1.4: blood vessels
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
types of blood vessels
-arteries: carry blood ____ (towards/ away?) from heart
-capillaries: site of ___ ___
-veins: carry blood ___ (towards/ away?) from heart
away, nutrient & gas exchange, towards
“v for venir”
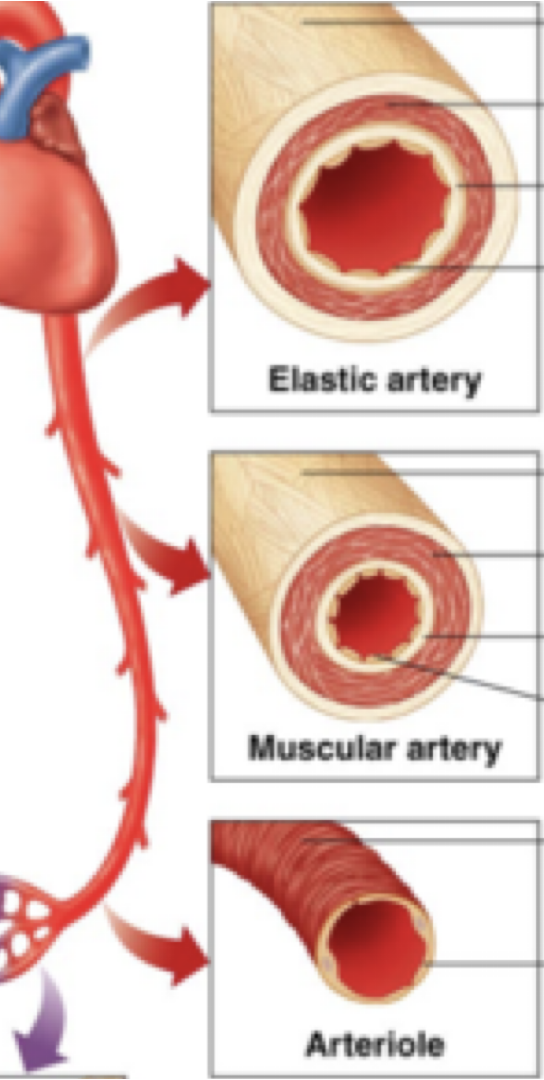
arteries
-muscular & maintain round shape
-___ blood flow bc of high pressure of blood in blood vessels
pulsatile
types of arteries: elastic/ conducting
-___ (high/ low?) elastic tissue content
→carry blood to ___ ___ of body
→expand during ___ (systole/ diastole?), recoil during ____ (systole/ diastole?)
-some arteries contain arterial sense organs:
→baroreceptors: monitor ____
→chemoreceptors: monitor ____
→help regulate __ __, respiration, vasomotion
high, large regions, systole, diastole, blood pressure, blood chemistry, heart rate
types of arteries: muscular/ distributing
distribute blood to ___ of the body
specific regions
types of arteries: arteriole
-control amount of ___ to organs
-prominent smooth muscle means high capacity for ___
→little elastic tissue
blood flow, vasomotion
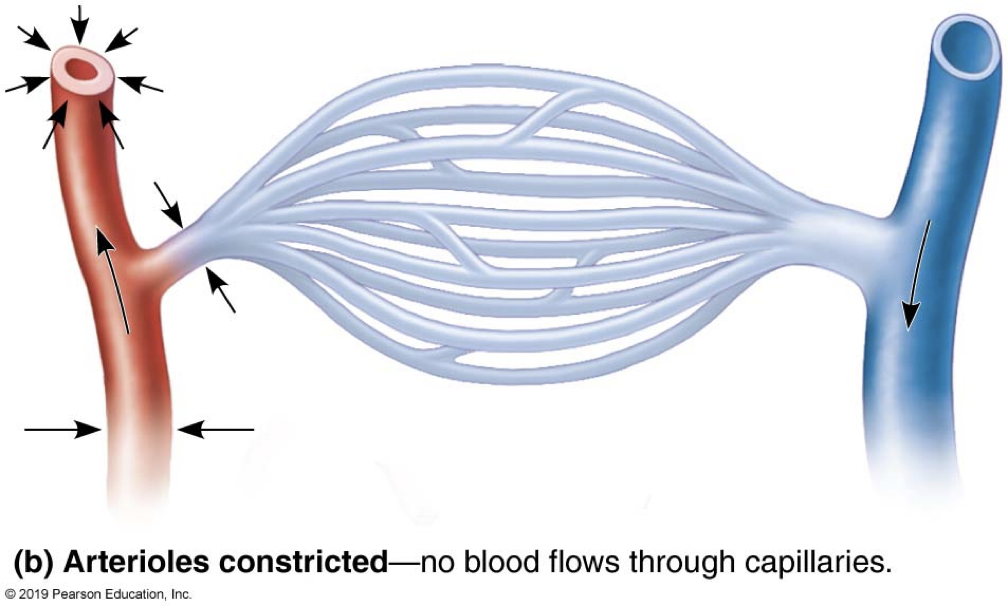
vasomotion
-vasoconstriction: blood vessel diameter decreases
→decreased internal volume = ____ pressure
-vasodilation: blood vessel diameter increases
→increased internal volume = ___ pressure
increased, decreased
functions of vasomotion
1) general raising/ lowering of blood pressure
-systemic vasodilation ___ (raises/ lowers) BP
-systemic vasoconstriction ___ (raises/ lowers) BP
-requires centralized control
2) ____ blood among regions/ modify perfusion of a specific organ
-either centrally or locally controlled
-constriction of specific artery/ arteriole reduces local flow
lowers, raises, reroute
capillaries
-supplied by which blood vessel? ___
-exchange vessels
-made up of endothelium & __ ___
arterioles, basement membrane
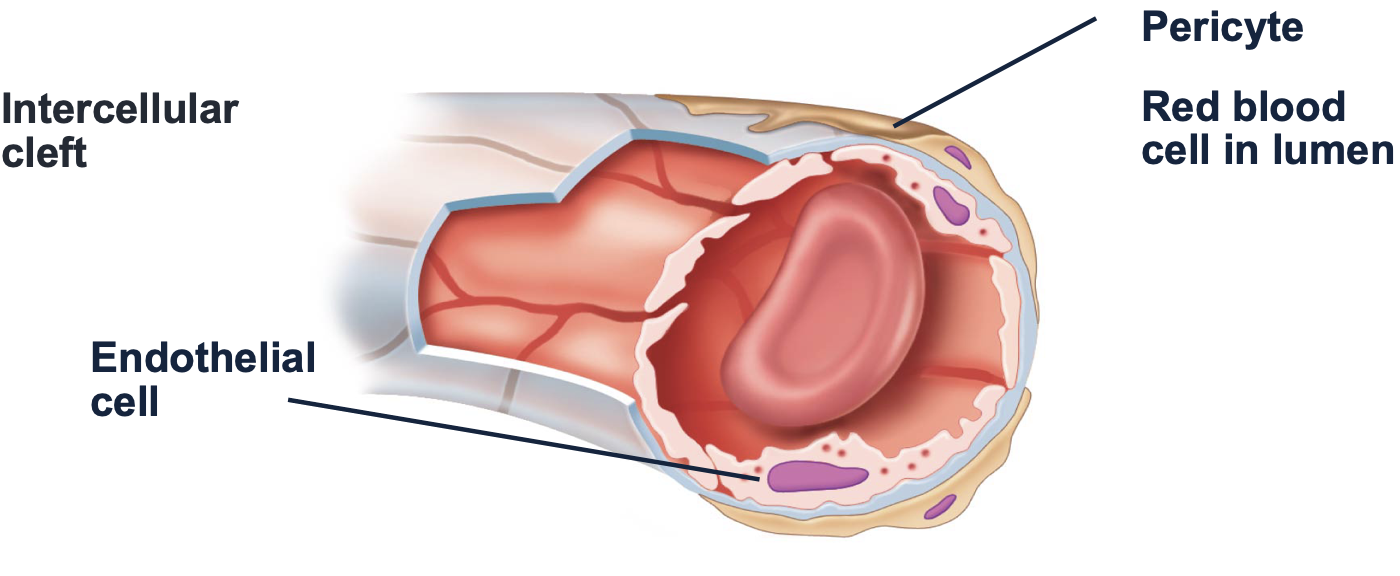
types of capillaries: continuous
-____ cells form continuous tube
-separated by intracellular ___
-found in most tissues
-small solutes can pass through
endothelial, clefts
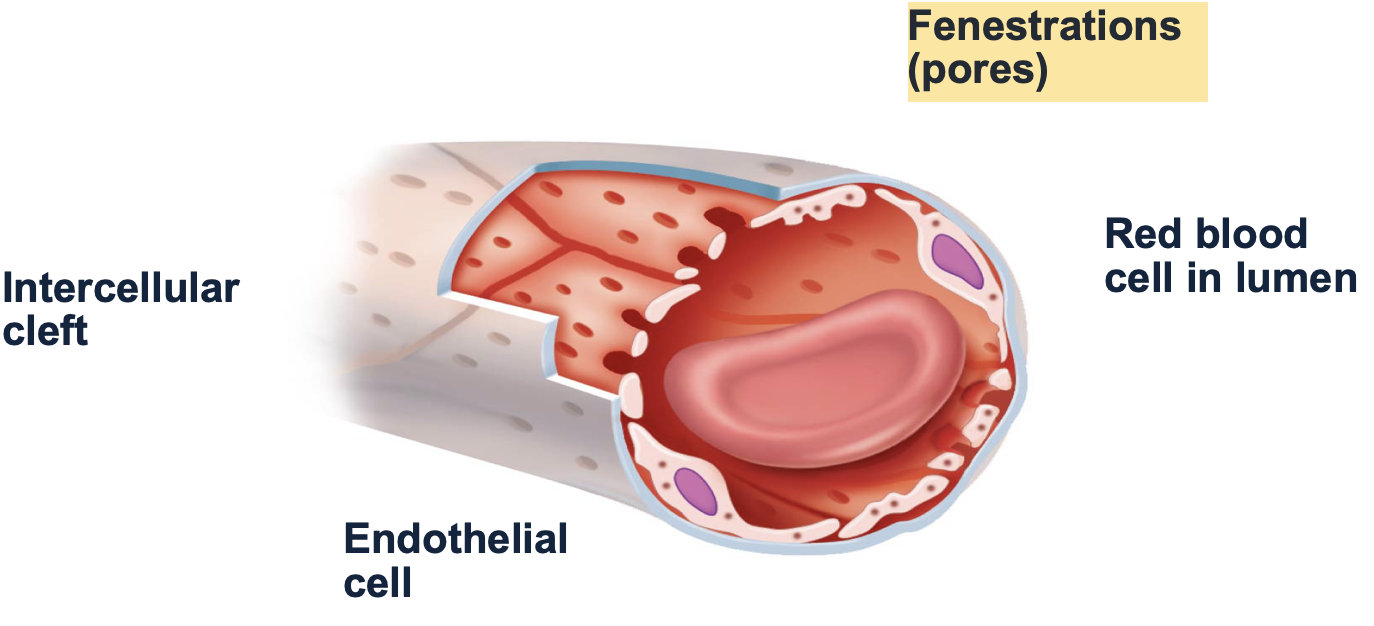
types of capillaries: fenestrated
-fenestrations ( aka ____) for passage of small molecules (more substances can pass through compared to continuous capillaries)
-found in organs that require ___ or filtration
small pores, absorption
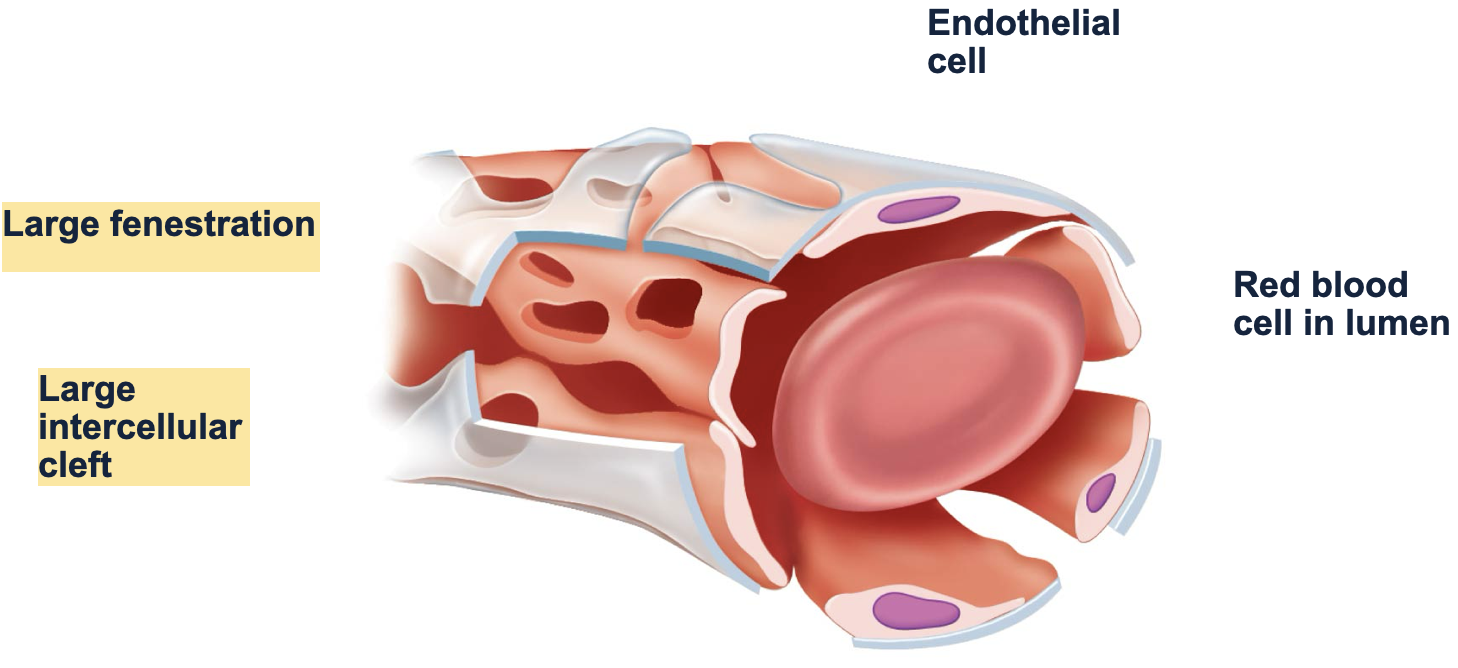
types of capillaries: sinusoid
-flattened, irregular shape
-___ (small, medium, large?) fenestrations, wide clefts, ___ (complete/ incomplete?) basement membrane
-found in areas where ____ are exchanged
large, incomplete, large molecules
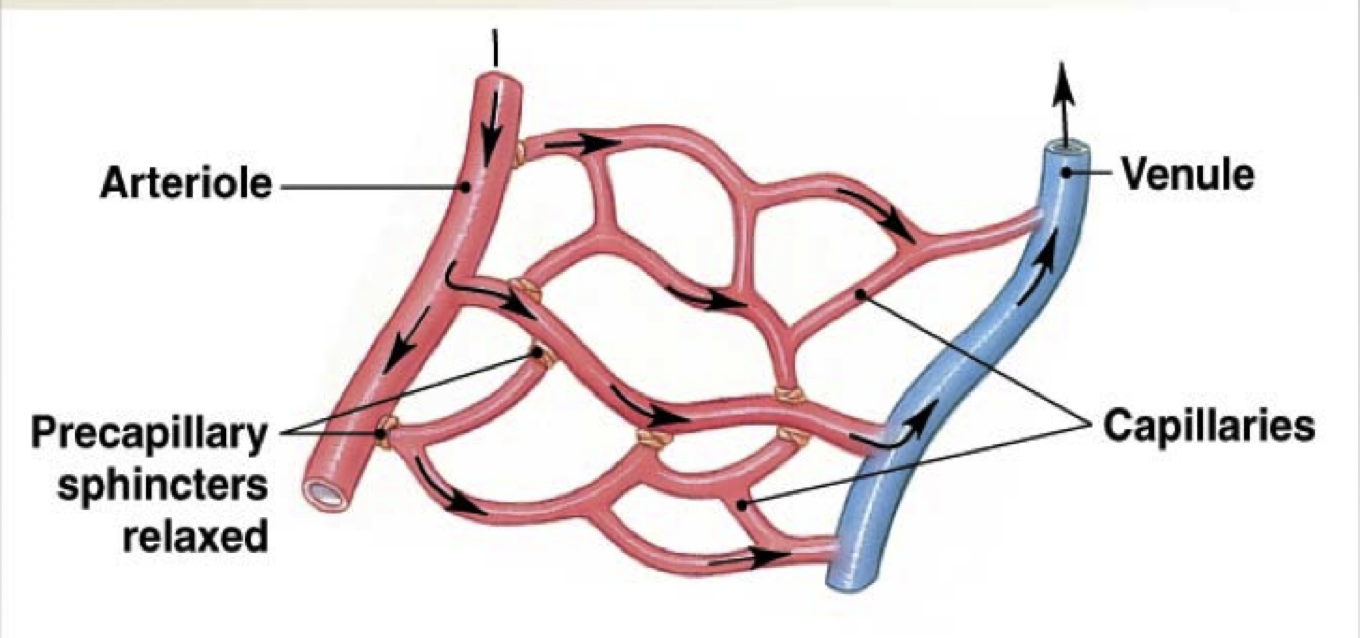
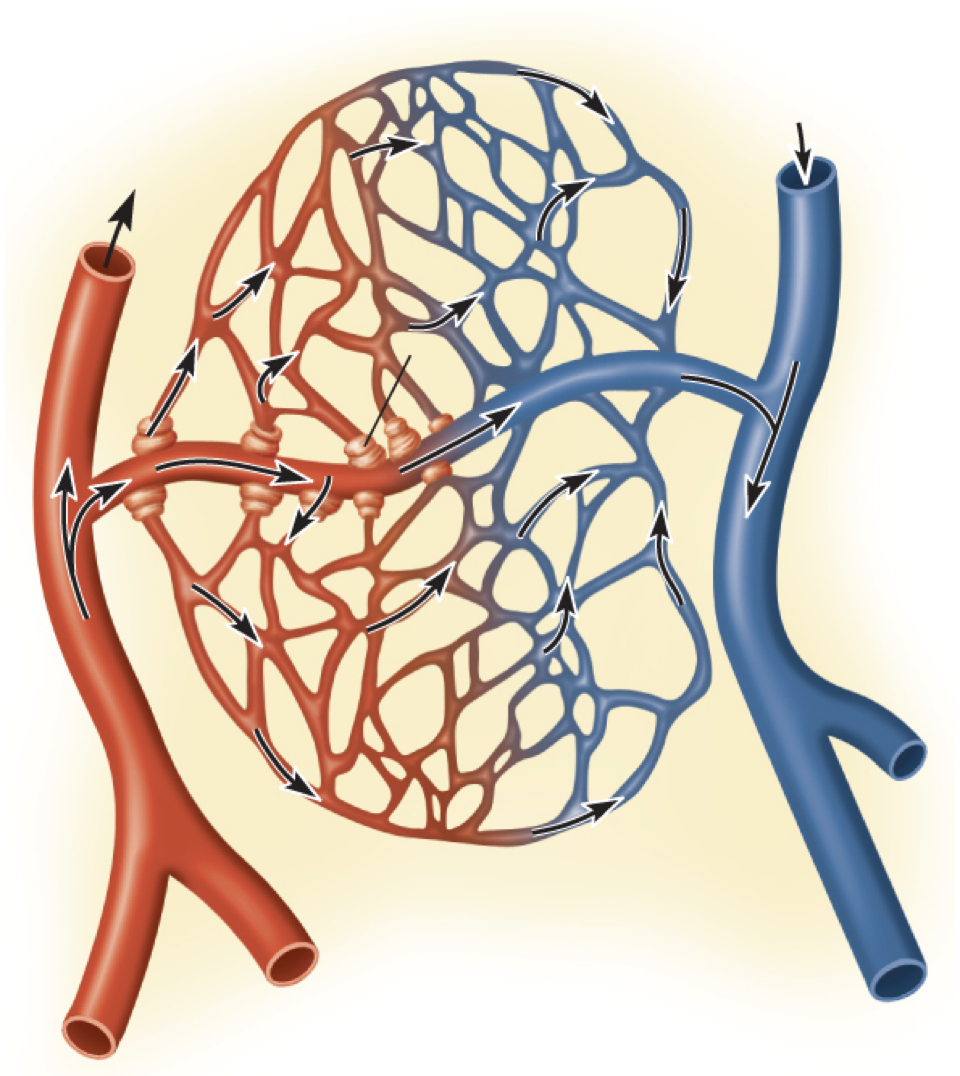
capillary bed: web of 10-100 capillaries supplied by single ____
-drain into ___ at distal ends
arteriole, venules
capillary perfusion: blood flow through ___
-depends on condition of body/ specific needs of organ
-regulated by arterioles: constrict/ dilate to ___ flow
capillary bed, adjust
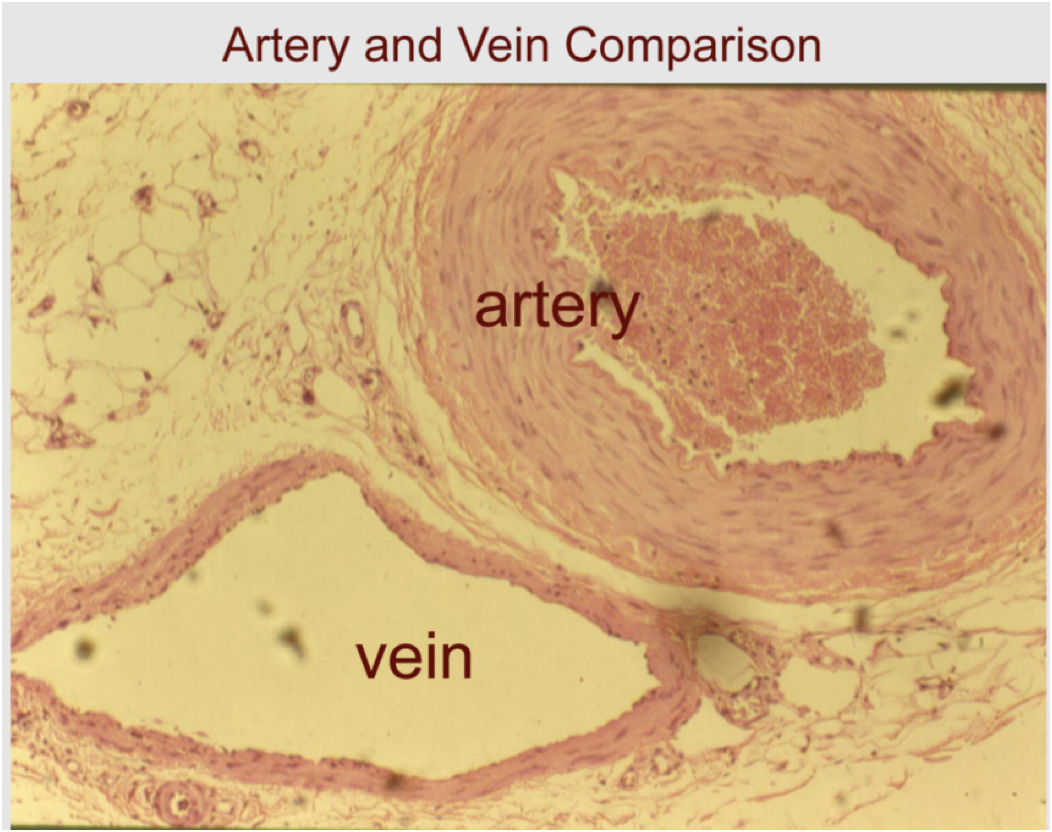
veins: less elastic
-steady blood flow
-relatively ___ (high/ low?) blood pressure
low
types of veins:
large: drain ___ regions of the body
medium: little smooth muscle
→venous valves: infolding of internal lining to prevent ___ of blood during venous return
venule: thin-walled
-little or no smooth muscle
large, backflow
circulatory routes
-simplest/ most common: heart → arteries → ___ →capillaries → ___ → ___
-blood passes through ___ (#?) network of capillaries
arterioles, venules, veins, one
circulatory routes
portal system: blood flows through ___ (#?) consecutive capillary networks before returning to heart
2
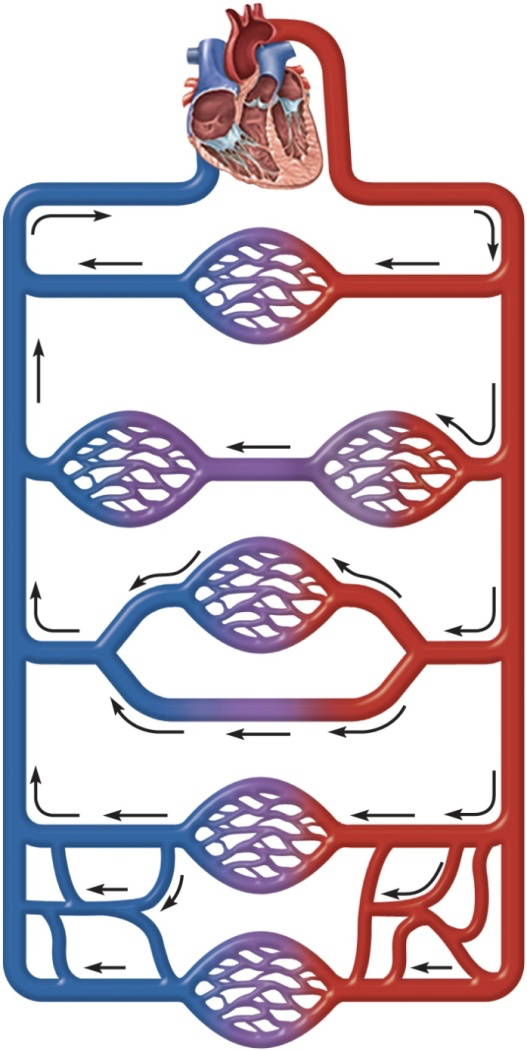
circulatory routes
anastomosis: convergence between ____ & other ____
→provides alternate route of blood flow
arteriovenous anastomosis (shunt): artery flows directly into ___ (bypassing capillaries)
arterial anastomosis: multiple ___ converge & branch
-provides ____ blood supply to tissue
-associated with joints
venous anastomosis: multiple ___ converge & branch
-provides alternate routes of drainage of an organ
blood vessels, capillaries, veins, arteries, collateral, veins