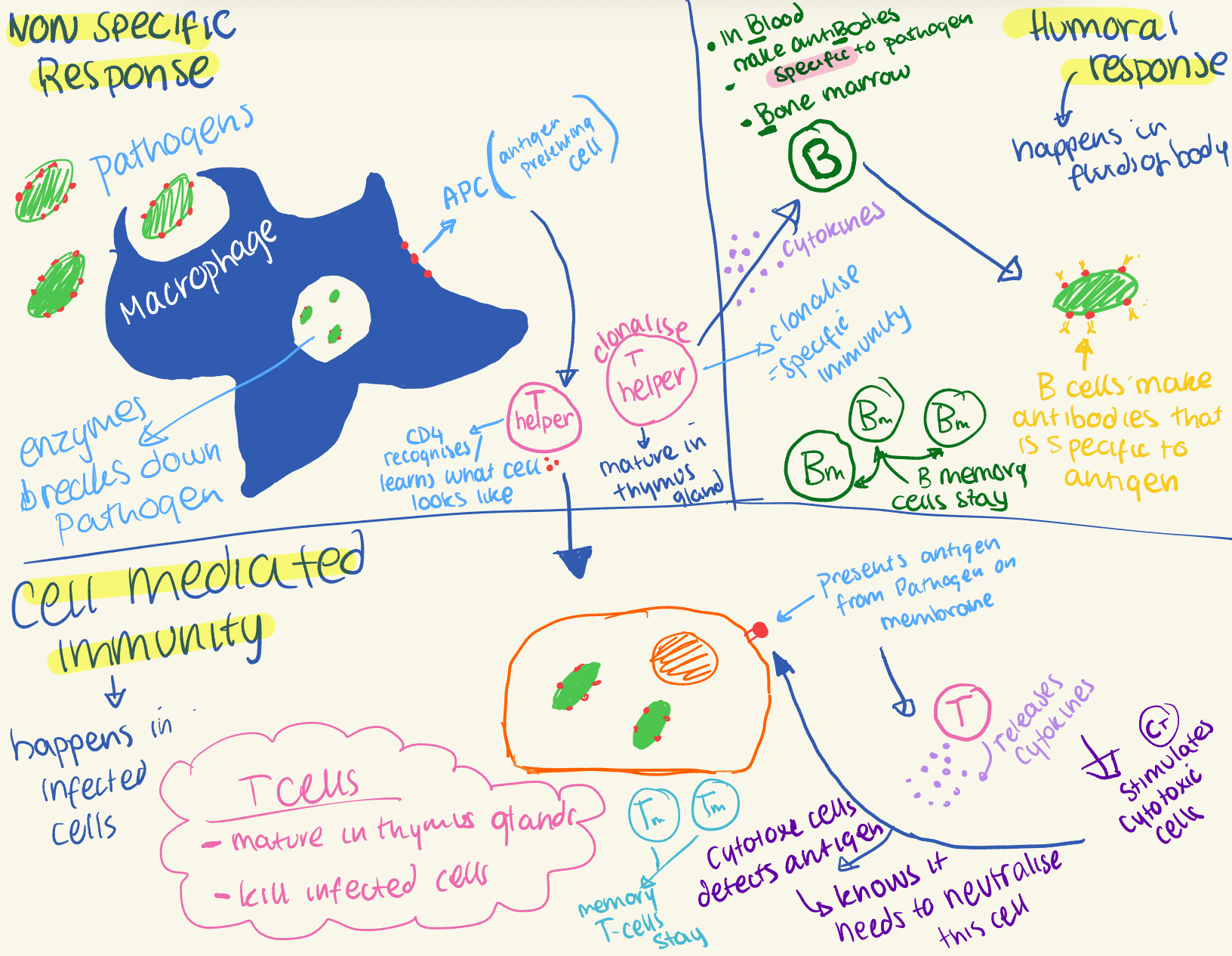
the immune system
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Non-specific/innate VS specific/adaptive
INNATE:
attack all foreign microbes
DOES NOT RETAIN MEMORY
Usually present from birth
ADAPTIVE:
recognises specific pathogens from previous infections
Rapid response
Can address infections around the whole body
Name the 5 types of main non-specific defences (P.I.I.NE)
P: phagocytosis
I: immunological surveillance
I: inflammatory response
N: natural anti microbial substances
E: epethilial barriers
What are memory B cells
live longer
Provide immunity by responding quickly to previously encouraged antigens
recognise and bind to antigens directly and produce antibodies
1st line non specific defence: epethilial barriers (C.U.N.S.S) — prevents entry of foreign microbes
Cilia: moves mucus + inhaled materials to throat — coughed up/swallowed
Urine: one way flow. Minimise risk of infection.
Nose hair: filter system. Stops foreign materials entering respiratory tract.
Sweat: contains antibacterial properties.
Skin: barrier against pathogens.
2nd line non-specific defence: antimicrobial substances (S.H.L.A.I)
Saliva: washes away antibodies
Hydrochloric acid: digests harmful antibodies in stomach
Lyzomes: found in teas and other bodily fluids.
Antibodies: bind to and destroys antigens
Interferons: activate immune cells. Prevent viral replication. Reduce spread of virus to healthy cells.
phagocytosis (M.N)
attack, digest and destroy foreign cells
Neutrophils:
most abundant type of WBC — first responders
Self destructive — once activated = destroy themselves
Macrophages:
live longer
After phagocytosis of an antigen, they displayed fragments of that antigen on their membrane — activates T cells — activates adaptive immune system.
Production and recruitment of neutrophils
inflammatory response
Occurs in response to injury or infection
purpose: inactive damaged tissues so healing can take place
Inflammatory response:
SCENARIO: needle with bacteria enters the skin
Mast cells release histamine molecules
Inflammatory mediators causes vasodilation — capillaries become larger. Fluid fills them up (responsible for redness that in inflammation — signs of healing)
EG: Increased temp: increase metabolic rate = faster repair
Histamines, chemokines (chemicals) being release into capillaries
Chemotaxis: chemical attraction of leukocytes (neutrophils and macrophages) WBC move towards these chemicals
Squeeze through capillary walls
Neutrophils — phagocytosis takes place. Engulf the bacteria that entered the body
What are the roles of the NK cells
patrol the body of abnormal host cells and kill infected cells
What imitates the expansion of T cells?
the recognition of a specific antigen presented by APC (antigen presenting cell)
Describe the difference between T cells and B cells
both produced in bone marrow however, T CELLS mature in thymus (thymosine hormone which stimualtes maturation and B CELLS mature in bone marrow
T cells provide CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY
Consist of:
Cytotoxic: directly inactive the cell
Helper: secretes cytokines to support cytotoxic cells
B cells provide (ANTIBODY MEDIATED IMMUNITY)
B cells produce antibodies (immunoglobulins)
Biden the and destroy antigens
Cell mediated immunity! Diagram (explain what is happening)