20. large animal med- diarrhea in sheep and goats
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
how is diarrhea in sheep/goats often noted?
because of extensive spiral colons for water conservation, diarrhea is often noted as softened fecal pellets rather than passage of watery feces
what is peste de petite ruminants?
a viral cause of diarrhea in sheep and goats
virus is related to rinderpest, and found in africa, india and middle east
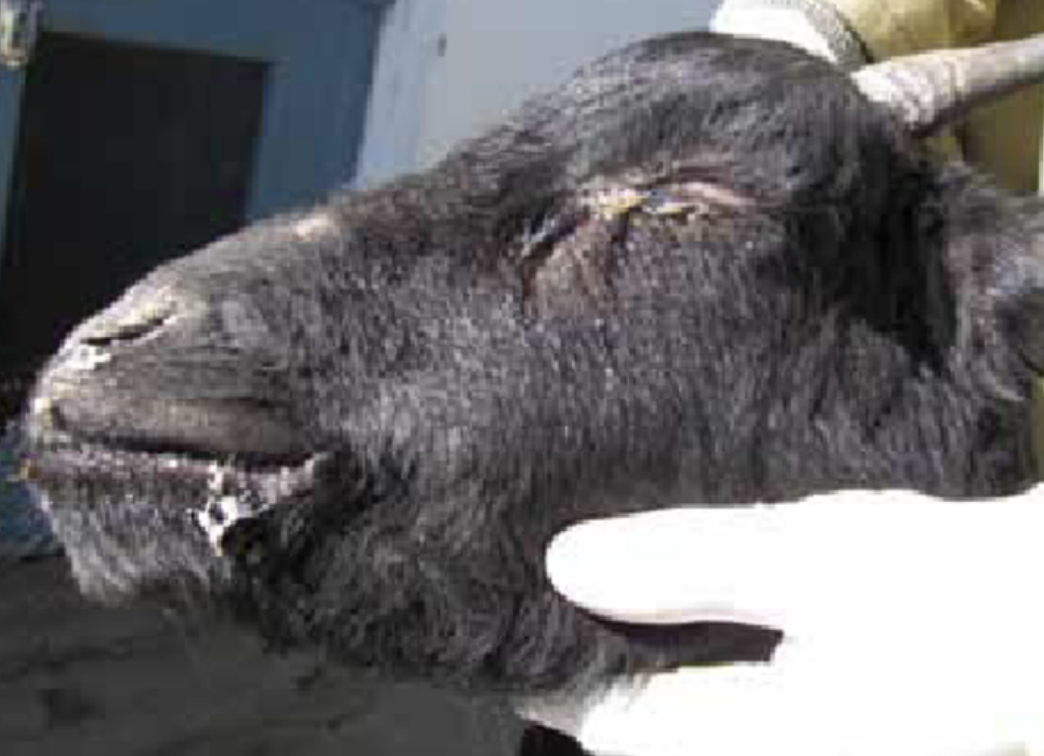
which animals does peste de petite ruminants cause more severe disease in?
goats get severe disease

can cows become infected with peste de petite ruminants?
yes, cows can be infected, but do not develop clinical signs
how is peste de petite ruminants transmitted?
oculonasal secretions, respiratory droplets, feces
indirect contaminated feeders (but virus is short lived in environment)
viral shedding start before onset of clinical signs, so spread is often thru transport of shedding animals (often sheep or cattle)
what are clinical signs of peste de petite ruminants?
-fever
-anorexia
-depression
-clear nasal discharge which progresses to thick, yellow discharge with crusts and occludes nostrils
-eyes may develop similar thick, matting discharge
-ulcers and inflammation on all oral MMs, and throughout GI tract
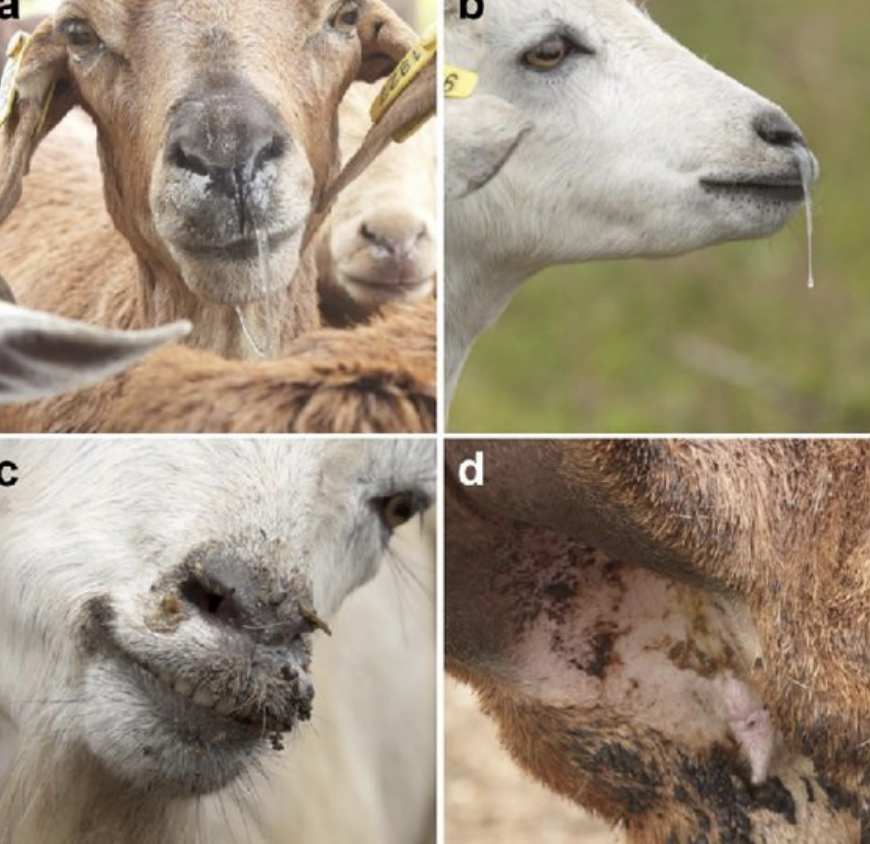

what are common disease sequelae to peste de petite ruminants?
-diarrhea with tenesmus
-pneumonia
-abortion
which animals is morbidity/mortality higher in with infections of peste de ruminants?
younger animals
death occurs 5-10 days after onset of fever in most cases, can also see peracute death
how are acute infections of peste de petite ruminants diagnosed?
PCR or ELISA on swabs of lesions or blood
how can peste de petite ruminants be differentiated from bluetongue and foot and mouth disease (FMD)?
bluetongue and FMD also cause oral ulcerative lesions, but either of these rarely cause diarrhea
-bluetongue rarely affects goats
-FMD only causes mild dz in small ruminants
what is the most important viral cause of diarrhea in young small ruminants?
rotavirus
what are clinical signs of rotavirus in small ruminants?
similar to bovine analogue, causing watery diarrhea due to damage to absorptive epithelium
which age of animals is rotavirus most common in?
most common in lambs <1 month old
occasionally see in kids <3 months old
how is rotavirus treated in small ruminants?
self-limiting with fluid treatment
what type of diarrhea is seen in small ruminants infected with coronavirus/adenovirus?
mild diarrhea
does caprine herpes virus commonly cause diarrhea in goats?
no- CHV has rarely been associated with ulcerative GI lesions and diarrhea in goats
what is the common disease seen in lambs due to e. coli infections?
ETEC due to K99 pilus adhesion and enterotoxin-stimulated secretory diarrhea in young lambs
what is the common disease seen in kids due to e. coli infections?
enteropathogenic e.coli is more common than ETEC in kids
how do e. coli infections differ in lambs vs kids?
kids tend to be sicker, with more blood in the feces and evidence of systemic toxemia
what is the most common salmonella serotype isolated from small ruminants?
salmonella typhimurium (likely spread by non-clinical shedders)
s. dublin and others also isolated, but are rarely endemic
what are the clinical signs of goats infected with salmonella typhimurium?
goats typically have profuse, watery foul diarrhea with high fever and leukopenia
death is common
how do salmonella infections differ in small ruminants (goats) vs cattle?
bloody diarrhea is extremely rare in goats, unlike in cattle
which small ruminants are more commonly infected with yersinia?
disease is seen more in goats than sheep
kids less than 6 months old get enteritis and bacteremia (get very sick and can die fairly quickly)
what type of diarrhea is seen in young goats (kids) infected with yersinia?
watery diarrhea (not bloody)--> causing dehydration
what are other clinical signs of yersinia infections in goats/small ruminants?
younger animals: severe toxemia and sudden death
older animals: chronic diarrhea and weight loss (seen due to gut wall and abdominal abscesses)
what other lesions are seen with yersinia infections?
multiple microabscesses in gut wall and mesenteric lymph nodes
how are yersinia infections diagnosed?
culture of lesions or demonstrating rising antibody titer
what is the most commonly used drug to treat yersinia infections?
tetracycline (organism is gram-negative, and sensitive to tetracycline)
is it common for a healthy ruminant with an appropriately functioning gut microbiome to get clostridium perfringens infections?
no
if in contact with these organisms, they are usually in small numbers and a properly working gut microbiome/peristalsis should just flush these organisms out
how do clostridium perfringens infections occur?
at times of abnormal motility or passage of fermentable feed into their environment
--> causes clostridia to proliferate, and their toxins to cause damage
how are clostridium perfringens infections diagnosed in small ruminants?
diagnosis often confounded by post-mortem or secondary proliferation of clostridial organisms
ie clostridia is a very common post-mortem overgrowth, so can be difficult to determine if sole cause of death/illness
what toxin does clostridium perfringens type B produce?
beta-toxin
what substance in the body inactivates beta-toxin produced by clostridia type B?
trypsin
why is clostridia type B most damaging in very young lambs or kids (less than 3 days old)?
in kids/lambs under 3 days old, trypsin production has not yet started
because the beta-toxin is inactivated by trypsin, and these animals lack trypsin== more susceptible to type B
what is the disease name for clostridia types B and C in neonates?
type B: lamb dysentery
type C: struck
what are the characteristic lesions of clostridia type B in lambs?
characteristic lesion: small ulcers in the small intestine surrounded by hemorrhage, as well as hemorrhagic gut contents
what is the pathogenesis of clostridia causing lesions in small intestine?
once in the gut, clostridia create permeable lesions in gut wall and induce a severe inflammatory response (neutrophils, pain, colic, tender abdomen, intestine distended with gas)
what are peracute/acute clinical signs of clostridia type B in lambs?
sudden death (peracute)
or
splinting/tenderness of abdomen with yellow-brown diarrhea (acute)
most lambs with clinical disease die
what is the result of lambs in a naive flock exposed to clostridia type B?
on first exposure, many lambs may suddenly die or get severe, rapidly progressing disease
how is clostridia type B diagnosed?
characteristic lesions seen at necropsy
lab assay can also be used to ID the beta-toxin
when should pregnant ewes be vaccinated against the beta-toxin of clostridia type B?
vaccines against toxin reduce morbidity and mortality when given to ewes several weeks before lambing
what is the treatment for clostridia type B?
antitoxin, fluids, NSAIDs, antibiotics (penicillin)
which clostridia perfringens type can cause peracute colic and death in adult sheep?
type C
how are clostridia types B and C infections prevented?
through toxoids and antitoxin
what toxins does clostridia perfringens type D secrete?
alpha-toxin and epsilon-toxin
epsilon-toxin is trypsin resistant (why this is also seen in adult animals)
what are causes of clostridia type D infections?
-feed and weather changes
-high concentrate diets
-overeating (clostridia love carbs)
-weaning
-combining groups
-confinement
-tapeworms
-basically any change in routine/alteration of gut microbiome
in addition to pneumonia, what is one of the main causes of death in feedlot lambs?
clostridiosis
what effects does the epsilon toxin of clostridia type D have on tissues?
toxin increases vascular permeability, which facilitates its own absorption from the gut
it is necrotizing to tissues, especially neurons
which animals tend to get a neurologic form of disease caused by clostridia type D? what are the clinical signs?
sheep get neuro form, will see:
-depression
-neurologic signs
-death with minimal diarrhea or gut lesions
what disease is seen more frequently in goats infected with clostridia type D?
localized enteric form; enterotoxemia or pulpy kidney disease
what is the peracute form of enterotoxemia/pulpy kidney dz seen in goats?
sudden death in fast growing young kids
or
rapid development of painful abdomen with vocalization, depression and bloody diarrhea
--> most die
what is the acute form of enterotoxemia/pulpy kidney dz seen in goats?
less severe pain than peracute form
-feces gradually change from pasty to watery
-the goats (often older than peracute form) develop abnormalities associated with diarrhea
-if not treated, die within 3-4 days
what is the chronic form of enterotoxemia/pulpy kidney dz seen in goats?
intermittent bouts over several weeks
-goats are dull with loose feces
-hard to recognize w/o aforeknowledge of acute form on farm
what clinpath changes are seen with clostridia infections in small ruminants?
leukocytosis
hyperglycemia and glucosuria at the end
how can clinpath changes differentiate clostridia infections from most gram-negative/viral infections?
clostridial dz: leukocytosis
viral/gram-negative bacteria: leukopenia
what lesions are seen with clostridia infections in small ruminants?
-fibronecrotic enteritis (goats)
-pulpy kidneys (sheep or goats)
-hemorrhage on many organs
how are clostridia infections in small ruminants treated?
-fluids
-NSAIDs
-antitoxins
-penicillins or sulfas
how are clostridia infections prevented?
vaccines- should be given every 6 months
what type of disease is seen in small ruminants infected with johne's disease? is diarrhea common?
in small ruminants, johne's primarily causes a weight loss syndrome
diarrhea is only intermittent or terminal
what is the most common cryptosporidium species isolated from kids less than 1 month old?
cryptosporidium parvum (and ubiquitum)
what type of disease does cryptosporidium parvum cause in young kids?
watery diarrhea (similar to calves)
what is the most common cause of diarrhea in lambs and kids between 3 weeks and 5 months old?
infections with eimeria species
most eimeria strains are species specific
when are eimeria infections most commonly seen?
-during hot weather
-when animals are put into group pens
-or at weaning
what are clinical signs of eimeria infections?
-diarrhea and tenesmus
-severe untreated infections can be fatal
-bloody diarrhea with more invasive eimeria species
how are eimeria infections in small ruminants treated?
similar to cattle (can use decoquinate, or monensin)
**remember that small ruminants are more sensitive to monensin toxicosis than cattle
if animals are infected with giardia, will clinical signs always be seen?
no, giardia can be isolated from symptomatic and asymptomatic animals
giardia E is what generally affects hoof-stock
how is giardia transmitted?
primarily from fecal-contaminated water sources or (seasonally) wet pasture
oocysts can survive 3 months in water at 4C
is clinical disease commonly seen in animals after the weaning period?
no, clinical disease is rare after the weaning period
how are giardia infections treated?
metronidazole (not for food animals) and fenbendazole
how are parasitic causes of diarrhea in small ruminants diagnosed?
fecal flotation
flock management
necropsy
what are possible non-infectious etiologies of diarrhea in small ruminants?
similar to cattle: indigestion, grain overload, overfeeding, copper deficiency
which animals are toxins especially an important cause of diarrhea in?
goats
what are examples of plants that can cause diarrhea in goats if ingested?
S³O²MBC
spurges
senna
selenium-accumulating plants
oleanders
oaks
morning glory
bladderpod
crab apple
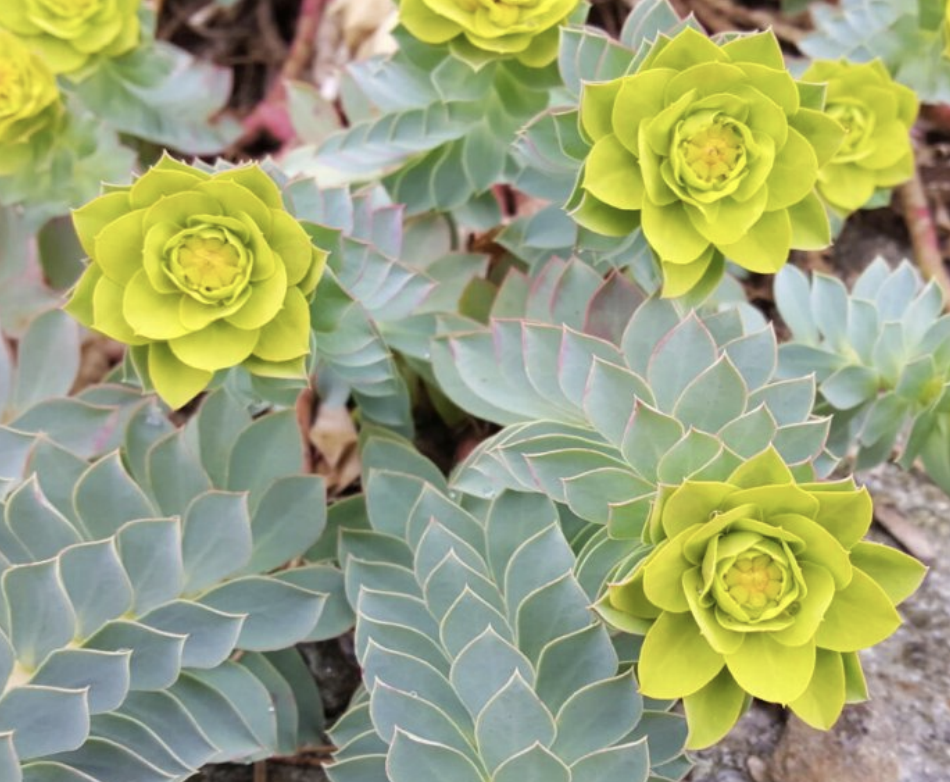

how are goats with plant toxicities treated?
removal from source is often sufficient
though, more aggressive tx is required if the goat is showing systemic signs (as seen with oleander)