Psych 257 - Lecture 6: Sleep-Wake Disorders
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
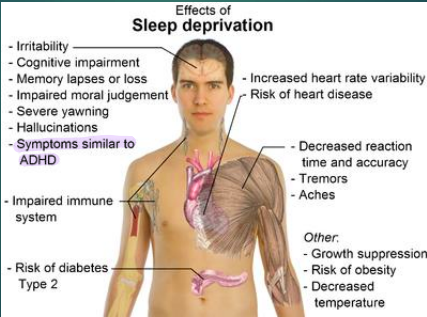
Sleep deprivation – physical effects
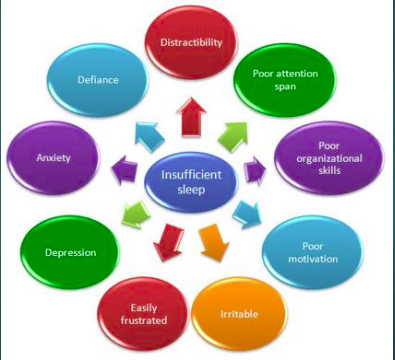
Sleep deprivation – psychological effects
Sleep-Wake Disorders (2)
1. Dyssomnias
Difficulties getting enough sleep
Difficulties with the quality of sleep
2. Parasomnias
The Major Dyssomnias
Insomnia disorder (most common - trouble sleeping)
Hypersomnolence disorders (too much sleep - sleepy through day)
Narcolepsy (awake but paralyzed like in REM sleep)
Breathing-related sleep disorders
Sleep apnea
Circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorders
Treatment & prevention
Medical
Environmental
Psychological
• Medications (e.g., benzodiazepines) vs. CBT
• Prolonged use of meds can cause dependence
• Rebound insomnia
• CBT is more effective, but can be hard work for patients
Prevention: Good sleep habits
Understanding Insomnia: A Cognitive Perspective
• Relative to good sleepers, those with insomnia are more likely to:
1) Have distorted perception of sleep length and sleep quality
2) Experience increased intrusive worries when they try to sleep
3) Endorse unhelpful, negative beliefs about sleep:
• Unrealistic expectations
• Catastrophizing
4) Endorse positive meta-beliefs about benefits of worrying in bed
5) Selectively attend to “threats,” in internal and external environments during both waking and sleeping hours:
• Monitor body for signs of fatigue
• Monitor mood for poor coping
• Monitor performance for indications of failure
6) Try to conserve energy during waking hours (e.g., cancel appointments, avoid exercise, social events)
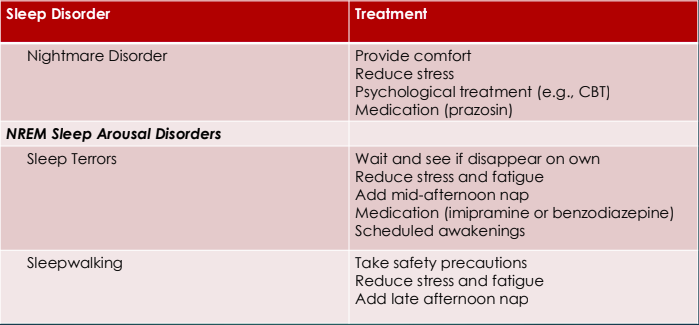
Parasomnias
Non-Rapid Eye Movement (NREM) Sleep Arousal Disorders
Sleep terrors
Sleepwalking
Nightmare Disorde