(7.4-7.9) Alpha, beta particles and gamma rays
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What is radiation?
Energy transfer via electromagnetic waves
Why does radiation occur?
Due to imbalances in the forces within the nucleus, being too big or having too many or too few neutrons, some nuclei are unstable.
They can emit radiation to become more stable, in the form of a high energy particle or wave.
The radiation taken some energy with it as it moves away, reducing the energy of the nucleus and making it more stab;e.
This is called radioactive decay, a random process that cannot be predicted.
How does nuclear radiation occur?
When an unstable nuclei decays, the radiation it emits is called nuclear radiation.
What are the three types of nuclear ionising radiation?
Alpha (α)
Beta (β-)
Gamma (γ)
Describe alpha particles in terms of:
atomic make up (particle/ray, creation, structure, charge)
range
penetration
ionisation
effects on atomic number
effects on mass number
equation + explanation
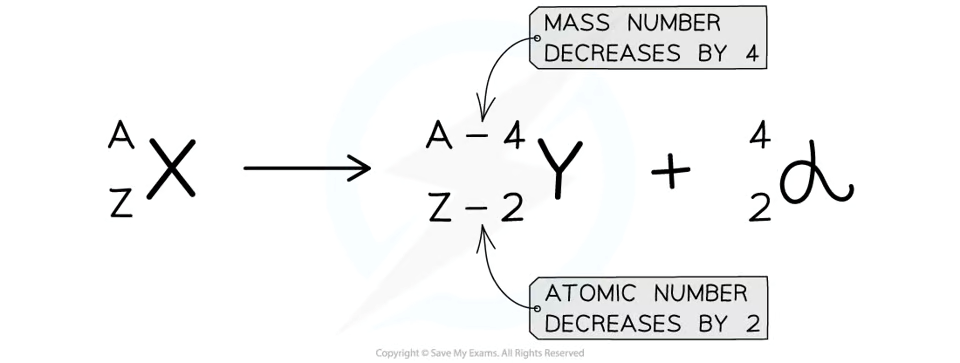
Alpha particle = helium nucleus (2 neutrons + 2 protons)
charge of +2 - can be affected by electric field
Range of a few cm
Penetration stopped by paper
High ionising power
When the alpha particle is emitted, mass no. decreases by 4, atomic no. decreases by 2. Charge also decreases by 2.
Describe beta particles in terms of:
atomic make up (particle/ray, creation, structure, charge)
range
penetration
ionisation
effects on atomic number
effects on mass number
equation + explanation
Beta particles are fast moving particles which are produced when a neutron becomes a proton and an electron
The electron is emitted, proton stays in the nuclei
Charge of -1, can be affected by electric field
Penetration stopped by aluminium
Medium ionisation
mass number stays the same
atomic number increases by one - proton

Describe gamma rays in terms of:
atomic make up (particle/ray, creation, structure, charge)
range
penetration
ionisation
effects on atomic number
effects on mass number
equation + explanation
A ray is emitted from an unstable nucleus
the nucleus becomes less energetic but does not change its structure
An infinite range
Penetration reduced by lead
Low ionisation
the mass and atomic number remain the same

Describe neutron emission in terms of:
atomic make up (particle/ray, creation, structure, charge)
effects on atomic number
effects on mass number
Small number of isotopes can decay through neutrons
The proton number does not change.
The nucleon number decreases by 1.
Detail the experiment to investigate the penetration powers of different types of radiation.
Measure background radiation with a Geiger-Muller counter for 1 minute. Repeat 3 times and average.
Place a radioactive source a fixed 3 cm from the tube and take readings of 1 minute.
Now take absorbers: paper, thicknesses of aluminium and thicknesses of lead.
One at a time, place these between the source and the tube and take another reading over a 1 minute period.
Repeat the experiment for other radioactive sources and measure against background noise and difference in counter.
What is a Geiger-Muller counter?
An electronic instrument used to measure ionising radiation through detecting ionised atoms. Counted in Becquerels.
How does photographic film detect radiation?
It becomes barker when it absorbs radiation and is used to monitor radiation exposure.