Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 4
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
Anabolic
In _______ reactions, larger molecules are constructed from smaller ones; a process requiring energy.
Catabolic
In ______ reactions, larger molecules are broken down, releasing energy.
Dehydration synthesis
The anabolic reaction known as ______ builds polymers by linking together the monomers (basic units) by removing the components of water molecules between each monomer
Dehydration synthesis
Polysaccharides, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids are constructed via _____
Dehydration synthesis
The following chemical equation demonstrates which type of anabolic reaction? A-OH + H-OB > A-O-B + H2O
Hydrolysis
The catabolic reaction known as ____ inserts a water molecule between the units of a polymer, breaking it into the individual monomers (basic units)
Hydrolysis
_______ is responsible for digestion
Hydrolysis
The following chemical equation represents which type of catabolic reaction? A-O-B + H2O > A-OH + H-OB
Enzymes
_____ (biological catalyst) control the rate of metabolic reaction in cells, because the body temperature is too low for reaction to run fast enough
Activation Energy
Enzymes act as biological catalyst by lowing the ________ needed for metabolic reactions
Small
Enzymes work in ____ quantities and are recycled by the cell (can be used again).
Substrate
Each enzyme is specific, acting on only one kind of ______; specified by their complementary shapes.
Active Site
Within the structure of an enzyme is an area that matches to the shape of its substrate. This area is known as the ___________
Enzyme-substrate complex
When the substate is attached to the active site of the enzyme, the _____ is formed
-In; -ase
The names of enzymes usually end in ____ or ____.
Metabolic pathways
Most metabolic reactions occur as a series of enzyme, controlled steps known as ________
Reactants
In a metabolic pathway, the products of one reaction becomes the ____ for the next reaction in the series of reactions
Cofactor
Some enzymes only become active when they combine with a nonprotein (inorganic) component called a _________
Coenzymes
Small organic cofactors are called ________, which are often vitamins
Denatured
Since most enzymes are proteins, they can be _____, which causes them not to function, by heat, changes in pH, and other environmental factors.
Energy
_______ is the capacity to do work
Heat, light, mechanical energy, chemical energy, sound, electrical energy
six common forms of energy
Chemical
Most metabolic reaction use ____ energy
Oxidation
Release of chemical energy in the cell often occurs through the _______ of glucose in a process called cellular respiration.
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
Chemical energy released during cellular respiration cannot be directly used by cells and must be stored in the molecules of _____
Released
Energy is ____ when the last phosphate is released from ATP to form ADP
Energy is stored when a third phosphate is added to ADP to form ATP
Describe how energy is stored using ADP (adenosine diphosphate)
Catabolic
Is cellular respiration an anabolic or a catabolic reaction?
Glycolysis, Transition stage, Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle), Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
List the four steps of aerobic cellular respiration, in their correct order.
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
The following chemical equation represents the general equation for __________ C6H12O6 + 6O2 > 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy (glucose + oxygen is converted into CO2 +Water+ATPs)
Aerobic
When a chemical reaction requires oxygen, it is known as a/an ____ reaction.
Anaerobic
When a chemical reaction can occur without the presence of oxygen, it is known as a/an ____ reaction.
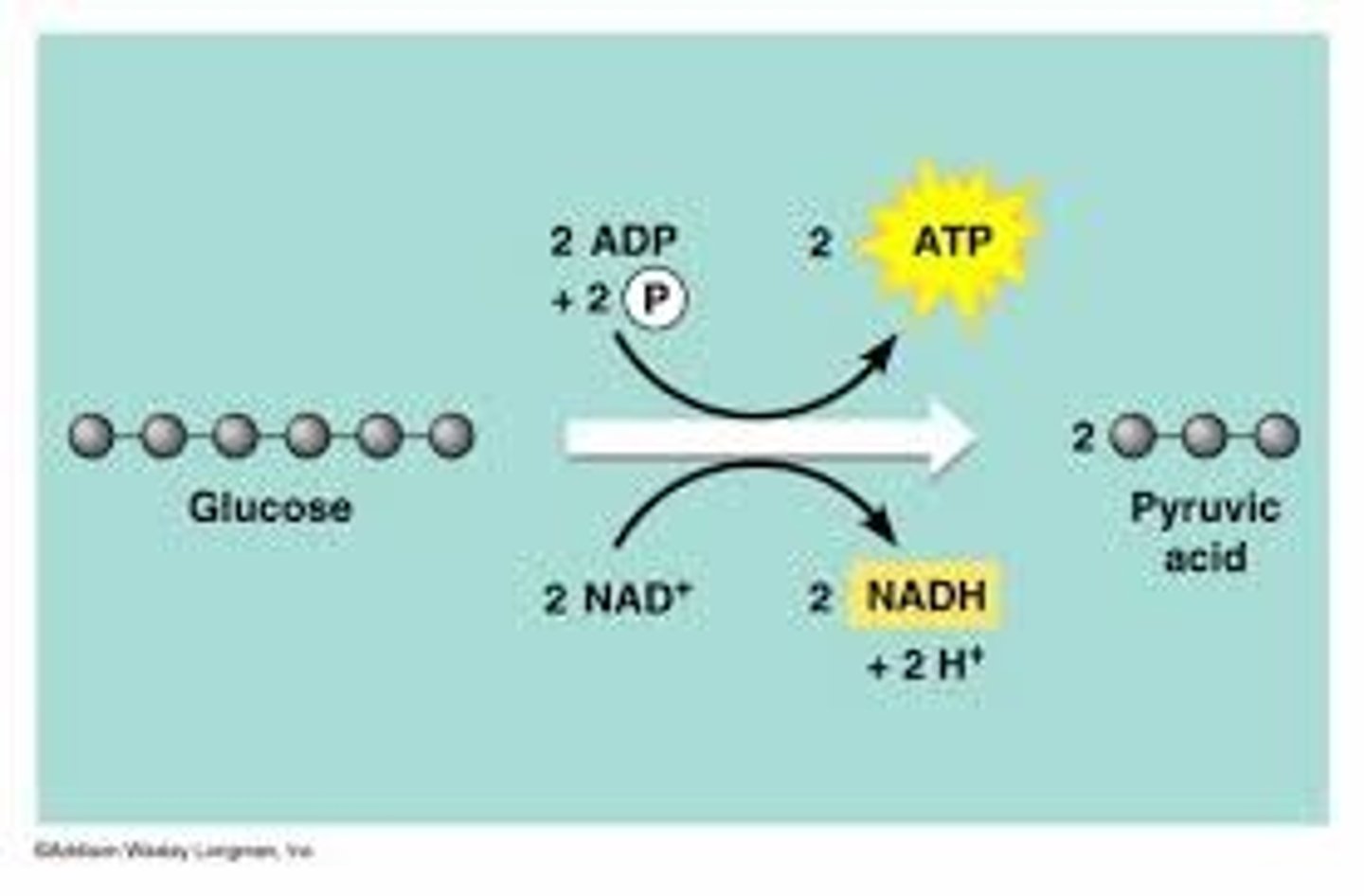
Glycolysis
First part of cellular respiration, occurs in cytoplasm, can take place without oxygen, so is referred to as being anaerobic. Products are 2 pyruvic molecules, 2 ATP, 2 NADHs
Cytoplasm
Glycolysis takes place in which part of cells?
Pyruvate (pyruvic acid)
At the end of the glycolysis reactions, one molecule of glucose has been split (oxidized) into two molecules of _______
2
How many ATP molecules are used to start the Glycolysis reaction?
4
How many total ATP molecules are produced during Glycolysis?
2
What is the net gain of ATP after completing glycolysis?
NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)
During glycolysis, 2 high energy electron carrier molecules, _____ are formed.
Transition Stage
During the ________ Pyruvic acid will lose a carbon and join with a coenzyme to form acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl Co-A) which can enter the Krebs (citric acid) cycle.
2 NADH, 2 CO2
In the transition stage, _________ are produced, __________ molecules and no ATPs are produced by substrate level phosphorylation. (Since there are 2 NADH, 2 CO22 pyruvates, this is the total using both)
Mitochondria
The transition stage transports pyruvate into the _____ for the completion of aerobic cellular respiration
2
At the end of 2 turns of the Krebs cycle, what is the total number of ATP's produced?
NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), FADH2 (Flavin adenine dinucleotide)
Name the two high energy electron carrier molecules produced by the Krebs cycle.
6
How many NADH molecules are produced during 2 turns of the Krebs cycle?
2
How many FADH2 molecules are produced during 2 turns of the Krebs cycle?
4
How many CO2 molecules are produced during 2 turns of the Krebs cycle?
Transition stage and Krebs cycle
Which two steps of aerobic cellular respiration form the CO2 that is released as a waste product?
The matrix of the mitochondria
Where does the Krebs cycle take place in cells?
ETC (electron transport chain)
NADH and FADH2 are used in the ____ stage of aerobic respiration during the production of 34 ATP from 1 glucose.
Along the cristae of the inner membrane in the mitochondria
Where does the ETC take place?
Enzyme carrier molecules
The ETC is a series of membrane ____ that allow for H+ ions released from NADH and FADHs to leave the matrix and enter the intermembrane space
Chemiosmosis
During the ETC, ATP is formed during ______, as H+ ions leave the intermembrane space through the enzyme carrier, ATP synthase.
Oxygen
______ is the last electron receptor in the ETC, and along with hydrogen, forms water.
3
For each molecule of NADH formed during aerobic cellular respiration, _____ molecules of ATP are formed
2
For each molecule of FADH2 formed during aerobic cellular respiration, ____ molecules of ATP are formed
34 (Explanation: 10 NADHs x 3 ATPs each = 30 ATPs, 2 FADH2 x 2 ATPs each = 4 ATPs)
Using the total number of NADH and FADH2 molecules produced during Glycolysis, Transition stage, and Krebs cycle, how many ATP molecules are formed during ETC?
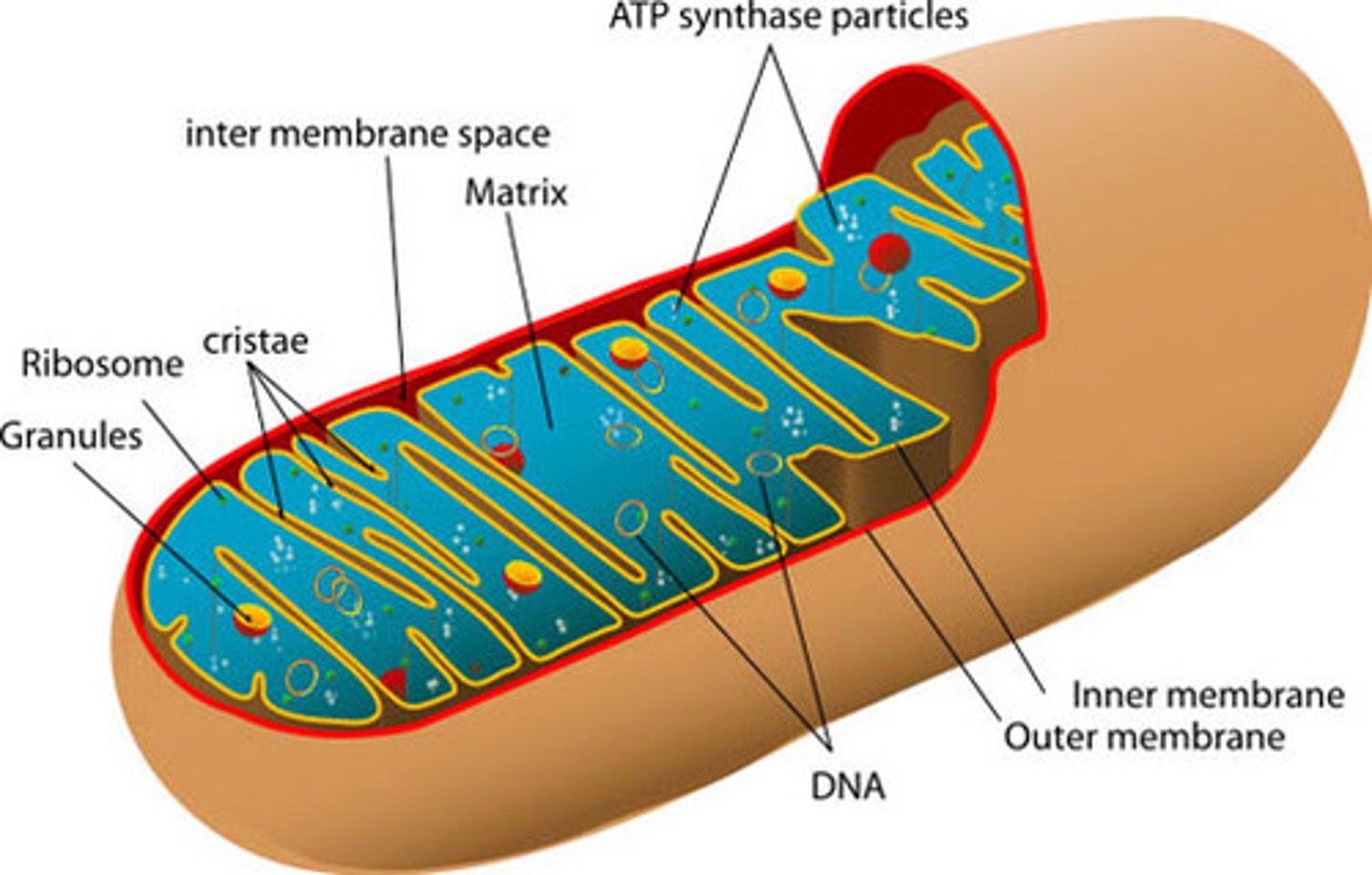
Inner membrane, Outer membrane, Cristae, Intermembrane space
Label the parts of the mitochondria
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
__________ contains the genetic code needed for the synthesis of each protein (including enzymes) required by the cell.
Gene
A ______ is a portion of a DNA molecule that contains the genetic information for making a single protein.
Genome
The complete set of gene instructions is the ________
Sugar-phosphate
The nucleotides of DNA form a ______ backbone with bases extending into the interior of the DNA ladder-like molecule.
Adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine
Name the four nitrogenous bases found in DNA
Thymine
In DNA, the complimentary base to adenine is ______
Guanine
In DNA, the complimentary base to cytosine is ______
Hydrogen
In DNA, the complimentary bases are held together by _____ bonds
Double helix
DNA twist to from the shape known as the _______________
Interphase (s phase)
DNA replication takes place during the ______ stage of the cell cycle
Hydrogen bonds
During DNA replication enzymes break the _____ between bases opening the molecule along its length.
DNA polymerase
The enzyme ____ brings in nucleotide bases to match to the complementary bases during DNA replication
Semi-conservative
Each new DNA molecule, produced by DNA replication, consists of one parental strand and one newly-synthesized strand of DNA, thus DNA replication is said to be ___________
TGAACCGGTAT
If one side of a DNA molecule has the bases ACTTGGCCATA, what are the complimentary bases for the other side?
Genetic code
The ________ is the sequence of base pairs of a gene that specifies an order of amino acids to make a particular protein.
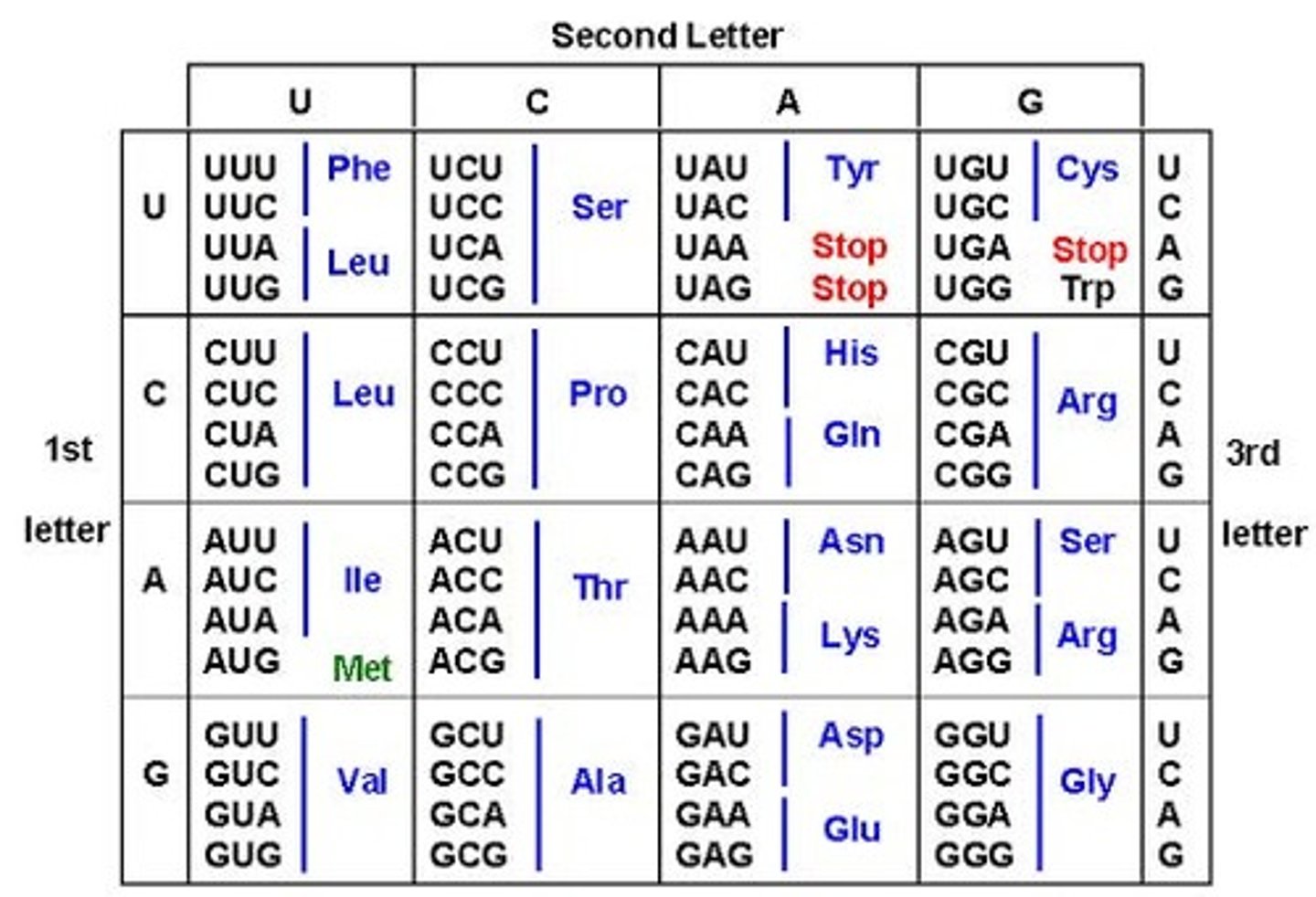
Codon
An amino acid is represented by a three-base sequence on DNA called ________
transcription, translation
The process of protein synthesis requires two sequential steps - 1. ______ and 2. _________.
RNA (ribonucleic acid)
The nucleic acids known as ____ work with DNA during protein synthsis.
Messenger RNA (mRNA),Transfer RNA (tRNA), Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Name the three types of RNA
function of mRNA
Uses the genetic code in DNA to produce the mRNA code and carry this to a Ribosome where amino acids are linked together into polypeptides
function of tRNA
Attaches to specific amino acids and transports them to ribosomes for protein synthesis
function of rRNA?
Makes up the ribosomes, the site of protein synthesis
Adenine, uracil, guanine, cytosine
Name the four nitrogenous bases found in all types of RNA
Uracil
For RNA, the complimentary base for adenine is _____
Single
Is a mRNA molecule a double or a single helix?
transcription in protein synthesis
Using the genetic code in DNA to use RNA nucleotides to produce a strand of mRNA
AUGACCGUGUGGUGA
Using the DNA genetic code, write the mRNA code (transcription) TACTGGCACACCACT
Met - Thr - Val - Trp - Stop
Use the mRNA code and the amino acid chart at the end of the study cards to translate it into the amino acids: AUGACCGUGUGGUGA
In the nucleus, along the DNA molecule (chromatin)
Where does the step of protein synthesis known as transcription take place?
At a ribosome
Where does the step of protein synthesis known as translation take place?
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
During translation, which type of RNA carriers amino acids to ribosomes so the amino acids can become part of the polypeptide chain?
Anticodon
What part of the tRNA molecule allows the tRNA to place the correct amino acid into it correct location in the polypeptide chain.
Dehydration synthesis
The ribosome contains enzymes needed to join the amino acids together by __________ forming peptide bonds.
Anabolic
Protein synthesis is an example of which type of chemical reaction? (catabolic or anabolic)
Mitochondria
parts Inner membrane, outer membrane, cristae, intermembrane space
Gentetic code
cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen occurs in 4 stages: glycolysis, transition stage, krebs cycle, and ETC
Krebs cycle
second stage of cellular respiration, in which pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions product is 2 ATPS, 6 NADHs, 2 FADH2, 4 molecules of CO2