ARCH 1013 Final Exam (Briar Jones)
1/219
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
220 Terms
Architecture responds to...
the needs of its users and rises to the level of art
Architecture is connected to...
a particular place and relates to the specifics of geography, climate and the surroundings
Why is architecture important?
because it permanently records a civilization's aesthetic tastes, material resources, political and social aspirations
What does architecture help define?
a place
what are the three principals Vitruvius felt was essential to architecture?
firmness, commodity, and delight
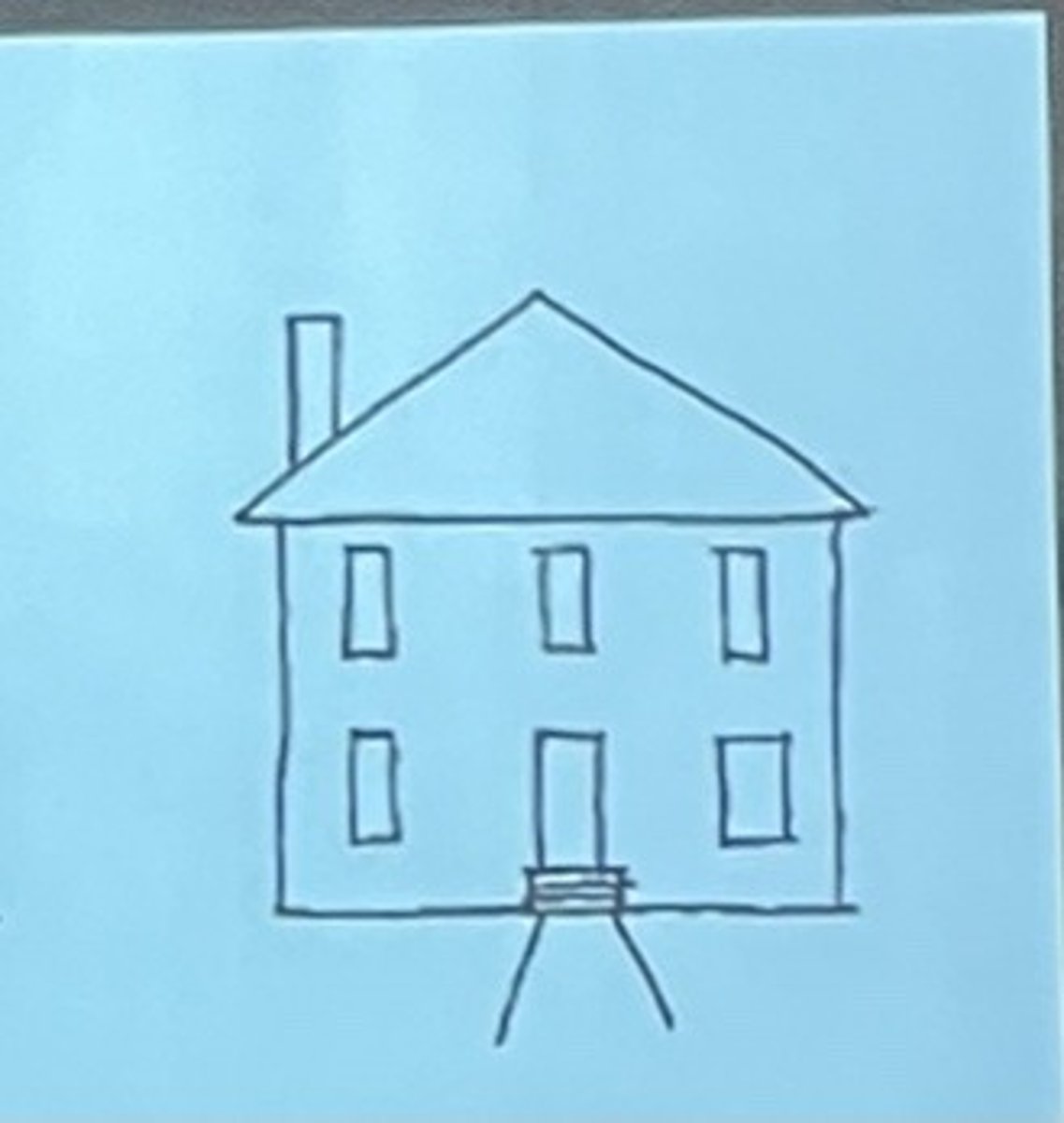
representative sketch

abstract sketch

symbolic sketch
solids and voids
the relationship between them creates architectural space
symmetry
designing one side of a space to mirror the opposite
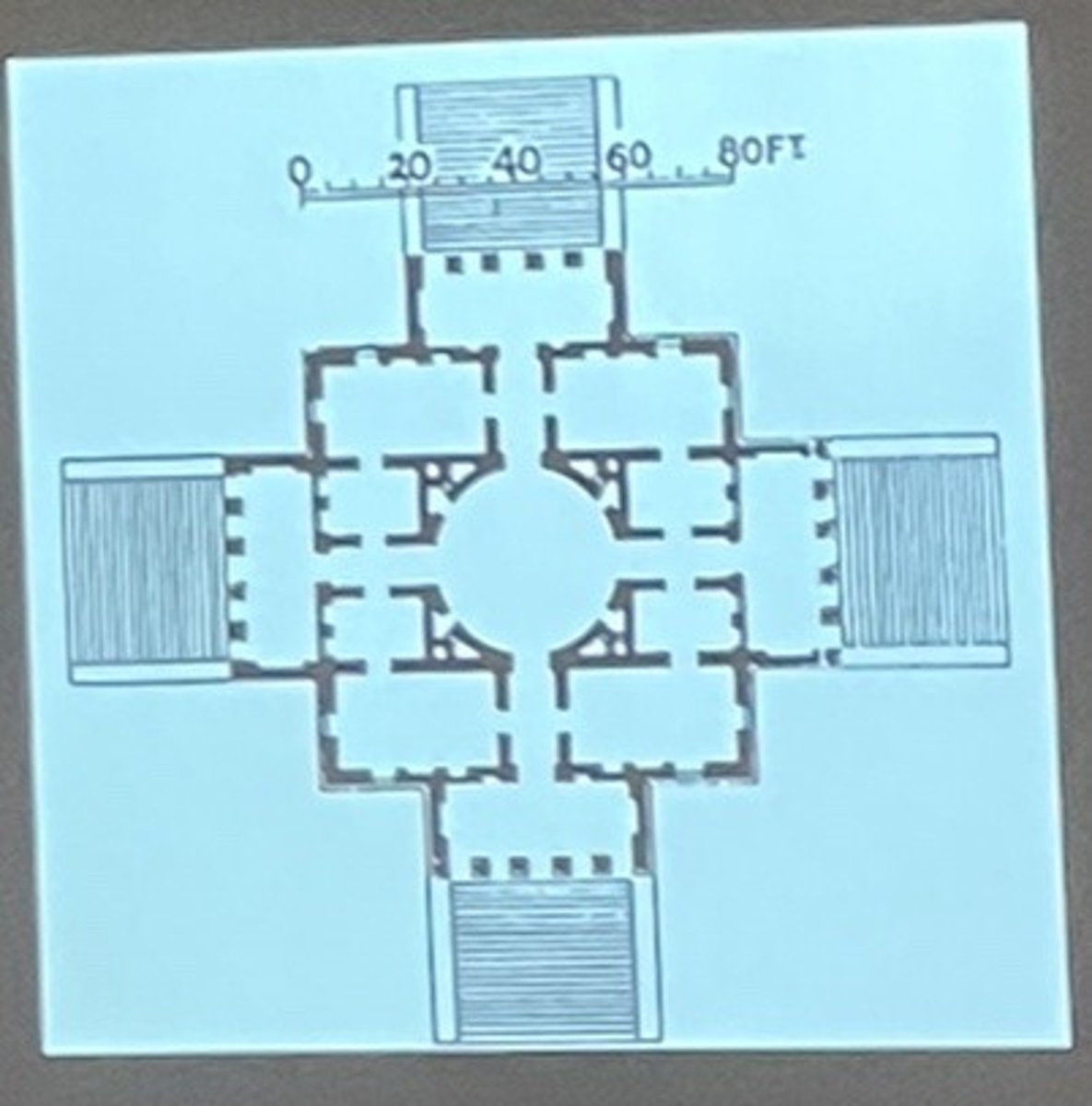
Asymmetry
architectural elements that are unevenly spaced in size, shape, and/or position
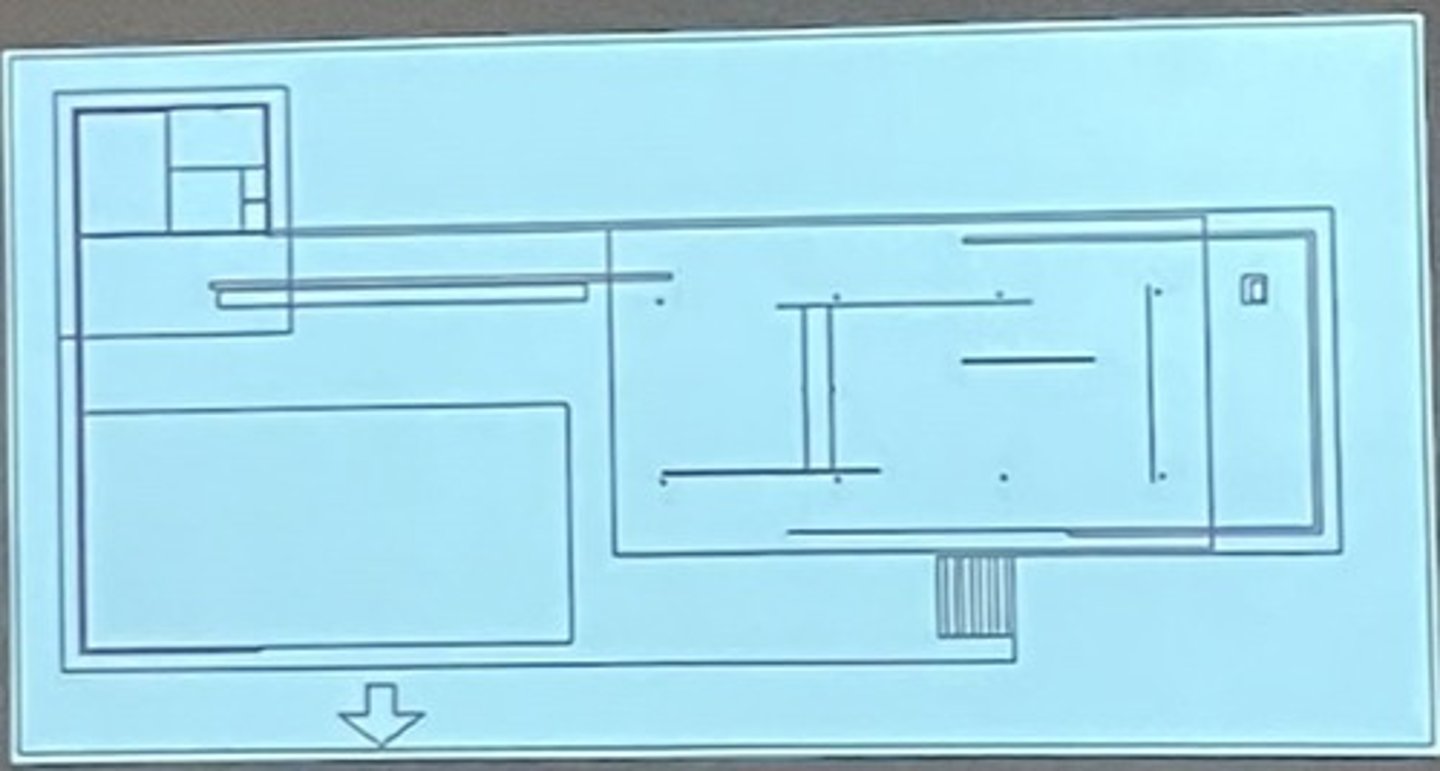
scale
the size or proportion a building element appears to have relative to other elements of know or assumed size
why do architects use scale figures?
to help convey visual scale
proportion
a quantified relationship among the parts of an element as well as the relationship of that element to the whole
golden section
known since the Greek mathematician Euclid, an irrational proportion with special mathematical and spatial relationships applicable to a wide variety of phenomena, including aesthetics, art, music, and nature
"a line cut in such a way that the smaller section is to the greater as the greater is to the whole"
golden section
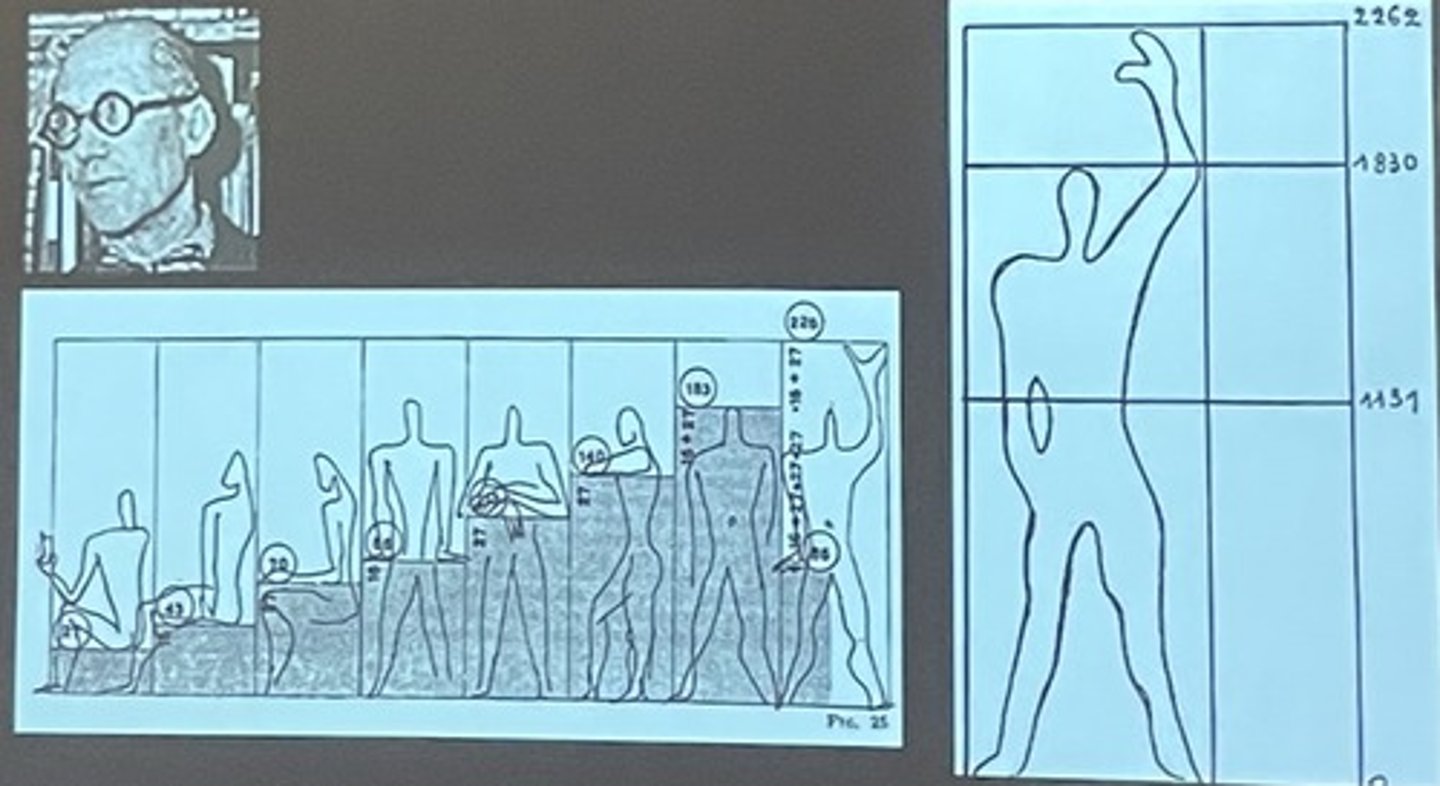
leonardo de vinci's drawing of body's balanced proportions

Le Corbusier's Modulor
a series of harmonic numbers; one was the average height of the human being, the other the height of a man with raised arms
massing
composing three-dimensional shapes or volumes into a building design
style
a particular or distinctive form of artistic expression characteristic of a person, people, or period
shed roof
slopes to one side

gable roof
slopes to two sides

hipped roof
sloping ends and sides that meet at a ridge
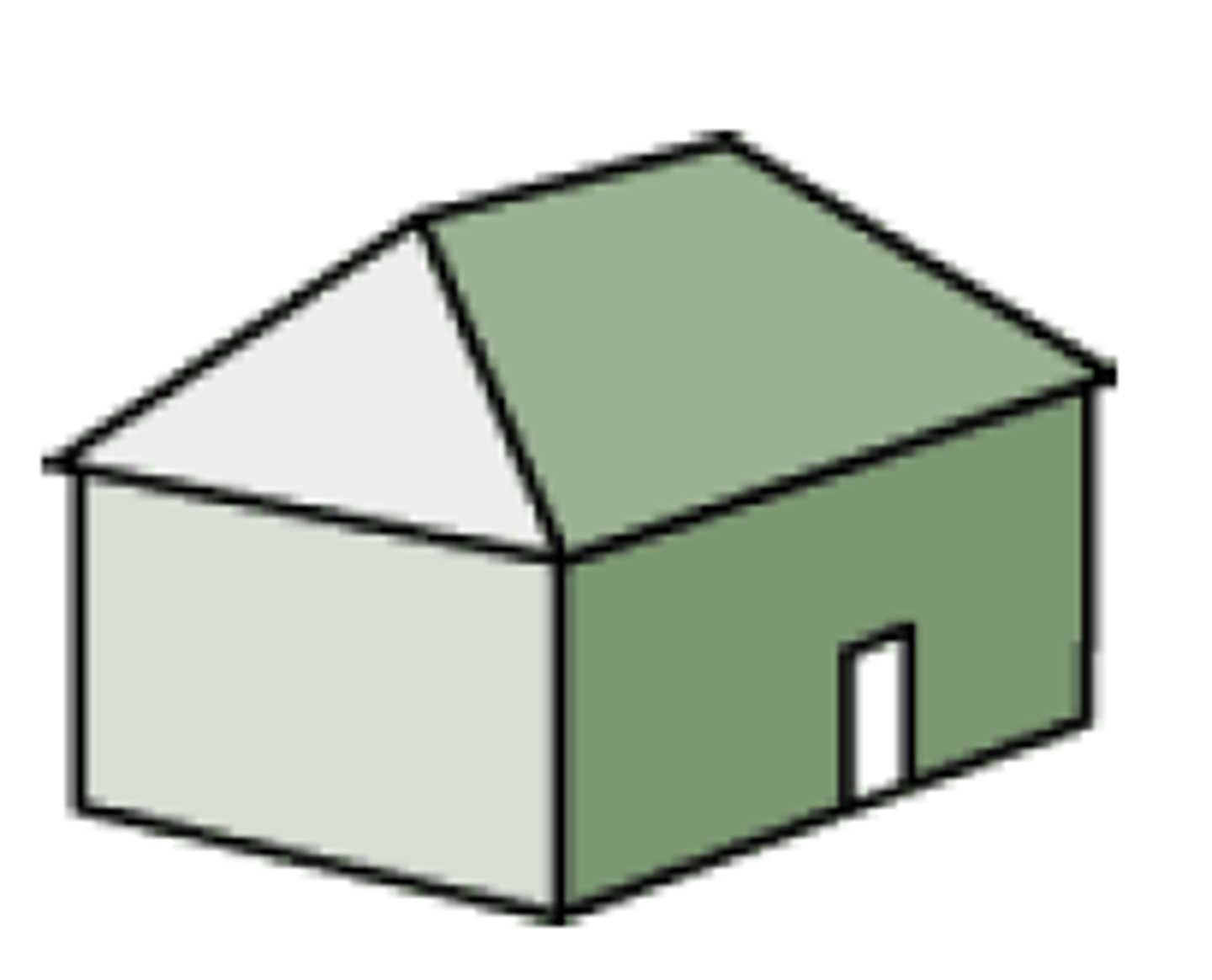
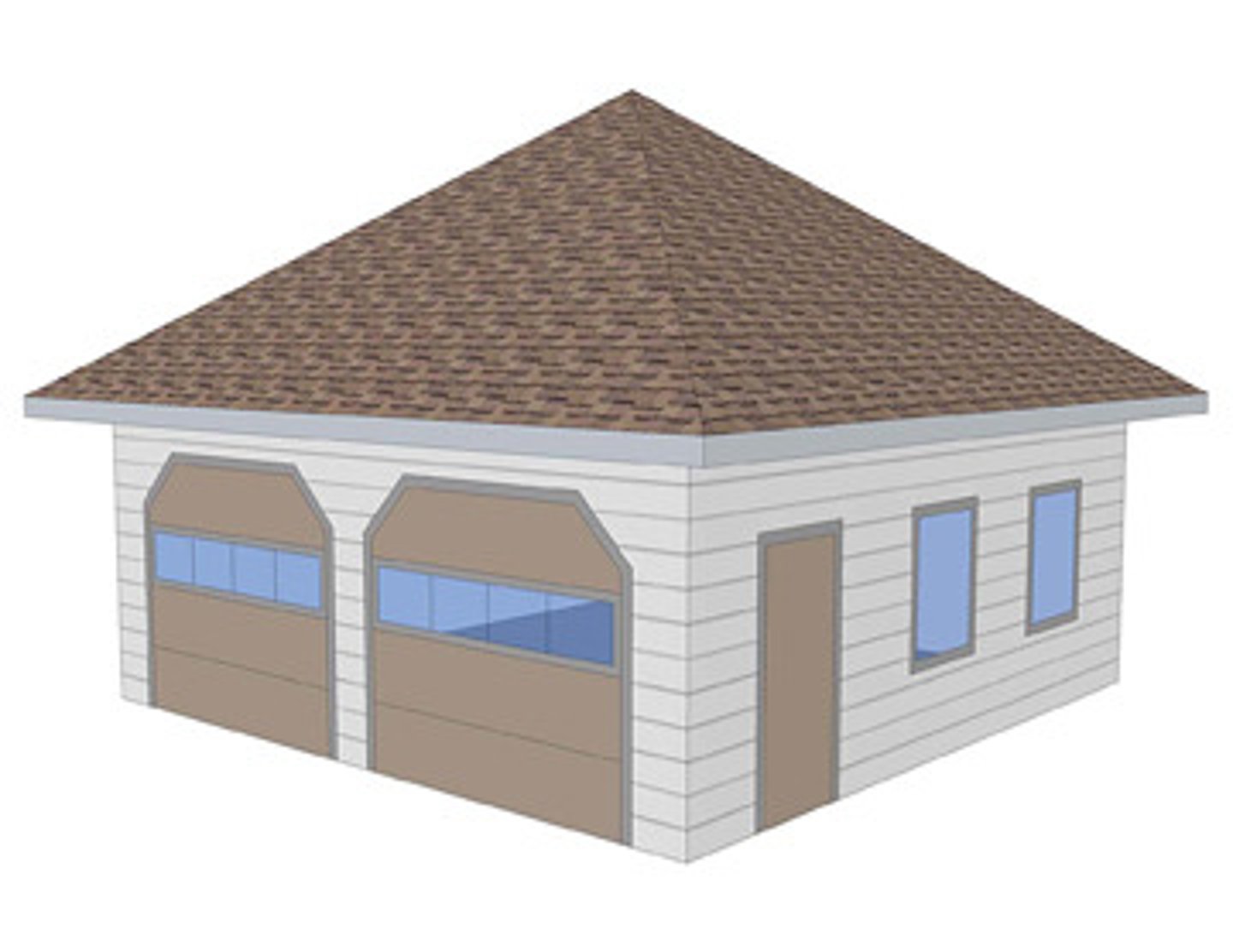
pavilion roof
shaped like a pyramid and is used to cover a square structure

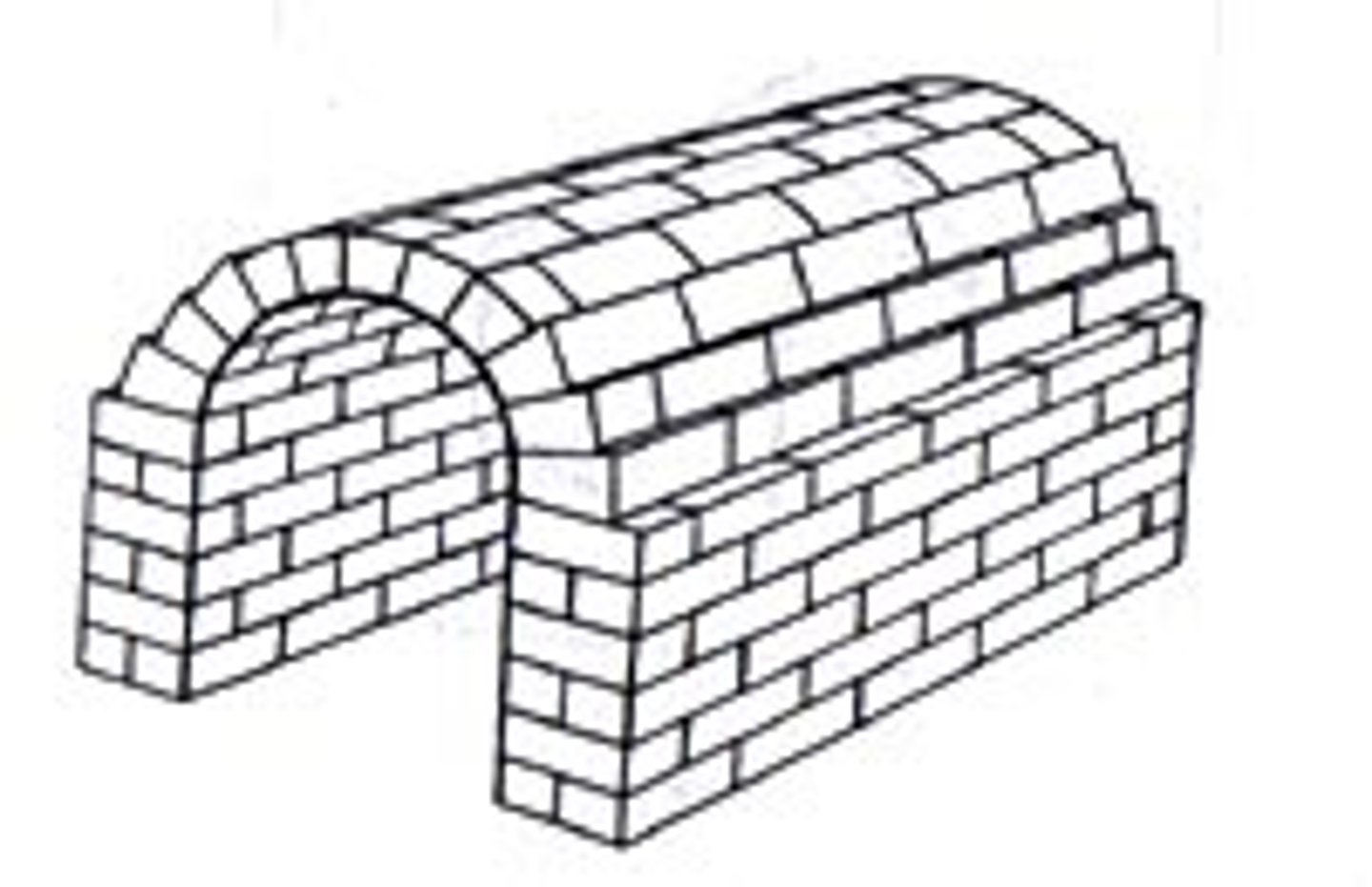
barrel vault
a semicircular roof
gambrel roof
combines two different pitches below the ridge
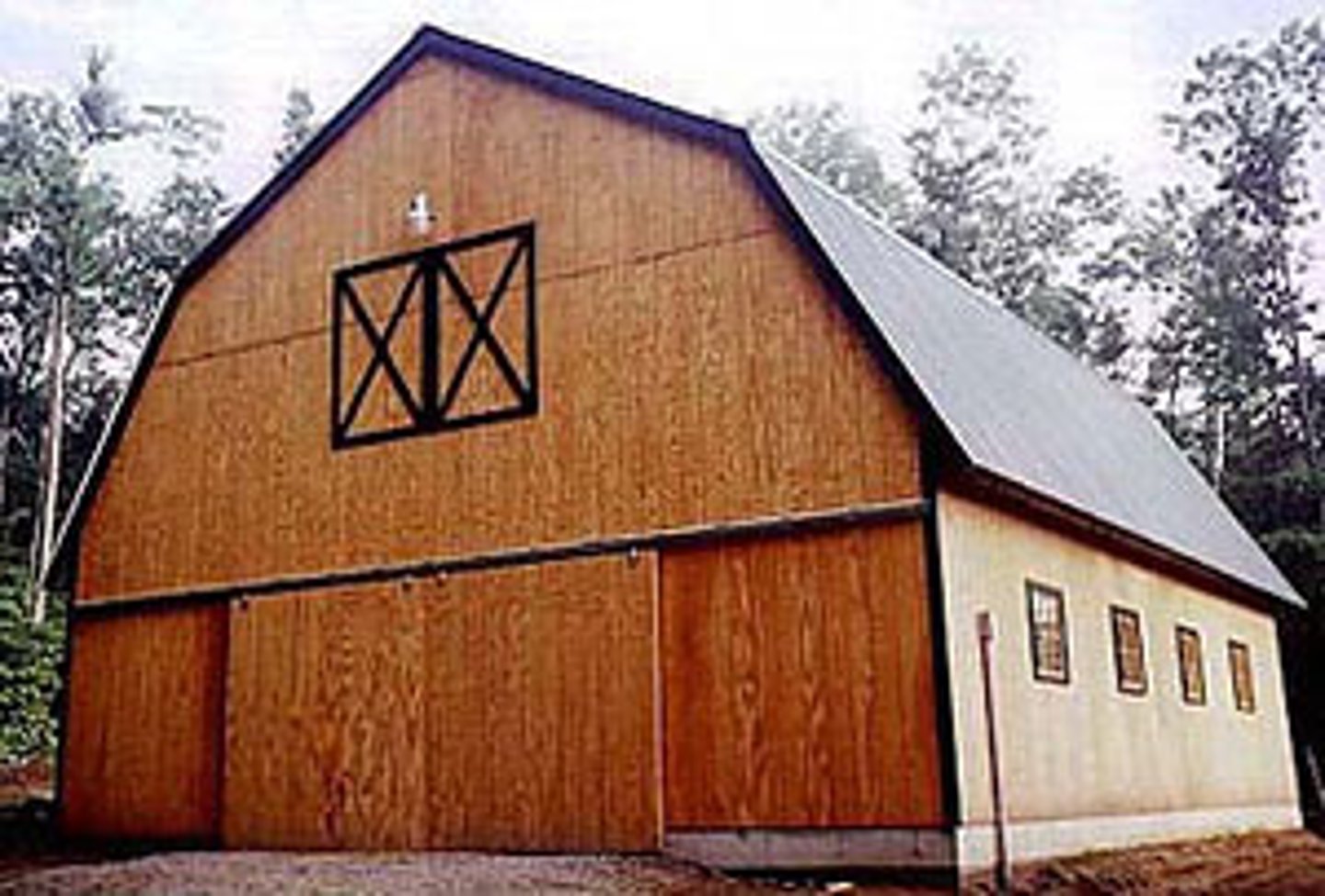

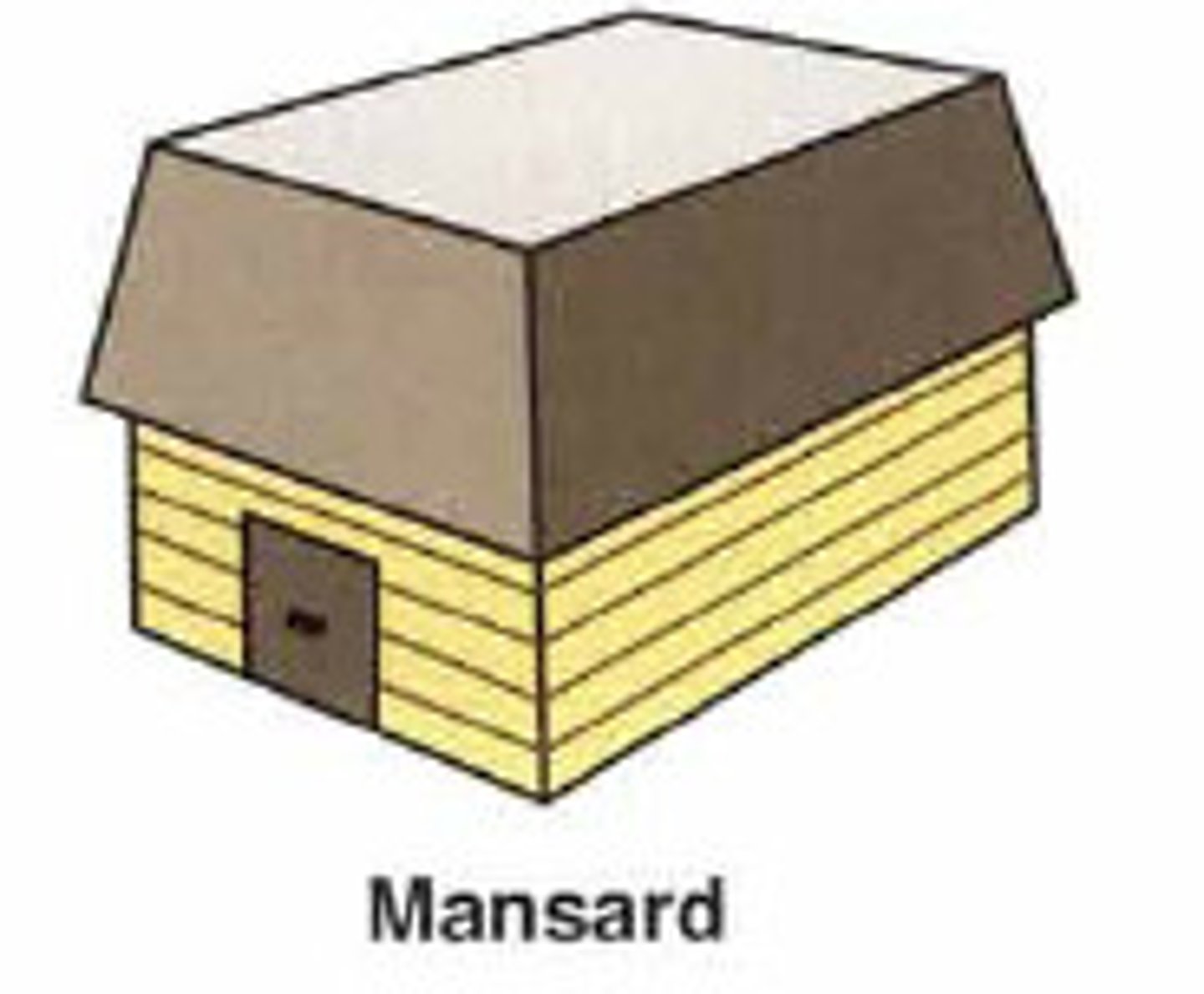
mansard roof
a roof that has four sloping sides, each of which becomes steeper halfway down
flat roof
makes it possible to put a roof over a building that has a large plan, very low slope
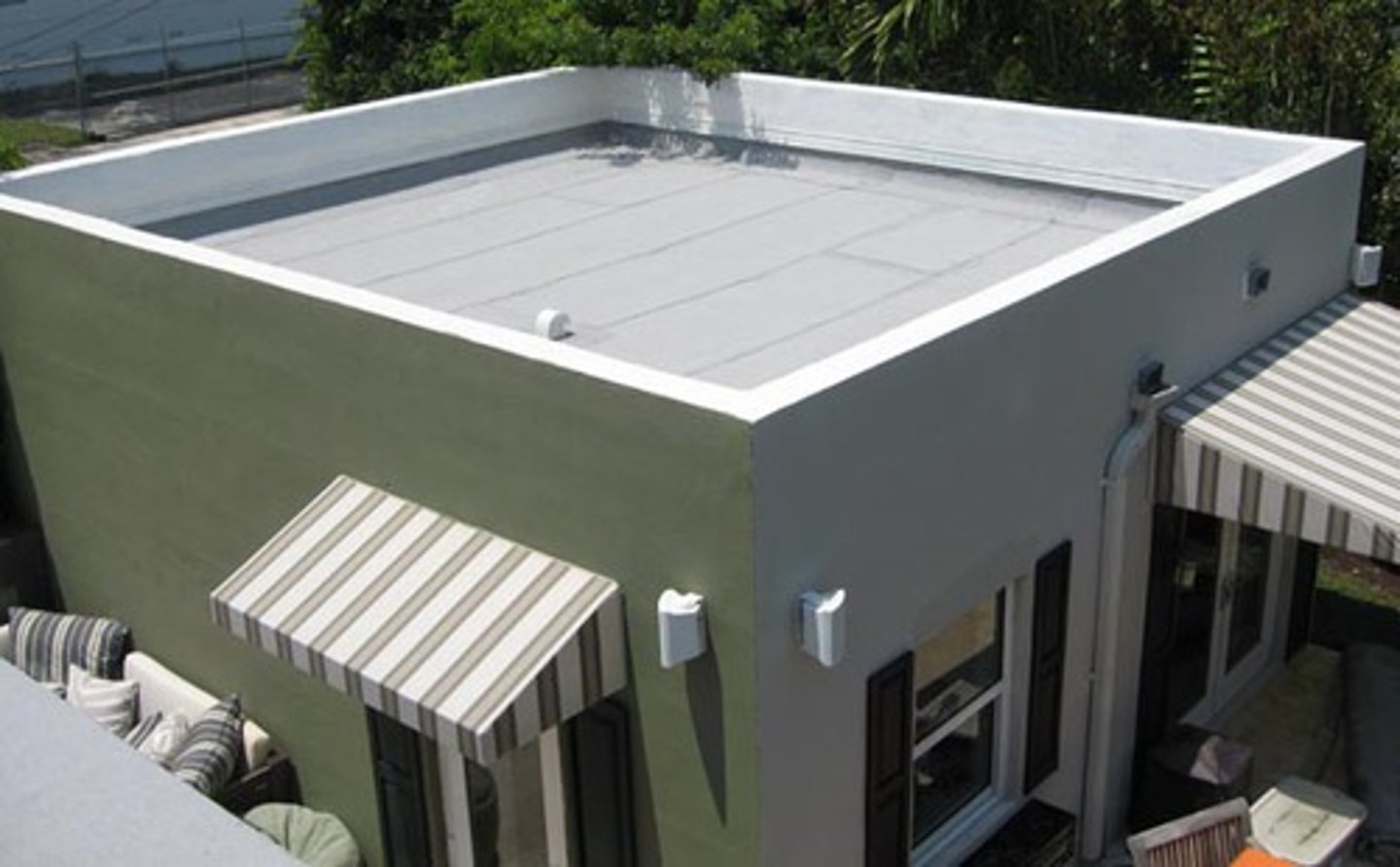

rusticated walls
made of stone that are typically rough and raised off the wall surface

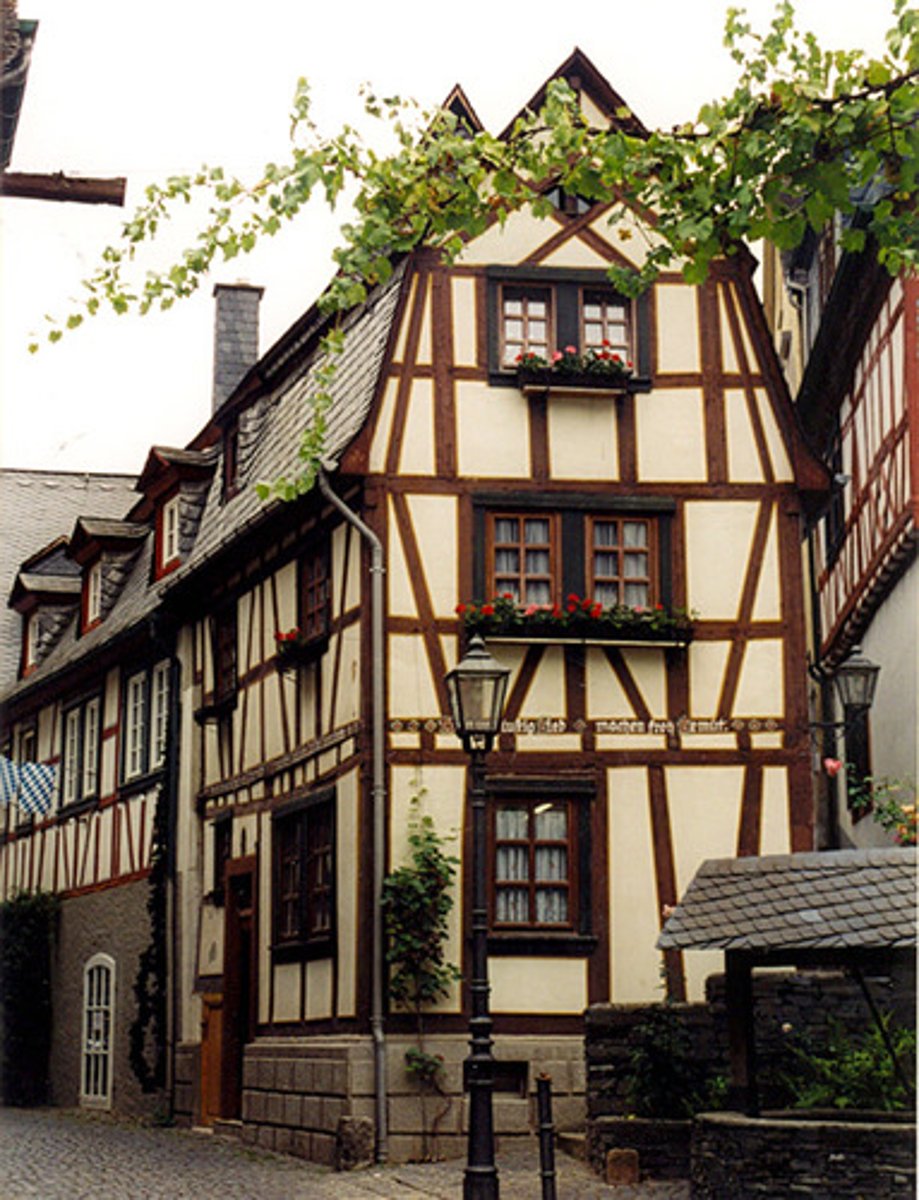
half timbered wall
having a timber framework with the spaces filled with masonry or plaster

clapboard siding
wood siding laid horizontally

board and batten siding
wood siding laid vertically consisting of wide boards and narrow battens
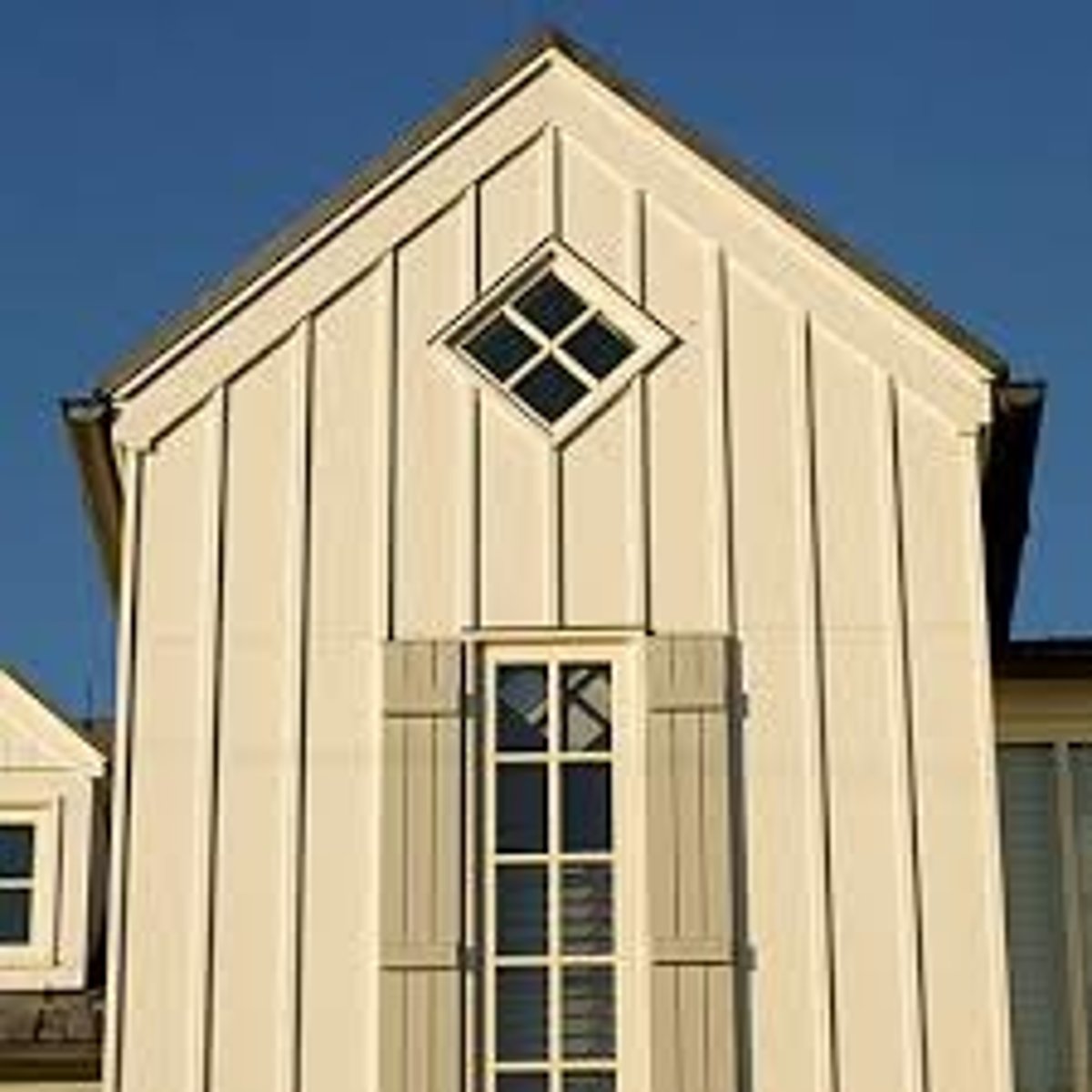

stucco wall
a course plaster composed of cement, sand and lime, mixed with water and used to cover exterior walls

masonry wall
brick/stone/concrete block

concrete wall
pre-cast and poured in place
lancet window
decorative stonework
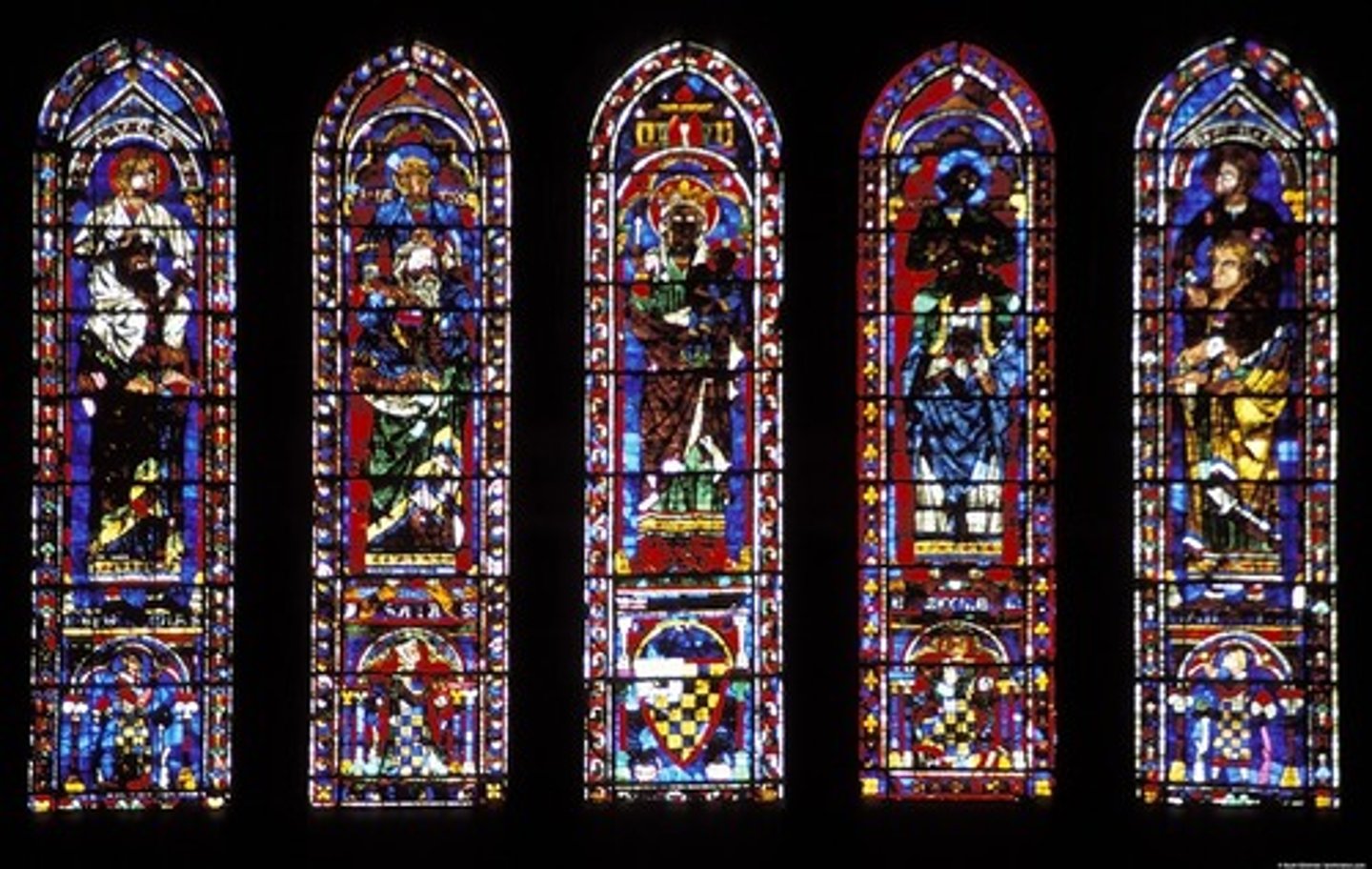

palladian window
a round headed window flanked by two smaller windows

double hung window
a window having two vertically hung sashes, each in separate tracks

dormer window
a vertical window in a projection built out on a sloping roof
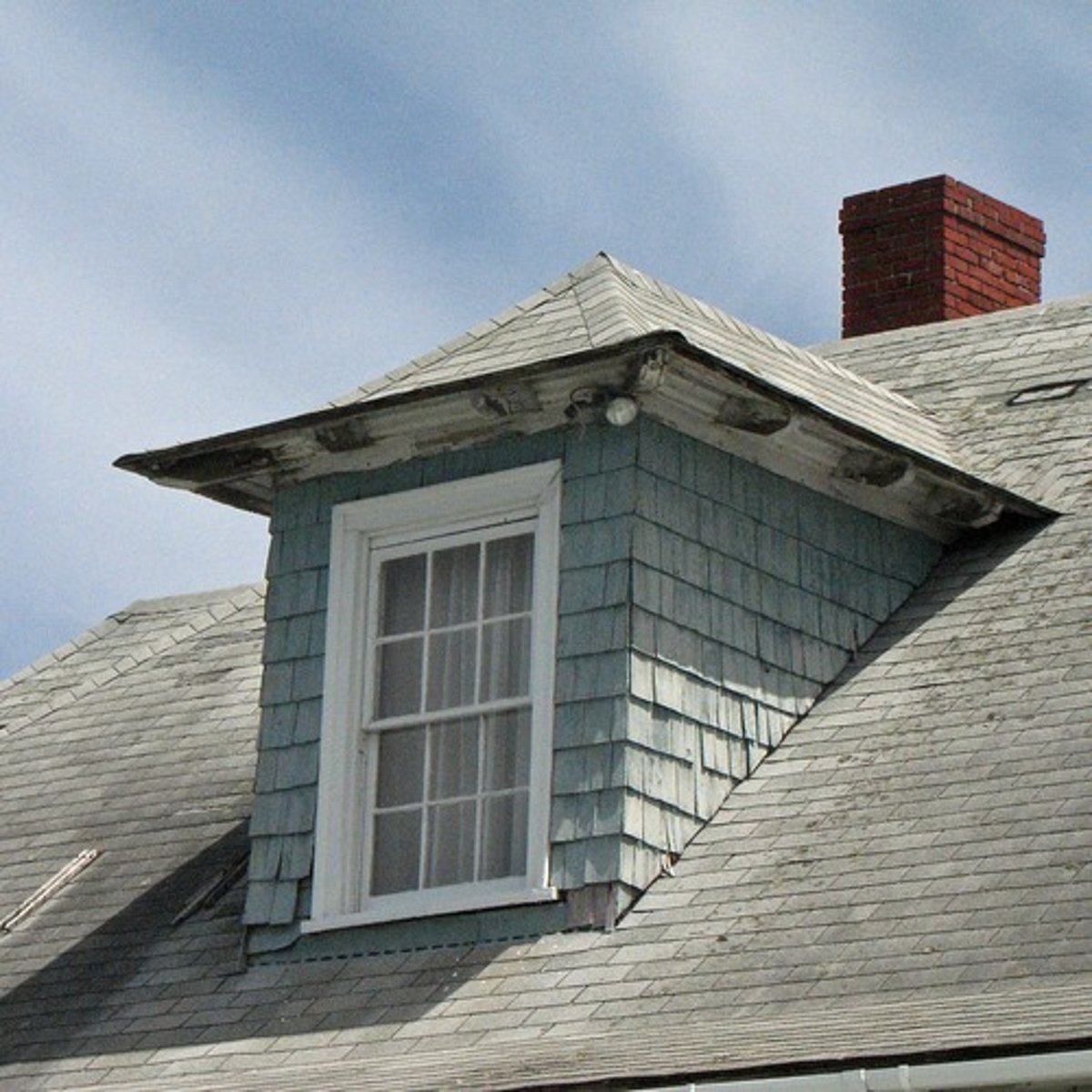

bay window
a window projecting from the surface of the wall to allow light from three sides
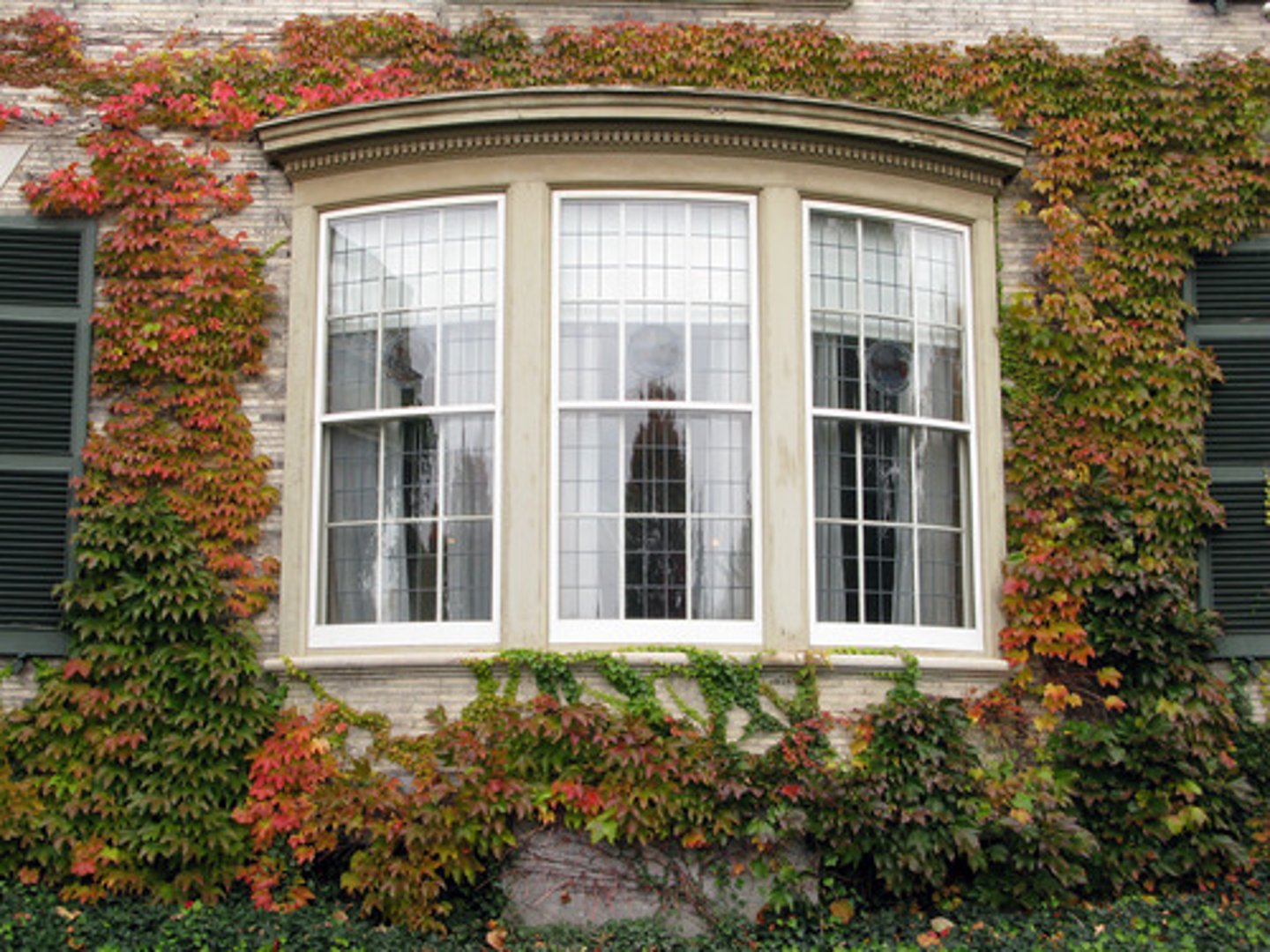

ribbon window
horizontal band of windows

casement window
a window sash opening on hinges generally attached to the vertical side of the frame
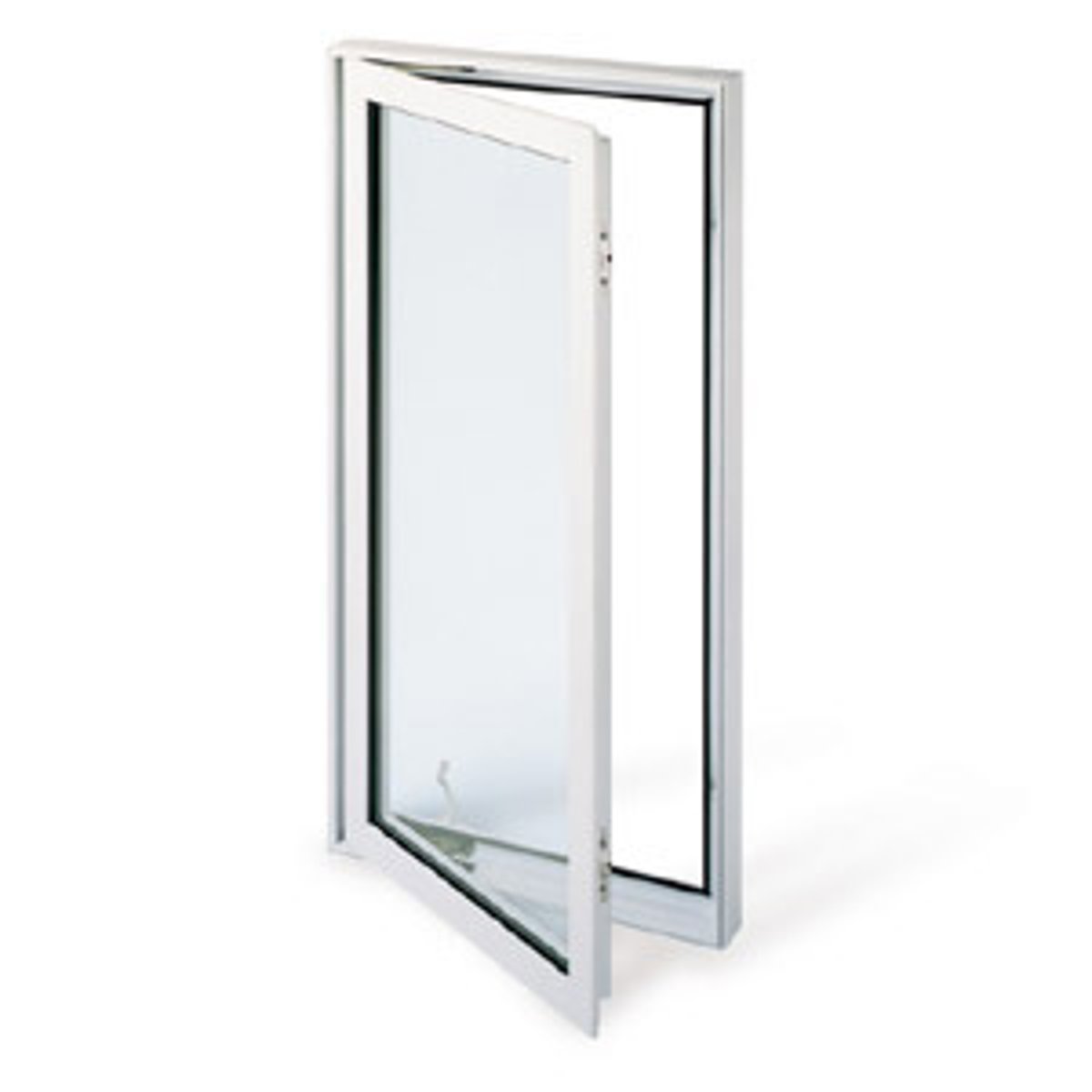

transom window
a window above the transom of a doorway
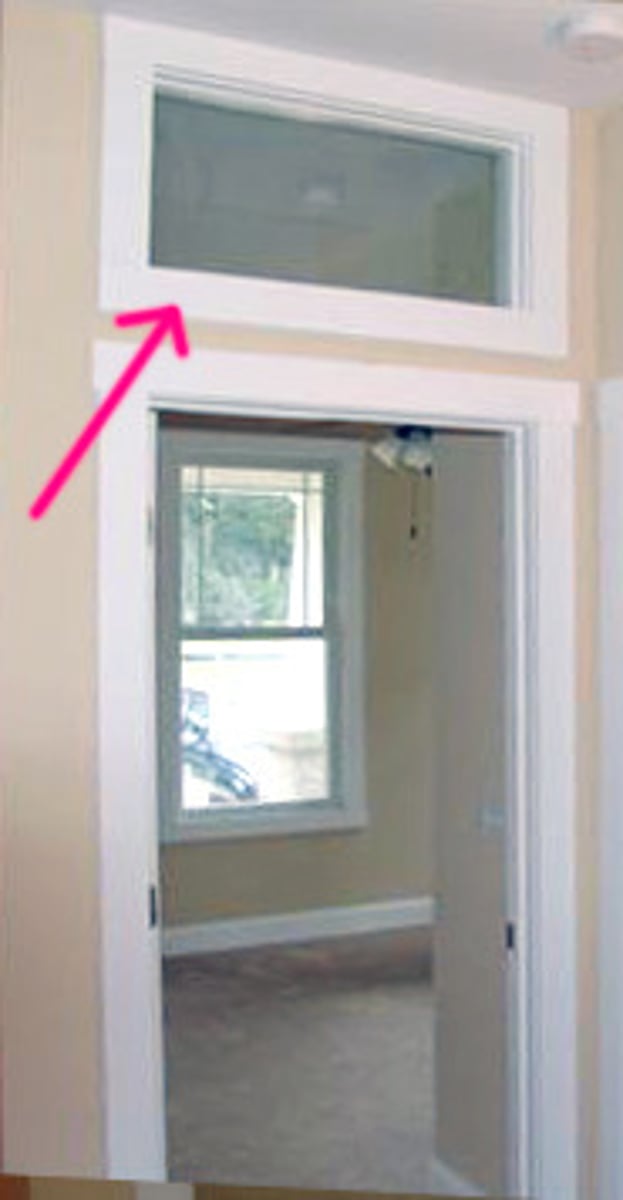

clerestory windows
a portion of an interior rising above adjacent rooftops and having windows to admit daylight

pedimented doorways
a triangular shaped element historically made of stone

arched doorway
associated with Romanesque and Gothic Architecture

venetian doorway
A door opening with a semicircular window above and flanked by vertical windows
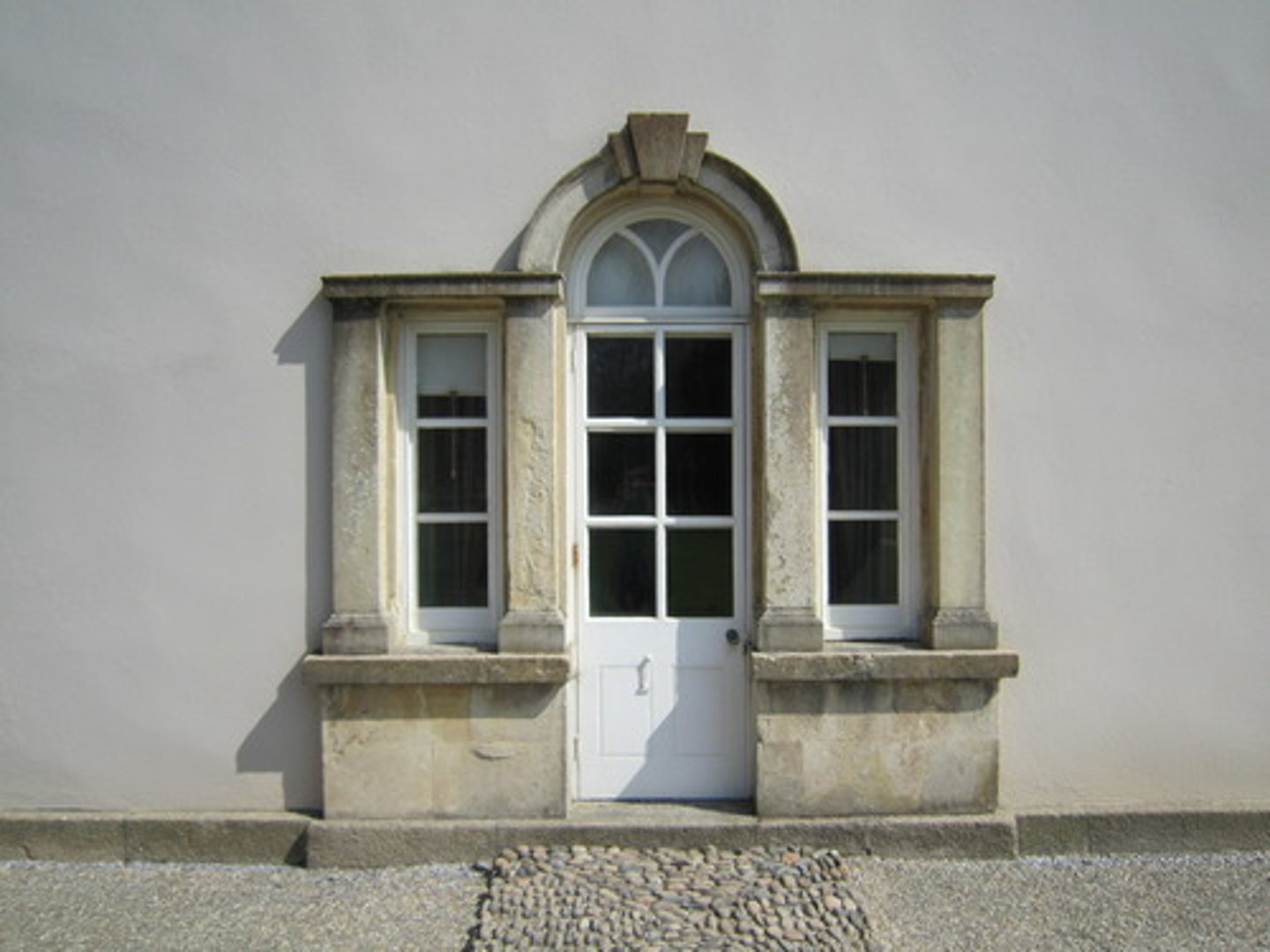

french doorway
door having rectangular glass panes extending throughout its length often hung in Paris

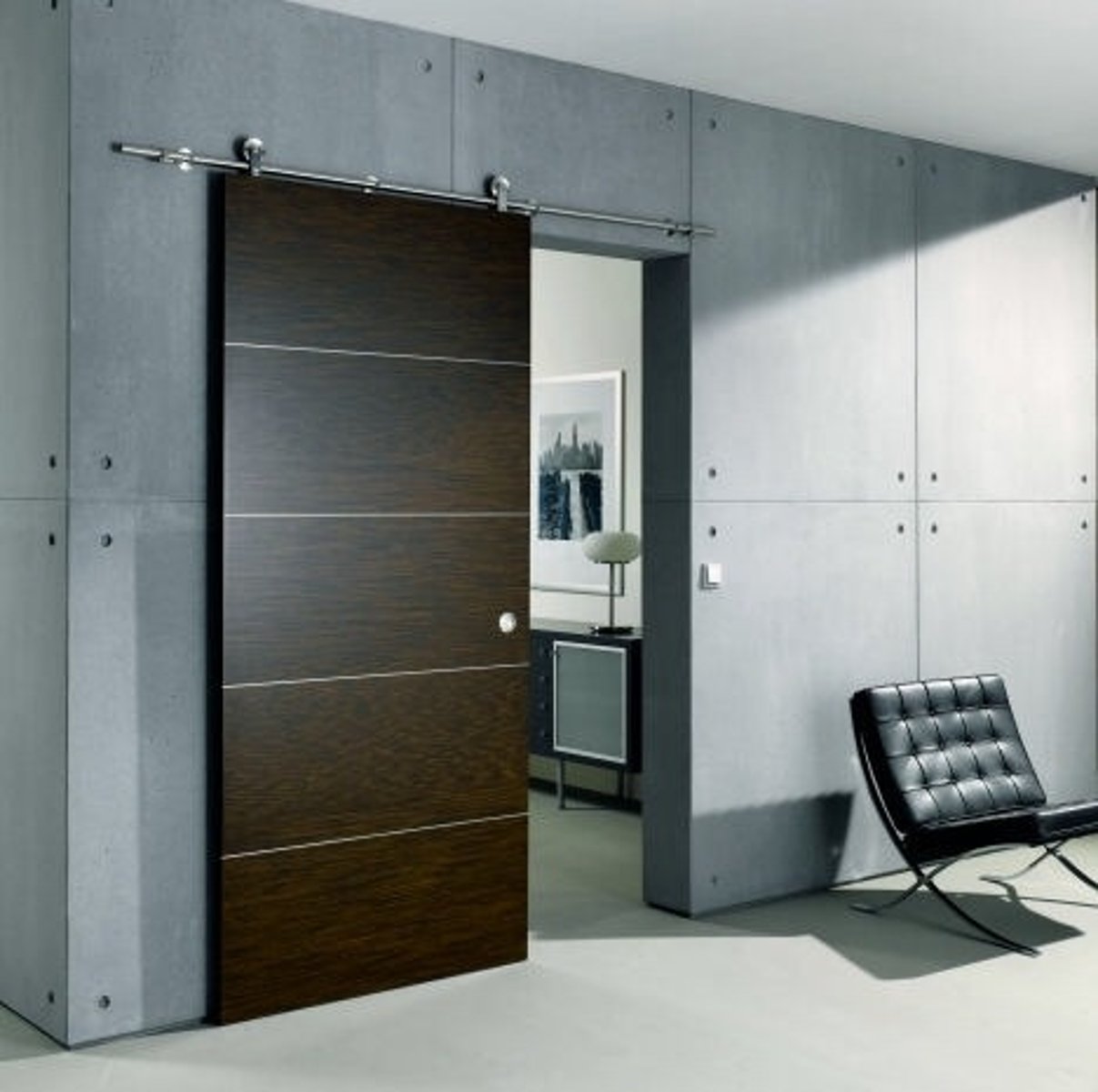
sliding door
a door that operates or moves by sliding on a track

building type
an architectural form which has become accepted by society through repeated use
the building program
a client's list of practical requirements for a design project
what are three things required for any architectural project?
need, land (site), and financing
Steps required to become a licensed Architect
-5-year BARC or 4+2 MARC or 3+ year MARC
- Minimum 3-year internship (minimum weeks of exposure to various aspects of practice)
- Pass 9 part ARE exam
Basic Architectural Services consist of the following phases:
- schematic design
- design development
- construction documents
- bidding and contract negotiation
- construction phase
what are the types of architectural drawings?
- orthographic
- axonometric
- perspective
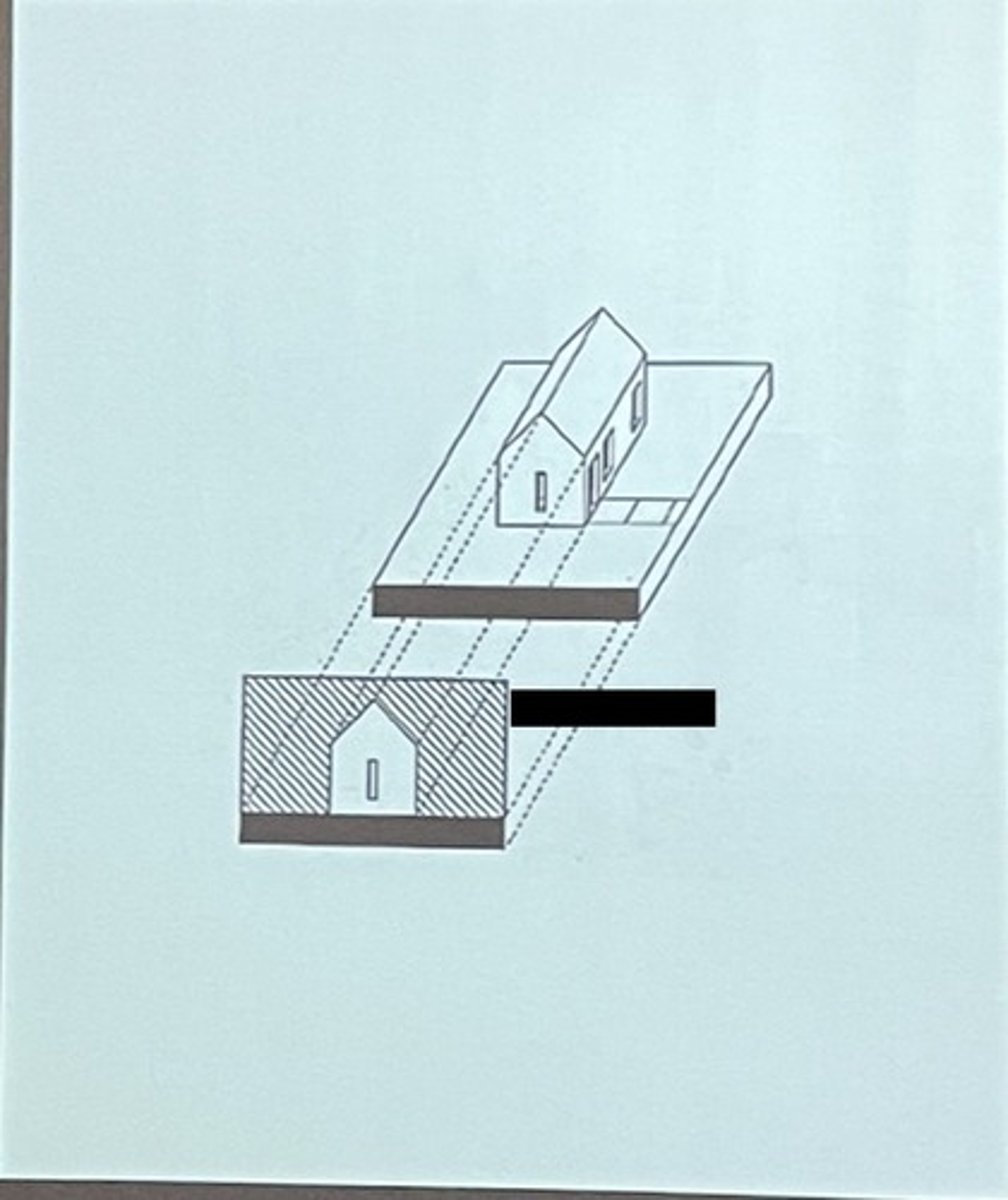
orthographic drawing
2D (plan, section, elevation)
plan drawing
section drawing
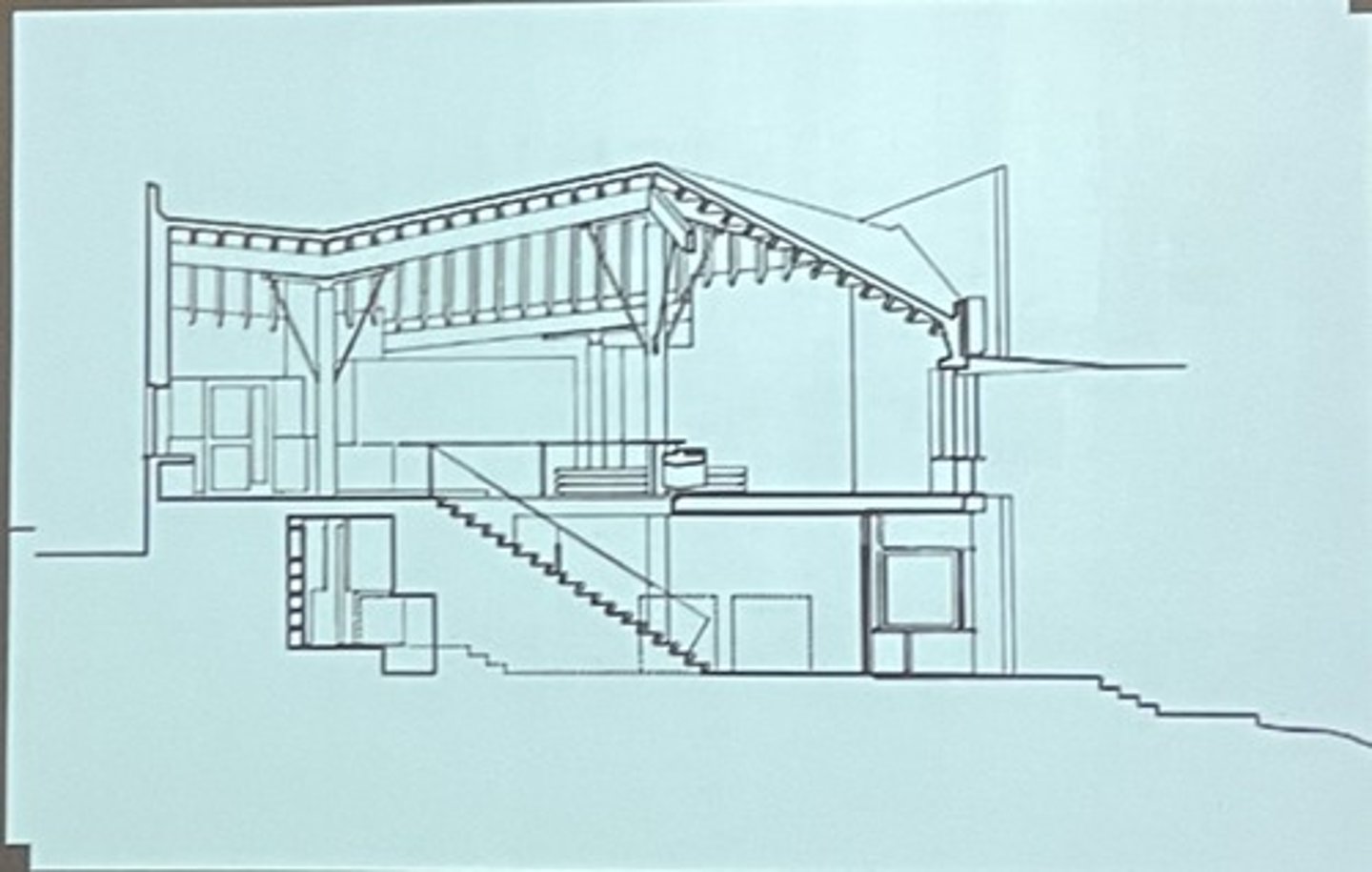
elevation drawing
live loads
forces from all the "movable" elements of a building (people, equipment, furniture, etc)
dead loads
forces from all the "immovable" elements of a building (weight of building materials, walls, floors, built-ins, etc.)
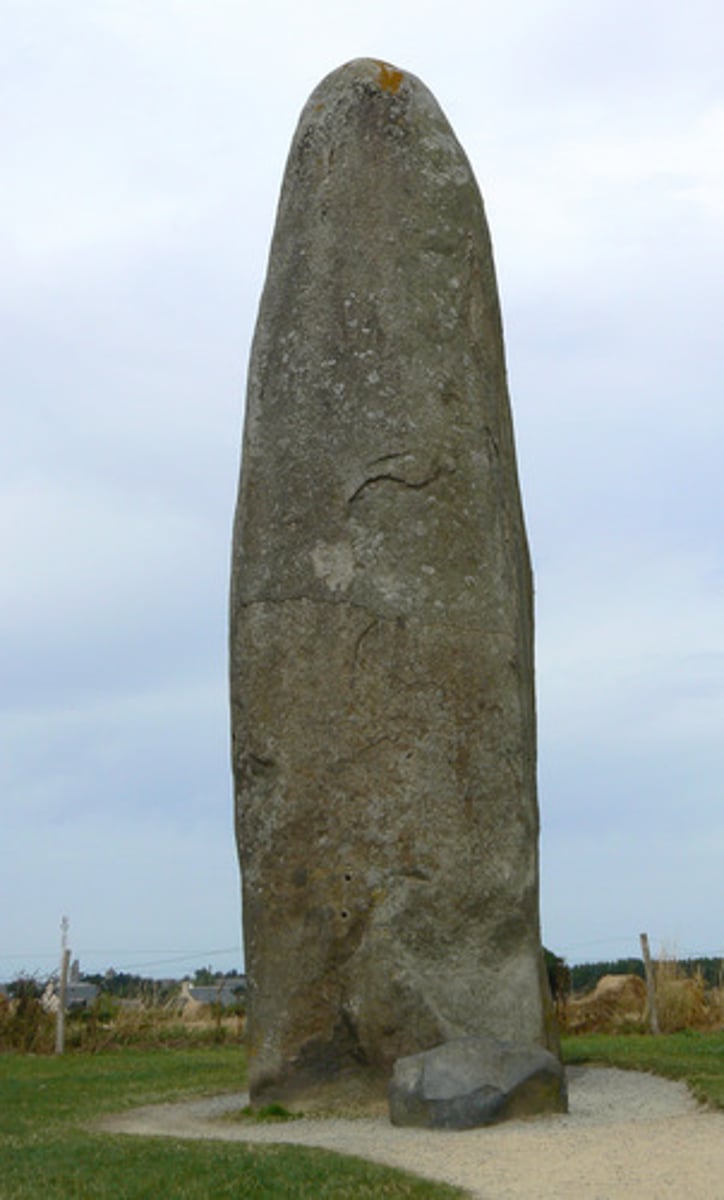
menhirs
single stone standing upright

dolmen
several stones supporting a horizontal stone slab
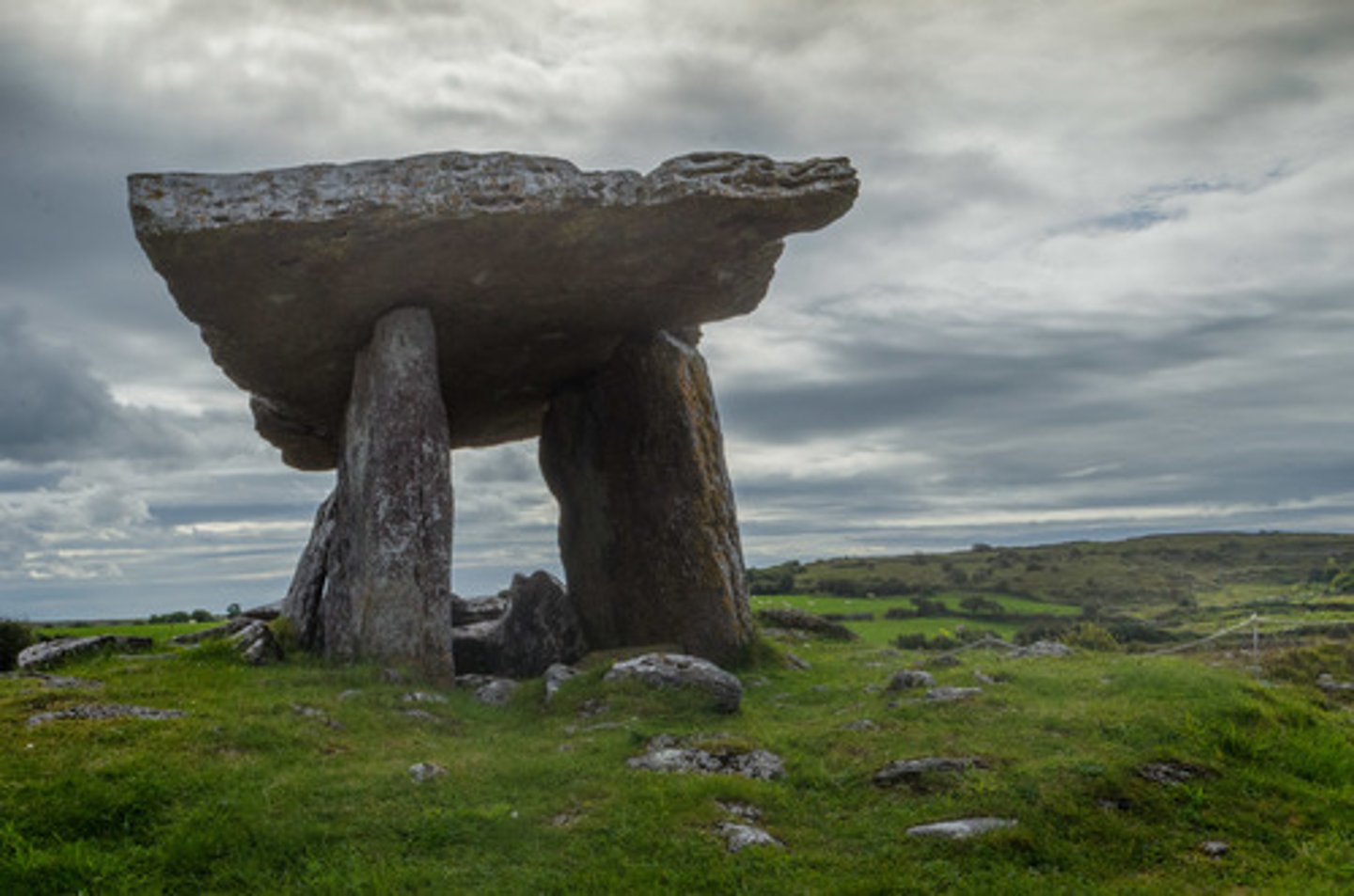

henges
circular ditches around which some megalithic monuments are arranged

cromlech
circle of stones
trabeation
post and lintels
what are the three types of pyramids?
Step, Bent, Straight
step pyramid
Saqqara Doser's pyramid

bent pyramid
Sneferu's South Pyramid, Dahshur, Egypt

straight pyramid
Cheop's Pyramid, Giza, Egypt
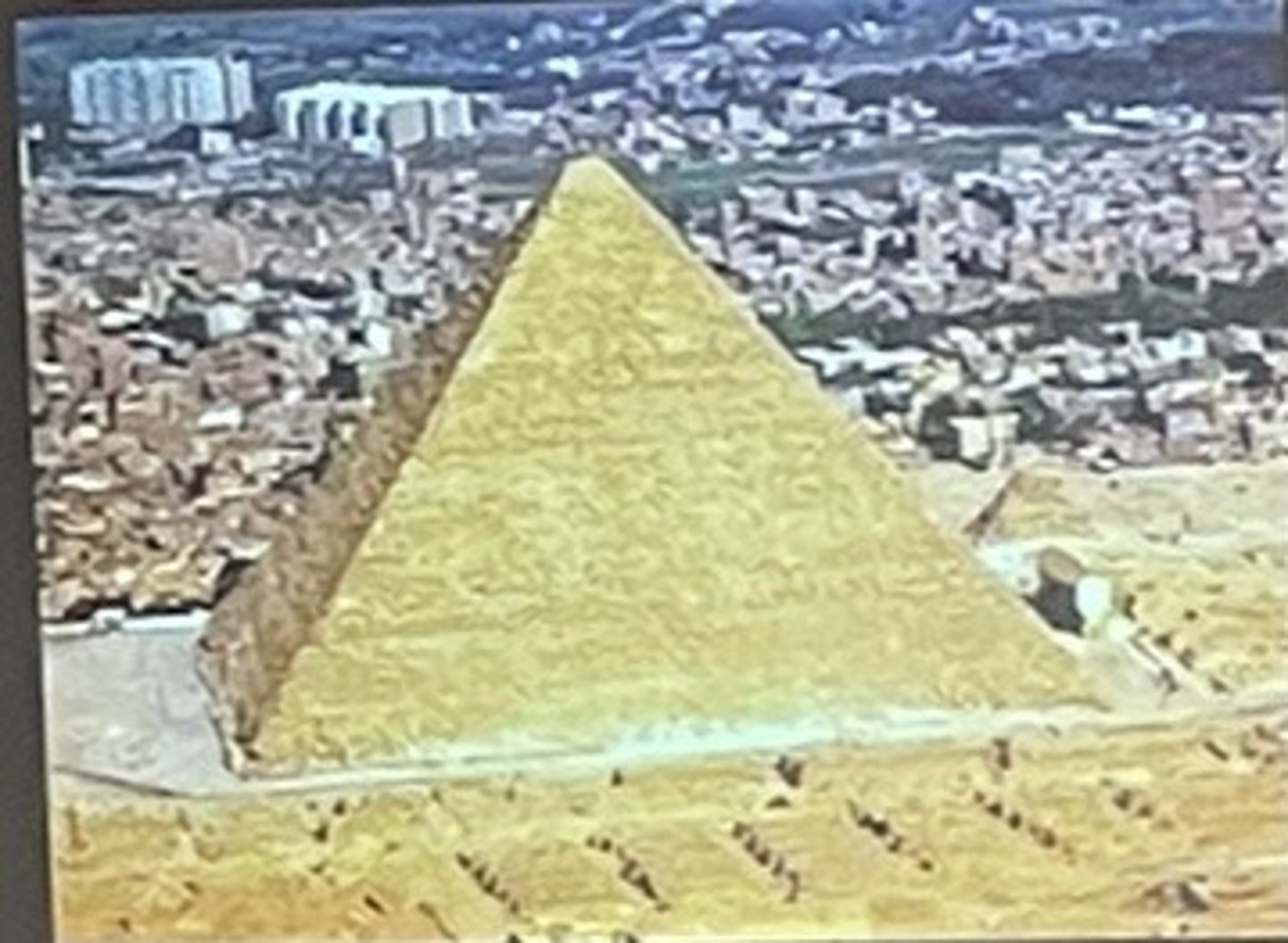

who was the first recorded architect?
Egyptian named Imhotep, the one who comes in peace, born a commoner
why did Zoser hire Imhotep?
to design and build his tomb
how did Imhotep "translate" traditional materials?
used stone instead of mud, wood, and reeds
what was Imhotep's other occupation?
astronomer, magician, and doctor
who was later worshipped by the Eygyptians as a god?
Imhotep
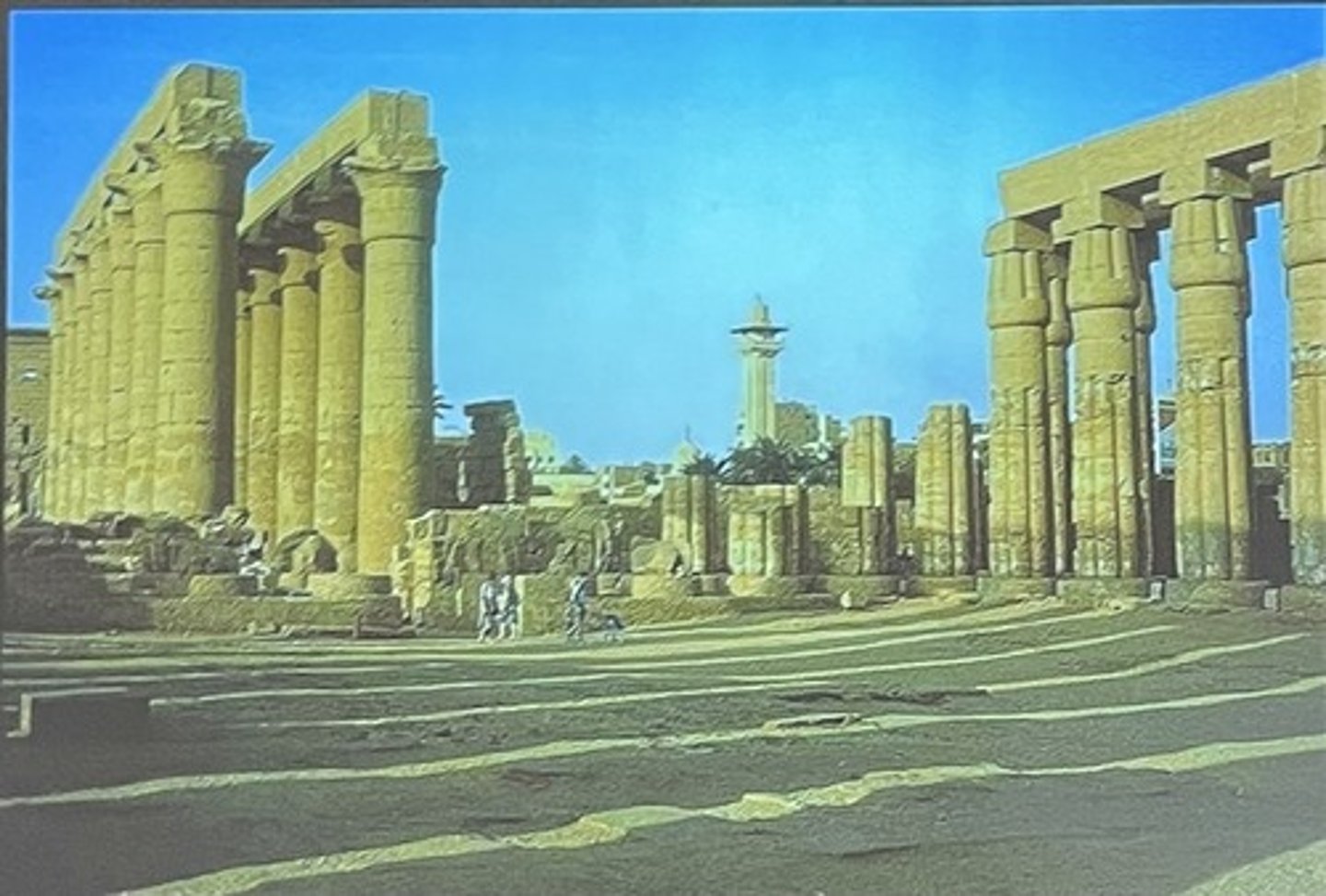
Temple at Karnac
bud columns, papyrus bundles

Lion's Gate
sense of structure was an inheritance from Neolithic period (post and lintel)
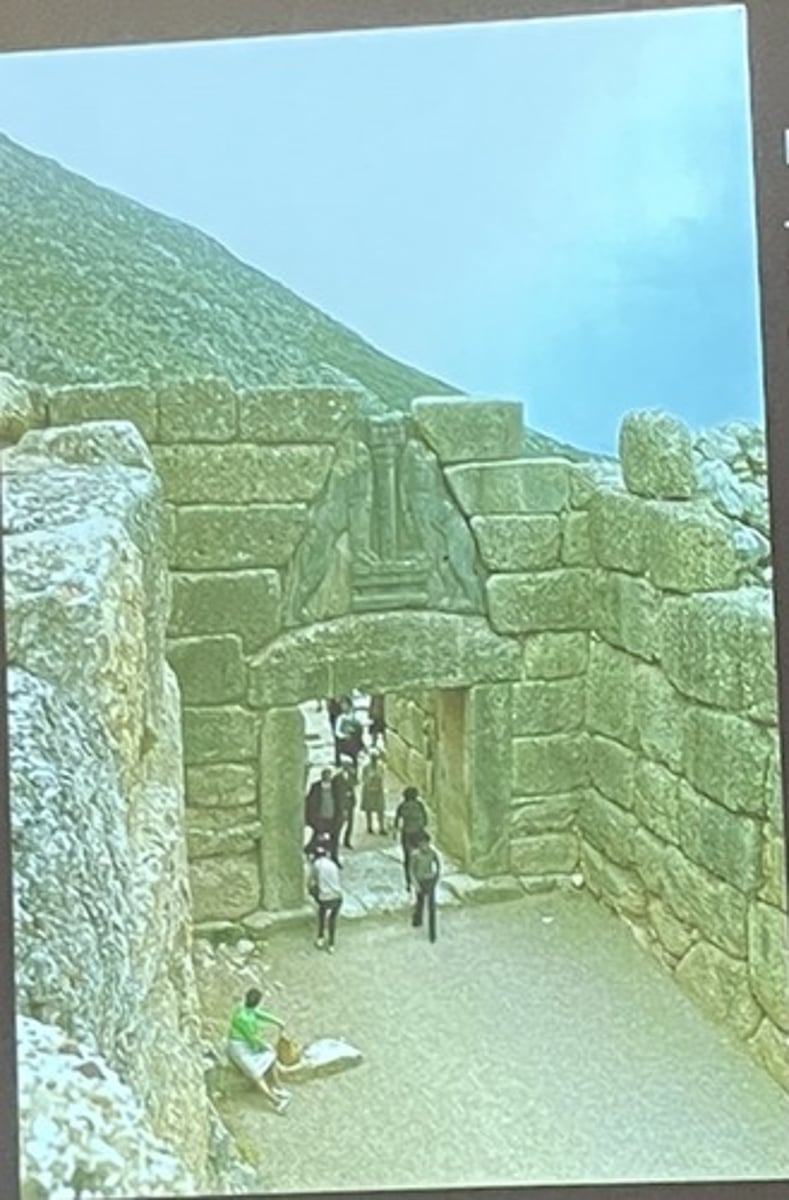

where was the lion element borrowed from at the Lion's Gate?
Egypt, but now more organic
why were the walls beyond narrow in the Lion's Gate?
to allow defenders increased opportunity to repeal attackers
Egyptians or Greeks. Who believed in an afterlife?
Egyptians
Egyptians or Greeks. Who believed in a collective eternity?
Egyptians
Egyptians or Greeks. Who sought immortality through achievement?
Greeks
Egyptians or Greeks. Who saw excellence in deeds?
Greeks
Egyptians or Greeks. Who recorded accomplishments so it was remembered forever?
Greeks
what type of building housed gods?
temples
how were temples built to impress non-Greeks?
used vivid colors to be seen from a great distance

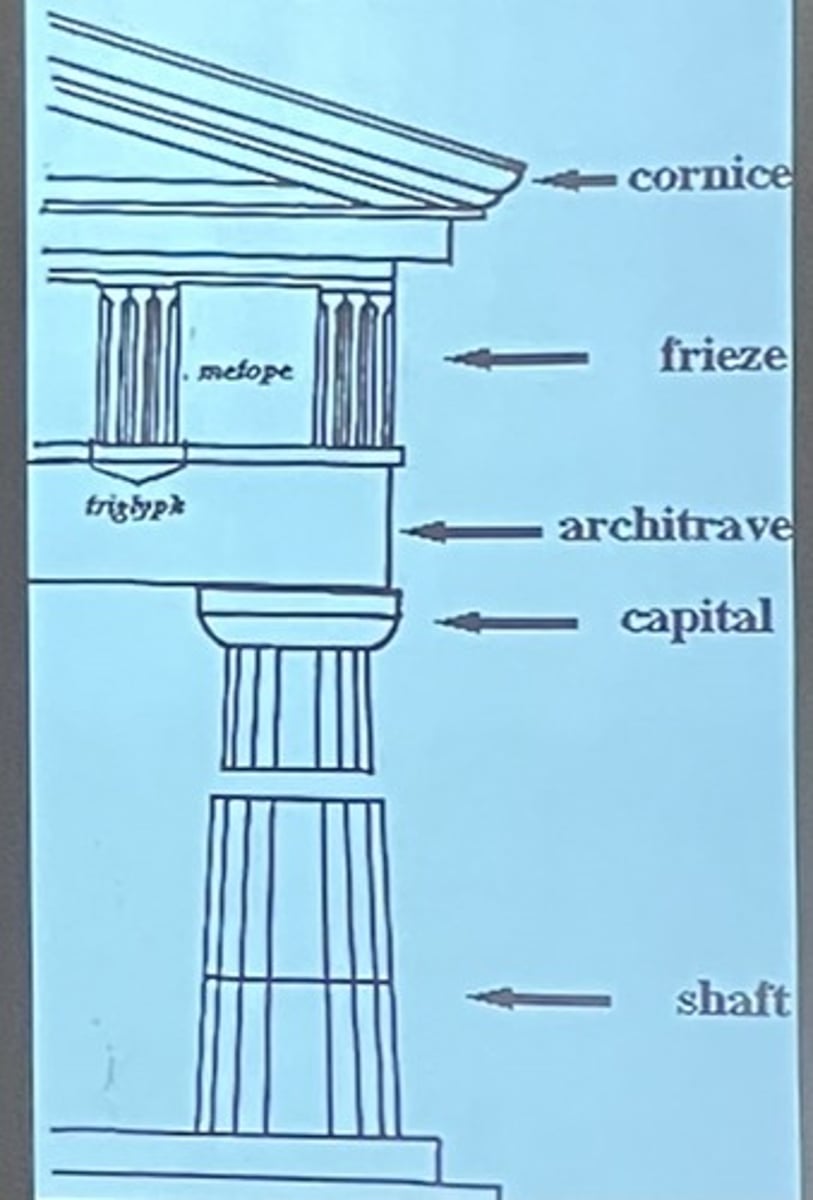
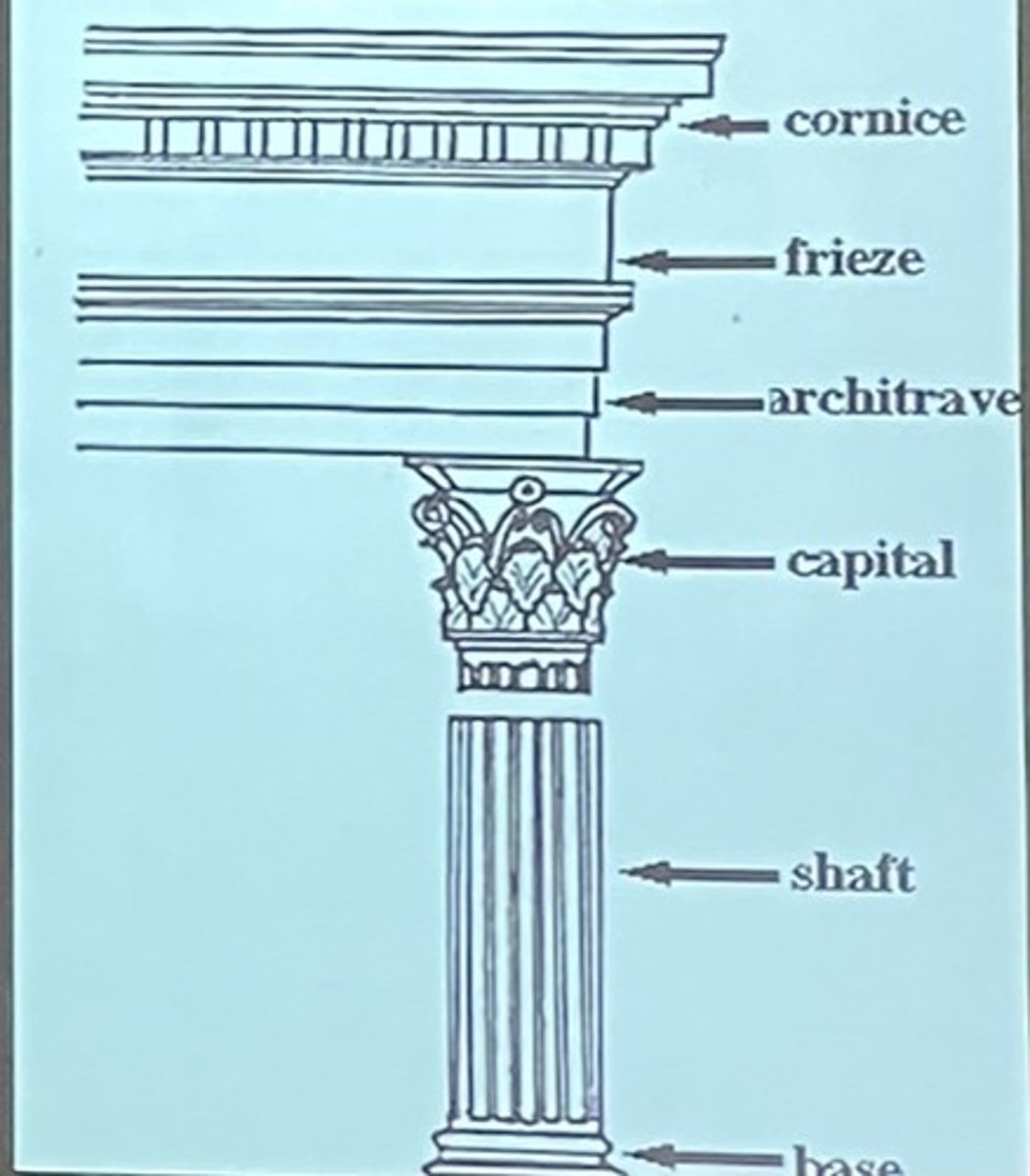
Doric order
-oldest, simplest, most massive
-columns placed close together, often no bases
-plain capitals
-entablatures have metopes and triglyphs
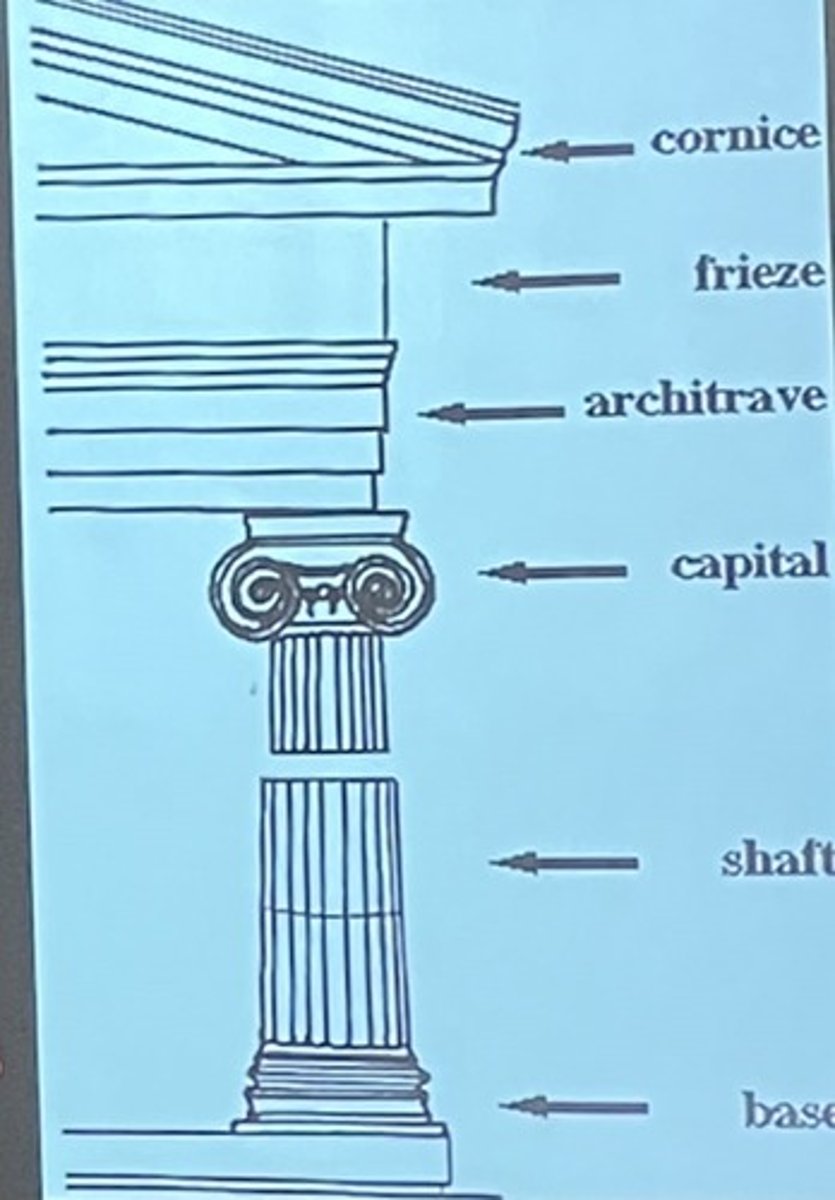
ionic order
-Developed in Ionian Islands
-Characterized as delicate order - "female"
-Contrasted with "male" Doric order
-Used for smaller buildings and interiors
-Easily recognizable by Volutes on Capital (based on nautilus shells or animal horns)
what is an example of perfect ionic order?
Temple of Athena Nike

corinthian order
-variation of Ionic Order
-same as Ionic except a new type of Capital
-capital is more ornate-acanthus leaves
-often found on interiors
entasis
the slight convex bulge given to a column to offset the optical illusion that it is thinner in the middle
The Acropolis
Athens, Greece

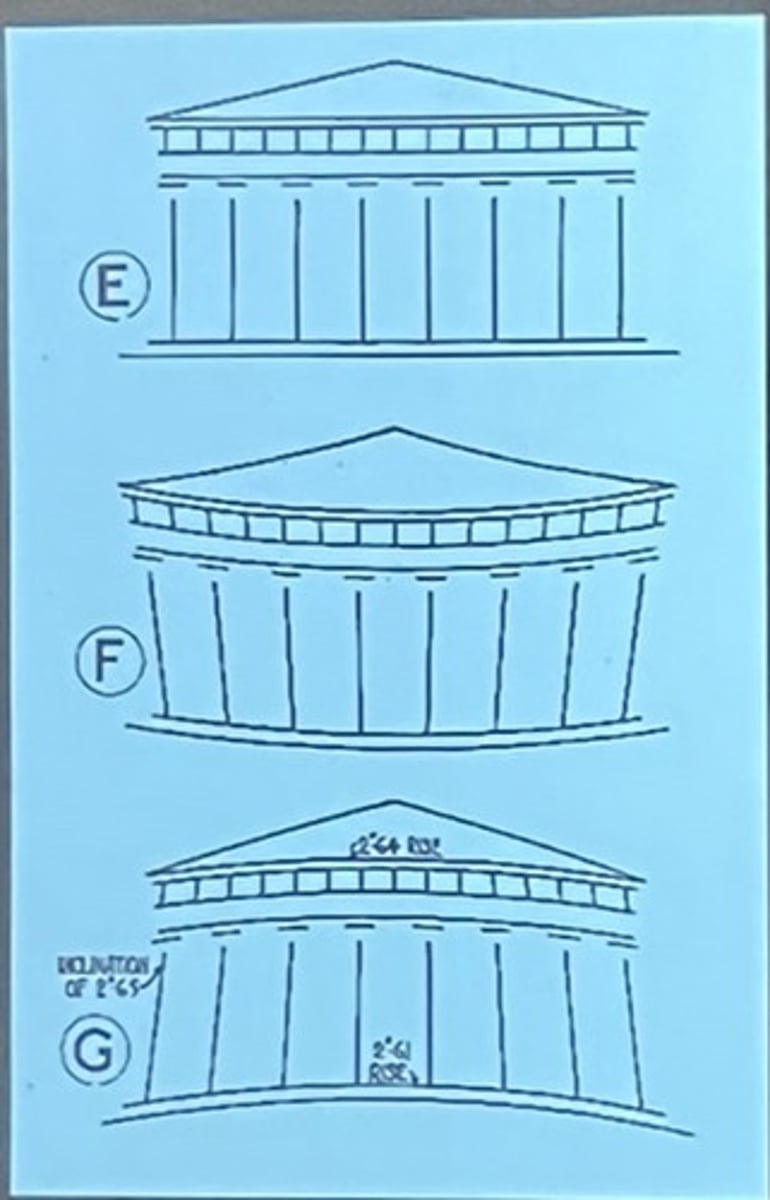
the "Parthenon"
- refined perfection of Doric order
- supreme example of classical

who purchased marbles from Turks?
Lord Elgin
caryatids
a sculptured female figure used as a column
atlas
a sculptured male figure used as a column
Greeks made objects in the landscape:
balance, harmony, refinement of form, NOT structural innovation
who used post and beams?
Greeks
who conquered the Greeks and brought classical architecture?
Romans (Etruscans)
Romans made spaces:
Made images in context, made innovations in construction and technology