hematology/oncology diseases & the eye
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
most common form of anemia
iron deficiency anemia
iron deficiency anemia
-most common type (50% of anemias)
-adults MC reason is blood loss (PU disease or colon cancer)
-other causes: malabsorption or decreased iron intake
the MC cause of ID anemia in children: malnutrition
lab tests for iron deficiency anemia
-CBC
low HgB
decreased MCV
any iron under 12 (M or F)
signs of iron deficiency anemia
-fatigue
-pale skin
-leg cramps
-brittle hair
-nail spooning
-pica
tx for iron deficiency anemia
-iron supplementation
-ferrous sulfate: MC used for constipation
-GI disease management
anaplastic anemia
-pancytopenia
-fatigue, skin rash, HA, dizziness, tachycardia, uncontrolled bleeding from minor cuts
-chronically damage kidneys synthesize inadequate amounts of EPO (hormone that stimulates RBC production in bone marrow)
causes:
-infection, radiation and drugs (Chloramphenicol, Acetazolamide, Chemo drugs)
anaplastic anemia lab test
-low Hgb, platelet, RBC, WBC
-normal MCV
tx for anaplastic anemia
-#1 blood transfusions
-drugs (immunosuppressors, hematopoietic growth factors)
-bone marrow transplant
sickle cell anemia
-MC form is caused by a mutation in the beta globin gene
Valine is substituted for glutamic acid
-low Hgb, increased bilirubin and crescent shape cells
-crescent cells → occlude retinal vessels → ischemia → neovascularization
sea fan, salmon patch hemes and black sunburts
stage 1 for sickle cell anemia
peripheral arterial occlusion
stage 2 of SCA
-peripheral arteriovenous anastomoses, representing dilated pre-existing capillaries (hairpin loop)
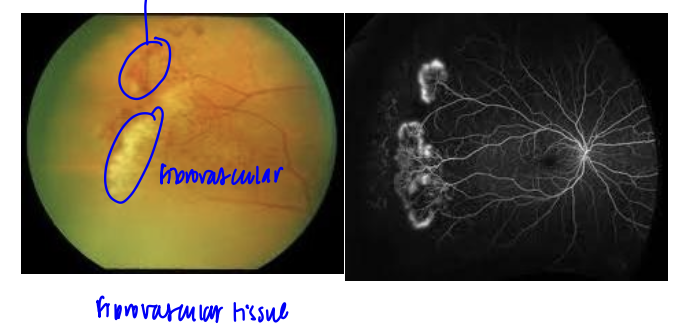
stage 3 SCA
-neovascular and fibrous proliferation
-seafan: due to auto-infarction of the neovasculature
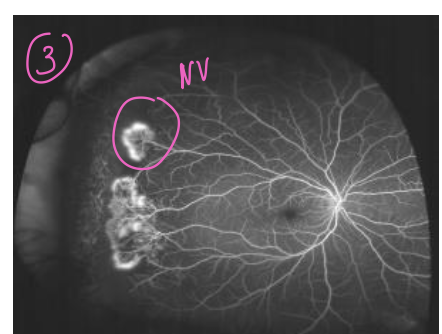
stage 4 SCA
vitreous heme
stage 5 SCA
tractional retinal detachment
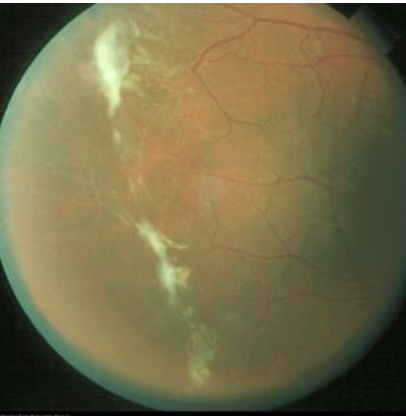
tx for SCA
-antimetabolites: hydroxyurea
-opioid analgesics: acute crisis (morphine, oxycodonem phentanyl)
-blood transfusion
-hydration
vit b12 def
-inadequate intake or malabsorption of vitamin B12
-caused by pernicious anemia: autoantibodies against the parietal cells of the stomach (@ parietal cells of stomach which also produce HCl)
-decreased production of intrinsic factor
-glossitis, mood changes, dizziness, sensations of pins and needles
tx for vit b12 def
cyanocobalamin
nasal spray or SC MC
folic acid deficiency
-in OB can increase risk of neural tube defects → s
-fatigue, red tongue, miscarriages, diarrhea, pale skin
tx for folic acid def
400mcg/d PO and in OB 600 mcg/d PO
multiple myeloma
proliferation of a malignant clone of plasma cells in the bone marrow
-extensive skeletal bone destruction
-unexplained anemia
-hypercalcemia
-acute renal failure
lymphoma
proliferation of malignant lymph cells in solid tissues
@ lymph nodes, spleen and GI tract
40% hodgkins
60% non hodgkins
hodgkin’s lymphoma
two peak age groups:
-15-30yo
-50yo
-night sweats, enlarged lymph nodes, fever and itching
-red-sternberg cells (owl eyes)
-itching & enlarged lymph nodes
-good prognosis if dx early
50% associated with EBV (cause my mononucleosis virus)
non-hodgkins lymphoma
-enlarged lymph nodes and GI tumors
-abdominal pain
-variable prognosis depending on the type
-bone marrow bx to determine type (T or B cells)
intraocular lymphoma
non-hodgkin is the MC type
-orbital is the MC 55% in adults
-leopard spots, conjuctival lymphoma, orbital lymphoma
-metastatic from CNS
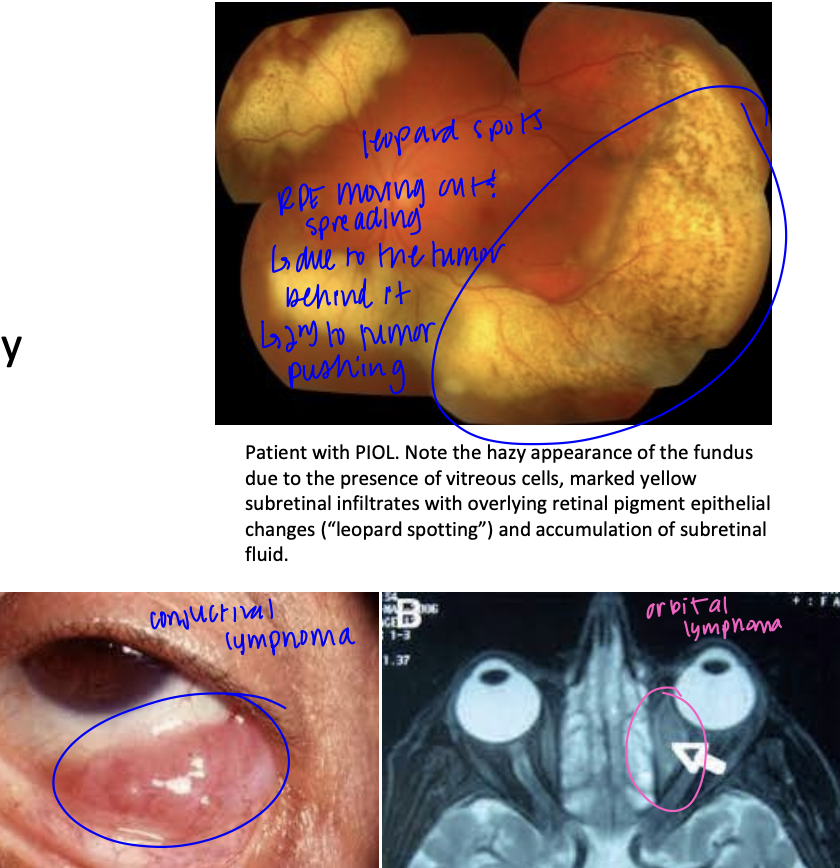
Tx for intraocular lymphoma
-chemoradiation
-survival rate 5 yrs
acute leukemia
-can affect all ages
-blast cells (immature cells) (B cells, T cells and Natural Killer cells)
Roth Spots
-retinal hem with a white spot in the middle
-also present in endocarditis
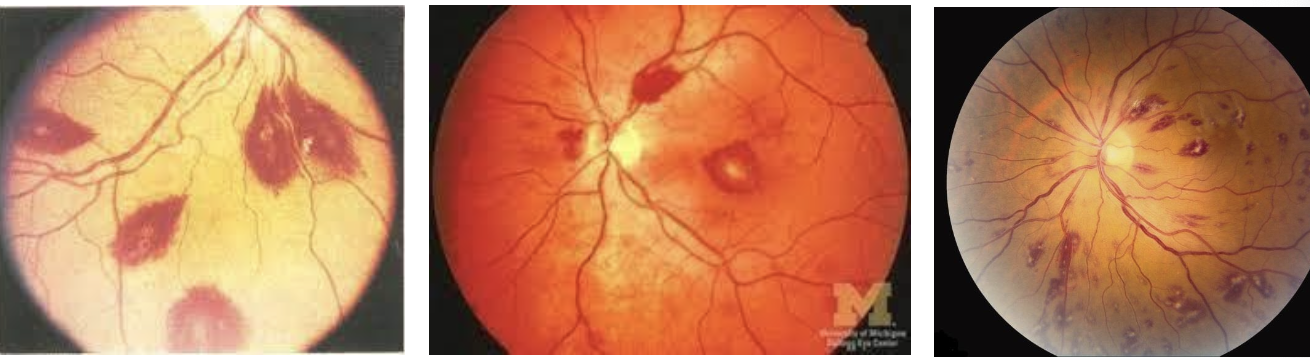
acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
-peak age is 2-10y
-normal WBC w. excessive lymphoblasts
-with tx: 75% remain disease free >5 yr
acute myeloblastic leukemia (AML)
-infants & middle age or older
-normal WBC with excessive myeloblasts
-Auer rods
chronic leukemia
-usually in older adults
-predominant cells are mature cells of the bone marrow
-often asymptomatic
-chronic myelocytic leukemia (CML) & chronic lymphocyte leukemia (CLL)
chronic myelocytic leukemia (CML)
-25-60yo
-poor prognosis 3 yr survival
-WBC 50,000 to 300,000 increased granulocytosis
-90% have the Philadelphia chromosome
chronic lymphocyte leukemia (CLL)
-age of onset is grater than 50yo
-M:F 2:1
-WBC 20,000 to 200,000
-5 to 10 yr survival rate
non-neoplastic disorders of blood cells
-leukopenia
-leukocytosis
-neutrophilia
-thrombocytosis
-pancytopenia
-thrombocytopenia
Leukopenia
-decreased number of WBC
-bone marrow injury, BM inactivation, #1 chemotherapy, antimetabolites (methotrexate)
leukocytosis
-#1 infections
-sx
-illness
-stress
-OB
neutrophilia
increase in absolute number of neutrophils
causes:
-stress
-exercise
-pain
-fever
-infections (typically bacterial)
thrombocytosis
-elevated platelet count
causes
-inflammation
-kidney disease
-spleen removal
pancytopenia
-decreased numbers of RBC and WBC
thrombocytopenia
-decreased platelets
causes
-infection
-lover failure
-BM disorders
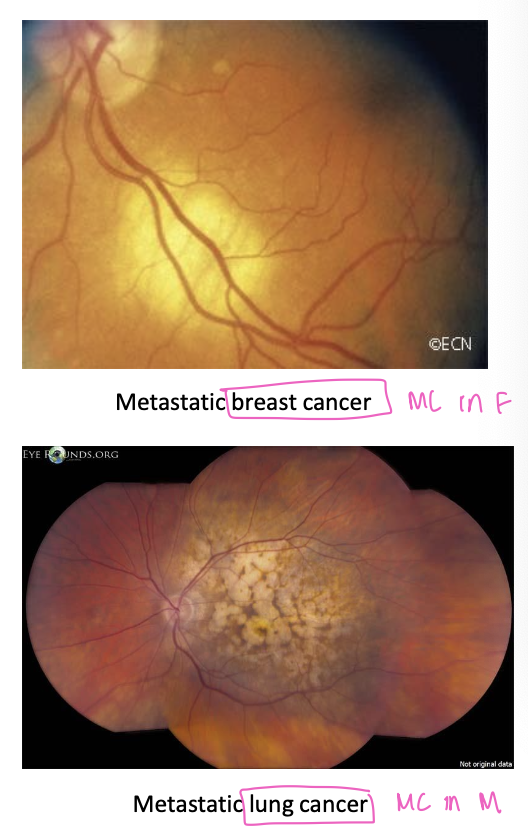
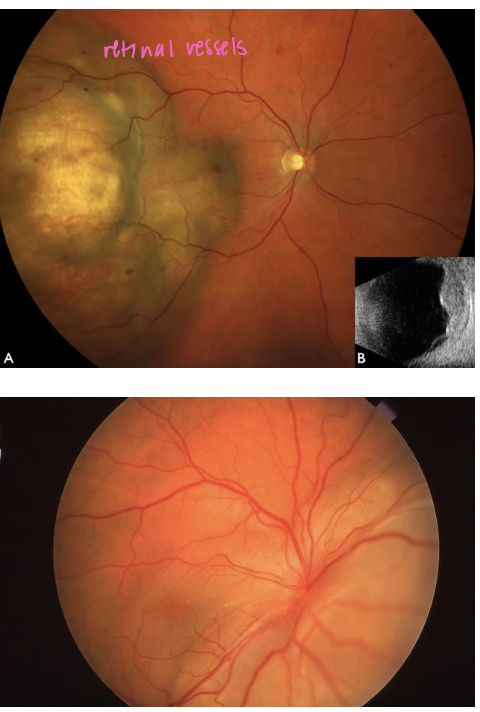
metastatic intraocular tumors
only 5% of the eye tumors are primary to the eye → 95% occur by metastasis
matastases to the eye occur only in adults → in choroid bc it is the organ with the most vascularization
women MC: breast cancer
men MC: lung cancer
what is the most common tumor that metastasize to the eye?
carcinoma
what is the most common site in the eye for metastatic tumor involvement and what signs would they experience?
macula
-painless loss of vision, choroidal tumor in the PP
dx for metastatic intraocular tumors
-US #1
-FA
-Bx
tx for metastatic intraocular tumors
-external beam radiotherapy and chemotherapy
-good prognosis of the eye
most common primary cancers in choroidal metastasis
female: breast
male: lung