PAG 4: Rates of Enzyme Controlled Reactions
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What specific reaction is used to investigate the effect of temperature on enzyme activity?
The breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by the enzyme catalase.
What are the independent and dependent variables in the temperature investigation?
Independent Variable: Temperature.
Dependent Variable: Rate of reaction (measured by volume of oxygen produced).
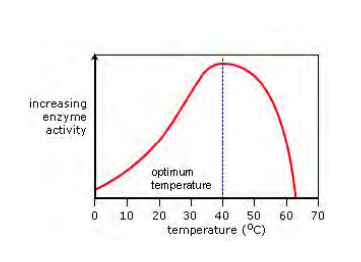
How do you control pH during the enzyme-temperature investigation?
By adding equal volumes of a suitable buffer solution to each boiling tube.
Why must the apparatus be allowed to equilibrate for 5 minutes before adding the enzyme?
To ensure the hydrogen peroxide solution reaches the target temperature of the water bath/ice bath.
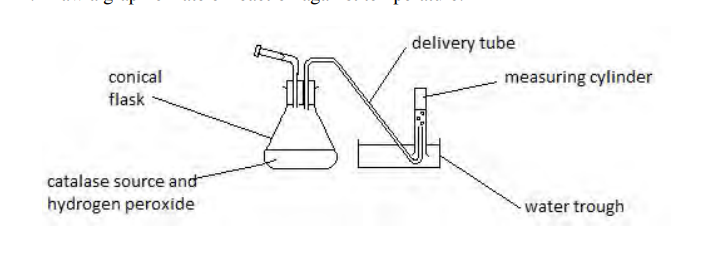
Describe the apparatus setup used to measure the rate of reaction for catalase.
A conical flask/boiling tube containing the reaction mixture is connected via a delivery tube to an upside-down measuring cylinder in a water trough to collect and measure the gas (O2) produced.
What reaction is used to investigate the effect of amylase concentration?
The breakdown of starch by amylase.
How is the rate of reaction measured in the amylase investigation?
By measuring the time taken for the starch to disappear (iodine test no longer turns blue-black).
What is the positive and negative result for the iodine test for starch?
Positive (Starch present): Dark blue-black.
Negative (Starch absent): Orange-brown.
How do you calculate the rate of reaction for the amylase experiment?
Rate = Concentration of starch / Time taken.
What are the independent and dependent variables when investigating substrate concentration?
Independent Variable: Concentration of hydrogen peroxide (substrate).
Dependent Variable: Rate of reaction (volume of gas produced).
How is the data analysed for the substrate concentration experiment?
Calculate the mean and standard deviation for each concentration14.
Calculate rate of gas production (cm3 min-1).
Plot a graph of rate of reaction against substrate concentration.
Describe the process of making a serial dilution with a dilution factor of 2.
Add a set volume (e.g., 2cm3) of distilled water to a series of tubes.
Add a set volume (e.g., 2cm3) of the starting solution (e.g., 2.00%) to the first tube containing water.
Mix, then take the same volume (2cm3) from this tube and add it to the next tube.
Repeat the process. This halves the concentration at each step.
If you start with a 2.00% solution and perform a serial dilution with a dilution factor of 2, what are the concentrations of the next three tubes?
1.00%, 0.50%, and 0.25%.