Materials Science Exam II
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Heat treating a metal that has been cold work means the effects of the cold work are __________.
Nullified
The word for heat treating a metal that has been cold worked.
Annealing
Three annealing stages
Recovery, Recrystallization, Grain Growth
During the recovery stage of annealing, there is a reduction and then annihilation of….
Dislocations
Form of shear, includes a drive shaft
Torsion
Torsion equation
Moment x 1/Area x 1/Radius
Simple Compression Equation
F x 1/Area
Tensile strain is in what direction?
y
Lateral strain is in what direction?
x
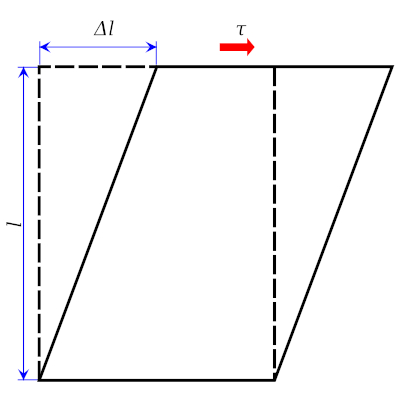
This is what type of deformation?
Shear strain
Reversible type of deformation
Elastic
Type of deformation with a linear stress/strain curve
Elastic
The slope of a stress/strain curve, E
Modulus of Elasticity
The elastic modulus of a material depends on what?
Interatomic bonds
Elastic moduli for materials are related only if those materials are what?
Isotropic
Permanent, nonrecoverable deformation
Plastic
Name for the maximum stress on an engineering stress-strain curve.
Tensile strength
For metals, the maximum on a stress-strain curve appears at the onset of noticeable…
Necking
The name for the amount of plastic deformation at failure.
Ductility
Ability of a material to absorb energy during elastic deformation
Resilience
Modulus of resilience for a linear stress-strain curve.
½ x stress x strain
The amount of energy absorbed before fracture.
Toughness
True Stress Equation
Stress(1 + strain)
True Strain Equation
ln(1 + strain)
True Stress, by definition
Force x 1/Instantaneous Area
True strain, by definition
ln(li / lo)
True stress in terms of true strain
True stress = K(true strain)^n
A material with a larger n (strain-hardening exponent) will experience (more/less) true stress compared to a material with a smaller n.
More
Reasons why ceramics are brittle
Dislocation motion (difficult when highly ionic)
Few slip systems
Resistance between like anions/cations
Order these from most ductile to least ductile.
Polymer, Elastomer, Plastic
Polymer, Plastic, Elastomer
Decreasing temperature (increases/decreases) modulus of elasticity.
Increases
Decreasing temperature (increases/decreases) tensile strength.
Increases
Decreasing temperature (increases/decreases) elongation %
Decreases
Increasing strain rate has what effects, as compared to decreasing temperature?
Same
Measure of resistance to surface plastic deformation (dent or scratch)
Hardness
GO OVER ROCKWELL VS BRINELL HARDNESS
Tm and Tg ___________ with increasing chain stiffness
Increase
Increasing chain stiffness
Bulky side groups
Polar groups
Double bonds and aromatic chain groups
The more random a polymers structure is, the _____ it is to form its crystalline structure.
Harder
Regularity of repeat unit arrangements affect (Tm or Tg) only.
Tm
Larger crystals are closer to ideal, and therefore have a _____ melting point.
Higher
Polymers with many imperfections are less crystalline and therefore have a _____ melting point.
Lower
Thermoplastics
Little crosslinking
Ductile
Soften with heat (remolding)