The human genome and genetic diseases
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
human genome
- 3.3 B DNA base pairs
- 22 pairs autosomes and 1 pair sex chromosomes (X or Y)
- 1.5% of genome codes for proteins
- 85% genome transcribed into RNA
- 80% genome devoted to regulation of gene expression
non-protein coding sequences
- promoters and enhancers
- noncoding regulatory RNAs (transcribed genes that aren't translated including mircoRNAs and long non-coding RNAs)
- transposons: mobile genetic elements
- telomeres and centromeres: structural regions of DNA
promoters and enhancers
- bind transcription factors
- binding sites for DNA-binding proteins that organize and maintain chromatin structure
epigenetic mechanisms
- covalent modifications of DNA (5-methylcytosine and 5-hydroxylmethylcytosine)
- Post-translational modifications of histones
- 3D chromatin structure
single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
- variants at single nucleotide positions
- in coding and non-coding regions
- non-coding SNPs may alter the regulation of gene expression
- coding SNPs may change protein sequence
- neutral SNPS have no effect on gene function or phenotype
- effect of individual SNPs on disease susceptibility is weak particularly for complex diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, or cancer
copy number variations (CNVs)
- variation in number of large contiguous stretches of DNA (about 50% CNVs involve coding sequences)
- duplications, triplications, deletions, inversions
mutations in protein-coding genes
mutations are changes in DNA sequence
point mutations (substitution of a single nucleotide base by a different base)
- missense: changes an amino acid
- nonsense: creates stop codon
frameshift mutations: insertion or deletion of 1-2 base pairs alters reading frame of the DNA strand
trinucleotide repeat mutation: amplification of repeated sequence of 3 bases
- repeat expansion/amplification: number of repeats increases during gametogenesis
Other alterations in protein-coding genes
structural variations: genomic rearrangement leads to amplifications, deletions, or translocations of chromosomal segments
- single genes to entire chromosomes
- Intra- or inter- chromosomal
gene editing (CRISPR)
- CRISPRs: clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats
- form of bacterial immunity
- gene editing using artificial guide RNAs that target DNA sequence of interest to introduce mutations
- 1st therapy approved in Dec 2023 to treat sickle cell disease (Casgevy)
epimutations
- changes in epigenetic mechanisms that change gene expression
- can have functional outcomes on gene expression and phenotype/disease
- epigenetic and genetic mechanisms in cancer: inactivation of tumor suppressor genes(promoter hypermethylation) and activation of oncogenes(promoter demethylation)
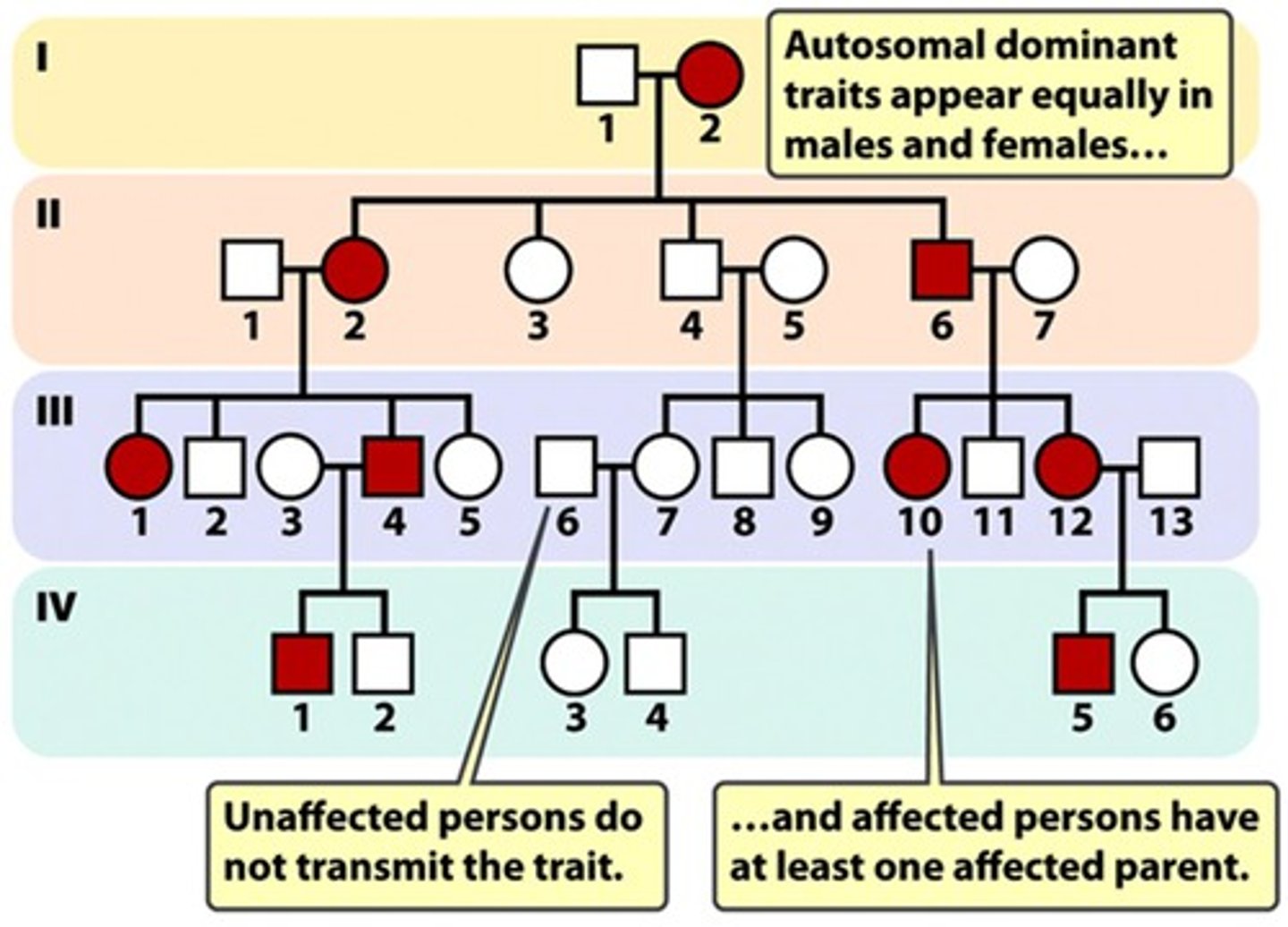
autosomal dominant: mendelian disorder
- doesn't skip generation
- affected offspring have affected parents
- male and female offspring are equally likely to be affected
- Ehler-Danlos syndrome has abnormal collagen, which is supposed to support structure and extracellular matrix --> dominant or recessive; genetic heterogeneity
- Huntington's disease has Huntingtin (trinucleotide repeat) --> genetic anticipation
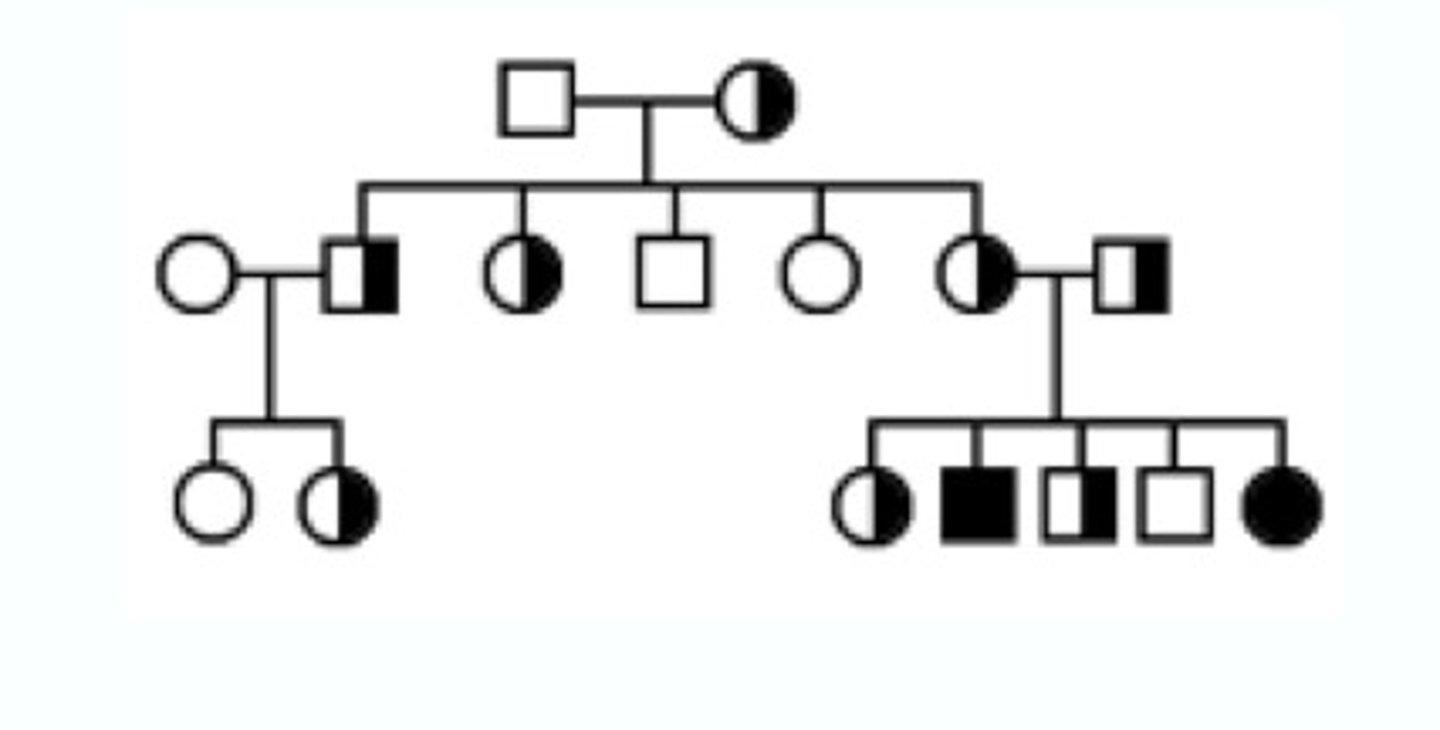
autosomal recessive: mendelian disorder
- typically skips generation
- affected offspring may have unaffected parents
- male and female offspring equally likely to be affected
- cystic fibrosis (CFTR-1 abnormal) --> genetic heterogeneity
- sickle cell diseases (abnormal hemoglobin involved in oxygen transport)
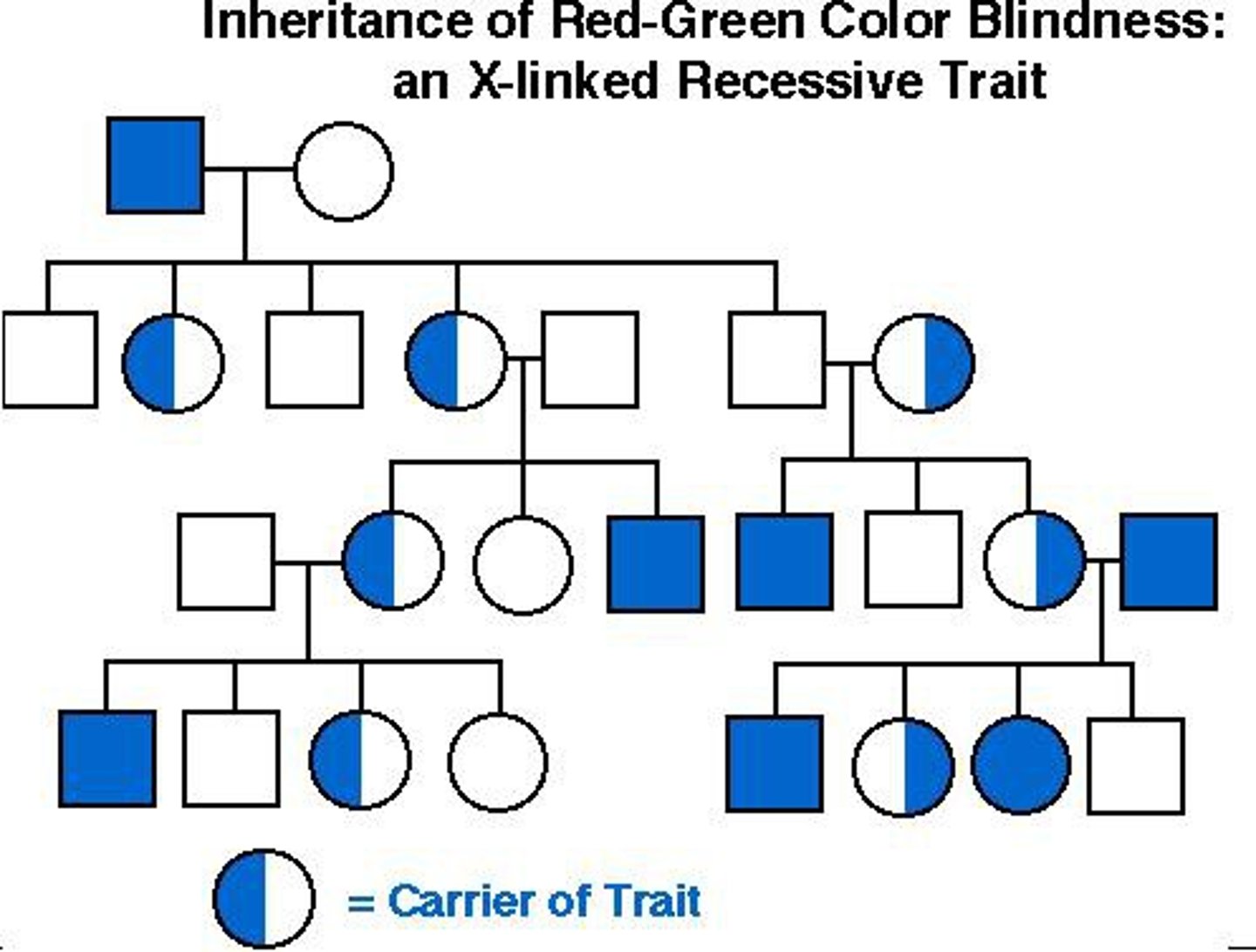
x-linked recessive: mendelian disorder
- typically skips generation
- affected sons may have unaffected mothers (carrier)
- affected daughters must have affected father AND affected or unaffected mother
- cannot be passed from father to son
- male offspring more likely to be affected
- fragile X syndrome (FMRP is a trinucleotide repeat and a problem in RNA translation) --> genetic anticipation
Mendelian Disorders: patterns of inheritance
- pleiotropy (1 gene mutation = many phenotype effects)
- genetic heterogeneity ( multiple genes = same trait)
- penetrance (proportion of individuals with the mutation that exhibit clinical symptoms among all individual with such mutation; BRCA1 mutations lead to incomplete penetrance)
- expressivity (degree to which a phenotype is expressed by individuals having particular genotype, like sickle cell anemia)
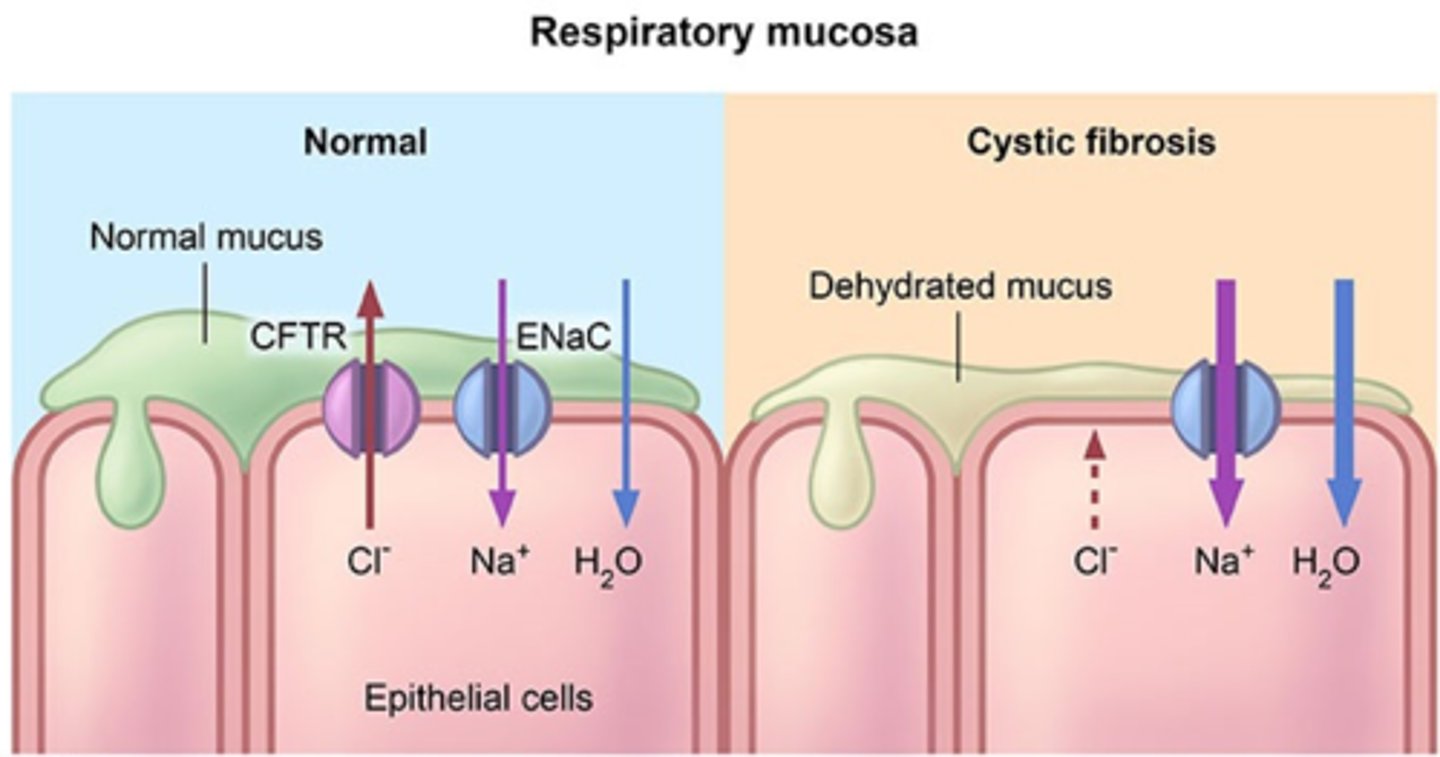
Cystic Fibrosis
- most common life limiting disease in US that is the disorder of epithelial CFTR (Cl- transporter) in respiratory, GI and reproductive tracts
- recurrent and chronic pulmonary infections
- pancreatic insufficiency
- male infertility
- High NaCl in sweat
- >2000 identified mutations in CFTR: protein production, processing, gating, conduction, and insufficient protein
- F508del: most common CF mutation, ~90% of CF population, protein processing mutation
- 2010: all 50 states adopt universal newborn screening
Trikafta
- approved in 2019 for carriers of the most common variant; expanded to people with CF 2 and older with F508del and 177 other mutations
- treats the defective CFTR in a majority of the CF population
- combinations of ivacafactor (chloride channel opener), and tezacaftor, elexacaftor (CFTR modulators)
- impact: median age of death went from 26 years to 66 years between 2008 and 2022
- 1/5 CF patients died before age 40 in 2022 vs almost 1/2 in 2016
- patients take no additional enzymes, no postural drainage, less inhalations from inhalers, no nebulizers, or ensure when on Trikafta vs not
translocation
Change to a chromosome in which a fragment of one chromosome attaches to a nonhomologous chromosome.
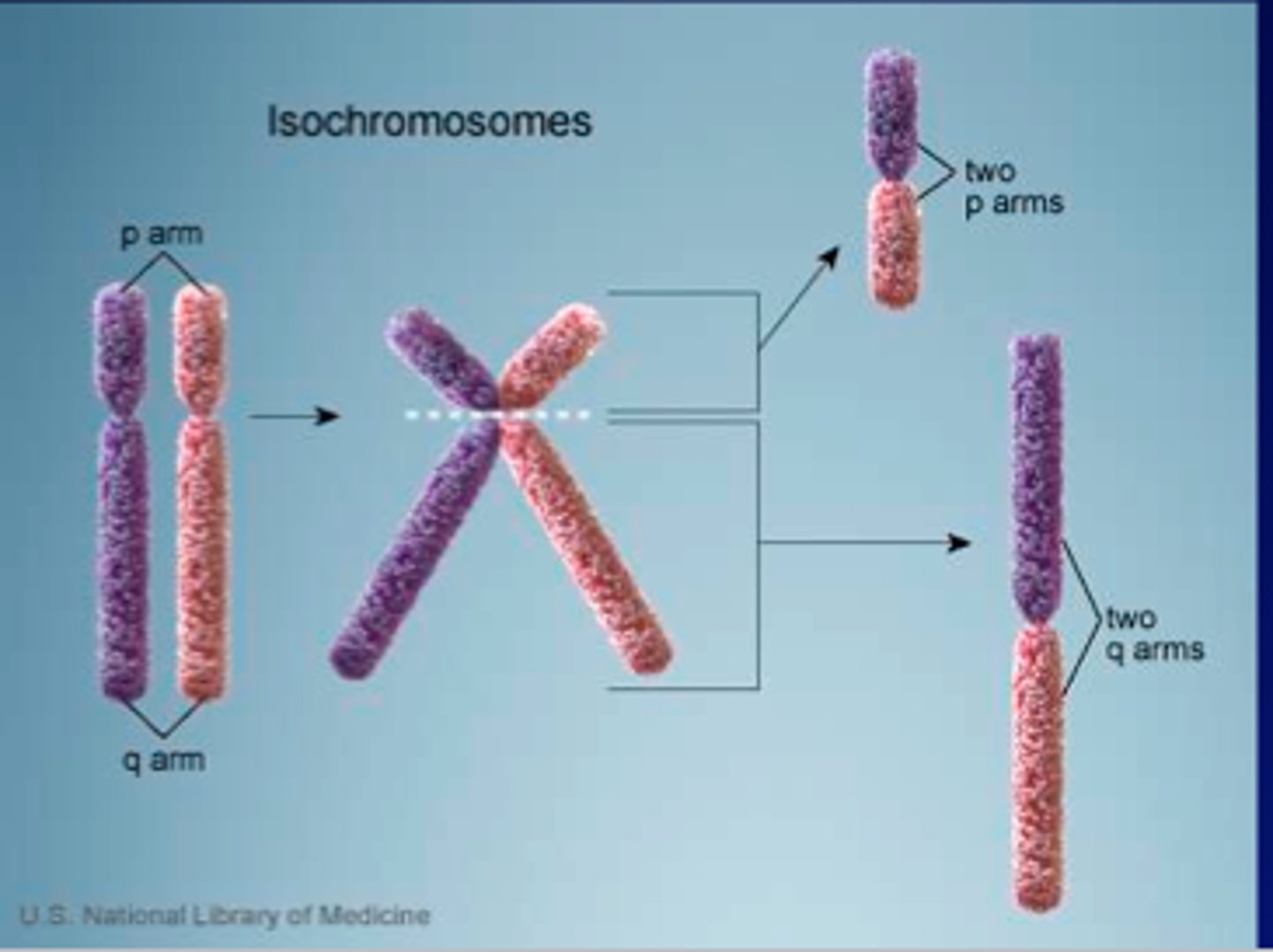
isochromosomes
Chromosomes with identical arms
Form when centromeres divide along the incorrect plane during meiosis
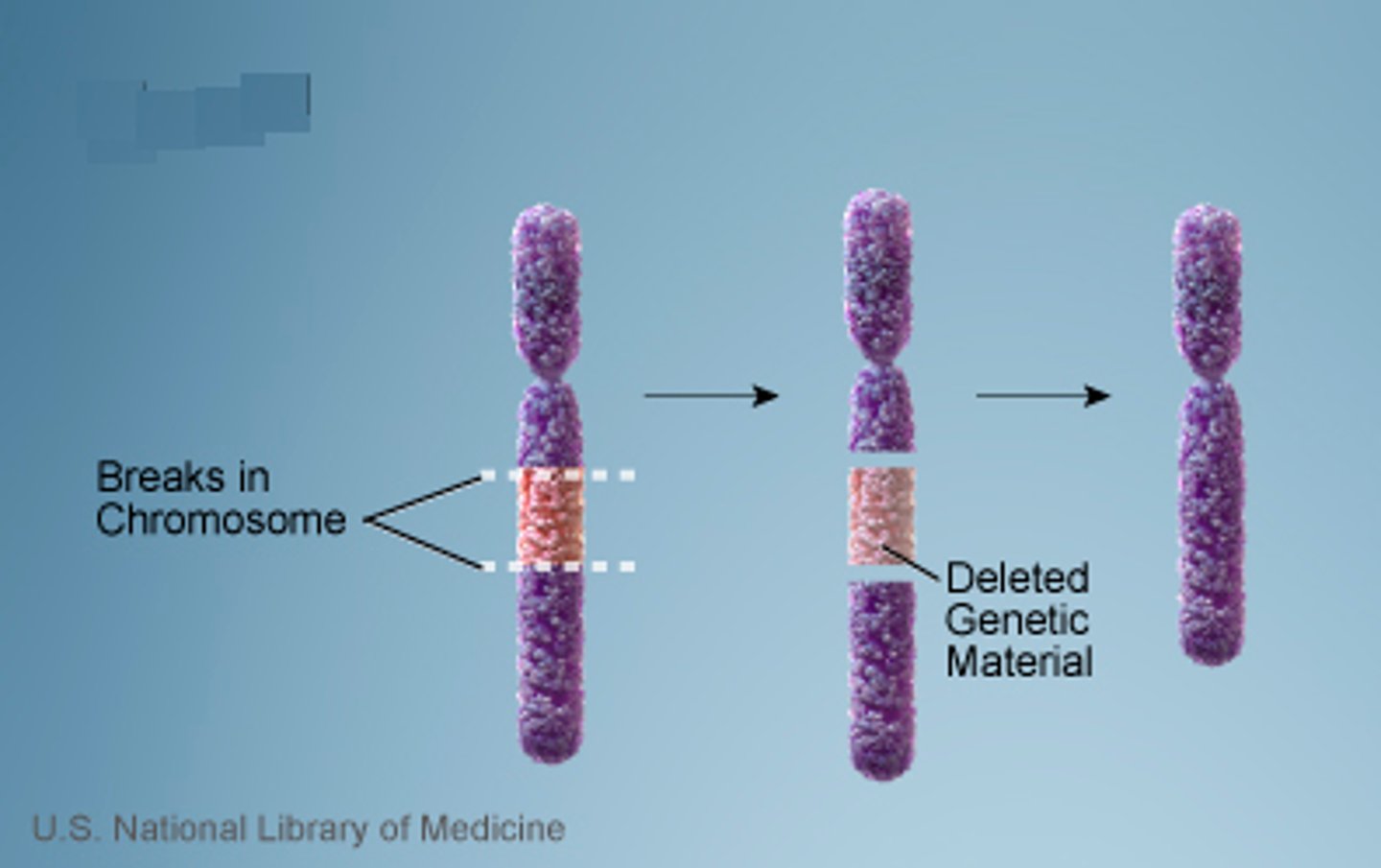
deletions
Mutation involving the removal of one or more nucleotide pairs from a gene
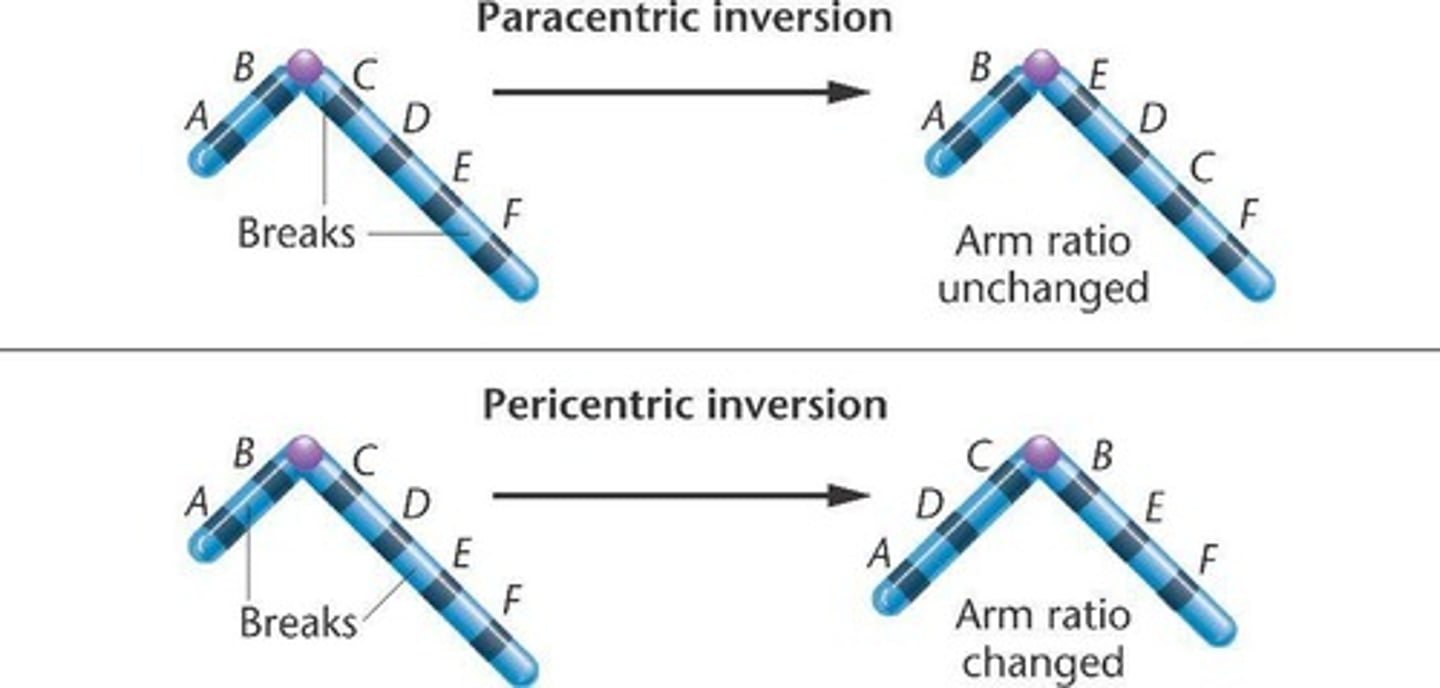
inversions
paracentric and pericentric
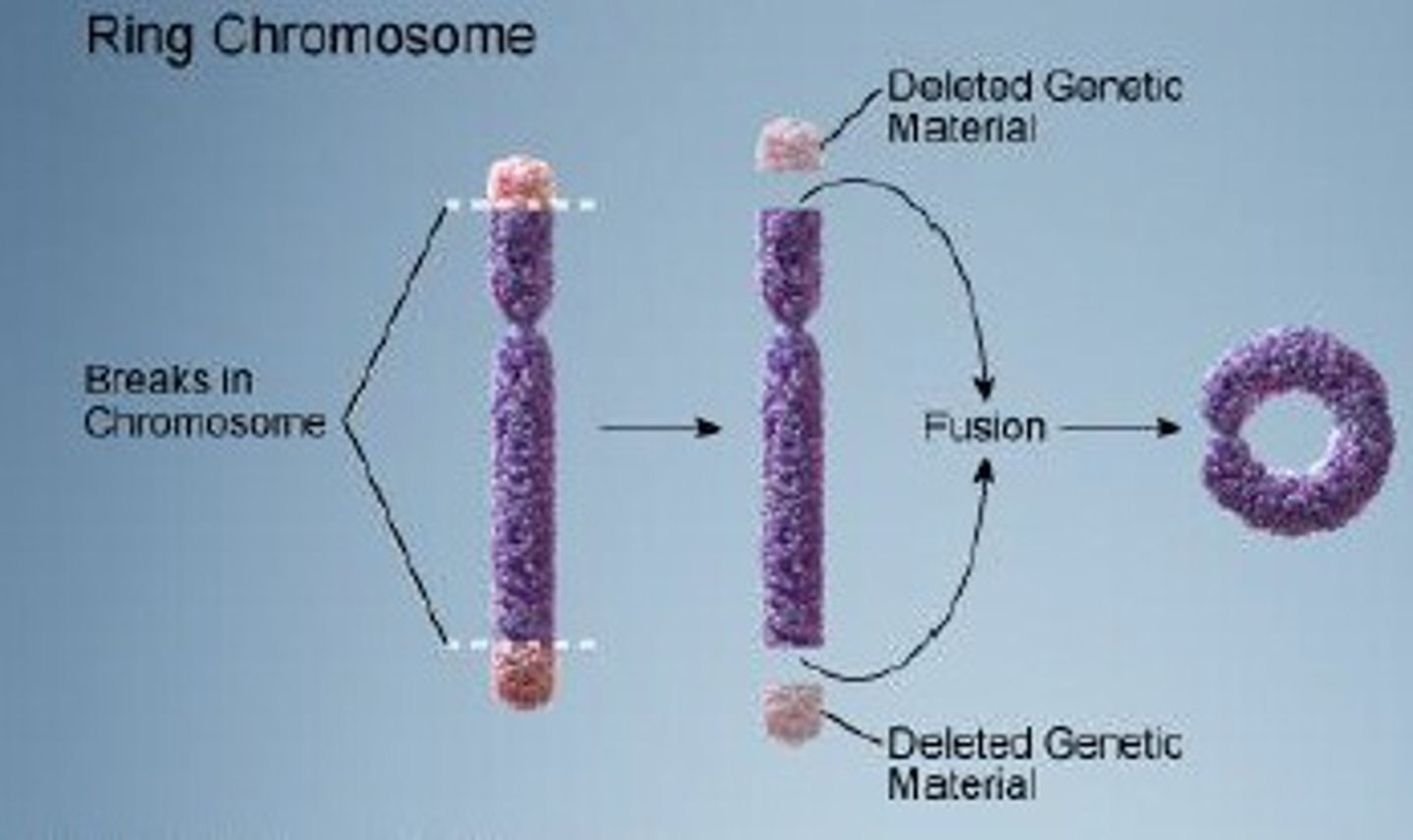
ring chromosomes
when telomeres break, becoming sticky and the chromosome connects at each ends with each other. Can cause symptoms
Down syndrome: trisomy 21
- extra copy of chromosome 21; visible on karyotype
- multiple genes disrupted, leading to intellectual disability and other symptoms (40% have congenital heart disease, 10-20 fold increased risk of acute leukemia, predisposed to serious lung infection and thyroid autoimmunity, nearly all down syndrome patients older than 40 have Alzheimer's pathology)
- median age 25 (1983) and is 60 due to improved medical care
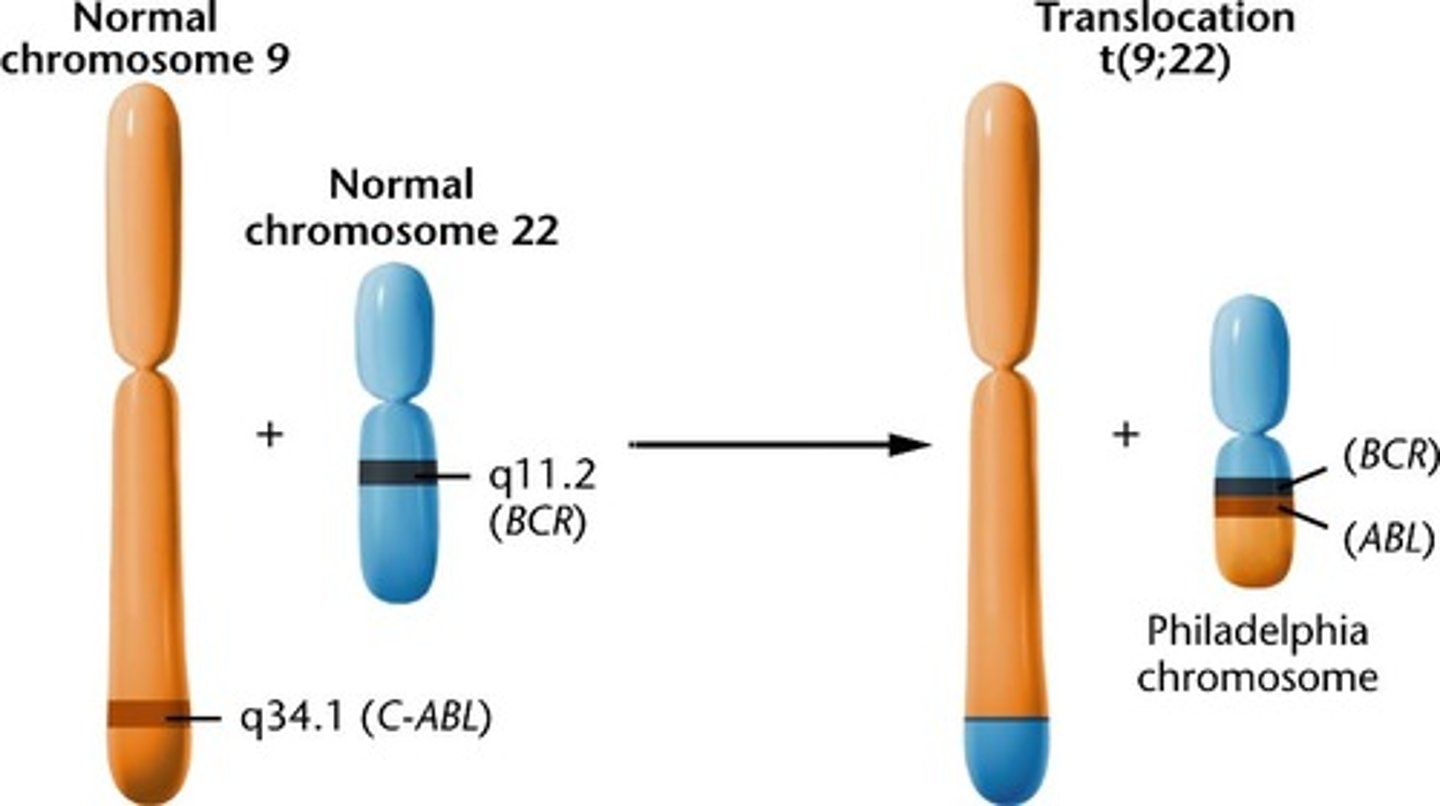
Philadelphia chromosome
An abnormal chromosome produced by translocation of parts of the long arms of chromosomes 9 (BCR gene) and 22 (ABL gene)
- almost all people with chronic myeloid leukemia and some people with acute lymphocytic leukemia or acute myelogenous leukemia
- Gleevec: 10 year survival rates increased from <20% to 85%
Fragile X syndrome
- Trinucleotide Repeat (CGG)
- X-linked Dominant
- FMR1 (Fragile X Mental Retardation 1)
Inheritance:
- X-Linked Dominant
- Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome and fragile X-associated primary ovarian insufficiency- primarily affects males
- genetic anticipation
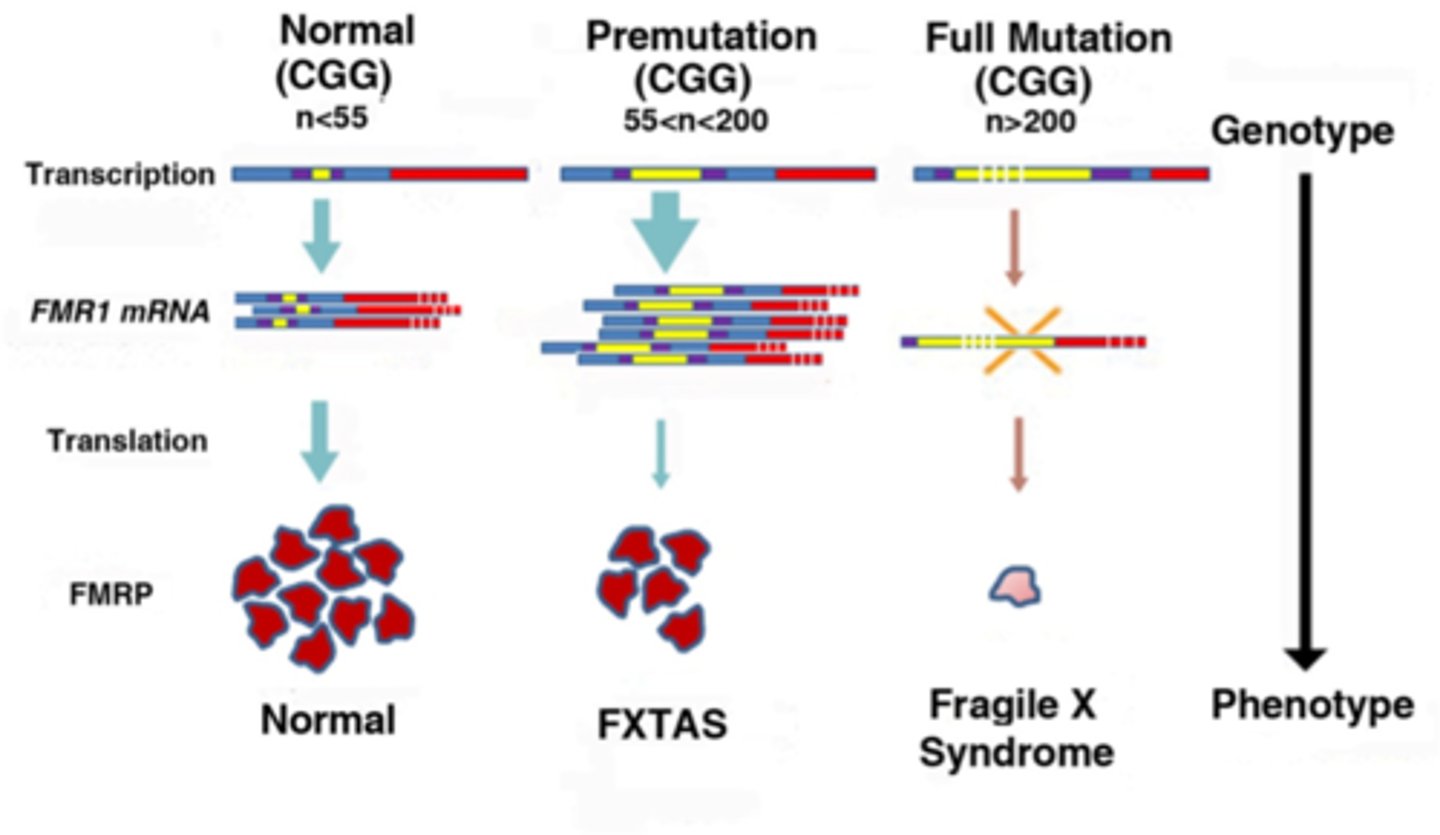
genetic anticipation
- clinical features worsen or begin earlier with each successive generation
complex multigenetic disorders
- hypertension/heart disease
- diabetes
- cancer
- autoimmune diseases
- parkinson's disease
- non-disease (hair, eye, skin color, height, intelligence)
- genetic variants, environmental factors and the interaction between them
- polymorphism (genetic variant that occurs in at least 1% of the population)
Common disease-common variant hypothesis
Complex diseases arise when many polymorphisms, each with a small effect and low penetrance, occur together
- different polymorphisms vary in significance
- polymorphisms can be disease-specific or shared by related diseases
- many disease-associated polymorphisms are in noncoding regions, so they may affect epigenetics and regulation of gene expression