13. ECG and Exercise Stress Tests
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
How is a lab result defined as "normal" or "abnormal" based on the mean and standard deviation
Normal is within two standard deviations from the mean; any result not falling within the middle 95% is considered "abnormal".
For any given test what percentage of healthy individuals may have an "abnormal" result based on the two standard deviation range
5% of healthy individuals will have an "abnormal" result outside of this range
What primary considerations should guide the ordering of diagnostic tests
Order tests that will change or guide your management; consider what will be done with the result; is it worth the risk and how it will affect the patient’s comfort.
Besides clinical utility what two factors related to resources and patient status should influence test ordering
Consider cost and invasiveness; save expensive and/or invasive tests for when you need them; sicker patients often warrant a more aggressive approach
What is the definition of an Indication for a diagnostic study
The specific reason or clinical rationale for performing the test; it is the condition; symptom; or clinical question that prompts a healthcare provider to order the study to confirm; rule out; or monitor a disease or medical condition.
What is the definition of a Contraindication for a diagnostic study
The specific reason or clinical rationale to NOT perform the study as it may be harmful to the patient.
List the primary indications for performing a cardiac stress test
To detect myocardial ischemia; infarction; myocardial wall dysfunction; to evaluate chest pain; EKG changes; to assess functional capacity (treadmill); to assess for exercise induced arrhythmia.
A 45-year-old male presents with new-onset, active chest pain consistent with unstable angina; which common diagnostic procedure is contraindicated in this patient?
Stress tests are contraindicated due to active chest pain/unstable angina
Name three specific contraindications for cardiac stress tests listed in the sources
Pregnancy; Active chest pain/ unstable angina; Severe Aortic Stenosis.
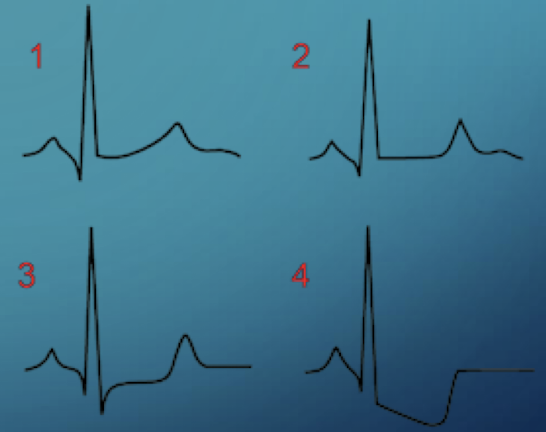
What specific EKG findings are considered positive for myocardial ischemia during a treadmill stress test
1 mm horizontal or downsloping ST depression at 0.08 seconds after the J point.
What criteria must a patient meet to have a technically adequate (negative) EKG response to a treadmill stress test
The patient must have achieved 85% age predicted maximum heart rate (calculated as 220 minus age).
What is the reported range for sensitivity and specificity for a standard treadmill stress test
Sensitivity and specificity range from 70-85%.
A patient cannot ambulate on a treadmill for a stress test combined with Myocardial Perfusion Scanning; what pharmacologic agents can be used to induce stress
Dipyridamole or adenosine.
What is the correlation between abnormal regional perfusion scans and coronary anatomy
There is a high correlation between abnormal regional perfusion scans and the presence of significant coronary artery occlusive lesions.
How does combining treadmill stress with Myocardial Perfusion Scanning affect the test's sensitivity and specificity
It increases sensitivity and specificity to 85%-95%.
What specific pharmaceutical agent is used to induce stress for a Stress Echocardiogram if a patient cannot exercise
Dobutamine.
How does reduced blood flow due to obstructive CAD manifest on a Stress Echocardiogram
Reduced blood flow results in reduced myocardial contraction in the anatomic area corresponding with the epicardial coronary artery involved; echo images detect exercise or pharmacologically-induced wall motion abnormalities.
What are the major risks associated with cardiac stress testing
Acute myocardial injury/Myocardial infarction; Malignant arrhythmia; Exertional hypotension; Death.
A patient is receiving a stress test using pharmacologic agents; what side effects should they be educated about
Pharmacologic agents may cause flushing; chest pain; nausea.
What is the clinical interpretation of a negative cardiac stress test result
A negative test does not mean no CAD; it means no significant obstruction.
What normal findings are expected on a stress test
Normal coronary perfusion; cardiac muscle function; and myocardial ejection fraction.
A 62-year-old patient undergoing a stress test has an EKG that shows a significant drop in the ST segment immediately following the J point; what EKG finding associated with ischemia is illustrated in the sources
ST depression
List the four types of EKG morphologies related to the ST segment illustrated in the sources
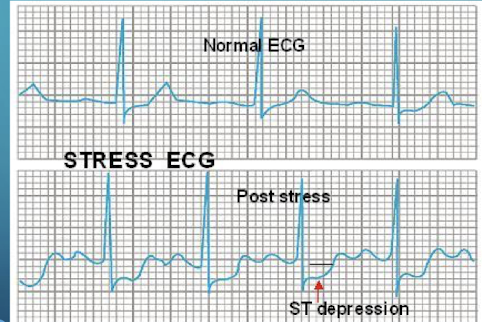
Normal; ST flattening; Horizontal ST depression; Downsloping ST depression.