Unit 2 TBT Terms
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
formed between two nonmetals, electrons are shared evenly
Polar Covalent Bonds
formed between two nonmetals, electrons are shared unevenly
Ionic Bonds
formed between metal and nonmetal, electrons are transferred
δ-
on more electronegative atom
δ+
on less electronegative atom
bond energy/bond strength
the amount of energy required to break a bond
(high bond energy = strong covalent bonds)
triple bond
shortest and strongest
1 σ bond and 2 π bonds
double bond
1 σ bond and 1 π bond
single bond
longest and weakest
1 σ bond
lattice energy
the energy required to separate the ions in an ionic lattice
(high lattice energy = strong ionic bonds)
Ionic bonds are stronger when…
1)
2)
1) the magnitude of the charge is greater
2) the ion size is smaller
Properties of Ionic Solids
High Melting Points
Low Volatility (don’t evaporate easily)
Poor Conductors as Solids, Good Conductors when Molten/Aqueous
Soluble in Water
Brittle (shatter)
Properties of Metallic Solids
High Melting Points
Good Conductors of Electricity
Good Conductors of Heat
Malleable (hammered into sheets)
Ductile (pulled into wires)
Metallic Bonds
formed between metals, electrons are delocalized into a “sea of electrons”
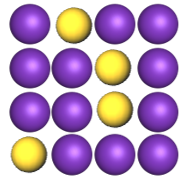
Substitutional Alloys
atoms of one metal are replaced by atoms of another
both metals have similar atomic radii
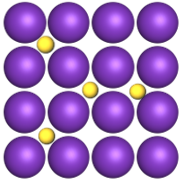
Interstitial Alloys
atoms of one element fill the gaps between atoms of a metal
one of the elements has a much smaller atomic radius
What is needed for a substance to conduct electricity?
charged particles (ions, delocalized electrons, etc.) that are able to move freely and carry charge
resonance structures
different valid drawings of the same molecule that differ only in electron (bond) placement, not atom positions
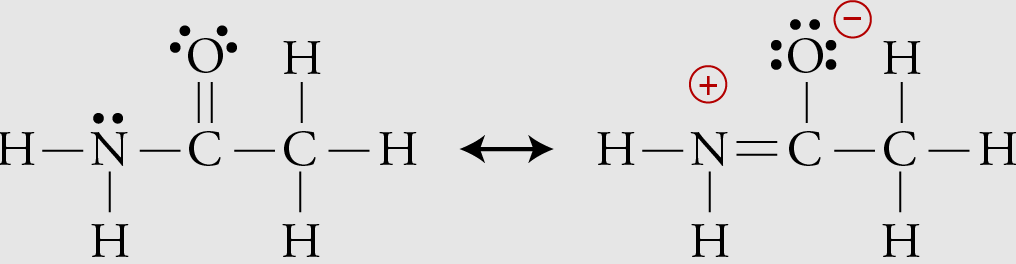
Formal Charge
# of Valence Electrons an Atom Starts With - # of Electrons Touching the Atom
The most valid resonance structure will…
1) minimize formal charge
2) put negative formal charge on the more electronegative atom
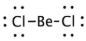
Geometry: Linear
Bond Angle: 180o
Hybridization: sp

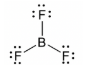
Geometry: Trigonal Planar
Bond Angle: 120o
Hybridization: sp2
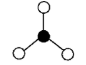
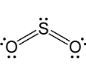
Geometry: Bent
Bond Angle: less than 120o
Hybridization: sp2
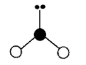
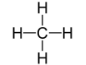
Geometry: Tetrahedral
Bond Angle: 109.5o
Hybridization: sp3
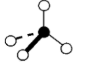
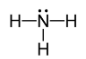
Geometry: Trigonal Pyramidal
Bond Angle: less than 109.5o
Hybridization: sp3
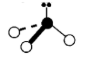
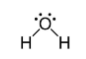
Geometry: Bent
Bond Angle: less than 109.5o
Hybridization: sp3
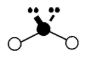
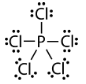
Geometry: Trigonal Bipyramidal
Bond Angle: 120o and 90o
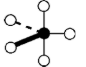
Geometry: Seesaw
Bond Angle: less than 120o and 90o
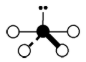
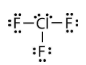
Geometry: T-Shaped
Bond Angle: less than 90o
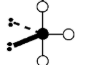
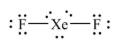
Geometry: Linear
Bond Angle: 180o
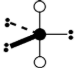
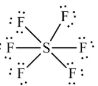
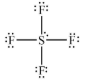
Geometry: Octahedral
Bond Angle: 90o
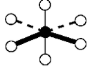
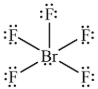
Geometry: Square Pyramidal
Bond Angle: less than 90o
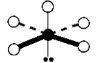
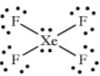
Geometry: Square Planar
Bond Angle: 90o
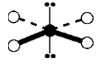
Isomers
different substances with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms
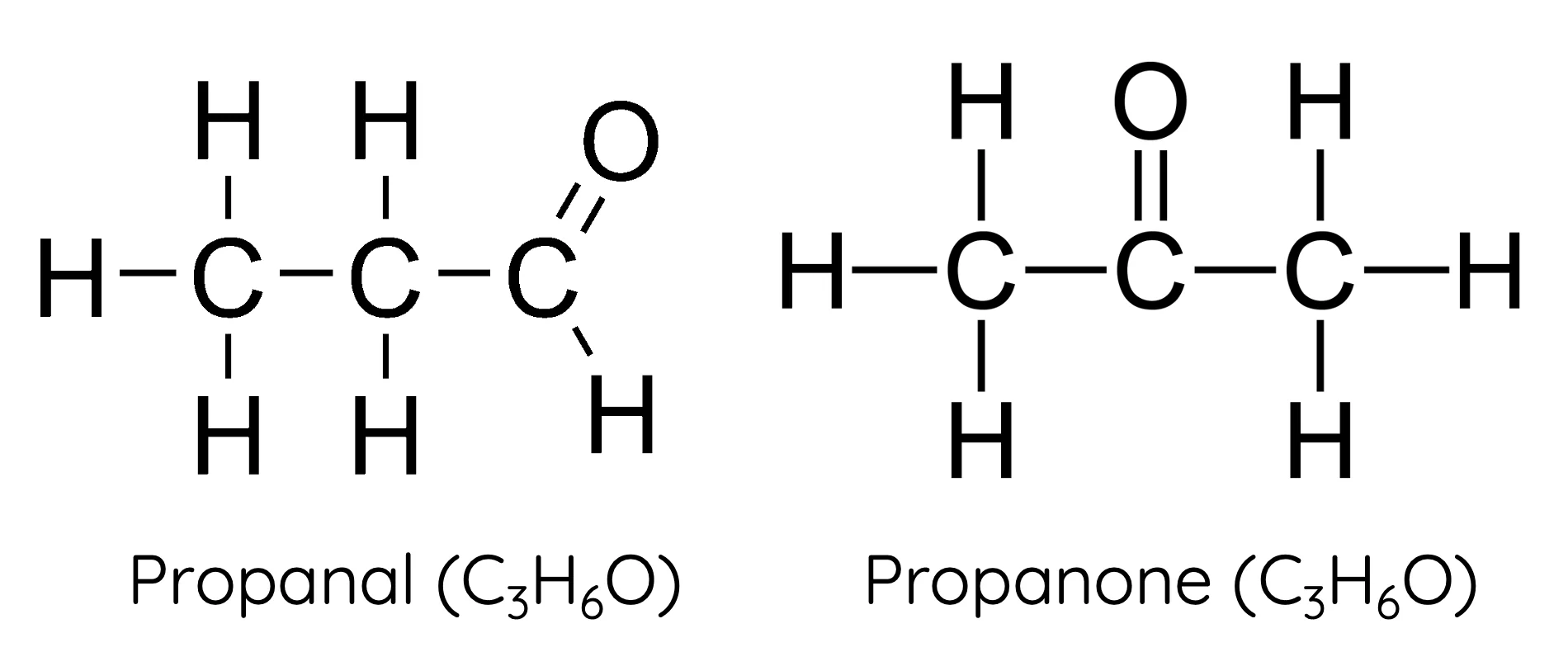
Sigma (σ) Bonds
head-on overlap of orbitals
stronger than pi (π) bonds
Pi (π) Bonds
side-by-side overlap of orbitals
weaker than sigma (σ) bonds
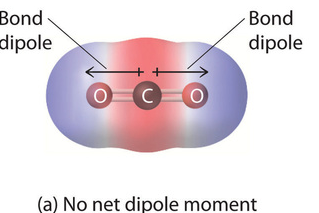
Polar Molecules
bond dipoles do not cancel out, resulting in a net dipole moment
usually have…
asymmetric geometry,
lone pairs on central atom, or
different terminal atoms
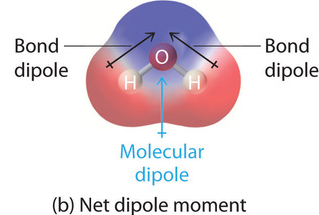
Nonpolar Molecules
bond dipoles cancel out
usually have…
symmetric geometry,
no lone pairs on central atom, and
identical terminal atoms