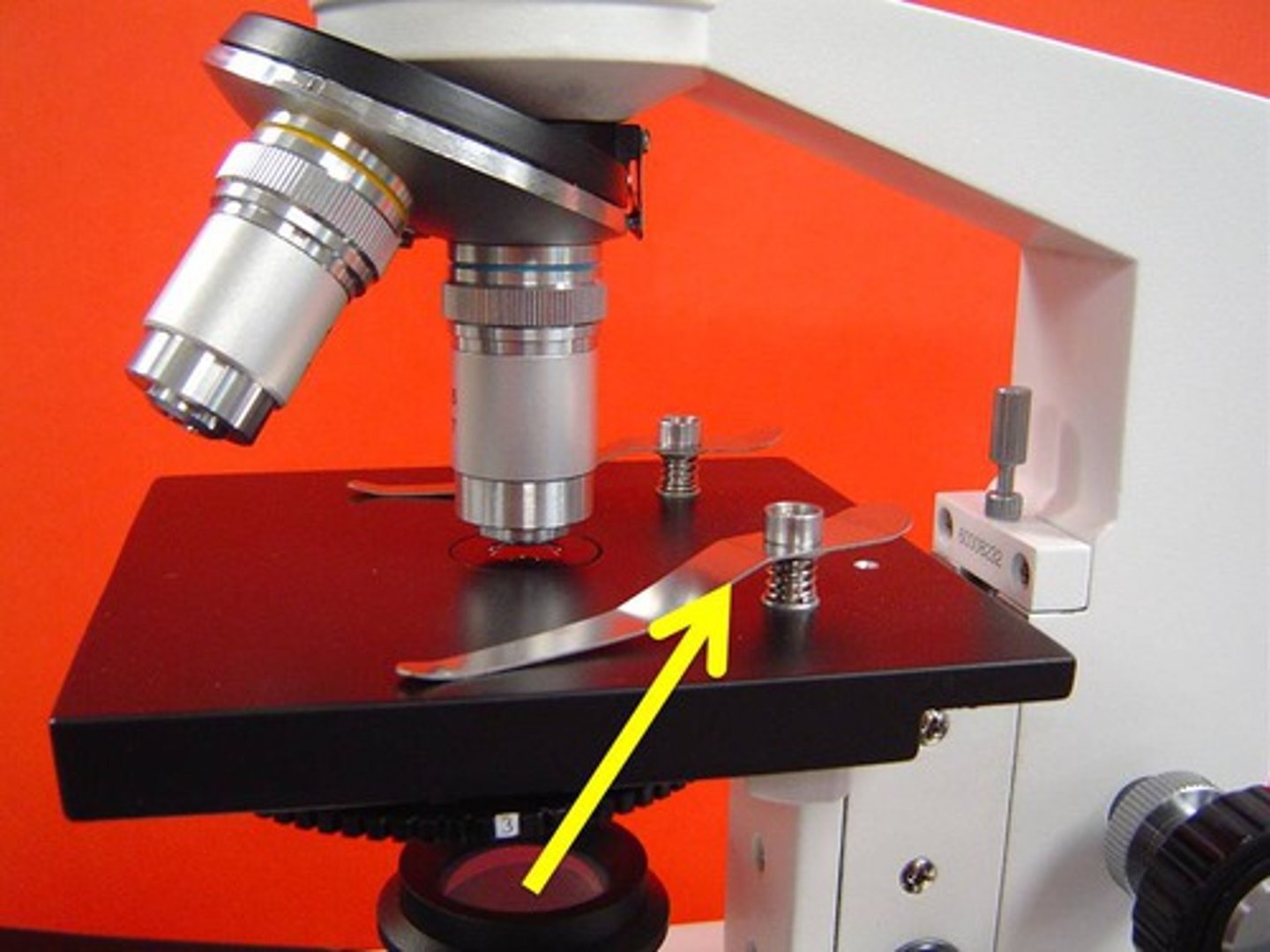
stage clips
holds the slide in place on the stage

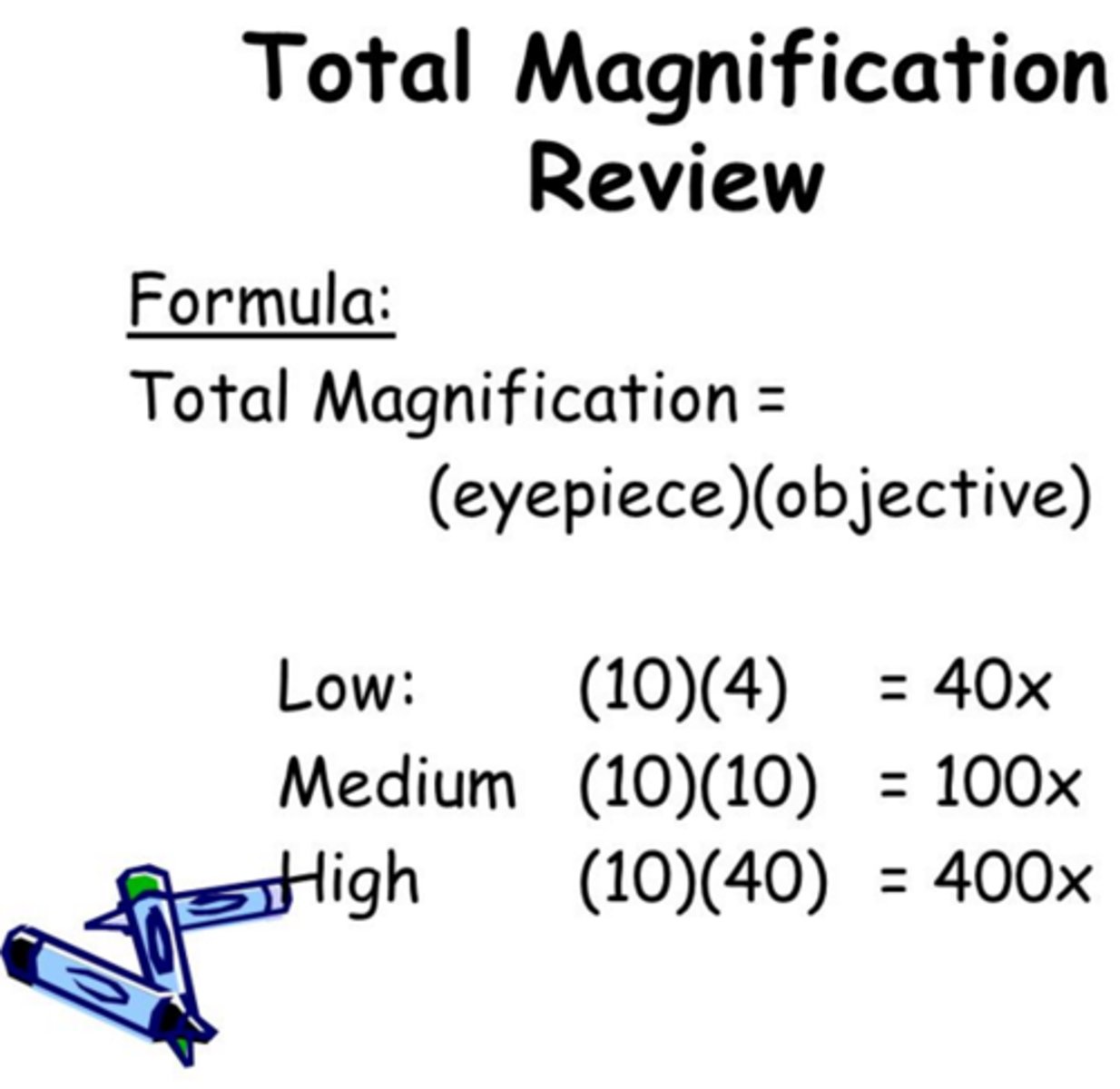
total magnification
objective lens x ocular (eyepiece) lens
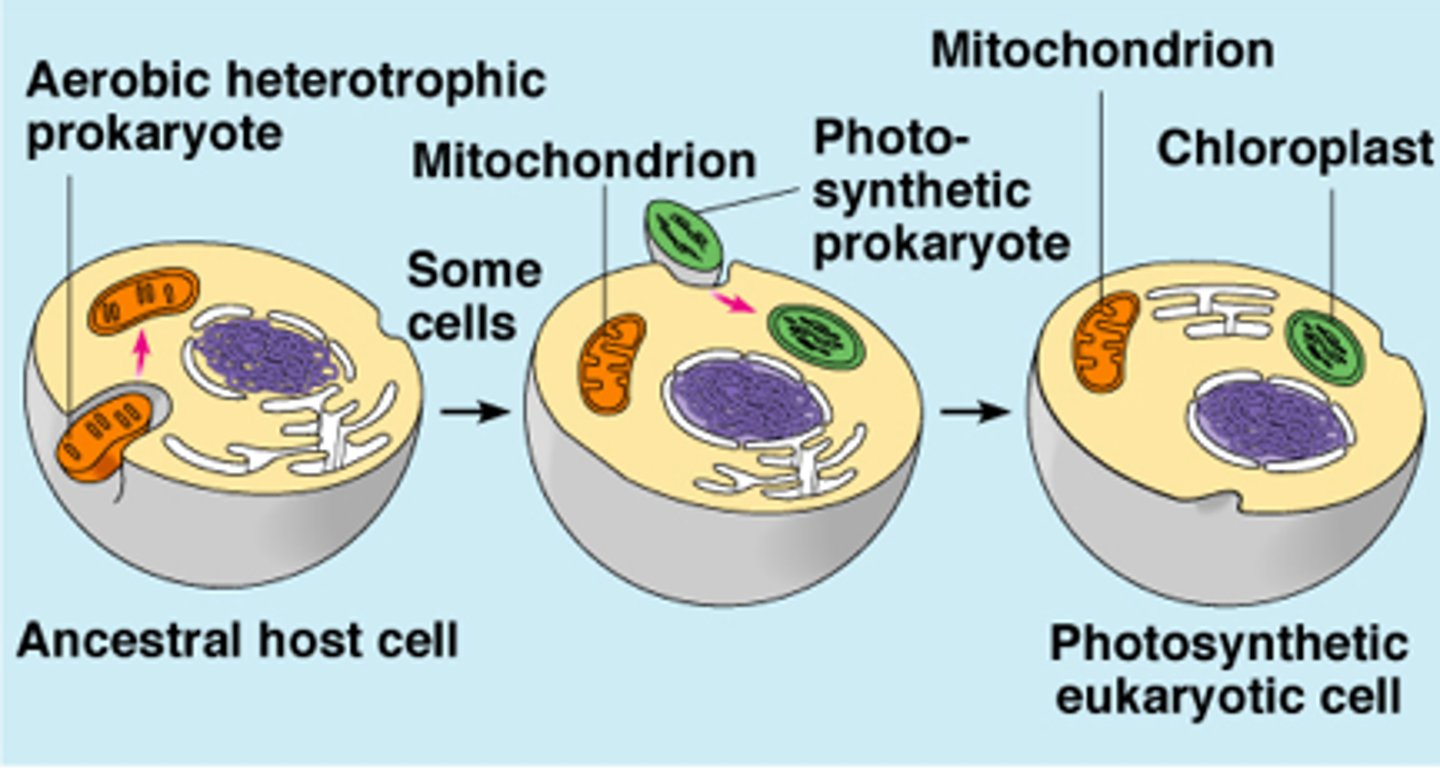
endosymbiotic theory
a theory that states that certain kinds of prokaryotes began living inside of larger cells and evolved into the organelles of modern-day eukaryotes
cell wall
strong, supporting layer around the cell membrane in plants, fungi, & prokaryotes, NOT found in animal cells