Innate immunity exam 3 diversity
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Protection against pathogens
your body needs to be eble to distinguish between self and nonself
some defenses always in-place (automatic always on)
skin-sweat, normal flora
Other defenses activated
Three phases of how an immune system operates
recgnition phase
activation phase
effector phase
Recognition phase
recognizing pathogen
Activation phase
mobilization of cells/ molecules to help
Effector phase
Inavder destroyed
Defense MEchanisms
innate
adaptive
innate defense mechanism
genetically programed
nonspecfic
first line of defense
physical barrier, toxic molecules, general phagocytic cells
relative quick response (min/hours)
Adaptive defense mechanism
targets specific pathogens
antibodies made to find specific pathogens
slow, long-lived
evolved in vertebrates
all animals have ___ defense
innate
physical / chem barriers
physical things to stop pathogens from getting in
hard exoskelton
egg shell
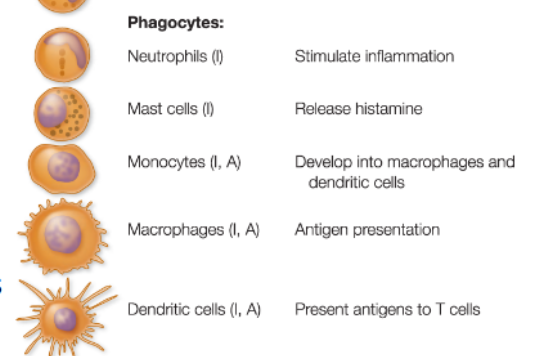
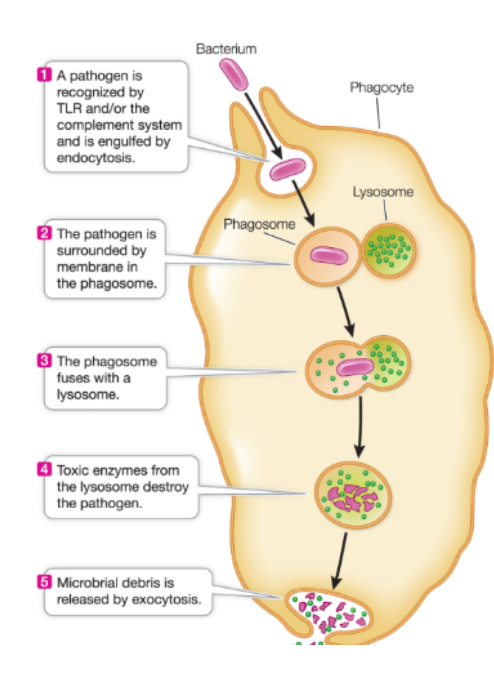
Phagocytic cells
the gaurds of defense. they “attack” any invaders if they’ve past the physical boundaries
large cells they ingest pathogens, by phagocytosis
molecules toxic to invading cells
peptides that disrupt pathogen cell membrane
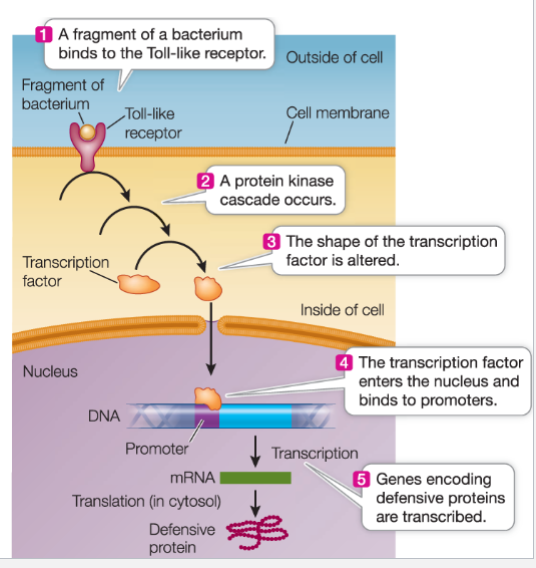
TLRs
Toll-Like Receptors
TLRs
recognition and activation phases developed early in animal evolution
they participate in innate defense
vertebrates
TLRs bind to conserved structures on microbes
pathogen-associated molecular patterns (pamps)
PAMPs binding triggers signal transduction pathways
PAMPs
Pathogen -associated molecular patterns
PAMP binding triggers signal transduction pathways
gene expression of anti-pathogen molecules
Flagellin, lipopolysaccharides, fungai chitin, neclic acid variant (viruses)
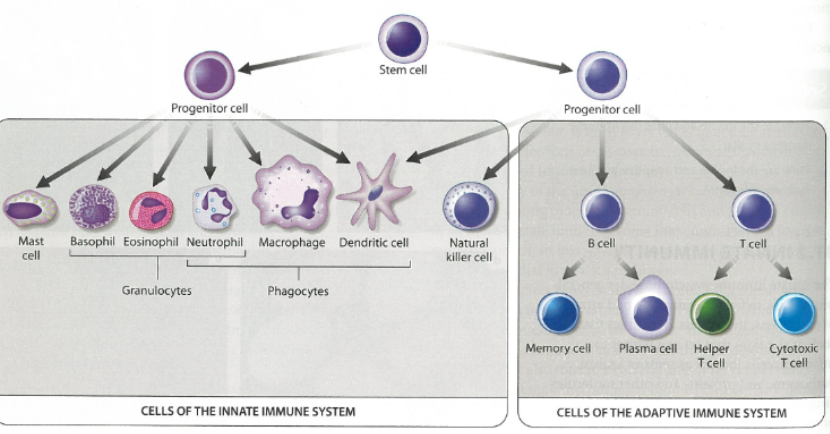
types of cells and their func.
white blood cells
phagocytes
lymphocytes
in 1 mL of human blood there are billion RBCs and _ billion WBCs
5
7

White blood cells
also known as leukocytes
specialized for immune system fuc.
Second line of defense
work in both ADAPTIVE & INNATE
develop from stem cells in bone marrow
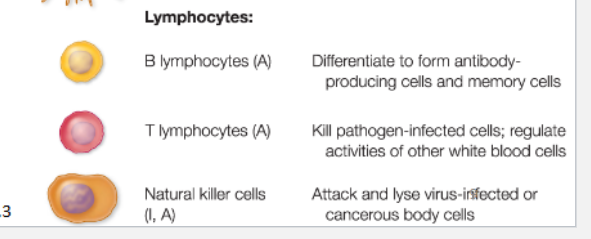
Lymphocytes
ADAPTIVE & INNATE
include T and B cells
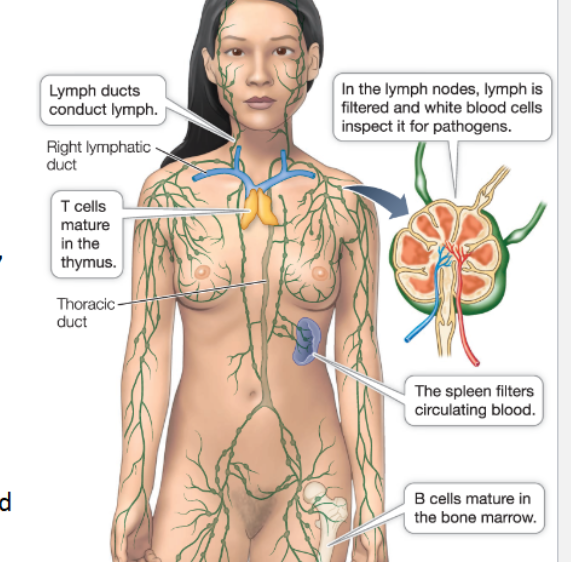
MAMMAL defense - lymphatic system
components of defense system throughout body
lymphoid tissue
blood plasma
lymph
Lymphoid tissue
thymus
bone marrow
spleen
lymph nodes
Blood plasma
solution with ions, small molecule solutes & soluble proteins
Lymph
fluid derived from blood and other tissues (no RBCs)
acc. in intercellular spaces in body
lymph nodes
sites along lymph vessels, fluid is check for pathogen and can respond
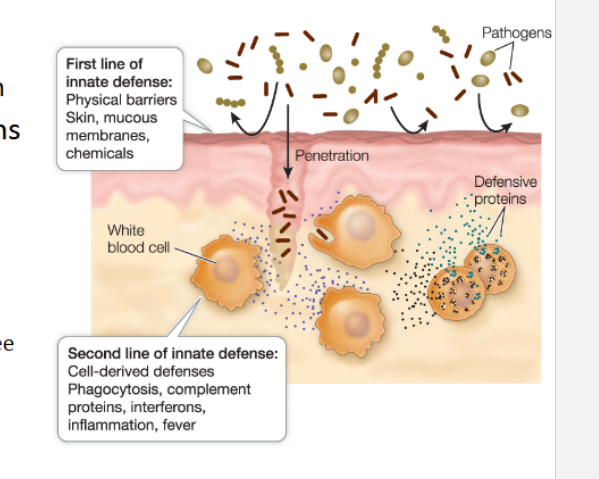
1st line of defense (MAMMALS)
External surfaces
skin,toxic molecules, pH, competetion
mucus membranes & internalo rgans
Mucus membranes & internal organs (MAMMALS)
mucus function
lysozyme production
Defensins
peptides inser to cell membranes → create “Free permeability”
toxic to bacteria, microbial EUKs, enveloped viruses
Harsh internal Environments
lysozyme production (MAMMALS)
mucus membranes and internal organs
cleaves bonds in cell walls of many pathogens
2nd line of Defense (MAMMALS)
activation of defensive cells
recognition by specfic receptors
PRRs
PAMPs
PRRs
Pattern recognition receptors
recognize PAMPs
mostly on phagocytic & NK cells in mammals
TLRs are examples of PRRs
Defense second line
Complement System
2o different proteins circulating in blood (vertebrate)
when activated, other downstream compliment (C) proteins are activated in sequence
like signal cascades
Complement system steps
1- one C protein binds to pathogen surface
helps phagocytes recognize and destroy invading pathogens
2-Another C protein activates inflammation
attracts phagocytes to infection site
3- other C proteins insert into pathogen membrane
create pores, invader cell dies
cytokines
signaling proteins
released from PRR activation
inflammatory cytokines
interferons
increased resistance of neighbor cells to infection(especially viral)
in many vertbrates
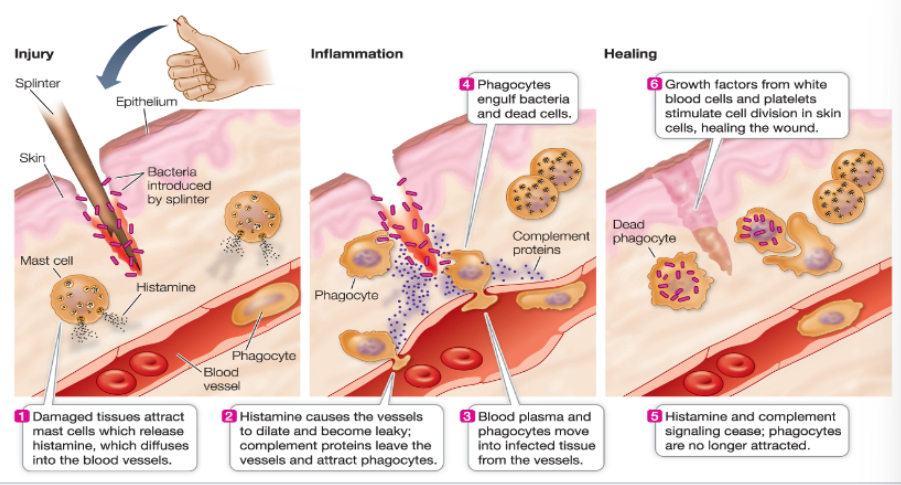
Inflammation
if tissue damaged - infection or injury
isolates area to stop infection spread
cells and m olecules recruited to site
early reponders - mast cells release chem. signals
pus - leaked fluid and dead cells
Early responders - mast cells, release chems that signal…
tumor necrosis factor
prostaglandins
histamines
Prostaglandins
helps with inflammation in nearby tissues
Histamines
increases permeability of blood vessels (for WBC and molecules)
Fever
phagocytes produce cytokines that can produce fever
due to pryogens
signal brain to increase body temp
some pathogens sensitive to temp
signal brain to increase body temp
accelerates lymphocyte production
increases phagocytosis
increases metabolism —> tissue repair
